Distribution of Pre-Cenozoic strata and petroleum prospecting directions in China Seas
-
摘要: 经过60年的油气调查与勘探,随着中国近海新生代盆地的勘探程度不断提高,油气发现难度逐渐加大,海洋油气勘探新领域的开拓成为当务之急。近年来的调查与勘探发现,中国海域前新生代盆地残留地层具有如下特征:① 厚度大,一般为4000~6000 m,最大厚度超过9000 m;② 分布广,有渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海-南海北部和南海南部5大分布区;③ 存在新元古界、下古生界、上古生界、中生界“下部层系”、中生界“中部层系”和中生界“上部层系”6套地层;④ 可划分东海-南海型和渤海-黄海型两类层型结构,前者仅由“单一”的中生代地层组成,后者由新元古界-古生界-中生界“叠合”构成;⑤ 发育下寒武统、下志留统、石炭系、二叠系、侏罗系和白垩系6套烃源岩,其中下寒武统、下志留统和二叠系烃源岩有机质丰度高,侏罗系烃源岩分布最广;⑥ 具有孔隙型、裂缝改造型和风化壳型3类储层,其中,孔隙型储层包括白云岩、礁滩相碳酸盐岩和砂岩储层,裂缝型储层与大型断裂带和挤压构造带伴生,风化壳储层可分前寒武系变质岩和混合花岗岩、古生代碳酸盐岩、中生代火山岩以及花岗岩、中生代碎屑岩4亚类,其物性及分布主要受构造作用、风化淋滤作用和埋藏条件3种因素控制;⑦ 具备“古生古储”、“古生中储”、“古生新储”、“中生中储”、“中生新储”和“上生下储”6类成藏组合。综合分析认为:中国海域前新生界油气前景广阔,南黄海海相中-古生界、东海南部-南海北部海域中生界、新生代富生烃凹陷内的潜山是中国海洋油气下一步勘查方向;北黄海盆地坳陷区的中生界和渤海海域的前新生界“自生自储”油气藏值得重视。Abstract: After 60 years of oil and gas investigation and exploration, the exploration degree of Cenozoic basins and the difficulty of oil and gas discovery in offshore China has increased, and the development of new fields for offshore oil and gas exploration has become an urgent task. Surveys and explorations in recent years have found that characteristics of the residual strata in the Pre-Cenozoic basins in offshore China could be summarized as follows: ① Huge thickness. The thickness of the Pre-Cenozoic varies in the range of 4000~6000 m with a maximum over 9000 m; ② Wide distribution. Pre-Cenozoic Strata are found in five major areas, i.e. the Bohai Sea, the North Yellow Sea, the South Yellow Sea, the East China Sea–the northern South China Sea and the southern South China Sea from north to south; ③ Six sets of strata, which include the Neoproterozoic, the Lower Paleozoic, the Upper Paleozoic, the Lower Mesozoic, the Middle Mesozoic, and the Upper Mesozoic; ④ Two types of stratigraphic architectures, i.e. the type of East China Sea-South China Sea composed only by the Mesozoic, and the type of Bohai-Yellow Sea superimposed by the Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, and Mesozoic; ⑤ Six sets of source rocks, which include the Lower Cambrian, the Lower Silurian, the Carboniferous, the Permian, the Jurassic, and the Cretaceous source rocks, among which the Lower Cambrian, the Lower Silurian, and the Permian source rocks have the highest organic matter content, and the Jurassic source rocks distribute the most widely; ⑥ Three kinds of reservoirs, namely the porous reservoirs, the fracture-modified reservoirs, and the weathering crust reservoirs. The porous reservoirs mainly consist of dolomite, reef-bank carbonate, and sandstone, and the fracture-modified reservoirs are often associated with large fault zones and/or compressive structural zones, and the weathering crust reservoirs can be further divided into four sub-types: Precambrian metamorphic rocks and magmatic granite, Paleozoic carbonate rocks, Mesozoic volcanic rocks and granite, and Mesozoic clastic rocks. The physical properties and distribution of reservoirs are mainly controlled by tectonics, weathering and leaching process, and burial conditions; ⑦ Six types of plays from the Paleozoic source to the Paleozoic reservoir, from the Paleozoic source to the Mesozoic reservoir, from the Paleozoic source to the Cenozoic reservoir, from the Mesozoic source to the Mesozoic reservoir, from the Mesozoic source to the Cenozoic reservoir, and from the Cenozoic source to the Pre-Cenozoic reservoirs. In conclusion, the Pre-Cenozoic petroleum has great potential and broad prospects in China Seas. Next exploration targets should be focused on the marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea, the Mesozoic-Cenozoic in the southern East China Sea and the northern South China Sea, and the buried hills in Cenozoic hydrocarbon-rich depressions. The Mesozoic in the North Yellow Sea and the self-generating source to self-storing reservoirs in the Pre-Cenozoic of the Bohai Sea should be paid attention.
-
Keywords:
- China Seas /
- Pre-Cenozoic /
- stratigraphic distribution /
- petroleum prospecting
-
经过60年的油气调查与勘探,中国海洋油气已在近海新生代盆地中取得了重大发现,在渤海、珠江口、琼东南、莺歌海、北部湾及东海陆架盆地已发现了一批油气田和含油气构造。截止2020年底,中国近海累计探明石油57.5×108 t,天然气1.5×1012 m3,累计采出石油8.1×108 t,天然气2183.4×108 m3①。随着勘探程度的深入,新生代盆地中获得油气发现的难度不断加大,开拓新的勘探层系或新的勘探领域已成为中国海洋石油勘探的当务之急。因此,中国海域的前新生代地层厚度和分布如何?资源潜力怎样?勘探方向在哪?这些问题成为当前中国海域油气勘查关注的热点。
对中国海域前新生代盆地地质特征和油气前景探讨始于20世纪80年代。张冰等[1]首次编绘了大陆架前第三纪地层分布示意图,预测了海域发育“上生下储”和“自生自储”基岩油气藏。此后,地质和地球物理学家们通过少量钻井、地球物理和古生物等资料证实了南黄海盆地[2]、东海盆地南部及台湾近海诸盆地[3]、渤海地区[4]发育侏罗系和白垩系,指出其具有油气资源潜力;在南海北部陆缘东北部和礼乐滩也识别出中生代地层[5-6],推测南海存在中生代特提斯域沉积盆地[7-9],并探讨了南海中生代坳陷地质结构[10]和南沙群岛含油气盆地的前新生代基底及其与北部陆缘的关系[11];分析了中国近海前新生代残留盆地特征[12]、东部海域中生界地质特征及成藏地质条件[13]。随着21世纪初中国油气勘探二次创业[14]的开启,中国地质调查局依托国土资源地质大调查及海洋地质调查专项项目,以评价中国海域中-古生界油气资源、拓展深部找油空间为目标,持续开展了20年的油气资源调查与研究。截止2020年底,完成综合地球物理和地球化学调查45个航次,二维多道地震17.1万km及相应的重力、磁力及水深测量,海底地震(OBS)16个站位,地质取样1081个站位;中海石油(中国)有限公司也先后立项开展了近海前新生代盆地油气地质条件研究;国内专家学者就渤海前新生界[15-24]、北黄海中生界[25-43]、南黄海中生界和古生界[44-112]、东海至南海中生界[113-172]、中国海域残留盆地地质特征和油气资源潜力[173-178]开展了大量研究,取得了一批重要的研究成果:① 通过一系列技术攻关,在南黄海崂山隆起获得中-古生界有效反射,突破了深部地震资料成像技术瓶颈,形成了针对强能量屏蔽层条件下的沉积盆地深部“高富强”地震探测技术[59, 69, 76, 103, 113]和复杂海况条件下单源单缆准三维地震探测技术[179-182];② 明确了海域古生界和中生界两大勘探层系,落实厚度超过2 000 m的中-古生界分布面积45.8×104 km2(结合重、磁、震资料解释及区域对比,推测管辖海域前新生代地层分布面积132.3×104 km2),圈定中国海域中-古生界油气远景区9个、有利勘探区带7个、重点目标8个,预测远景资源量115×108 t油当量,新增远景资源量56×108 t油当量;③ 南黄海科探井首次在崂山隆起发现了中-古生代地层,证实了扬子地台向东延伸到南黄海海域的科学论断,发现了分布面积达2.4×104 km2的构造稳定带,指出南黄海海域中-古生界具备形成大型油气田的物质基础,崂山隆起是下古生界的油气远景区,勿南沙隆起是上古生界的油气远景区,崂山隆起高石稳定带是有利区带;④ 建立了东海南部-南海北部的“大东海”中生代盆地的构造沉积格架,指出东海南部和南海北部中生界具备形成油气田的基本地质条件;⑤ 中国海域前新生界是下一步调查和勘探的战略领域,南黄海是“古生古储”的首选突破区,渤海海域应关注太古界、元古界、古生界和中生界潜山油气藏。
1. 地层分布
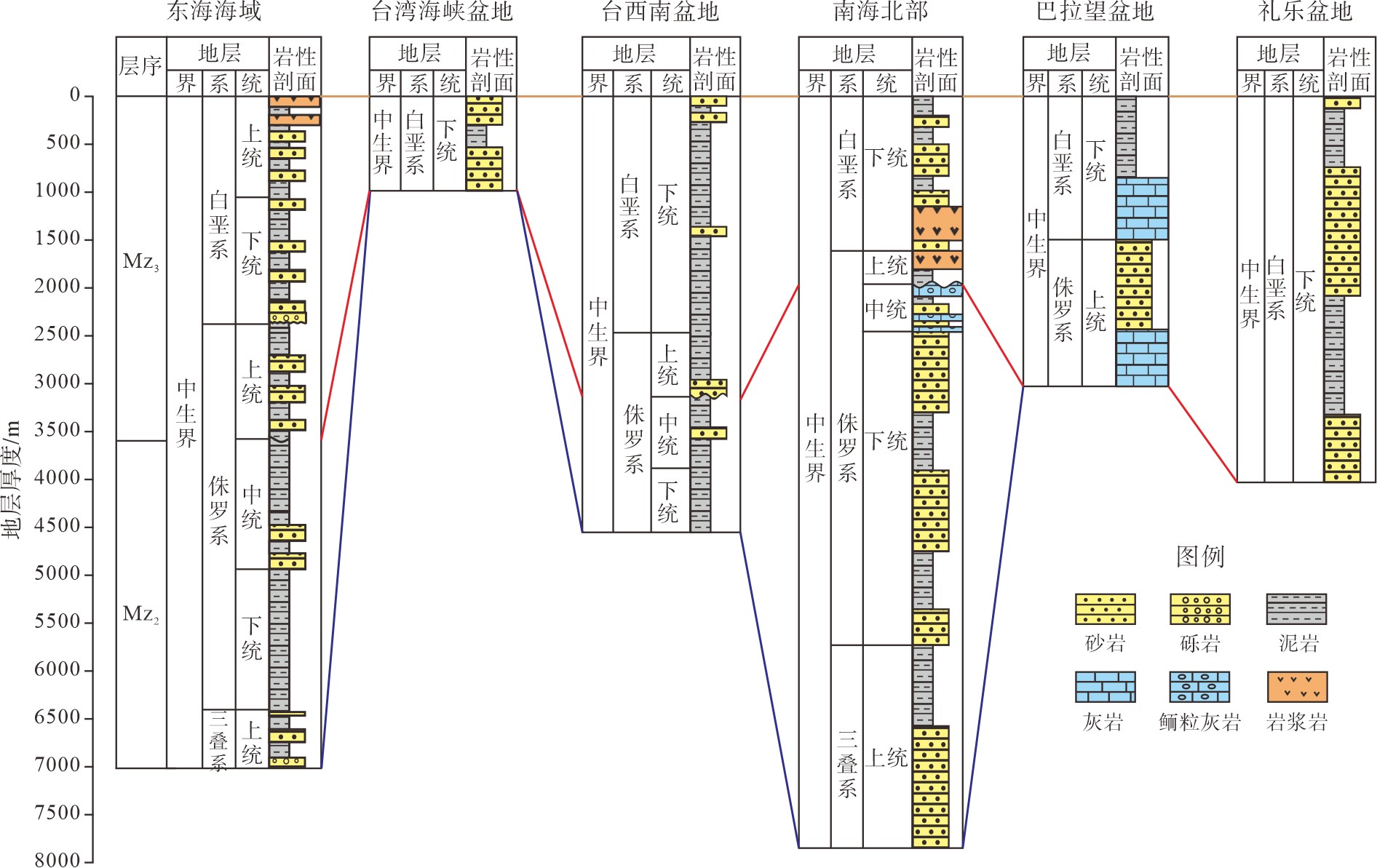
中国海域前新生代地层分布于渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海-南海北部和南海南部海域(图1),面积分别为6.8×104、4.3×104、18.4×104、41.9×104和60.9×104 km2,总面积达132.3×104 km2。纵向上发育两类层型结构,即东海-南海型(“单一型”)和渤海-黄海型(“叠合型”)(图2-3)。前者主要由中生代地层组成,包括中下三叠统构成的中生界“下部层系”、上三叠统—中侏罗统构成的中生界“中部层系”和上侏罗统—白垩系构成的中生界“上部层系”,发育早中三叠世、晚三叠世—中侏罗世及晚侏罗世—白垩纪3期沉积盆地,主要分布于东海和南海海域;后者为新元古界-古生界-中生界“叠合型”层型结构,在中生界之下,发育厚度较大的新元古代和古生代沉积地层,主要分布于渤海-黄海海域(表1)。
表 1 中国海域前新生代地层及最大厚度Table 1. Distribution of Pre-Cenozoic strata in China Seas (strata type and maxmum thickness)m 地层层序 渤海 黄海 东海-南海北部 南海南部 北黄海 南黄海 东海 台湾海峡 台西南 南海北部 巴拉望 礼乐 中生界 上部层系 3000 4000* 3000 3500* >1082 3000* 3500* 3000* 4000* 中部层系 1000 2000 >2195 4500* 缺失 600 5300* 缺失 缺失 下部层系 1200 1500 3000* ? ? ? ? ? ? 古生界 上古生界 1400 >2000 4500* ? 缺失 缺失 缺失 ? ? 下古生界 >310 >472 4500* ? 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 元古界 新元古界 不详 >931 1200* 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 叠合面积 67616 km2 43279 km2 183917 km2 419433 km2 608921 km2 层型结构 “叠合型”(新元古界-古生界-中生界) “单一型”(中生界) 注:表中*为地震资料解释最大厚度;?表示情况不明。 1.1 渤海-黄海型层型结构(“叠合型”)
该类层型结构主要分布于渤海、北黄海和南黄海海域,以古生界碳酸盐岩为主,未变质,厚度大,其上覆盖有中生代地层。
1.1.1 渤海海域
区域构造分析和钻井揭示,渤海盆地是在太古宇—古元古界变质岩基底之上发育的叠合盆地。其前新生界具有典型的华北地台地层层序特征,中新元古界为火山碎屑岩-台地碳酸盐岩沉积,寒武系—奥陶系为台地碳酸盐岩为主的沉积,石炭系—三叠系为海陆交互相碎屑岩及碳酸盐岩台地沉积,侏罗系—白垩系为火山岩及冲积-湖相碎屑岩沉积,之间存在区域不整合。
(1)元古界
钻井资料揭示,渤海海域局部地区沉积了中、新元古界石英砂岩夹海绿石砂岩以及白云质灰岩[183],相当于青白口系,北部以灰岩为主,南部以碎屑岩为主[19],属于典型的华北克拉通地层系统。
(2)下古生界
以寒武系和奥陶系碳酸盐岩为主,在渤海西部分布较为稳定。秦皇岛428潜山钻遇厚310 m寒武系徐庄组泥岩、张夏组鲕粒灰岩、崮山组竹叶状灰岩和炒米店组燧石条带灰岩[184],属陆表海沉积;渤中21-2-A井钻遇了厚280 m的奥陶系冶里组灰云岩、亮甲山组白云岩和云灰岩、马家沟组灰岩,各组顶部均含粉砂质泥岩[185],为局限台地及潮坪沉积。受加里东运动影响,该区下古生界与上覆石炭系—二叠系呈平行不整合接触。燕山运动以来强烈的构造运动使郯庐断裂带东侧下古生界几乎剥蚀殆尽,沙垒田凸起、石臼坨凸起等区也遭受了严重剥蚀。
(3)上古生界
主要为石炭系和二叠系。渤海海域大量钻井钻遇上古生界,包括本溪组、太原组、山西组、下石盒子组和上石盒子组,以砂岩为主,夹泥岩和煤层,下部灰岩,为浅海相和海陆过渡相沉积。受印支运动影响,上古生界在渤海南部呈近东西向分布,具有西薄东厚特征;在渤海北部受郯庐走滑断裂改造明显,呈北东向展布,具有北薄南厚特点(图4),最大地层残余厚度大于1200 m。
(4)中生界
QK17、JZ16和BZ6等潜山的钻井揭示,“下部层系”由下三叠统砂岩构成,分布局限;“中部层系”由下侏罗统和中侏罗统构成,为砂砾岩夹泥岩及煤层,仅分布于渤中凹陷西南部,残留厚度200~600 m,最厚1000 m;“上部层系”由上侏罗统和下白垩统构成,以火山岩为主,夹砂泥岩、白云岩及生物碎屑灰岩,分布范围相对较广,残留厚度500~2000 m,在黄河口凹陷南部和渤中凹陷北部存在两个残留厚度中心,最大残留厚度3000 m,在辽东凸起、辽西凸起、辽西南凸起、石臼坨凸起、沙垒田凸起、渤南低凸起、庙西凸起等地区缺失。
1.1.2 北黄海海域
属华北地台地层层序,612井和401井有钻遇。元古界为变质岩,下古生界以海相碳酸盐岩为主,上古生界为海陆过渡相含煤碎屑岩沉积及海相碳酸盐岩沉积。
(1)元古界
重磁资料表明,北黄海海域是胶辽隆起在海区的延伸。盆地东部的612井钻遇结晶基底,401井在1872~2803 m井段钻遇元古界,岩性为白云岩、灰岩,千枚岩、板岩和石英岩。海域北部岛屿出露的地层与辽东地区基本相同,由下元古界的辽河群浪子山组、大石桥组、盖县组和震旦系下统的钓鱼台组、南芬组组成,主要岩性为石英片岩、石英岩、长石石英岩、大理岩、千枚状板岩;海域西部庙岛群岛出露的地层基本与胶东地区地层相同,由震旦系蓬莱群豹山口组和辅子夼组组成,岩性以千枚状板岩、板岩、少量片岩与石英岩、长石石英岩互层为特征。区域对比及重磁反演认为,北黄海盆地在华北地台太古界—元古界变质基底之上存在震旦系[186-187]。
(2)下古生界
主要由寒武系和奥陶系组成。北黄海盆地东部的401井钻遇472 m的寒武系,岩性为灰色—暗灰色灰岩和泥质灰岩、暗灰色泥岩互层[45],见Lingullela sp.、Acrotheles sp.、Acrotreta sp.、Obolella、Ovolus sp.、Acrotheles sp.等典型寒武纪腕足类化石。611、605井均钻遇中上奥陶统碳酸盐岩,有油气显示。20世纪80年代,朝鲜根据其陆域平南台向斜平壤古坳陷内大量的古生物资料确定了下志留统谷山组和中志留统月阳里组的存在[26],表明其与典型的华北地台层序略有区别。
(3)上古生界
在北黄海盆地东部钻井揭示有中-上泥盆统、石炭系、二叠系[26]。中-上泥盆统由泥岩、粉砂岩和砂岩互层组成,直接叠置在奥陶系顶部不整合面上,其上为以泥岩为主的下石炭统;中石炭统为薄煤层与砂岩、泥岩和灰岩;上石炭统为砂泥岩夹薄煤层,二叠系以灰岩为主,少量砂泥岩,夹煤层。从盆地东部揭示的古生代地层来看,其与华北地台陆域最大的区别是发现了中-上泥盆统和下石炭统。
(4)中生界
北黄海盆地东部坳陷大量的钻井钻遇了中生界,地震资料解释对比认为,该套地层广泛分布在西部、中部和东部坳陷及南部凹陷群,“下部层系”未钻遇;“中部层系”仅存在中侏罗统;“上部层系”包括上侏罗统和下白垩统,最大残留厚度分别为2500、3000和4000 m,为一套河流、三角洲、湖相砂泥岩沉积。
中侏罗统:上部为泥岩与细砂、粉砂岩互层,中下部以泥岩、粉砂质泥岩为主,局部夹砾岩、辉绿岩、花岗斑岩、玄武岩,底部以厚层砂砾岩为主,夹薄层泥岩。
上侏罗统:自下而上整体呈由粗变细的正旋回。下部为细砂岩、含砾细砂岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩与泥岩、粉砂质泥岩互层,局部夹薄煤层和碳质泥岩,上部主要为大套深灰色泥岩,偶夹灰岩、粉砂岩。除上述沉积岩外,还钻遇岩浆岩,岩性主要为花岗斑岩、英安斑岩。
下白垩统:目前钻井揭示厚度1316 m,岩性组合呈三段式特征。下部仅在盆地内部钻遇,岩性主要为灰色、灰褐色泥岩与灰色含砾不等粒砂岩、细砂岩、灰质砂岩及灰色泥质粉砂岩互层;中部以大段浅灰色含砾不等粒砂岩、细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、灰质砂岩及杂色砂砾岩为主,夹薄层褐色泥岩;上部以褐色、灰色泥岩为主夹薄层浅灰色含砾不等粒砂岩、细砂岩、灰质砂岩、灰质粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩。
1.1.3 南黄海海域
南黄海海域海相中-古生界与下扬子陆区的苏、浙、皖地区中-古生界是一个统一的沉积盆地。盆地的结晶基底是元古代初始海盆的一部分,沉积盖层是较为完整的海相沉积层和叠置其上的陆相沉积层[188]。
(1)震旦系
南黄海海域钻井未钻遇震旦系,在下扬子陆上露头和部分钻井中都有揭露。自下而上分为南沱组、陡山沱组和灯影组。南沱组下段和上段均为大陆冰碛岩,中段为含锰岩系;陡山沱组下部以页岩、泥岩夹砂岩为主,上部为泥质或硅质条带状灰岩;灯影组分布较广,厚度800~1200 m,以微晶白云岩、隐晶白云岩、叠层石白云岩、葡萄状白云岩及含石膏隐晶白云岩为主。
(2)古生界
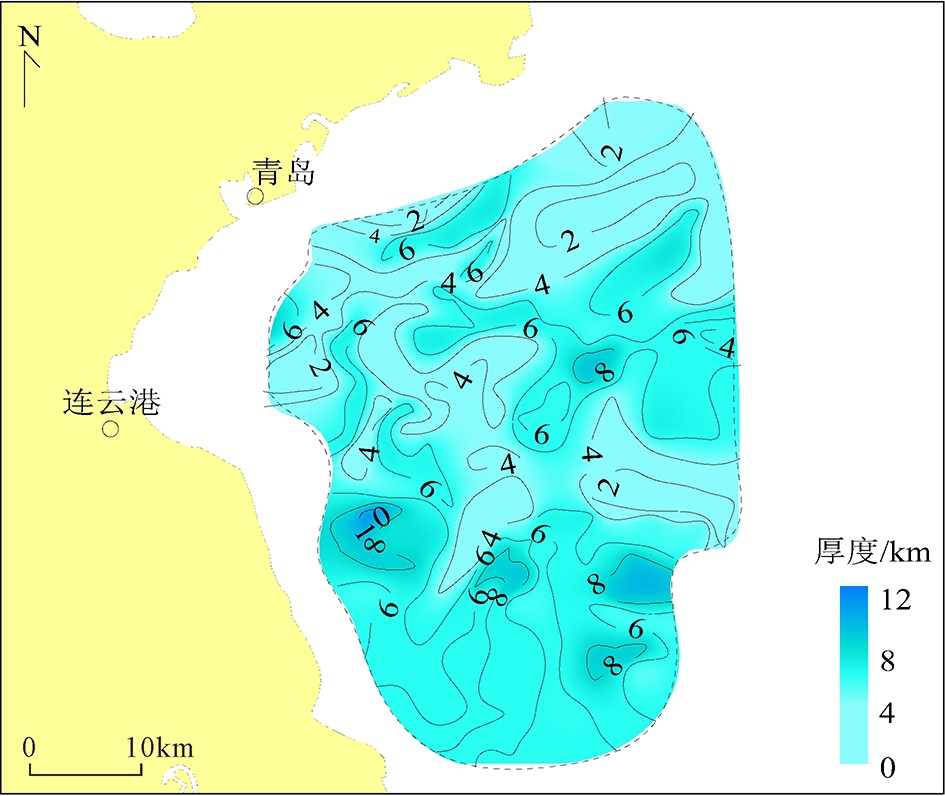
仅CSDP-2井钻遇志留系(未穿)。根据地震资料解释和海域对比,南黄海古生代地层齐全,由下往上发育寒武系、奥陶系、志留系、上泥盆统、石炭系和二叠系,地层厚度大,一般为4000~6000 m,在勿南沙隆起最厚超过8000 m(图5),以海相沉积为主,分布面积超过18×104 km2。
寒武系包括幕府山组、炮台山组和观音台组,以碳酸盐岩为主,与下伏灯影组假整合接触。幕府山组下部为灰黑色含磷泥岩、灰黑色碳质泥岩夹泥晶、粉晶白云岩,含石煤层;上部为泥质白云岩。炮台山组和观音台组以白云岩为主,含硅质团块和条带。
奥陶系自下而上分为仑山组、红花园组、大湾组、汤山组、汤头组和五峰组,岩性以介壳相碳酸盐岩为主,笔石页岩次之。仑山组为白云质灰岩、白云岩,含硅质条带或团块;红花园组以灰岩为主,底部为灰色粉晶白云质灰岩;大湾组为灰岩夹泥晶灰岩,顶为泥晶生物灰岩;汤山组为泥粉晶灰岩、生屑灰岩、瘤状灰岩;汤头组下部为生屑灰岩、泥质灰岩,局部夹瘤状灰岩;五峰组为灰黑、黑色泥岩,富含硅质及黄铁矿。
志留系自下而上为高家边组、坟头组和茅山组。高家边组下部为黑色泥页岩,上部主要为浅灰色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩,局部夹泥晶灰岩条带,CSDP-2井在高家边组上部钻遇2层白云岩;坟头组为灰色细砂岩与灰绿色粉砂质泥岩、红褐色泥岩互层;茅山组为细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,夹灰绿色、红褐色泥岩。
上泥盆统为五通组,岩性为灰色细、中砂岩与灰绿色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩互层,底部为砂砾岩及含砾砂岩。由于加里东运动导致缺失中、下泥盆统。
石炭系在CSDP-2井和CZ12-1-1A井有揭示,自下而上为高骊山组、和州组、老虎洞组、黄龙组、船山组。高骊山组为杂色页岩、泥岩、粉砂岩夹长石石英砂岩。和州组为灰岩、泥质灰岩夹钙质泥岩。老虎洞组为白云岩,溶孔发育;黄龙组为厚层微晶灰岩、生屑灰岩,藻灰岩和角砾灰岩;船山组为纯灰岩,含薄层硅质条带。
二叠系在CZ35-2-1、CSDP-2、WX13-3-1和WX5-ST-1等井均钻遇。自下而上发育栖霞组、孤峰组、龙潭组和大隆组。栖霞组以灰色、深灰色灰岩为主,局部夹泥灰岩和黑色页岩;孤峰组为硅质泥页岩;龙潭组下部发育灰色砂岩和泥岩,中部发育深灰色泥岩、灰色砂质泥岩夹煤层,上部为深灰色-灰色泥岩;大隆组为泥岩、硅质泥岩夹粉砂岩。
(3)中生界
南黄海海域的中生界具有特殊性,包括海相中下三叠统和陆相中侏罗统和白垩系。
“下部层系”:在南黄海海域广泛分布,包括下三叠统青龙组和中三叠统周冲村组,残留厚度0~3000 m,具有北薄南厚特征,是扬子陆表海沉积产物。下三叠统青龙组在CSDP-2井、WX5-ST-1井、CZ35-2-1井、CZ24-1-1井和WX4-2-1井均钻遇,以灰色灰岩为主,夹薄层泥质灰岩、泥岩。其中WX5-ST-1井揭示的青龙组厚度为1402 m,分上、下两段:下段为微晶灰岩、白云岩夹泥岩、粉砂质泥岩,局部砾屑灰岩;上段以微晶灰岩为主,发育水平或波状交错层理,间夹杂色泥岩及粉砂岩。勿南沙隆起的地震剖面显示,在青龙组之上发育一套厚达2 000 m的层状反射,推测为周冲村组,其岩性在下扬子陆域为砾屑灰岩、白云质灰岩、泥质灰岩和白云岩互层,局部夹灰绿色粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩及膏溶角砾岩。
“中部层系”:仅在烟台坳陷东北部有分布,RC20-2-1井1078~3217 m井段钻遇(未穿),厚度大于2195 m,岩性为深灰色、灰黑色泥岩夹灰褐色、褐色粉砂岩,为河湖相沉积,含孢粉化石。野外露头见长石石英砂岩。
“上部层系”:钻井和地震资料解释表明发育白垩系葛村组、浦口组、赤山组和泰州组,厚度1000~3000 m,主要分布于烟台坳陷和青岛坳陷,为一套河流、三角洲和湖相沉积。葛村组仅见于Kachi-1井,主要为红褐色泥岩、粉砂岩,偶夹砂岩,局部含黑色泥岩、火山岩;浦口组见于ZC7-2-1和Kachi-1井,岩性为大套的褐色砾岩、砂砾岩与褐色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩互层,夹流纹质凝灰岩和隐晶质中-基性火山岩;赤山组见于ZC7-2-1、H7和Kachi-1井,上部为褐色泥岩与粉细砂岩互层,下部为褐色砾岩、砂砾岩、粉砂岩与浅褐色泥岩互层;泰州组见于H7、ZC1-2-1、ZC7-2-1、CZ24-1-1和WX5-ST-1井,下部为棕红色咖啡色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩与棕红、棕灰色砂岩互层,上部为灰色、灰黑色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩夹页岩、粉细砂岩和鲕状灰岩,含丰富的非海相化石。
1.2 东海-南海型层型结构(“单一型”)
该类型的前新生代地层的典型特征是由单一的中生代地层组成,包括东海、台湾海峡、台西南、南海北部和南海南部海域,中生界厚度大[126-129],北东向展布,残留厚度一般为1500~4000 m,在东海基隆凹陷和南海北部潮汕坳陷发育两个残留厚度中心,最大残留厚度达7000 m(图6)。该区在中生代时期受古太平洋和古特提斯洋的共同影响,形成了晚三叠世—早中侏罗世及晚侏罗世—白垩纪两期盆地。早期为被动陆缘背景的坳陷型盆地,沉积了海相为主的“中部层系”;晚期为活动陆缘背景的裂陷盆地,火山活动强烈,沉积了以火山岩和火山沉积岩为主的海退沉积序列,夹碎屑岩的“上部层系”。区内总体缺失中生界“下部层系”,台湾海峡缺失中生界“中部层系”。
南海南部海域“上部层系”发育较完整,由上侏罗统和白垩系组成。广泛分布于南薇滩-安渡滩-礼乐滩及曾母盆地海区,在东部大体呈北东向分布,南部大体呈北西向分布,厚度一般为500~1500 m(图7),在礼乐滩和曾母盆地海区有两个残留厚度中心,最大厚度3000~4000 m。
1.2.1 东海海域
东海有30多口井钻遇中生界“中部层系”和“上部层系”,其中FZ10-1-1和FZ13-2-1井揭示较全[120]。由下往上为福州组、厦门组、渔山组、闽江组和石门潭组。
(1)“中部层系”
FZ10-1-1井钻遇了上三叠统—中侏罗统福州组(未穿),为一套暗色碎屑岩夹数层薄煤或炭质泥岩。下部为灰、深灰色泥岩与灰白色砂岩互层,夹数层薄煤,底部为厚层状砂岩夹薄层泥岩;上部为灰白色砂岩与褐色、浅灰色、灰色泥岩呈不等厚互层,顶部产薄煤层。
(2)“上部层系”
区内钻井揭示了上侏罗统厦门组、下白垩统渔山组、上白垩统闽江组和石门潭组。厦门组上部为褐、灰褐、棕褐色泥岩,棕红色泥岩和灰白色、杂色砂岩不等厚互层;下部为浅灰、灰、灰绿色泥岩及少量棕红色泥岩与浅灰、灰白色砂岩互层。渔山组下部为杂色砂砾岩夹棕红色泥岩,上部为棕红、棕褐色泥岩夹薄层粉砂岩,与上覆地层呈假整合接触。闽江组为褐灰、灰、浅灰、棕褐色泥岩与浅灰色粉砂岩、砂岩互层,局部夹灰黑色粉砂质泥岩条带;石门潭组以棕红色、棕紫色、深棕色泥岩为主,夹灰色、灰白色砂岩。
1.2.2 台湾海峡盆地
“上部层系”:台湾岛和海峡地区共有40余口井钻遇中生界[189],PK-1、PK-2、PK-3、WG-1、NK-2和WH-1等井均钻遇云林组,岩性为长石砂岩、粉砂岩和泥页岩互层,夹灰岩、凝灰岩和硅质条带,富含炭质碎屑。因含白垩纪纽康姆期和阿普第期瓣鳃类、菊石及3个超微化石带,证实为早白垩世(图3),钻遇地层厚度63~1082 m。WH-1井钻遇侏罗系[189],难以确定是否属于“中部层系”。
1.2.3 台西南盆地
台湾石油公司在台西南盆地的许多钻井钻遇了中生界,包括中生界“中部层系”的中下侏罗统和“上部层系”的下白垩统。
(1)“中部层系”:CF-1等14口井在下白垩统之下钻遇一套超过600 m厚的海相黑色泥岩,地震剖面显示与上覆下白垩统呈不整合接触,孢粉化石鉴定为中下侏罗统。
(2)“上部层系”:CF-1、GET-1等井揭示白垩系岩性为砂岩、页岩和凝灰岩,孢粉化石和钙质超微化石鉴定为下白垩统,厚度2000~3000 m。
1.2.4 南海北部
潮汕坳陷LF35-1-1井钻井揭示了中侏罗世—白垩纪地层,地震资料解释及海陆对比认为,南海北部发育上三叠统、下侏罗统、中侏罗统和白垩系。
(1)“中部层系”
区内发育上三叠统—中侏罗统[190]。
上三叠统:地震资料解释厚约2300 m,海陆对比预测岩性为长石石英砂岩、粉砂岩、含砾砂岩及泥岩。
下侏罗统:地震资料解释厚约3000 m,海陆对比预测岩性为长石石英砂岩、粉砂岩、含砾砂岩及泥岩。
中侏罗统:LF35-1-1井钻遇,岩性为灰色泥岩、泥质粉砂岩夹砂岩、灰岩及鲕粒灰岩,含孢粉化石。
(2)“上部层系”
LF35-1-1井完整揭示了“上部层系”,包括上侏罗统和下白垩统。
上侏罗统:岩性为放射虫硅质页岩夹灰黑色纹层状泥岩及泥质粉砂岩、细碧岩,为浅海—半深海沉积。
下白垩统:分为下中上三段,下段以玄武岩为主,夹少量流纹岩和砂泥岩及灰岩;中段为灰色纹层状泥岩、粉砂岩及砂岩;上段紫红色砂泥岩、粉砂岩夹泥灰岩。
1.2.5 礼乐盆地
“中部层系”:未钻遇。
“上部层系”:礼乐滩的Sampaguita-1井在3400 m处钻遇下白垩统[191],钻遇厚度520 m。下部有火山集块岩和砾岩,夹砂岩和粉砂岩,上部为砂泥岩与粉砂岩互层,含煤层。孢粉化石反映为早白垩世。
1.2.6 巴拉望盆地
“中部层系”:未钻遇。
“上部层系”:见于巴拉望盆地北部,Galoc-1、Cadlao-1、Destacado-1、Guntao-1、Catalat-1和Penascosa-1等井钻遇。钙质超微化石和孢粉组合显示为上侏罗统—下白垩统。中下部为灰岩与页岩互层,夹火山岩、粉砂岩和砂岩,上部为凝灰质页岩[191]。
2. 油气前景
2.1 烃源岩特征
按照烃源岩生烃潜力评价等级划分标准[78],中国海域前新生界发育6套主要的烃源岩,包括下古生界的下寒武统和下志留统、上古生界的石炭系和二叠系、中生界“中部层系”的中下侏罗统和“上部层系”的白垩系。其中下寒武统、下志留统和二叠系烃源岩有机质丰度高,中下侏罗统烃源岩分布最广。
2.1.1 古生界烃源岩
2.1.1.1 下古生界烃源岩
(1)下寒武统
海域未钻遇。根据地震剖面解释和海陆对比,推测南黄海海域发育下寒武统幕府山组烃源岩。下扬子区陆域钻井数据统计如表2所示,苏东121井下寒武统幕府山组烃源岩有机碳为0.55%~4.84%,均值为3%,达到很好级别的烃源岩厚度146 m;皖2井幕府山组烃源岩有机碳分布区间为0.57%~10%,均值为3.6%,有80%的样品达到很好级别的烃源岩,有机质类型以I型和II1型为主。崂山隆起地震资料解释推测,下寒武统有效烃源岩厚度达500 m,有机质丰度和有机质类型与下扬子陆域具有可比性。
表 2 下扬子区下寒武统幕府山组烃源岩厚度及有机质丰度Table 2. Statistical table of thickness and total organic abundance of source rocks in the Lower Cambrian Mufushan Formation in the lower Yangtze region序号 井号 厚度/m TOC/% 最小 最大 平均 1 苏东121井 368 0.55 4.84 3 2 皖2井 465 0.57 10 3.6 3 官地1井 442 0.51 47.7 9.82 (2)下志留统
目前海域未钻遇。地震资料解释和海陆对比推测南黄海发育,有效厚度达600 m。在下扬子陆域,下志留统高家边组露头见厚层深灰色、黑色页岩,为中等烃源岩。N4、苏页1井以及南京汤山和句容仑山地质浅井揭示高家边组黑色笔石页岩有机质丰度较高,TOC一般为2%~4%,有效厚度大于80 m,干酪根类型为I型和II1型。
2.1.1.2 上古生界烃源岩
(1)石炭系
分布有限,仅局限于渤海海域的渤西和渤中西侧地区,岩性为含煤的黑色泥岩,是一套海陆交互相的含煤地层,位于三角洲-沼泽相带。平均TOC为7.61%,(S1+S2)为5.93 mg/g,有效厚度大于120 m,干酪根类型为III型,评价为很好烃源岩。
(2)二叠系
二叠系烃源岩主要分布于南黄海海域,其次为渤海海域。
在南黄海有CSDP-2、WX13-3-1、CZ35-2-1和WX5-ST-1等井揭示。CSDP-2井钻遇栖霞组泥岩70.1 m,孤峰组硅质泥岩6.1 m,龙潭组暗色泥岩172 m,大隆组黑色泥岩138 m。地震剖面解释及钻井标定,下二叠统栖霞—孤峰组和上二叠统龙潭—大隆组烃源岩分布广泛。栖霞组为灰色、灰黑色钙质泥岩,局部见炭质泥岩;孤峰组以硅质页岩为主;龙潭—大隆组岩性整体为灰黑色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、黑色页岩、炭质泥岩和煤层。栖霞组泥岩的TOC范围为0.45%~1.52%,为中等—好烃源岩;孤峰组泥岩有机碳含量分布范围0.92%~12.5%,平均2.22%,为好烃源岩。龙潭组TOC范围0.75%~5.43%,平均1.7%,为中等—好烃源岩。大隆组烃源岩TOC范围0.92%~3.48%,平均2.077%,为好烃源岩。南黄海与下扬子陆域钻井岩心的干酪根碳同位素分析表明,二叠系烃源岩干酪根类型为Ⅱ-Ⅲ型,其中栖霞组和孤峰组为Ⅱ型,龙潭组、大隆组为Ⅱ-Ⅲ型。
渤海海域钻遇二叠系下石盒组和上石盒组煤系地层,为三角洲-潟湖相沉积,TOC分布范围0.94%~29%;沥青“A”含量范围0.01%~0.18%,平均值为0.03%,综合评价为中等烃源岩。
2.1.2 中生界烃源岩
中生界“中部层系”烃源岩主要为下中侏罗统黑色泥岩,钻井证实,分布于渤海、北黄海、东海和南海北部等海域。中生界“上部层系”烃源岩分布于渤海、南黄海、东海和南海海域。
2.1.2.1 中生界“中部层系”烃源岩
(1)渤海
早-中侏罗世,渤西地区挠曲沉降形成“渤西湖”,分布比较局限[19]。中下侏罗统烃源岩TOC范围0.87%~16.62%,平均2.077%;S1+S2范围1.31~48.11 mg/g,干酪根类型为II型,综合评价为中等烃源岩。
(2)北黄海
北黄海在西部、中部和东部坳陷发育的中侏罗统半深湖相暗色泥岩,TOC范围0.14%~5.34%,平均值2.0%;S1+S2范围0.29~11.75 mg/g,平均2.74 mg/g;氯仿沥青“A”范围0.005%~0.492%,平均0.185%;总烃范围(20~2091)×10−6,平均688×10−6,综合评价为好烃源岩[43]。
(3)东海
东海发育上三叠统—中侏罗统烃源岩,主要分布在基隆凹陷带和闽江斜坡带,区域上呈“东厚西薄”展布。钻井揭示岩性以深灰色泥岩为主,夹薄煤层,泥岩TOC范围1.4%~1.6%,氯仿沥青“A”含量范围0.103%~0.140%,生烃潜量(S1+S2)为1.60~2.78 mg/g,有机质类型为II2–III型,镜质体反射率(Ro)为0.65%~1.2%,综合评价为中等–好烃源岩,泥岩所夹薄煤层的有机碳含量为67.0%~75.0%,生烃潜量(S1+S2)为155.0~169.6 mg/g,有机质类型以III型为主,部分为II型[115,192],按煤系源岩的标准[193]评价,属差烃源岩。FZ13-2-1井和FZ10-1-1井在下-中侏罗统钻获油浸砂岩,经油源对比认为来自侏罗系。
(4)台西南
台西南海域钻遇中下侏罗系浅海相黑色页岩,有机碳含量为0.59%~1.78%,Ro值0.68%~1.38%,有机质类型为III型,成熟—高成熟,为中等烃源岩[36]。
(5)南海
根据地震资料解释和海陆对比,中生界“中部层系”烃源岩在南海广泛发育,目前仅在南海北部潮汕坳陷钻遇,LF35-1-1井揭示中-上侏罗统下部为浅海泥岩,TOC为1.00%~1.48%,平均值为1.32%,有机质类型以III型为主,含有少量II型,为中等—好烃源岩[163],累计厚度为46.16 m。
2.1.2.2 中生界“上部层系”烃源岩
(1)渤海
地震资料解释和钻井标定,上侏罗统—下白垩统广泛分布于渤海海域渤中、秦南、黄河口、埕北凹陷和辽中凹陷南部,暗色泥岩发育,白垩系泥岩TOC为1.55%~2.02%,生烃潜量(S1+S2)为4.25~5.84 mg/g,有机质类型为II型,综合评价为中等—好烃源岩[19]。
(2)北黄海
钻井揭示层位为上侏罗统,岩性为半深湖相泥岩。有机质丰度较高,暗色泥岩TOC范围0.1%~6.08%,平均1.33%;生烃潜量(S1+S2)为0.02~105.6 mg/g,平均值为6.84 mg/g;氯仿沥青“A”范围0.001%~0.445%,平均值为0.076%;总烃为(85.55~1836.9)×10−6,平均542.42×10−6,综合评价为中等—好烃源岩。
(3)南黄海
ZC1-2-1井揭示层位为上白垩统泰州组,岩性为黑色、深灰色湖相泥岩。TOC范围1.0%~2.0%,平均1.53%;S1+S2范围2~10 mg/g,平均5 mg/g;氯仿沥青“A”范围0.1%~0.4%,平均为0.253%;热解氢指数范围100~500 mg/g,平均425 mg/g,Ro为0.8%。干酪根类型以I型和II1型为主,综合评价为好烃源岩。
(4)台湾海峡海域
WX-1井揭示下白垩统云林组地层厚度959 m,其中深灰色—黑色海相泥岩厚度约为500 m,TOC范围0.573%~0.818%;PK-3井和GH-1井下白垩统烃源岩TOC达到1.0%;CCT-1井在2 231 m泥质岩TOC为1.56%[189]。
(5)台西南海域
CFC-3井揭示下白垩统TOC含量0.6%~0.95%,炭质泥岩最高可达2.45%以上,Ro值多为0.6%~1.0%,属中等—较好的成熟烃源岩[194]。CFC构造凝析油油源对比显示为中生界烃源岩供烃的混源油[143],说明中生界是有效烃源岩。
(6)南海海域
南海北部LF35-1-1井钻遇中-上侏罗统上部为半深海-深海沉积,暗色泥岩累计厚度达82.87 m,有机碳含量为0.50%~1.15%,平均值为0.67%,有机质类型以III型为主,含有少量II型,综合评价为差—中等烃源岩[163]。
南海南部礼乐盆地Sampaguita-1井钻遇的下白垩统泥岩TOC最高达2.0%,属于中等—好烃源岩[195]。
2.2 成藏组合类型
2.2.1 储层特征
中国海域前新生界油气储层可分为三大类:孔隙型、裂缝改造型和风化壳型。
2.2.1.1 孔隙型储层
这类储层包括白云岩储层、礁滩相碳酸盐岩储层和砂岩储层。
(1)白云岩储层
南黄海、渤海和北黄海的古生界发育这类储层,以南黄海中上寒武统、石炭系和下三叠统青龙组白云岩为典型代表。钻井揭示,白云岩储层岩性以残余颗粒白云岩为主,其中粉—中晶白云岩为中孔低渗储集层,孔隙度为2%~4.9%,渗透率为(0.14~5.27)×10−3 μm2,孔隙类型以晶间溶孔、晶间孔和不规则溶孔为主。WX5-ST-1井在下三叠统青龙组2302~2327 m井段发现一层25 m厚的白云岩,其中2305~2315 m井段为高孔高渗白云岩,有效孔隙度6%~8%[57]。根据四川盆地的勘探证实,白云岩有效孔隙度达到6%就是优质高产储层。
(2)礁滩相碳酸盐岩储层
南黄海、渤海和北黄海的古生界,以及南海南部的中生界发育这类储层。南黄海WX13-3-1井2100~2118.2 m井段取芯发现,二叠系有富含单体珊瑚、有孔虫、腕足、瓣鳃、兰藻、苔藓等化石的生物灰岩,中子测井孔隙度为5%~7%,有不规则的原生裂隙,为较好的储层。CZ12-1-1井石炭系船山组中下部发育礁滩相及台地边缘相灰岩,钻遇厚度133 m。
海陆对比认为南黄海中、上寒武统发育的陆棚相沉积具交代白云岩储层和滩相储层两种类型。
(3)砂岩储层
这类储层见于全海域的中生界和南黄海、渤海、北黄海海域的古生界。沉积相类型包括河流、三角洲、滨浅湖相和滨浅海相。如东海南部海域FZ13-2-1和FZ10-1-1井揭示的侏罗系和白垩系,埋深小于2300 m的砂岩孔隙度为18.5%~26.5%,渗透率为(1.3~128)×10−3 μm2,属于中—高孔、中渗型储层;2300~3100 m的砂岩储层,孔隙度可达10%[129]。礼乐盆地下白垩统平均孔隙度为17.2%,平均渗透率为10.3×10−3 μm2[195]。
2.2.1.2 裂缝改造型储层
中国海域前新生界裂缝改造型储层见于渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海和南海诸海域,与大型断裂带和挤压构造带伴生,如渤海的郯庐断裂带、南黄海的崂山南部断裂带、东海的西-基断裂带发育这类储层。与南黄海处于同一区域构造单元的苏北黄桥地区海相碳酸盐岩裂缝改造型储层相当发育,钻井过程多见放空、泥浆漏失、井涌、井喷等现象。由于构造成因裂隙和成岩差异压实作用产生的裂隙改善了岩石的原生孔渗性能,使低孔-低渗的碳酸盐岩储层转化为有效的碳酸盐储集岩。根据测井资料计算结果,扬子区陆域N11井岩石裂缝孔隙度(1008.2~1899.6 m井段)平均为5%,N12井为2%,裂缝孔隙度虽小,但储集能力很强,1%裂缝孔隙度相当于5%~8%[64]。
2.2.1.3 风化壳储层
这类储层广泛发育于渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海和南海诸海域,以渤海最为典型,形成了许多大型、特大型潜山油气田。根据地层时代和岩性可分4个亚类,即前寒武系变质岩和混合花岗岩、古生代碳酸盐岩、中生代火山岩以及花岗岩、中生代碎屑岩[188]。其中碳酸盐岩潜山储层包括孔隙、溶洞和裂缝3种储集空间,形成了裂缝-孔隙型、孔隙-裂缝型和裂缝型储层,孔隙度2%~5%,渗透率为(0.01~49.3)×10−3 μm2,为低孔低渗型储层,储层展布受构造-断裂和岩溶作用的控制,纵向上自上而下可分为低渗层、有效储层及致密层,平面上构造高部位和断裂发育区是有利储层发育位置[185]。碎屑岩风化壳储层物性受埋藏条件、淋滤作用、构造条件和成岩环境等因素的控制。渤海海域C12和Q17构造碎屑岩风化壳储层研究表明[196],碳酸盐胶结物含量高,构造活动强烈、淋滤作用时间长是优质储层发育的有利因素。火山岩风化壳储层的储集空间包括原生气孔、溶蚀孔以及裂缝,其中溶蚀孔与构造裂缝是主要的储集空间类型,优势岩相、断裂活动以及风化作用共同控制了优质储层的形成[197]。胡志伟等[198]研究蓬莱9-1油田花岗岩储层后认为,风化淋滤作用控制储层的宏观特征,断裂与节理加速储层内幕改造,横向上储层厚度展布范围与断裂发育密度正相关,垂向上可划分为黏土带、砂质带、碎裂带、裂缝带和基岩带,其中砂质带、碎裂带和裂缝带为有利储层发育带。
南黄海7口井钻遇风化壳储层,所有井都钻遇印支面风化壳,其中CSDP-2和CZ12-1-1井钻遇石炭系内部风化壳层(位于和州组和黄龙组顶面),风化壳可分为充填带和裂隙渗流带,次生孔隙发育,钻井过程中泥浆漏失严重[55]。
东海FZ13-2-1井钻遇中生界顶面风化壳储层,上白垩统石门潭组发育3层共计厚20 m的风化壳砂岩储层,孔隙度为26.25%~29.04%。
总体而言,风化壳储层物性及分布受构造作用、风化淋滤作用和埋藏条件等多重因素控制。
2.2.2 油气成藏组合
中国海域前新生界存在6种类型的油气成藏组合。古生界生烃古生界储烃称之为“古生古储”成藏组合,古生界生烃中生界储烃称之为“古生中储”成藏组合,古生界生烃新生界储烃称之为“古生新储”成藏组合,中生界生烃中生界储烃称之为“中生中储”成藏组合,中生界生烃新生界储烃称之为“中生新储”成藏组合,新生界生烃前新生界潜山储烃称之为“上生下储”成藏组合。
“古生古储”:在南黄海已得到CSDP-2井的钻井证实,在中志留统坟头组和上志留统茅山组砂岩储层发现了古油藏[93],油气包裹体特征和生物标志物特征证实古油藏烃源来自下志留统高家边组泥岩。
“古生中储”:南黄海CSDP-2井在下三叠统青龙组见到油浸和油斑,油源对比认为其来自古生界二叠系烃源岩。推测这类组合在渤海海域存在,渤中凹陷和黄河口凹陷中的石炭系—二叠系具有生烃条件,中生界具备储集和盖层条件。
“古生新储”:推测在渤海、北黄海和南黄海海域存在这类组合。如在南黄海海域,烃源岩为古生界龙潭组和大隆组,储层为阜宁组和泰州组砂岩,直接盖层为阜宁组一段薄层的含膏泥岩,区域盖层为阜宁组二段厚层泥岩。与南黄海盆地相连的苏北盆地朱家墩气田就是此类成藏组合。
“中生中储”:这类组合在渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海和南海发育。北黄海盆地东部坳陷在下白垩统砂岩中钻获了液体原油,发现小型油藏,油源对比显示,原油来自于上侏罗统上部烃源岩[43]。这类成藏组合在台西南盆地也得到钻井证实。
“中生新储”:根据烃源岩、储层和盖层的发育层位,这类成藏组合在渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海和南海广泛发育。
“上生下储”:这类成藏组合形成潜山油气藏,在渤海、南海北部和南海南部找到了大型、特大型潜山油气田,储层为风化壳储层,储层的地层时代包括前寒武系、古生界和中生界(表3),储层岩性包括碳酸盐岩、碎屑岩、火山岩和变质岩[199]。
表 3 中国海域潜山油气藏生储盖组合特征Table 3. Characteristics of source rock, reservoir and cap rocks assemblages of buried hill reservoirs in China Seas潜山油气藏 构造 地层时代 烃源岩(层位) 储层岩性 盖层(层位) 蓬莱9-1 庙西北凸起 中生界 沙河街组及东营组 二长花岗岩 馆陶组 锦州25-1S 辽西北凸起 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 二长片麻岩、斜长片麻岩 沙河街组及东营组 曹妃甸11-6 沙垒田凸起 太古界 东营组 混合化黑云母花岗岩 馆陶组 曹妃甸18-2 沙垒田凸起 太古界 东营组 二长花岗岩 馆陶组 渤中26-2 渤海凸起 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 英云闪长岩、花岗闪长岩 东营组及明化镇组 锦州20-2 辽西低凸起 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 混合岩、碎屑岩 沙河街组及东营组 渤中19-6 渤中凹陷 太古界 沙河街组 变质岩 沙河街组与东营组 渤中13-2 渤中凹陷 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 花岗片麻岩 中生界 渤中28-1 渤南凸起 古生界奥陶系 沙河街组 碳酸盐岩 沙河街组 岐口17-9 岐口凹陷 中生界 海沟房组、沙河街组 碎屑岩 沙河街组 428W、428E 石臼坨凸起 古生界 沙河街组及东营组 花岗岩 东营组 曹妃甸2-1 沙垒田凸起 古生界 沙河街组 碳酸盐岩 沙河街组 涠6-1、涠10-3N等 涠西南凹陷 古生界 流沙港组 碳酸盐岩 流沙港组 惠州26-6 惠州凹陷 中生界 文昌组、恩平组 花岗岩 文昌组、珠海组 永乐8-1 松南低凸起 中生界 始新统、渐新统崖城组 花岗岩 中新统 3. 勘查方向
前期研究表明,中国海域前新生界油气资源前景广阔,下列领域是油气调查与勘探的方向。
3.1 南黄海的海相中-古生界
3.1.1 崂山隆起是下古生界的油气远景区
崂山隆起是南黄海中-新生代陆相沉积盆地的隆起,面积约4×104 km2,海相中-古生界残留厚度4000~6000 m。该隆起上主要发育二叠系及其以下地层,下古生界厚度大,埋藏相对较浅;发育下寒武统和下志留统两套区域性烃源岩,震旦系、寒武系、奥陶系和石炭系碳酸盐岩储层以及志留系和二叠系砂岩储层,下寒武统、下志留统和二叠系区域性盖层;因存在厚度较大的下志留统高家边组泥岩滑脱层,使得下古生界构造变形弱,油气保存条件好;发育“古生古储”成藏组合,大型局部构造发育,是下古生界的油气远景区。崂山隆起南部高石稳定带大型圈闭发育,单个圈闭面积最大达1 986 km2,圈闭远景资源量大,各圈闭继承性发育、闭合幅度大,形成时间早,有利于油气的捕获和保存。
3.1.2 勿南沙隆起是上古生界的油气远景区
勿南沙隆起位于南黄海盆地南部,面积约6×104 km2,海相中-古生界残留厚度5000~7000 m,最厚超过8000 m。区内海相中-古生代地层齐全,发育下寒武统、下志留统和二叠系3套区域性烃源岩,震旦系、寒武系、奥陶系和石炭系碳酸盐岩储层以及志留系和二叠系砂岩储层,下寒武统、下志留统和二叠系3套区域性盖层;“古生古储”成藏组合完整,大型局部构造发育,上古生界埋藏相对较浅。因此,勿南沙隆起是上古生界的油气远景区。
3.2 东海南部-南海北部的中生界
3.2.1 南海北部潮汕坳陷
地震资料解释和综合研究表明,潮汕坳陷中生界分布面积约3.95×104 km2,地层保存较完整,最大厚度超过5000 m,发育“中部层系”上三叠统—下侏罗统、“上部层系”中-上侏罗统两套烃源岩,预测烃源岩分布面积约1.64×104 km2,最大厚度800 m,平均厚度420 m,干酪根类型为II1型,属中等—好烃源岩,均处于成熟或过成熟阶段。预测发育中-上侏罗统滨浅海相砂岩、三角洲砂岩以及浊积扇、海底扇砂岩储层,白垩系滨浅海相砂岩、河流-湖泊相砂岩等储层。侏罗系浅海相、半深海相泥岩、晚渐新世及早中新世海相泥岩是区域盖层,发育“中生中储”和“中生新储”成藏组合。
3.2.2 东海南部闽江-基隆凹陷
闽江-基隆凹陷中生界分布面积约6×104 km2,厚度3500~6000 m,发育中下侏罗统烃源岩、侏罗系和白垩系砂岩储层、中-下侏罗统海相泥岩以及上侏罗统和白垩系湖相泥岩盖层,存在“中生中储”和“中生新储”成藏组合。
3.3 新生代富生烃凹陷内潜山油气藏
中国海域新生代盆地内富生烃凹陷发育。凹陷内基岩突起或内部构造脊被多个烃源岩灶包围,接受多个富生烃凹陷生成的油气;因经历多次构造运动和长期暴露,风化壳储层发育;其上直接覆盖新生界泥岩盖层;具有“上生下储”成藏组合,是油气聚集的有利区。下一步的勘查重点有:渤海盆地的渤中、黄河口、辽中、埕北、南堡凹陷内基岩凸起以及内部构造脊;东海陆架盆地西湖、基隆凹陷和丽水凹陷内基岩凸起以及内部构造脊;珠江口盆地的西江、恩平、惠州和白云凹陷内基岩凸起及大型构造脊;北部湾盆地内的涠南、海州、海头、乌石和福山凹陷内基岩凸起及大型构造脊;南黄海盆地蓬莱、牟平、栖霞、海阳、龙口、胶州和胶南凹陷内基岩凸起及大型构造脊;南沙海域大型富生烃凹陷内基岩凸起及大型构造脊。
3.4 北黄海盆地坳陷区的中生界
北黄海盆地西部、中部和东部坳陷中生界厚度大,生油岩具有一定的分布范围,发育“中生中储”成藏组合,已在东部坳陷发现油气,下一步应以储层预测为重点在有效生油岩范围内寻找“中生中储”油气藏,并兼顾“中生新储”油气藏和“上生下储”潜山油气藏。
3.5 渤海海域的前新生界
近年来的勘探实践和科技攻关证实,华北地台的新元古界、古生界和中生界具有生烃潜力,发育碳酸盐岩和碎屑岩储层及区域性泥岩盖层。因此,针对渤海海域的前新生界,除重视潜山油气藏外,还应关注“自生自储”油气藏,如“古生古储”、“古生中储”和“中生中储”成藏组合。
4. 结论
(1)中国海域前新生界厚度大,最厚逾8000 m,发育新元古界、下古生界、上古生界、中生界“下部层系”、中生界“中部层系”和中生界“上部层系”6套地层,有渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海南部—南海北部和南海南部5大分布区,预测分布面积达132.3×104 km2。
(2)中国海域前新生界纵向上发育东海-南海型和渤海-黄海型两类层型结构。前者由“单一型”的中生代地层组成,包括“中部层系”上三叠统—中侏罗统和“上部层系”上侏罗统—白垩系,它们是2期沉积盆地的产物,分布于东海和南海海域;后者为新元古界-古生界-中生界“叠合型”层型结构,分布于渤海、北黄海和南黄海海域。
(3)中国海域前新生界发育6套主要的烃源岩,包括下古生界的下寒武统和下志留统、上古生界的石炭系和二叠系、中生界“中部层系”的中下侏罗统和“上部层系”的白垩系。其中下寒武统、下志留统和二叠系烃源岩有机质丰度高,中下侏罗统烃源岩分布最广。
(4)中国海域前新生界油气储层可分为孔隙型、裂缝改造型和风化壳型3大类型。其中,孔隙型储层见于渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海及南海诸海域,包括白云岩、礁滩相碳酸盐岩和砂岩储层;裂缝改造型储层见于渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海和南海诸海域,与大型断裂带和挤压构造带伴生,由构造成因、差异压实产生的裂缝改善岩石原生孔渗性能而成;风化壳储层广泛分布于渤海、北黄海、南黄海、东海和南海诸海域,根据地层时代和岩性可分前寒武系变质岩和混合花岗岩、古生代碳酸盐岩、中生代火山岩以及花岗岩、中生代碎屑岩4亚类,储层物性及分布主要受构造作用、风化淋滤作用和埋藏条件3种因素控制。
(5)中国海域前新生界存在6种类型的油气成藏组合,即“古生古储”、“古生中储”、“古生新储”、“中生中储”、“中生新储”和“上生下储”成藏组合。
(6)中国海域前新生界具有较好的油气资源前景。南黄海崂山隆起是下古生界的油气远景区;南黄海勿南沙隆起是上古生界的油气远景区;南海北部潮汕坳陷和东海南部闽江-基隆凹陷是中生界的油气远景区;海域新生代盆地富生烃凹陷内基岩突起或内部构造脊是“上生下储”型油气藏的有利区;北黄海盆地坳陷区的中生界值得重视;渤海海域的前新生界“自生自储”油气藏值得关注。
-
表 1 中国海域前新生代地层及最大厚度
Table 1 Distribution of Pre-Cenozoic strata in China Seas (strata type and maxmum thickness)
m 地层层序 渤海 黄海 东海-南海北部 南海南部 北黄海 南黄海 东海 台湾海峡 台西南 南海北部 巴拉望 礼乐 中生界 上部层系 3000 4000* 3000 3500* >1082 3000* 3500* 3000* 4000* 中部层系 1000 2000 >2195 4500* 缺失 600 5300* 缺失 缺失 下部层系 1200 1500 3000* ? ? ? ? ? ? 古生界 上古生界 1400 >2000 4500* ? 缺失 缺失 缺失 ? ? 下古生界 >310 >472 4500* ? 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 元古界 新元古界 不详 >931 1200* 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 缺失 叠合面积 67616 km2 43279 km2 183917 km2 419433 km2 608921 km2 层型结构 “叠合型”(新元古界-古生界-中生界) “单一型”(中生界) 注:表中*为地震资料解释最大厚度;?表示情况不明。 表 2 下扬子区下寒武统幕府山组烃源岩厚度及有机质丰度
Table 2 Statistical table of thickness and total organic abundance of source rocks in the Lower Cambrian Mufushan Formation in the lower Yangtze region
序号 井号 厚度/m TOC/% 最小 最大 平均 1 苏东121井 368 0.55 4.84 3 2 皖2井 465 0.57 10 3.6 3 官地1井 442 0.51 47.7 9.82 表 3 中国海域潜山油气藏生储盖组合特征
Table 3 Characteristics of source rock, reservoir and cap rocks assemblages of buried hill reservoirs in China Seas
潜山油气藏 构造 地层时代 烃源岩(层位) 储层岩性 盖层(层位) 蓬莱9-1 庙西北凸起 中生界 沙河街组及东营组 二长花岗岩 馆陶组 锦州25-1S 辽西北凸起 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 二长片麻岩、斜长片麻岩 沙河街组及东营组 曹妃甸11-6 沙垒田凸起 太古界 东营组 混合化黑云母花岗岩 馆陶组 曹妃甸18-2 沙垒田凸起 太古界 东营组 二长花岗岩 馆陶组 渤中26-2 渤海凸起 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 英云闪长岩、花岗闪长岩 东营组及明化镇组 锦州20-2 辽西低凸起 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 混合岩、碎屑岩 沙河街组及东营组 渤中19-6 渤中凹陷 太古界 沙河街组 变质岩 沙河街组与东营组 渤中13-2 渤中凹陷 太古界 沙河街组及东营组 花岗片麻岩 中生界 渤中28-1 渤南凸起 古生界奥陶系 沙河街组 碳酸盐岩 沙河街组 岐口17-9 岐口凹陷 中生界 海沟房组、沙河街组 碎屑岩 沙河街组 428W、428E 石臼坨凸起 古生界 沙河街组及东营组 花岗岩 东营组 曹妃甸2-1 沙垒田凸起 古生界 沙河街组 碳酸盐岩 沙河街组 涠6-1、涠10-3N等 涠西南凹陷 古生界 流沙港组 碳酸盐岩 流沙港组 惠州26-6 惠州凹陷 中生界 文昌组、恩平组 花岗岩 文昌组、珠海组 永乐8-1 松南低凸起 中生界 始新统、渐新统崖城组 花岗岩 中新统 -
[1] 张冰, 李堃年, 王铁良. 中国大陆架前第三纪地质结构的探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1986, 7(3):197-206 doi: 10.11743/ogg19860301 ZHANG Bing, LI Kunnian, WANG Tieliang. Study of pre-tertiary geological tectonics on the continental shelf of China [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1986, 7(3): 197-206. doi: 10.11743/ogg19860301
[2] 李培廉. 南黄海的白垩系: 一个值得重视的找油领域[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1986, 6(4):51-55 LI Peilian. The Cretaceous of South Huanghai Sea: A potential frontier oil prospecting [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1986, 6(4): 51-55.
[3] 郝服光. 东海盆地南部及台湾近海诸盆地白垩系及下第三系沉积特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1988, 2(1):13-20 HAO Fuguang. Sedimentary characteristics of Cretaceous and Eogene in southern East China Sea Basin and offshore basins of Taiwan [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1988, 2(1): 13-20.
[4] 王香婷, 毕力刚. 渤海地区中侏罗世和早白垩世孢粉组合[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1998, 12(5):319-327 WANG Xiangting, BI Ligang. Sporo-pollen assemblages of middle Jurassic and early Cretaceous in Bohai region [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1998, 12(5): 319-327.
[5] 姚伯初, 曾维军, 陈艺中, 等. 南海北部陆缘东部中生代沉积的地震反射特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(1):81-90 YAO Bochu, ZENG Weijun, CHEN Yizhong, et al. Seismicreflectlve characteristics of mesonoic sediments on the eastern continental margin in the north of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(1): 81-90.
[6] 王平, 夏戡原, 黄慈流. 南海东北部中生代海相地层的分布及其地质地球物理特征[J]. 热带海洋, 2000, 19(4):28-35 WANG Ping, XIA Kanyuan, HUANG Ciliu. Distribution and geological & geophysical characteristics of mesozoic marine strata in northeastern part of south China sea [J]. Tropical Oceanography, 2000, 19(4): 28-35.
[7] 蔡乾忠. “残留特提斯”的猜想: 从中国近海域发现海相中生界-古新统谈起[J]. 中国地质, 1998(4):39-41 CAI Qianzhong. Tethys remains, a hypothesis based on the discovery of marine Mesozoic and Paleogene in China's mar-ginal sea areas [J]. Geology in China, 1998(4): 39-41.
[8] 蔡乾忠, 刘守全, 莫杰. 寻找海相油气新领域: 从南海北部“残留特提斯”谈起[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(3):157-162 CAI Qianzhong, LIU Shouquan, MO Jie. Search for new domains of marine-origin petroleum: “Remained Tethys” in the northern south China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2000, 14(3): 157-162.
[9] 夏戡原, 黄慈流. 南海中生代特提斯期沉积盆地的发现与找寻中生代含油气盆地的前景[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(3):227-238 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.03.021 XIA Kanyuan, HUANG Ciliu. The discovery of Meso-Tethys sedimentary basins in the South China Sea and their oil and gas perspective [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(3): 227-238. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.03.021
[10] 苏乃容, 曾麟, 李平鲁. 珠江口盆地东部中生代凹陷地质特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1995, 9(4):228-236 SU Nairong, ZENG Lin, LI Pinglu. Geological features of Mesozoic sags in the eastern part of Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1995, 9(4): 228-236.
[11] 钟建强. 南沙群岛含油气盆地的前新生代基底及与北部陆缘的关系[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1997, 11(2):124-130 ZHONG Jianqiang. Pre-Cenozoic basement of oil and gas bearing basins in Nansha islands and its relationship with northern continental margin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1997, 11(2): 124-130.
[12] 刘光鼎, 宋海斌, 张福勤. 中国近海前新生代残留盆地初探[J]. 地球物理学进展, 1999, 14(3):1-8 LIU Guangding, SONG Haibin, ZHANG Fuqin. A preliminary study of Chinese offshore pre-cenozoic residual basins [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 1999, 14(3): 1-8.
[13] 王国纯. 中国东部海域中生界地质特征及成藏地质条件[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1994, 8(2):91-98 WANG Guochun. Mesozoic geological characteristics and hydrocarbon potential in the East China Sea Area [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1994, 8(2): 91-98.
[14] 刘光鼎. 论中国油气二次创业[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2002, 18(11):1-3 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2002.11.003 LIU Guangding. The second round of oil & gas exploration of China [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2002, 18(11): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2002.11.003
[15] 吉治平. 渤海残留盆地油气地球物理研究综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2005, 20(4):1039-1046 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2005.04.026 JI Zhiping. A review of progress on geophysics of Bohai residual basin [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2005, 20(4): 1039-1046. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2005.04.026
[16] 徐亚, 郝天珧, 戴明刚, 等. 渤海残留盆地分布综合地球物理研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2007, 50(3):868-881 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.03.028 XU Ya, HAO Tianyao, DAI Minggang, et al. Integrated geophysics research on distribution of residual basins of Bohai Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2007, 50(3): 868-881. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.03.028
[17] 郝天珧, 杨长春, 刘洪, 等. 环渤海地区前新生代油气资源的综合地质、地球物理研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(4):1269-1279 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.04.037 HAO Tianyao, YANG Changchun, LIU Hong, et al. Integrated geological and geophysical study for pre-cenozoic hydrocarbon resources in the circum-Bohai area [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(4): 1269-1279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.04.037
[18] 张善文, 隋风贵, 林会喜, 等. 渤海湾盆地前古近系油气地质与远景评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 124-128 ZHANG Shanwen, SUI Fenggui, LIN Huixi, et al. Petroleum Geology and Perspective Evaluation on Pre-paleogene System in Bohai Bay Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009: 124-128.
[19] 周静, 吕大炜, 陈龙, 等. 渤海海域区前古近纪构造对上古生界-中生界烃源岩的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(2):146-150 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201302146 ZHOU Jing, LÜ Dawei, CHEN Long, et al. Influence of pre-paleogene tectonics on Upper Paleozoic-Mesozoic source rocks in Bohai Sea area [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2013, 35(2): 146-150. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201302146
[20] 李卓, 郭诚, 周立业, 等. 渤海S油田下古生界碳酸盐岩储层主控因素分析[J]. 广东石油化工学院学报, 2019, 29(3):5-9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2562.2019.03.002 LI Zhuo, GUO Cheng, ZHOU Liye, et al. Analysis on main controlling factors of lower paleozoic carbonate reservoir in Bohai S oilfield [J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Petrochemical Technology, 2019, 29(3): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2562.2019.03.002
[21] 徐长贵, 侯明才, 王粤川, 等. 渤海海域前古近系深层潜山类型及其成因[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(1):21-32 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.01.003 XU Changgui, HOU Mingcai, WANG Yuechuan, et al. Type and genesis of Pre-Tertiary deep buried hills in the Bohai Sea area [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(1): 21-32. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.01.003
[22] 杨纪磊, 曹洁, 魏文艳, 等. 渤海海域下古生界牙形类生物地层初探[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2020, 37(3):238-244 YANG Jilei, CAO Jie, WEI Wenyan, et al. Lower paleozoic conodonts from the Bohai Sea area and their stratigraphic significance [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2020, 37(3): 238-244.
[23] 薛永安, 李慧勇, 许鹏, 等. 渤海海域中生界覆盖型潜山成藏认识与渤中13-2大油田发现[J]. 中国海上油气, 2021, 33(1):13-22 XUE Yongan, LI Huiyong, XU Peng, et al. Recognition of oil and gas accumulation of Mesozoic covered buried hills in Bohai sea area and the discovery of BZ 13-2 oilfield [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2021, 33(1): 13-22.
[24] 蔡峰. 北黄海盆地中生界源岩地化特征分析[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1997(9):4-7 CAI Feng. Geochemical characteristics of Mesozoic source rocks in north Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 1997(9): 4-7.
[25] 蔡峰. 北黄海盆地基底地质特征[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1999(12):1-3 CAI Feng. Basement geological characteristics of north Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 1999(12): 1-3.
[26] 陈洁. 北黄海前新生代残留盆地勘探潜力分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2005, 20(3):757-760 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2005.03.029 CHEN Jie. Potential analysis of exploration for pre-cenozoic marine residual basins in northern Yellow Sea [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2005, 20(3): 757-760. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2005.03.029
[27] 陈玲, 白志琳, 李文勇. 北黄海盆地中新生代沉积坳陷特征及其油气勘探方向[J]. 石油物探, 2006, 45(3):319-323 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2006.03.021 CHEN Ling, BAI Zhilin, LI Wenyong. The character of mid-cenozoic sedimental depression and oil-gas explorating direction in north Yellow Sea [J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2006, 45(3): 319-323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2006.03.021
[28] 刘振湖, 高红芳, 胡小强, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷中生界含油气系统研究[J]. 中国海上油气, 2007, 19(4):229-233 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.04.003 LIU Zhenhu, GAO Hongfang, HU Xiaoqiang, et al. A study on the Mesozoic petroleum system in East depression, North Yellow Sea basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2007, 19(4): 229-233. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.04.003
[29] 龚建明, 温珍河, 陈建文, 等. 北黄海盆地中生代地层的地质特征和油气潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(2):69-77 Gong J M, Wen Z H, Chen J W, et al. Geologic characteristics and hydrocarbon-generating potential of mesozoic strata in the North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(2): 69-77.
[30] 梁世友, 李凤丽, 付洁, 等. 北黄海盆地中生界烃源岩评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(3):249-252 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.03.008 LIANG Shiyou, LI Fengli, FU Jie, et al. Evaluation of meso-cenozoic hydrocarbon source rocks in north yellow sea basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(3): 249-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.03.008
[31] 张莉, 周永章, 王嘹亮, 等. 北黄海盆地生烃条件研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2009, 29(1):21-25 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.01.005 ZHANG Li, ZHOU Yongzhang, WANG Liaoliang, et al. A study on hydrocarbon generation conditions in the North Yellow Sea basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(1): 21-25. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.01.005
[32] 李文勇, 曾祥辉, 黄家坚. 北黄海中、新生代盆地: 残留盆地还是叠合盆地?[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(9):1269-1275 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.09.007 LI Wenyong, ZENG Xianghui, HUANG Jiajian. Meso-cenozoic North Yellow Sea: residual basin or superimposed basin? [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(9): 1269-1275. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.09.007
[33] 王强, 王应斌, 张友. 北黄海中生代残留盆地砂岩成岩作用及其对孔隙的影响[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(8):16-25 WANG Qiang, WANG Yingbin, ZHANG You. Sandstone diagenesis in mesozoic residual basin of North Yellow Sea and its impact on porosity [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2011, 27(8): 16-25.
[34] 梁杰, 温珍河, 肖国林, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷储层特征及影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第纪地质, 2013, 33(2):111-119 LIANG Jie, WEN Zhenhe, XIAO Guolin, et al. Reservoir characteristics and influential factors in the eastern depression of the North Yellow Sea basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(2): 111-119.
[35] 刘金萍, 王改云, 杜民, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷中生界烃源岩特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(4):12-16 LIU Jinping, WANG Gaiyun, DU Min, et al. Analyzing characteristics of Mesozoic hydrocarbon source rocks in the Eastern depression, North Yellow Sea basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(4): 12-16.
[36] 刘振湖, 王飞宇, 刘金萍, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷油气成藏时间研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(5):550-554 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201405550 LIU Zhenhu, WANG Feiyu, LIU Jinping, et al. Time of hydrocarbon accumulation in eastern depression of North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2014, 36(5): 550-554. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201405550
[37] 王后金, 王嘹亮, 冯常茂. 北黄海盆地的成盆动力学机制探讨[J]. 石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院学报), 2014, 36(5):1-7 WANG Houjin, WANG Liaoliang, FENG Changmao. On dynamic mechanism of tectonic evolution in the north Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology (Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute), 2014, 36(5): 1-7.
[38] 王改云, 刘金萍, 王后金, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷中生界沉积特征及演化[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(3):561-567 WANG Gaiyun, LIU Jinping, WANG Houjin, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of Mesozoic in the eastern depression, North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(3): 561-567.
[39] 胡小强, 沈艳杰, 高丹, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷沉积层序充填与盆地演化[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(4):1042-1051 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.04.016 HU Xiaoqiang, SHEN Yanjie, GAO Dan, et al. Filled characteristics of depositional sequence and evolution of eastern sag in North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Global Geology, 2015, 34(4): 1042-1051. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.04.016
[40] 赵青芳, 李双林, 温珍河, 等. 北黄海盆地LV井侏罗系烃源岩特征及油源对比[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(4):794-802 ZHAO Qingfang, LI Shuanglin, WEN Zhenhe, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Jurassic source rocks from well LV and oil-source correlation in North Yellow Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(4): 794-802.
[41] 王改云, 刘金萍, 简晓玲, 等. 北黄海盆地中生界沉积充填及有利生储盖组合[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(1):191-198 WANG Gaiyun, LIU Jinping, JIAN Xiaoling, et al. Sedimentary filling and favorable source-reservoir-seal rock assemblage of mesozoic in the North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2016, 52(1): 191-198.
[42] 肖国林, 蔡来星, 郭兴伟, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷勘探突破对我国近海残留“黑色侏罗系”油气勘探的启示[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2019, 49(1):115-130 XIAO Guolin, CAI Laixing, GUO Xingwei, et al. Exploration Enlightenment on Residual “Black Jurassic” in Chinese offshore from exploration breakthrough in eastern sag of the North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2019, 49(1): 115-130.
[43] 冯志强, 姚永坚, 曾祥辉, 等. 对黄海中、古生界地质构造及油气远景的新认识[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2002, 16(6):367-373 FENG Zhiqiang, YAO Yongjian, ZENG Xianghui, et al. New understanding of mesozoic-paleozoic tectonics and hydrocarbon potential in Yellow Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2002, 16(6): 367-373.
[44] 戴春山, 李刚, 蔡峰, 等. 黄海前第三系及油气勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(4):225-231 DAI Chunshan, LI Gang, CAI Feng, et al. The pretertiary and its hydrocarbon exploration targets in Yellow Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(4): 225-231.
[45] 李刚, 陈建文, 肖国林, 等. 南黄海海域的海相中-古生界油气远景[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2003, 19(8):12-16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.08.004 LI Gang, CHEN Jianwen, XIAO Guolin, et al. Petroleum prospect of marine paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2003, 19(8): 12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.08.004
[46] 李刚, 张燕, 陈建文, 等. 黄海海域陆相中生界地震反射特征及靶区优选[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2004, 34(6):1069-1074 LI Gang, ZHANG Yan, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Seismic reflection characteristics and selection of hydrocarbon prospective areas in the terrestrial mesozoic strata of the Yellow Sea [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2004, 34(6): 1069-1074.
[47] 戴春山, 杨艳秋, 闫桂京. 南黄海中-古生代海相残留盆地埋藏生烃史模拟及其意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(1):49-56 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.01.008 DAI Chunshan, YANG Yanqiu, YAN Guijing. Modelling of burial and hydrocarbon-generation histories of Meso-Paleozoic marine residual basins in South Yellow Sea and its geologic significance [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(1): 49-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.01.008
[48] 曲希玉, 刘立, 陈建文, 等. 南黄海盆地北部坳陷白垩系沉积特征[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2005, 35(4):443-448 QU Xiyu, LIU Li, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Sedimentary characteristics for the Cretaceous strata in the northern depression of the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2005, 35(4): 443-448.
[49] 马立桥, 陈汉林, 董庸, 等. 苏北-南黄海南部叠合盆地构造演化与海相油气勘探潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(1):35-42 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.01.005 MA Liqiao, CHEN Hanlin, DONG Yong, et al. Tectonic evolution of Subei-South Nanhuanghai superimposed basin from the Late Mesozoic to the Cenozoic and marine petroleum potential [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2007, 28(1): 35-42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.01.005
[50] 蔡峰, 熊斌辉. 南黄海海域与下扬子地区海相中-古生界地层对比及烃源岩评价[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2007, 23(6):1-6 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.06.001 CAI Feng, XIONG Binhui. Comparison of marine mesozoic-paleozoic strata and hydrocarbon source rocks in the South Yellow Sea and Lower Yangtze area [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2007, 23(6): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.06.001
[51] 张海啟, 陈建文, 李刚, 等. 地震调查在南黄海崂山隆起的发现及其石油地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(3):107-113 ZHANG Haiqi, CHEN Jianwen, LI Gang, et al. Discovery from seismic survey in Laoshan uplift of the South Yellow Sea and the significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(3): 107-113.
[52] 王丰, 李慧君, 张银国. 南黄海崂山隆起地层属性及油气地质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2):95-102 WANG Feng, LI Huijun, ZHANG Yinguo. Stratigraphic geologic attribute and hydrocarbon geology in Laoshan uplift of South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(2): 95-102.
[53] 黄松, 郝天珧, 徐亚, 等. 南黄海残留盆地宏观分布特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(6):1344-1353 HUANG Song, HAO Tianyao, XU Ya, et al. Study on macro distribution of residual basin of South Yellow Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(6): 1344-1353.
[54] 梁杰, 张银国, 董刚, 等. 南黄海海相中-古生界储集条件分析与预测[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5):101-108 LIANG Jie, ZHANG Yinguo, DONG Gang, et al. A discussion on marine mesozoic-palaeozoic reservoirs in South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 101-108.
[55] 龚建明, 王建强, 李小豫, 等. 南黄海崂山隆起古生界页岩气远景区[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(6):115-120 GONG Jianming, WANG Jianqiang, LI Xiaoyu, et al. Exploration targets of paleozoic shale gas at the Laoshan uplift, South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(6): 115-120.
[56] 张银国, 梁杰. 南黄海盆地二叠系至三叠系沉积体系特征及其沉积演化[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2014, 44(5):1406-1418 ZHANG Yinguo, LIANG Jie. Sedimentary system characteristics and their sedimentary evolution from the permian to Triassic in the Southern Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Jilin Unviersity:Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(5): 1406-1418.
[57] 高顺莉, 周祖翼. 南黄海盆地东北凹侏罗纪地层的发现及其分布特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 2014, 20(2):286-293 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.013 GAO Shunli, ZHOU Zuyi. Discovery of the Jurassic strata in the north-east sag of South Yellow Sea [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2014, 20(2): 286-293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.013
[58] 高顺莉, 张敏强, 陈华. 大震源长缆深沉放地震采集技术在南黄海中古生代盆地的应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1):95-101 GAO Shunli, ZHANG Minqiang, CHEN Hua. A large-scale seismic source, deep gun and cable sinking and long cable pength application in mesozoic-paleozoic basin in the South Huanghai Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(1): 95-101.
[59] 张银国, 陈清华, 陈建文. 南黄海盆地上二叠统—下三叠统基准面旋回特征及沉积充填模式[J]. 海相油气地质, 2015, 20(3):10-16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.03.002 ZHANG Yinguo, CHEN Qinghua, CHEN Jianwen. Upper permian-lower triassic base-level cycle and depositional filling model, South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2015, 20(3): 10-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.03.002
[60] 高顺莉, 谭思哲, 侯凯文, 等. 南黄海海域侏罗系分布与构造意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(4):7-12 GAO Shunli, TAN Sizhe, HOU Kaiwen, et al. Distribution pattern of the Jurassic in the South Yellow Sea and its tectonic implications [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(4): 7-12.
[61] 张银国, 陈清华, 陈建文, 等. 下扬子海相中-古生界烃源岩发育的控制因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):8-12 ZHANG Yinguo, CHEN Qinghua, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Controlling factors on the mesozoic-paleozoic marine source rocks in the lower Yangtze Platform [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1): 8-12.
[62] 张鹏辉, 陈建文, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海盆地海相储层成岩作用与储层发育特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):35-42 ZHANG Penghui, CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, et al. Diagenesis and characteristics of the marine reservoirs in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1): 35-42.
[63] 吴淑玉, 陈建文, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海海相中-古生界碳酸盐岩储层特征及成藏模式: 对比四川盆地和苏北盆地[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):13-21 WU Shuyu, CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, et al. Characteristics of mesozoic-palaeozoic marine carbonate reservoir in the South Yellow Sea Basin and hydrocarbon accumulation: comparison between the Sichuan Basin and the Subei Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1): 13-21.
[64] 张银国, 陈建文, 吴淑玉, 等. 南黄海崂山隆起下石炭统和州组至下二叠统栖霞组储层预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(10):60-64 ZHANG Yinguo, CHEN Jianwen, WU Shuyu, et al. Reservoir prediction for deposits from Hezhou Formation of Lower Carboniferous to Qixia Formation of Lower Permian on the Laoshan uplift of the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(10): 60-64.
[65] Yuan Y, Chen J W, Zhang Y G, et al. Sedimentary system characteristics and depositional filling model of Upper Permian–Lower Triassic in South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(12): 2910-2928. doi: 10.1007/s11771-018-3962-x
[66] 梁杰, 陈建文, 张银国, 等. 南黄海盆地中、古生界盖层条件[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2):353-360 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.02.010 LIANG Jie, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Conditions of the mesozoic-paleozoic cap rocks in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(2): 353-360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.02.010
[67] 陈建文, 施剑, 刘俊, 等. 南黄海海相中-古生界地震地质条件[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(10):1-8 CHEN Jianwen, SHI Jian, LIU Jun, et al. Seismic geological conditions of the marine Meso-Paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(10): 1-8.
[68] 陈建文, 张异彪, 刘俊, 等. 南黄海“高富强”地震勘查技术及其应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(10):9-17 CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yibiao, LIU Jun, et al. The “HRS” seismic exploration technology and its application in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(10): 9-17.
[69] 张敏强, 漆滨汶, 高顺莉, 等. 南黄海中古生界勘探进展及油气潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(3):7-15 ZHANG Minqiang, QI Binwen, GAO Shunli, et al. New exploration progress and hydrocarbon potential of the Meso-Paleozoic systems in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(3): 7-15.
[70] 雷宝华, 陈建文, 李刚, 等. 南黄海盆地二叠系地震地层特征与识别[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):29-34 LEI Baohua, CHEN Jianwen, LI Gang, et al. Seismic stratigraphic features and recognition of the Permian in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1): 29-34.
[71] 袁勇, 陈建文, 张银国, 等. 南黄海盆地崂山隆起海相中-古生界构造地质特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):49-53 YUAN Yong, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Geotectonic features of the marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic on the Laoshan uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1): 49-53.
[72] 陈建文. 下扬子地块南黄海海相层系具备良好的油气形成条件[J]. 中国地质调查成果快讯, 2016, 2(12):1-5 CHEN Jianwen. Good oil and gas formation conditions of marine strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin of Lower Yangtze Block [J]. Results Express of China Geological Survey, 2016, 2(12): 1-5.
[73] 陈建文. 南黄海海相中生界-古生界具有形成大型油气田的物质基础[J]中国地质调查成果快讯, 2016, 2(12): 6-10 CHEN Jianwen. Material base of great resources in marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Results Express of China Geological Survey, 2016, 2(12): 6-10.
[74] 王文娟, 陈建文, 张银国, 等. 以海陆对比优选南黄海海相中-古生界油气勘探目标区[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(10):65-70 WANG Wenjuan, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Discussion on exploration targets of marine Mesozoic and Paleozoic hydrocarbon in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(10): 65-70.
[75] 陈建文, 施剑, 张异彪, 等. 地震调查技术突破南黄海海相中-古生界成像技术瓶颈[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(6):847-858 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.06.01 CHEN Jianwen, SHI Jian, ZHANG Yibiao, et al. The application of “HRS” seismic exploration technology to making breakthrough of the seismic imaging “Bottleneck” of the marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 847-858. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.06.01
[76] 袁勇, 陈建文, 梁杰, 等. 海陆对比看南黄海海相中-古生界的生储盖组合特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2):195-202,212 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702195 YUAN Yong, CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, et al. Source-reservoir-seal assemblage of marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in South Yellow Sea Basin by land-ocean comparison [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 195-202,212. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702195
[77] 梁杰, 张鹏辉, 陈建文, 等. 南黄海盆地中-古生代海相地层油气保存条件[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(5):10-19 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.05.002 LIANG Jie, ZHANG Penghui, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Hydrocarbon preservation conditions in Mesozoic–Paleozoic marine strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(5): 10-19. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.05.002
[78] 蔡来星, 王蛟, 郭兴伟, 等. 南黄海中部隆起中-古生界沉积相及烃源岩特征: 以CSDP-2井为例[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2017, 47(4):1030-1046 CAI Laixing, WANG Jiao, GUO Xingwei, et al. Characteristics of sedimentary facies and source rocks of Mesozoic-Paleozoic in Central uplift of South Yellow Sea: A case study of CSDP-2 coring well [J]. Journal of Jilin Unviersity:Earth Science Edition, 2017, 47(4): 1030-1046.
[79] 肖国林, 蔡来星, 郭兴伟, 等. 南黄海中部隆起CSDP-2井中-古生界烃源岩精细评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(12):24-36 XIAO Guolin, CAI Laixing, GUO Xingwei, et al. Detailed assessment of Meso-Paleozoic hydrocarbon source rocks: Implications from well CSDP-2 on the Central uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(12): 24-36.
[80] 陈建文, 雷宝华, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海盆地油气资源调查新进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):1-23 CHEN Jianwen, LEI Baohua, LIANG Jie, et al. New progress of petroleum resources survey in South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 1-23.
[81] 陈建文, 张银国, 欧光习, 等. 南黄海古生界油气多期成藏的包体证据[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(2):69-70 CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, OU Guangxi, et al. The inclusion evidences of multi-accumulation of Paleozoic in South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(2): 69-70.
[82] 张银国, 陈建文, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海盆地崂山隆起古油藏证据(英文)[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 1(4):566-567 doi: 10.31035/cg2018067 ZHANG Yinguo, CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, et al. Evidence of the existence of paleo-reservoirs in Laoshan uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. China Geology, 2018, 1(4): 566-567. doi: 10.31035/cg2018067
[83] 陈建文. 南黄海海相中生界—古生界具有重要的油气资源前景[J]. 中国地质调查成果快讯, 2018, 4(27):35-40 CHEN Jianwen. The Mesozoic and Paleozoic Marine strata in the South Yellow Sea have important oil and gas resource prospects [J]. Results Express of China Geological Survey, 2018, 4(27): 35-40.
[84] 雷宝华, 陈建文, 梁杰, 等. 印支运动以来南黄海盆地的构造变形与演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):45-54 LEI Baohua, CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, et al. Tectonic deformation and evolution of the South Yellow Sea basin since Indosinian movement [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 45-54.
[85] 许振强, 梁杰, 陈建文, 等. 南黄海崂山隆起中、古生界油气保存条件分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):125-133 XU Zhenqiang, LIANG Jie, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Evaluation of hydrocarbon preservation on the Laoshan uplift [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 125-133.
[86] 王建强, 龚建明, 张莉, 等. 南黄海盆地“三明治”结构的页岩气保存条件探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):134-142 WANG Jianqiang, GONG Jianming, ZHANG Li, et al. Discussion on preservation conditions of shale gas with “Sandwich” structure in South Yellow Sea basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 134-142.
[87] 施剑, 陈春峰, 陈建文, 等. 南黄海海相地层速度的提取及其特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):175-185 SHI Jian, CHEN Chunfeng, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Extraction of seismic velocity of marine strata and their characteristics in the South Yellow Sea basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 175-185.
[88] 刘俊, 陈建文, 吴淑玉, 等. 南黄海崂山隆起石炭系—下二叠统海相碳酸盐岩叠前三参数反演储层预测[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):186-198 LIU Jun, CHEN Jianwen, WU Shuyu, et al. Prestack three-term seismic inversion for prediction of Carboniferous-lower Permian carbonate reservoir on the Central uplift of South Yellow Sea basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 186-198.
[89] 雷宝华, 陈建文, 吴志强, 等. 苏北-南黄海盆地海相中-古生界密度和速度分析及其地震反射模型构建[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(3):558-567 LEI Baohua, CHEN Jianwen, WU Zhiqiang, et al. Density and velocity analysis and seismic reflection model construction of marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in the North Jiangsu-to-South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53(3): 558-567.
[90] Yuan Y, Chen J W, Zhang Y X, et al. Tectonic evolution and geological characteristics of hydrocarbon reservoirs in marine mesozoic-paleozoic strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17(5): 1075-1090. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3583-x
[91] 吴淑玉,陈建文,刘俊,等. 叠前同时反演技术在南黄海崂山隆起储层预测中的应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):161-174 WU Shuyu, CHEN Jianwen, LIU Jun, et al. Application of pre-stack simultaneous inversion in the reservoir prediction in South Yellow Sea basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3): 161-174.
[92] 陈建文, 张银国, 欧光习. 南黄海崂山隆起志留系古油藏的深部烃源证据[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(1):74-76 CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, OU Guangxi. Deep source evidence of Silurian paleoreservoirs in Laoshan uplift, South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(1): 74-76.
[93] 许明, 陈建文, 雷宝华, 等. 南黄海海域中生代前陆盆地形成的构造背景[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1):13-24 XU Ming, CHEN Jianwen, LEI Baohua, et al. Tectonic background of mesozoic foreland basin development in the Southern Yellow Sea [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(1): 13-24.
[94] Chen J W, Xu M, Lei B H, et al. Prospective prediction and exploration situation of marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic oil and gas in the South Yellow Sea [J]. China Geology, 2019, 2(1): 67-84. doi: 10.31035/cg2018072
[95] Liang J, Chen J W, Zhang Y G, et al. New evidence of Silurian hydrocarbon accumulation is discovered by fluid inclusion analysis in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. China Geology, 2019, 2(1): 110-111. doi: 10.31035/cg2018077
[96] Zhang Y X, Chen J W, Zhou J Y, et al. Sedimentological sequence and depositional evolutionary model of Lower Triassic carbonate rocks in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. China Geology, 2019, 2(3): 301-314.
[97] Yuan Y, Chen J W, Liang J, et al. Hydrocarbon geological conditions and exploration potential of mesozoic–paleozoic marine strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2019, 18(6): 1-15.
[98] Chen J W, Shi J, Zhang Y B, et al. The “HRS” seismic exploration technology of deep strata in China Sea Areas: a case of the South Yellow Sea basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2019, 93(S2): 388-389.
[99] Liang J, Chen J W, Wang J Q, et al. Hydrocarbon geological conditions and exploration prospects of marine strata in the Laoshan Uplift, South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2019, 93(S2): 303-304.
[100] Wu S Y, Liu J, Chen J W, et al. Pre-stack simultaneous inversion in the marine carbonate reservoir prediction of the South Yellow Sea Basin, China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2019, 93(S2): 420-421.
[101] 陈建文, 袁勇, 施剑, 等. 中国海域深部“高富强”地震探测技术与南黄海盆地海相地层的发现[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2019, 42(3):46-57 CHEN Jianwen, YUAN Yong, SHI Jian, et al. “High, rich, and strong” seismic technologies for deeper layers in offshore China and discoveries in marine strata of South Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2019, 42(3): 46-57.
[102] 陈建文, 许明, 雷宝华, 等. 华北-扬子板块碰撞结构的识别: 来自南黄海海域的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):1-12 CHEN Jianwen, XU Ming, LEI Baohua, et al. Collision of North China and Yangtze Plates: Evidence from the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 1-12.
[103] 陈建文. 崂山断隆带西部发现大型有利构造带[J]. 中国地质调查成果快讯, 2020, 6(18):40-42 CHEN Jianwen. A large favorable tectonic belt was found in the west of Laoshan fault-uplift belt [J]. Results Express of China Geological Survey, 2020, 6(18): 40-42.
[104] 陈建文, 张异彪, 陈华, 等. 南黄海盆地海相中−古生界地震探测技术攻关历程及效果[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(4):1-17 CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yibiao, CHEN Hua, et al. Research experiences and application of seismic exploration technology to the Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine strata in the South Yellow Sea basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(4): 1-17.
[105] 张鹏辉, 梁杰, 陈建文, 等. 中国叠合盆地深部海相地层油气保存条件剖析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(1):1-11 ZHANG Penghui, LIANG Jie, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Hydrocarbon preservation analysis for marine strata in superimposed basins of China [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(1): 1-11.
[106] 高顺莉, 谭思哲, 陈春峰, 等. 下扬子-南黄海二叠纪岩相古地理特征及油气勘探启示[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(4):53-60 GAO Shunli, TAN Sizhe, CHEN Chunfeng, et al. Permian lithofacies paleogeography of the South Yellow Sea area, lower yangtze plate and its implications for petroleum exploration [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(4): 53-60.
[107] 王文娟, 陈建文, 雷宝华, 等. 下扬子巢湖鼓地1井五峰-高家边组生物地层及部分笔石带缺失原因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(4):61-67 WANG Wenjuan, CHEN Jianwen, LEI Baohua, et al. Cause of the partial missing of graptolite zones in Wufeng and Kaochiapien formations of well GD-1, Chaohu area, lower Yangtze region [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(4): 61-67.
[108] 张玉玺, 陈建文, 张银国. 下扬子-南黄海地区下三叠统“错时相”沉积及成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(4):68-76 ZHAGN Yuxi, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo. Anachronistic facies and its origin of the lower Triassic in the lower Yangtze-South Yellow Sea area [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(4): 68-76.
[109] 周江羽, 陈建文, 张玉玺, 等. 下扬子地区幕府山组古环境和构造背景: 来自细粒混积沉积岩系元素地球化学的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(6):1693-1711 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.003 ZHOU Jiangyu, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yuxi, et al. Paleoenvironment and tectonic background of Mufushan Formation in Lower Yangtze area: evidence from geochemistry of fine-grained mixed-siliciclastic-calcareous deposits [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(6): 1693-1711. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.003
[110] Xu M, Chen J W, Liang J, et al. Basement structures underneath the northern South Yellow Sea basin (East China): Implications for the collision between the North China and South China blocks [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 186: 104040. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104040
[111] 陈建文. 南黄海崂山隆起海相中-古生界发现多个大型圈闭构造[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(4):69-70 CHEN Jianwen. Several large traps were found in the marine Mesozoic Paleozoic of Laoshan uplift in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(4): 69-70.
[112] 冯晓杰, 张川燕, 王春修, 等. 东海陆架和台西南盆地中生界及其油气勘探潜力[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2001, 15(5):306-310,316 FENG Xiaojie, ZHANG Chuanyan, WANG Cunxiu, et al. Mesozoic in the East China Sea shelf and Taixinan Basin and its petroleum potential [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2001, 15(5): 306-310,316.
[113] 陈建文, 李刚, 陈国威. 东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带的中生界和古新统油气远景[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2003, 19(8):17-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.08.005 CHEN Jianwen, LI Gang, CHEN Guowei. Petroleum prospects of mesozoic and paleocene in the western depression of the East China Sea shelf basin [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2003, 19(8): 17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.08.005
[114] 冯晓杰, 蔡东升, 王春修, 等. 东海陆架盆地中新生代构造演化特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):33-37 FENG Xiaojie, CAI Dongsheng, WANG Chunxiu, et al. The Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution in East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 33-37.
[115] Yang C Q, Sun J, Yang Y Q, et al. Key factors controlling Mesozoic hydrocarbon accumulation in the southern East China Sea basin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 118: 104436. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104436
[116] 舒良树, 周新民, 邓平, 等. 中国东南部中、新生代盆地特征与构造演化[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(9):876-884 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.09.008 SHU Liangshu, ZHOU Xinmin, DENG Ping, et al. Geological features and tectonic evolution of Meso-Cenozoic basins in southeastern China [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(9): 876-884. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.09.008
[117] 须雪豪, 陈琳琳, 汪企浩. 东海陆架盆地中生界地质特征与油气资源潜力浅析[J]. 海洋石油, 2004, 24(3):1-7,55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2004.03.001 XU Xuehao, CHEN Linlin, WANG Qihao. Analysis of Mesozoic geological characteristics and resource potential in the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Offshore Oil, 2004, 24(3): 1-7,55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2004.03.001
[118] 高乐. 东海陆架中生代残余盆地特征及勘探方向探讨[J]. 中国海上油气, 2005, 17(3):148-152 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2005.03.002 GAO Le. Mesozoic remnant basin characteristics and hydrocarbon exploration direction on East China Sea shelf [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2005, 17(3): 148-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2005.03.002
[119] 刘建华, 黎明碧, 方银霞. 东海陆架盆地海相中生界及其与邻近古海洋关系探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(2):1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.001 LIU Jianhua, LI Mingbi, FANG Yinxia. Mesozoic strata in East China Sea shelf basin and their relationship with adjacent Palaeo-seas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(2): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.001
[120] 唐建. 东海及邻近地区中生代沉积地层展布研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2007 TANG Jian. Study on the Mesozoic sedimentary strata distribution of East China and adjacent areas[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2007.
[121] Shu L S, Zhou X M, Deng P, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Southeast China block: new insights from basin analysis [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 376-391. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.06.004
[122] 杨艳秋, 李刚, 戴春山. 东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带中生界分布特征及其有利区探讨[J]. 世界地质, 2011, 30(3):396-403 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2011.03.011 YANG Yanqiu, LI GANG, DAI Chunshan. Characteristics of Mesozoic distribution and discussion on its favourable area in western depression zone of East China Sea Shelf basin [J]. Global Geology, 2011, 30(3): 396-403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2011.03.011
[123] 胡文博. 东海陆架盆地南部中生界沉积体系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012 HU Wenbo. The Mesozoic sedimentary systems in the Southern East China Sea Shelf basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012.
[124] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 李刚, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代构造演化与原型盆地性质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):105-111 YANG Changqing, YANG Chuansheng, LI Gang, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution and Prototype Basin characters in the Southern East China Sea shelf basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 105-111.
[125] 李刚, 龚建明, 杨长清, 等. “大东海”中生代地层分布: 值得关注的新领域[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):98-104 LI Gang, GONG Jianming, YANG Changqing, et al. Stratigraphic features of the mesozoic “Great East China Sea”: a new exploration field [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 98-104.
[126] 蒋玉波, 龚建明, 曹志敏, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部及邻区陆域中生界对比[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(10):1-7 JIANG Yubo, GONG Jianming, CAO Zhimin, et al. Correlation of the Mesozoic between Southern East China Sea shelf basin and its adjacent areas [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(10): 1-7.
[127] 杨长清, 李刚, 龚建明, 等. 中国东南海域中生界油气地质条件与勘探前景[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2015, 45(1):1-12 YANG Changqing, LI Gang, GONG Jianming, et al. Petroleum geological conditions and exploration prospect of the Mesozoic in Southeast China Sea area [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(1): 1-12.
[128] 梁杰, 陈建文, 张银国, 等. 东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带中生界储层类型及成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5):131-138 LIANG Jie, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Type and origin of mesozoic reservoirs in western depression zone of East China Sea shelf basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(5): 131-138.
[129] 杨长清, 韩宝富, 杨艳秋, 等. 东海陆架盆地中生界油气调查进展与面临的挑战[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(4):1-8 YANG Changqing, HAN Baofu, YANG Yanqiu, et al. Oil and gas exploration in the mesozoic of East China Sea shelf basin: progress and challenges [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(4): 1-8.
[130] 江东辉, 唐建, 王丹萍, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部及邻近陆域中生代地层格架对比[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(4):16-21 JIANG Donghui, TANG Jian, WANG Danping, et al. Mesozoic stratigraphic framework of the Southern East China Sea shelf basin and its correlation with adjacent areas [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(4): 16-21.
[131] Yang C Q, Yang Y Q, Li G, et al. The Mesozoic basin-mountain coupling process of the Southern East China Sea Shelf Basin and its adjacent land area [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2016, 90(3): 1051-1052. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12748
[132] 陈虹宇, 胡广. 中国东南沿海早白垩世大地构造演化分析: 来自浙江东部沿海石浦群沉积岩的证据[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(S1):269-270 CHEN Hongyu, HU Guang. Analysis of Tectonic evolution during early Cretaceous in coastal area of SE China: A Case from sedimentary rock of Shipu Group in eastern Zhejiang province [J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(S1): 269-270.
[133] 崔幸, 王亮亮, 罗洪明, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代盆地性质与演化: 砂箱物理模拟检验[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(4):181-192 CUI Xing, WANG Liangliang, LUO Hongming, et al. Sandbox modeling test for Mesozoic basins in Southern East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(4): 181-192.
[134] 杨传胜, 杨长清, 李刚, 等. 东海陆架盆地中—新生界油气勘探研究进展与前景分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2):136-147 YANG Chuansheng, YANG Changqing, LI Gang, et al. Prospecting of Meso-cenozoic hydrocarbon in the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(2): 136-147.
[135] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 孙晶, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代演化与动力学转换过程[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2019, 49(1):139-153 YANG Changqing, YANG Chuansheng, SUN Jing, et al. Mesozoic evolution and dynamics transition in southern shelf basin of the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2019, 49(1): 139-153.
[136] 郝沪军, 林鹤鸣, 杨梦雄, 等. 潮汕坳陷中生界: 油气勘探的新领域[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2004, 16(2):73-83 HAO Hujun, LIN Heming, YANG Mengxiong, et al. The mesozoic in chaoshan depression: a new domain of petroleum exploration [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2004, 16(2): 73-83.
[137] 颜佳新, 周蒂. 南海北部陆缘区中特提斯构造演化研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(4):49-54 YAN Jiaxin, ZHOU Di. Advancement on the Meso-Tethys along the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(4): 49-54.
[138] 杨少坤, 林鹤鸣, 郝沪军. 珠江口盆地东部中生界海相油气勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 2002, 23(5):28-33 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2002.05.006 YANG Shaokun, LIN Heming, HAO Hujun. Oil and gas exploration prospect of Mesozoic in the eastern part of Pearl River mouth Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2002, 23(5): 28-33. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2002.05.006
[139] 林鹤鸣, 郝沪军. 珠江口盆地东部和台湾西部海域中生界地质构造特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2002, 16(4):231-237 LIN Heming, HAO Hujun. Mesozoic tectonics in the eastern Pearl River mouth basin and offshore western Taiwan [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2002, 16(4): 231-237.
[140] 刘海龄. 南海及邻区地层对比[M]//刘昭蜀. 南海地质. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 233-254 LIU Hailling. Contrast of strata in South China Sea and its adjacent areas[M]//LIU Zhaoshu. Geology of the South China Sea. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 233-254.
[141] 颜佳新, 周蒂. 南海及周边部分地区特提斯构造遗迹: 问题与思考[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2002, 21(2):43-49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.02.005 YAN Jiaxin, ZHOU Di. Reviews on Tethyan trace in South China Sea and some adjacent regions [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2002, 21(2): 43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.02.005
[142] 周蒂. 台西南盆地和北港隆起的中生界及其沉积环境[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2002, 21(2):50-57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.02.006 ZHOU Di. Mesozoic strata and sedimentary environment in SW Taiwan Basin of NE South China Sea and Peikang High of western Taiwan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2002, 21(2): 50-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.02.006
[143] 杨静, 冯晓杰, 范迎风, 等. 南海东北部中晚中生代构造、古地理背景及油气远景分析[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(2):89-92,103 YANG Jing, FENG Xiaojie, FAN Yingfeng, et al. An analysis of middle-late mesozoic tectonics, paleogeography and petroleum potential in the northeastern South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(2): 89-92,103.
[144] 张莉, 李文成, 曾祥辉. 礼乐盆地地层发育特征及其与油气的关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(5):469-472,480 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.05.009 ZHANG Li, LI Wencheng, ZENG Xianghui. Stratigraphic sequence and hydrocarbon potential in Lile Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2003, 25(5): 469-472,480. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.05.009
[145] 周蒂, 颜佳新, 丘元禧, 等. 南海西部围区中特提斯东延通道问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(4):469-477 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.014 ZHOU Di, YAN Jiaxin, QIU Yuanxi, et al. Route for the eastern extension of meso-tethys in the western environs of the South China Sea [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(4): 469-477. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.014
[146] 陈汉宗, 孙珍, 周蒂. 华南中生代岩相变化及海相地层时空分布[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2003, 22(2):74-82 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.02.008 CHEN Hanzong, SUN Zhen, ZHOU Di. Distributions of mesozoic lithofacies and marine strata in South China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2003, 22(2): 74-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.02.008
[147] 周蒂, 颜佳新, 丘元禧, 等. 南海西部围区中生代岩相古地理及中特提斯东延通道[M]//李家彪, 高抒. 中国边缘海海盆演化与资源效应. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2003: 150-169 ZHOU Di, YAN Jiaxin, QIU Yuanxi, et al. Mesozoic litho-facies and paleo-geography of western environs of South China Sea and their bearing on the eastern extension of Meso-Tethys[M]//LI Jiabiao, GAO Shu. Studies on the Formation and Evolution of the China's Marginal Seas, Volume 2. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2003: 150-169.
[148] 周蒂, 陈汉宗, 孙珍, 等. 南海及其围区中生代岩相古地理及有关大地构造和资源问题[M]//李家彪, 高抒. 中国边缘海岩石层结构与动力过程. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2004: 65-76 ZHOU Di, CHEN Hanzong, SUN Zhen, et al. Mesozoic lithofacies and paleogeography of South China Sea and surrounding areas and their bearing on tectonics and resources[M]//LI Jiabiao, GAO Shu. Studies on the Formation and Evolution of the China's Marginal Seas, Volume 3. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2004: 65-76.
[149] 郝沪军, 汪瑞良, 张向涛, 等. 珠江口盆地东部海相中生界识别及分布[J]. 中国海上油气, 2004, 16(2):84-88 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2004.02.002 HAO Hujun, WANG Ruiliang, ZHANG Xiangtao, et al. Mesozoic marine sediment identification and distribution in the eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2004, 16(2): 84-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2004.02.002
[150] 夏戡原, 黄慈流, 黄志明. 南海及邻区中生代(晚三叠世—白垩纪)地层分布特征及含油气性对比[J]. 中国海上油气, 2004, 16(2):73-83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2004.02.001 XIA Kanyuan, HUANG Ciliu, HUANG Zhiming. Upper Triassic-Cretaceous sediment distribution and hydrocarbon potential in South China Sea and its adjacent areas [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2004, 16(2): 73-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2004.02.001
[151] 邱燕, 温宁. 南海北部边缘东部海域中生界及油气勘探意义[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(2):142-146 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.02.007 QIU Yan, WEN Ning. Mesozoic in the eastern sea area of the northern margin of the South China Sea and its significance for oil/gas exploration [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(2): 142-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.02.007
[152] 刘海龄, 杨恬, 朱淑芬, 等. 南海西北部新生代沉积基底构造演化[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(3):54-67 LIU Hailing, YANG Tian, ZHU Shufen, et al. Tectonic evolution of Cenozoic sedimentary basements in the northwestern South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(3): 54-67.
[153] 刘海龄, 阎贫, 张伯友, 等. 南海前新生代基底与东特提斯构造域[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(1):15-28 LIU Hailing, YAN Pin, ZHANG Boyou, et al. Pre-Cenozoic basements of the South China Sea and Eastern Tethyan realm [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(1): 15-28.
[154] 周蒂, 陈汉宗, 孙珍, 等. 南海中生代三期海盆及其与特提斯和古太平洋的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(2):16-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.003 ZHOU Di, CHEN Hanzong, SUN Zhen, et al. Three Mesozoic Sea basins in eastern and Southern South China Sea and their relation to tethys and paleo-pacific domains [J]. Ournal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(2): 16-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.003
[155] 倪金龙, 夏斌, 刘海龄. 南海及邻区前中生代构造演化与东特提斯构造域[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2005, 21(10):11-16 NI Jinlong, XIA Bin, LIU Hailing. Pre-mesozoic tectonic evolution in the South China Sea and Adjacent Area and eastern tethyan realm [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2005, 21(10): 11-16.
[156] 钟广见, 易海, 林珍, 等. 粤东和南海东北部陆坡区中生界及烃源岩特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2007, 28(6):676-680 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2007.06.004 ZHONG Guangjian, YI Hai, LIN Zhen, et al. Characteristic of source rocks and Mesozoic in continental slope area of Northeastern the South China Sea and East Guangdong of China [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2007, 28(6): 676-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2007.06.004
[157] 邵磊, 尤洪庆, 郝沪军, 等. 南海东北部中生界岩石学特征及沉积环境[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(2):164-169 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.02.003 SHAO Lei, YOU Hongqing, HAO Hujun, et al. Petrology and depositional environments of Mesozoic strata in the northeastern South China Sea [J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53(2): 164-169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.02.003
[158] 吴国瑄, 王汝建, 郝沪军, 等. 南海北部海相中生界发育的微体化石证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(1):79-85 WU Guoxuan, WANG Rujian, HAO Hujun, et al. Microfossil evidence for development of marine Mesozoic in the north of south China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(1): 79-85.
[159] 刘海龄, 谢国发, 阎贫, 等. 南沙海区中生界岩相分布及构造特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(3):272-278 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2007.03.014 LIU Hailing, XIE Guofa, YAN Pin, et al. Tectonic implication of Mesozoic marine deposits in the Nansha islands of the South China Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38(3): 272-278. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2007.03.014
[160] 杨树春, 仝志刚, 贺清, 等. 潮汕坳陷中生界生烃历史及火成岩侵入影响分析: 以LF35-1-1井为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2008, 20(3):152-156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.03.003 YANG Shuchun, TONG Zhigang, HE Qing, et al. Mesozoic hydrocarbon generation history and igneous intrusion impacts in Chaoshan depression, South China sea: a case of LF35-1-1 well [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2008, 20(3): 152-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.03.003
[161] 孙龙涛, 孙珍, 周蒂, 等. 南沙海区礼乐盆地沉积地层与构造特征分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2008, 32(2):151-158 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2008.02.003 SUN Longtao, SUN Zhen, ZHOU Di, et al. Stratigraphic and structural characteristics of lile basin in Nansha area [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2008, 32(2): 151-158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2008.02.003
[162] 郝沪军, 施和生, 张向涛, 等. 潮汕坳陷中生界及其石油地质条件: 基于LF35-1-1探索井钻探结果的讨论[J]. 中国海上油气, 2009, 21(3):151-156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.03.002 HAO Hujun, SHI Hesheng, ZHANG Xiangtao, et al. Mesozoic sediments and their petroleum geology conditions in Chaoshan sag: a discussion based on drilling results from the exploratory well LF35-1-1 [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2009, 21(3): 151-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.03.002
[163] 姚永坚, 高红芳, 何家雄, 等. 南海东北部潮汕坳陷及陆上邻区中生界烃源岩初步研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(6):862-871 YAO Yongjian, GAO Hongfang, HE Jiaxiong, et al. Preliminary studies on the Mesozoic source rocks in Chaoshan depression, Northeastern South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(6): 862-871.
[164] 沈艳杰, 程日辉, 王嘹亮, 等. 粤东地区上白垩统盐湖沉积及其在南海北部中生界油气勘探中的意义[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2009, 39(5):759-766 SHEN Yanjie, CHENG Rihui, WANG Liaoliang, et al. Salt lake sediments of the Upper Cretaceous in Eastern Guangdong and its significance in oil and gas exploration of the Mesozoic in the Northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2009, 39(5): 759-766.
[165] 王嘹亮, 程日辉, 李飞, 等. 南海北部陆缘中生代沉积层序、对比和油气地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2009, 39(2):175-182 WANG Liaoliang, CHENG Rihui, LI Fei, et al. The Mesozoic sedimentary sequences, Correlation and Geological significance for petroleum of the north margin of South China Sea [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2009, 39(2): 175-182.
[166] 孙龙涛, 孙珍, 詹文欢, 等. 南沙海域礼乐盆地油气资源潜力[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(1):137-145 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.014 SUN Longtao, SUN Zhen, ZHAN Wenhuan, et al. Petroleum potential prediction of the Lile Basin in Nansha [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(1): 137-145. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.014
[167] 段九春, 米慧芬. 潮汕坳陷中生界地震相与沉积相研究[J]. 资源与产业, 2012, 14(1):100-105 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2464.2012.01.019 DUAN Jiuchun, MI Huifen. Seismic facies and sedimentary facies study of Mesozoic in Chaoshan sag [J]. Resources & Industries, 2012, 14(1): 100-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2464.2012.01.019
[168] 刘宝明, 刘海龄. 南海及邻区中生界—新的油气勘探领域[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(2):105-109 LIU Baoming, LIU Hailing. The mesozoic in the South China Sea and adjacent areas: new targets for hydrocarbon exploration [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(2): 105-109.
[169] 张莉, 耿安松, 王嘹亮, 等. 华南陆缘中生界烃源岩条件评价[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):99-108 ZHANG Li, GENG Ansong, WANG Liaoliang, et al. Assessment of Mesozoic source rocks at the Margin of South China continent [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(1): 99-108.
[170] 王利杰, 姚永坚, 孙珍, 等. 南沙地块东部中生界分布及构造变形特征[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(S1):77-80 WANG Lijie, YAO Yongjian, SUN Zhen, et al. Mesozoic distribution and tectonic deformation in the eastern Nansha block [J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(S1): 77-80.
[171] 刘守全, 蔡乾忠, 莫杰. 中国海域油气勘探的新领域: 应当重视海域中生界油气资源[J]. 中国地质, 2001, 28(11):4-9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2001.11.002 LIU Shouquan, CAI Qianzhong, MO Jie. A new field of petroleum exploration in sea areas of China-Attention should be paid to Mesozoic marine petroleum resources [J]. Chinese Geology, 2001, 28(11): 4-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2001.11.002
[172] 赖万忠. 中国海域中生界油气勘探[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2001, 15(5):311-316 LAI Wanzhong. Mesozoic petroleum exploration in offshore China [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2001, 15(5): 311-316.
[173] 陈建文, 肖国林, 刘守全, 等. 中国海域油气资源勘查战略研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(4):77-82 CHEN Jianwen, XIAO Guolin, LIU Shouquan, et al. Strategy of oil and gas resources explorations in China seas [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(4): 77-82.
[174] 肖国林, 董贺平, 杨长清, 等. 我国近海非常规油气资源勘探态势及其地质有利性[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(7):73-76 XIAO Guolin, DONG Heping, YANG Changqing, et al. Exploration status and geological advantages of unconventional oil and gas resources in China Off shore [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(7): 73-76.
[175] 蔡东升, 冯晓杰, 高乐, 等. 中国近海前第三纪残余盆地及其勘探潜力与方向[J]. 中国海上油气, 2004, 16(1):1-17 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2004.01.001 CAI Dongsheng, FENG Xiaojie, GAO Le, et al. Petroleum potential and exploration direction of pre-Tertiary remnant basins in offshore China [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2004, 16(1): 1-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2004.01.001
[176] 刘光鼎, 陈洁. 中国海域残留盆地油气勘探潜力分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2005, 20(4):881-888 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2005.04.001 LIU Guangding, CHEN Jie. Potential analysis of petroleum explortation in residual basins of the China sea [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2005, 20(4): 881-888. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2005.04.001
[177] 温珍河, 刘守全, 陈建文, 等. 值得重视的海域海相油气勘探[J]. 海相油气地质, 2007, 12(3):5-9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2007.03.002 WEN Zhenhe, LIU Shouquan, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Oil and gas explor ation in marine formation of China sea ar eas [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2007, 12(3): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2007.03.002
[178] 陈建文, 梁杰, 张银国, 等. 中国海域油气资源潜力分析与黄东海海域油气资源调查进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(6):1-29 CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Regional evaluation of oil and gas resources in offshore China and exploration of marine Paleo-Mesozoic oil and gas in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(6): 1-29.
[179] 丘学林, 赵明辉, 徐辉龙, 等. 南海深地震探测的重要科学进程: 回顾和展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(3):1-9 QIU Xuelin, ZHAO Minghui, XU Huilong, et al. Important processes of deep seismic surveys in the South China Sea: Retrospection and expectation [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(3): 1-9.
[180] 邢涛, 詹文欢, 李福元, 等. 东沙海域复杂海况下单源单缆长排列地震资料处理[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(4):91-99 XING Tao, ZHAN Wenhuan, LI Fuyuan, et al. Single-source, single-cable, long-array, seismic data processing in complex sea conditions of Dongsha sea area [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 91-99.
[181] 陈华, 张亚斌, 徐翔之, 等. 中深层地震采集方法研究: 以东海盆地X海域为例[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(5):219-223,409 CHEN Hua, ZHANG Yabin, XU Xiangzhi, et al. Study on seismic data acquisition in mid-deep zone: by taking X trough in East China Sea Basin for example [J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2010, 32(5): 219-223,409.
[182] 邓桂林, 丁龙翔, 李福元, 等. 海洋长排列单源单缆准三维窄方位地震资料处理技术[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(4):828-834 Deng Guilin, Ding Longxiang, Li Fuyuan, et al. The processing technology of narrow azimuth Quasi three-dimensional seismic data acquisition by single source and single long streamer system in marine seismic exploration [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(4): 828-834.
[183] 吴庆勋, 高坤顺, 吴昊明, 等. 渤海海域前新生代基底特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4):802-810,819 WU Qingxun, GAO Kunshun, WU Haoming, et al. Characteristics of pre-cenozoic basement in Bohai Sea and its significance in oil and gas exploration [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(4): 802-810,819.
[184] 徐春强, 张震, 王晨杰, 等. 渤海海域428潜山地层结构特征及勘探潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(11):52-58 XU Chunqiang, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Chenjie, et al. Stratigraphic framework and exploration potential of buried hill 428 in the Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(11): 52-58.
[185] 陈丽祥, 牛成民, 李慧勇, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中21-2构造碳酸盐岩储层发育特征及其控制因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(2):16-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2016.02.003 CHEN Lixiang, NIU Chengmin, LI Huiyong, et al. Carbonate reservoir characteristics and its controlling factors in Bozhong 21-2 structure, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(2): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2016.02.003
[186] 李乃胜. 黄海三大盆地的构造演化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1995, 26(4):355-362 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.04.003 LI Naisheng. Tectonic evolution of three structuralbasins in the Yellow Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1995, 26(4): 355-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.04.003
[187] 肖国林, 孙长虹, 郑浚茂. 北黄海盆地东部前中生界基底特征[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(2):261-266 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.015 XIAO Guolin, SUN Changhong, ZHENG Junmao. Pre-mesozoic basement characteristics in the eastern depression of the North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(2): 261-266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.015
[188] 陈建文, 吴志强, 李慧君, 等. 南黄海前第三系油气前景研究[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2010 CHEN Jianwen, WU Zhiqiang, LI Huijun, et al. Oil and gas prospects of Pre- Tertiary in South Yellow Sea[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2010.
[189] 邱燕, 王立飞, 黄文凯, 等. 中国海域中新生代沉积盆地[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016: 233 QIU Yan, WANG Lifei, HUANG Wenkai, et al. Mesozoic Cenozoic Sedimentary Basins in China Sea Area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016: 233.
[190] 国土资源部油气资源战略研究中心. 海域油气资源战略调查与选区[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013: 238 Compiled by the Oil and Gas Resources Strategic Research Center of the Ministry of Land and Resources. Strategic Investigation and Selection of Offshore Oil and Gas Resources[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2013: 238.
[191] 龚再升, 李思田, 谢泰俊, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997 GONG Zaisheng, LI Sitian, XIE Taijun, et al. Continental Margin Basin Analysis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the Northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997.
[192] 肖国林, 王明健, 杨长清, 等. 东海南部中生界烃类生成、运聚与成藏数值模拟[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(6):138-149 XIAO Guolin, WANG Mingjian, YANG Changqing, et al. Numerical simulation of Mesozoic hydrocarbon generation, migration and accumulation in the southern East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(6): 138-149.
[193] 陈建平, 赵长毅, 何忠华. 煤系有机质生烃潜力评价标准探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1997, 24(1):1-5 CHEN Jianping, ZHAO Changyi, HE Zhonghua. Criteria for evaluating the hydrocarbon generating potential of organic matter in coal measures [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1997, 24(1): 1-5.
[194] 张莉, 雷振宇, 许红, 等. 台西盆地地层沉积特征与成烃-成藏地质条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(1):152-161 doi: 10.11743/ogg20190115 ZHANG Li, LEI Zhenyu, XU Hong, et al. Sedimentary features and geological conditions for hydrocarbon generation and accumulation in Taixi Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(1): 152-161. doi: 10.11743/ogg20190115
[195] 张莉, 沙志彬, 王立飞. 南沙海域礼乐盆地中生界油气资源潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(4):97-102 ZHANG Li, SHA Zhibin, WANG Lifei. Hydrocarbon resources potential of Mesozoic in Liyue Basin, Northeastern Nansha Sea areas [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(4): 97-102.
[196] 卢欢, 徐长贵, 王清斌, 等. 碳酸盐胶结物形成机制及其对渤海海域C12和Q17构造中生界碎屑岩储层的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(6):1270-1280 doi: 10.11743/ogg20190611 LU Huan, XU Changgui, WANG Qingbin, et al. Genetic mechanism of carbonate cements and its impact on the Mesozoicclastic reservoir quality of the C12 and Q17 structures, Bohai Sea area [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(6): 1270-1280. doi: 10.11743/ogg20190611
[197] 王保全, 王志萍, 汤国民, 等. 渤海海域中部地区中生界火山岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(8):36-42 WANG Baoquan, WANG Zhiping, TANG Guomin, et al. Characteristics of Mesozoic volcanic reservoir rocks and their main controlling factors in the central Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(8): 36-42.
[198] 胡志伟, 徐长贵, 杨波, 等. 渤海海域蓬莱9-1油田花岗岩潜山储层成因机制及石油地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(3):274-285 doi: 10.7623/syxb201703004 HU Zhiwei, XU Changgui, YANG Bo, et al. Reservoir forming mechanism of Penglai 9-1 granite buried-hills and its oil geology significance in Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(3): 274-285. doi: 10.7623/syxb201703004
[199] 王建强, 梁杰, 陈建文, 等. 中国海域基岩油气藏特征及未来勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(6):151-162 WANG Jianqiang, LIANG Jie, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Characteristics of the recently bedrock hydrocarbon reservoir in China Seas and future exploration directions [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(6): 151-162.
-
期刊类型引用(13)
1. 杨艳秋,李森,梁杰,孙晶. 南黄海盆地南部海相构造层研究新进展. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(02): 12-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 袁勇,陈建文,骆迪,李清,梁杰,蓝天宇,王建强,曹珂,赵化淋. 南黄海盆地烟台坳陷新生界二氧化碳封存地质条件与封存前景. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(03): 35-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张银国,陈建文,龚建明,梁杰,廖晶,王建强,杨长清,赵青芳,孙晶,杨传胜,雷宝华,袁勇. 青岛海洋地质研究所45年来海域油气资源调查进展. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(03): 1-22 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 徐长贵,杨海风,王飞龙,彭靖淞. 渤海湾盆地海域深层——超深层大型复合潜山油气藏形成条件. 石油勘探与开发. 2024(06): 1227-1239 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. XU Changgui,YANG Haifeng,WANG Feilong,PENG Jingsong. Formation conditions of deep to ultra-deep large composite buried-hill hydrocarbon reservoirs in offshore Bohai Bay Basin, China. Petroleum Exploration and Development. 2024(06): 1421-1434 .  必应学术
必应学术
6. 陈春峰,陈忠云,万延周,陈建文,徐东浩,冯桢鸣,俞伟哲,姜雪. 东海盆地西湖凹陷南部花港组上段浅水曲流河三角洲发育特征. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(06): 175-185 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 何拥军,梅燕雄,姚鹏. 中国东海油气勘探现状和油气资源潜力. 矿产勘查. 2024(11): 2089-2098 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 吴飘,陈建文,张银国,龚建明,蓝天宇,薛路,可行. 南黄海地区二叠系孤峰组硅质烃源岩的地球化学特征及上升流成因. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2023(01): 138-158 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 曹倩,李海华,单帅强,戚家振,李风勋,王斌,韩彧. 南黄海盆地南部坳陷二叠系烃源岩演化及资源潜力. 石油实验地质. 2023(02): 280-287 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 梁光河. 贝加尔裂谷和汾渭地堑成因与印度—欧亚碰撞的远程效应. 地学前缘. 2023(03): 282-293 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 赵青芳,谢德智,陈建文,梁杰,张银国,王建强,董贺平,袁勇. 下扬子区二叠系烃源岩评价与生源环境. 地质通报. 2023(07): 1154-1165 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 李廷栋,刘勇,丁孝忠,庞健峰. 中国区域地质研究的十大进展. 地质学报. 2022(05): 1544-1581 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 刘曾勤. 东营凹陷南坡东段油气成藏模式及勘探潜力. 海洋地质前沿. 2022(07): 57-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: