Progress in marine oil and gas survey in Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology over the past 45 Years
-
摘要:
石油和天然气资源是重要的能源矿产和战略性资源,海洋蕴含着丰富的油气资源,青岛海洋地质研究所(简称青岛所)自1979年重建始,便开启了海域油气资源调查、研究与评价工作的序幕。45年来,青岛所持续开展了海域及邻区含油气盆地对比、黄东海新区新层系油气资源调查评价、中国海域和海丝路海域油气勘探开发形势分析,并于2019和2021年开展了2个航次的北印度洋重点海域联合地质科学考查。本文回顾了45年以来青岛所海域油气调查与研究历史,梳理了取得的主要进展,重点介绍了海域新区新层系油气资源调查技术、东部海域新区新层系油气地质新认识、印度扇近海盆地的科学考查发现与认识、海域油气资源勘探开发总体形势与战略性方向,梳理了面临的主要挑战,同时展望了油气调查主要领域和方向,这对进一步摸清海域油气资源家底、服务海域油气矿政管理和国家能源资源安全保障具有重要意义。
Abstract:Oil and natural gas resources are important energy minerals and strategic resources. The ocean contains abundant oil and gas resources. Since its reconstruction in 1979, the Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology (the Qingdao Institute in short) has begun the investigation, research, and evaluation of marine oil and gas resources. Over the past 45 years, the Qingdao Institute has been continuing to carry out the studies in the correlation of oil and gas bearing basins in the sea area and adjacent areas, the investigation and evaluation of oil and gas resources in new area and new strata in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea, the analysis of oil and gas exploration and development situation in China's sea area and the Sea Silk Road sea area, and the joint geological and scientific survey of key marine areas in the North Indian Ocean. This article reviews the 45-year history of oil and gas exploration and research in the sea area by the Qingdao Institute, summarizes the main achievement, and focuses on introducing the investigation techniques for oil and gas resources in the new areas and new strata, the new geological understanding of oil and gas in the new areas and new strata of the eastern sea area, the scientific research findings and understanding of the Indus Fan basin, the exploration and development situation, and strategic direction of oil and gas resources in the sea area; and puts forward the main challenges faced. At the same time, it looks forward to the main fields and directions of future oil and gas investigation, which is of great significance for further understanding of the wealth of oil and gas resources in the sea area, serving the management of oil and gas mining in the sea area, and ensuring national energy security.
-
石油和天然气资源是重要的能源矿产和战略性资源[1],是保证国家经济运行的能源大动脉[2],是国家发展的源动力。海洋蕴含着丰富的油气资源[3],青岛海洋地质研究所(下简称“青岛所”)自1979年重建以来,就一直从事我国海域油气资源调查、研究与评价工作。青岛所坚持基础性、公益性、战略性定位,锚定新区、新层系、新类型、新领域油气资源调查与研究工作,持续开展了海域及邻区含油气盆地对比、黄东海新区新层系油气资源调查评价、中国海域和海丝路海域油气勘探开发形势分析,并于2019和2021年开展了2个航次的北印度洋重点海域联合地质科学考查。通过多年的努力,青岛所在海域油气勘探理论、技术方法、地质认识等方面取得了一系列创新性成果,为我国海域油气资源调查事业做出了重要贡献。
本文回顾了青岛所45年来油气调查与研究历史,总结了取得的重要成果与认识,梳理了面临的主要挑战,展望了未来海域油气调查的领域和方向。
1. 油气资源调查研究历史
青岛所1979年组建了油气地质室,重点针对我国海域盆地地质研究与资源评价开展工作。依据勘探和认识程度,将45年来青岛所在海域油气勘探与评价的工作划分为3个阶段,包括中国海域地质研究与资源评价阶段(1979—2004年)、中国东部海域新区新层系调查评价阶段(2005—2018年)和管辖内与管辖外海域调查研究阶段(2019年至今)。
1.1 中国海域地质研究与资源评价阶段(1979—2004年)
该阶段,以彭世福等为代表的石油地质学家一方面总结中国海域及邻区在该时期的勘探开发成果和地质认识,另一方面依托国家“六五”到“十五”期间的攻关项目、原地质矿产部项目、国家专项项目、国家海洋“八六三”专项项目课题等[4],开展了中国东部与朝鲜半岛陆域地质考察及主要构造单元的区域地质对比,中国海域及邻区盆地油气地质条件对比,黄、东海海域二维地震路线调查、中国海域油气资源快速综合评价等工作。通过该阶段攻关与综合研究,取得了以下主要成果认识。
(1)胶东地块是下扬子地块的组成部分,与朝鲜半岛京畿地块相对应。通过朝鲜半岛临津群和山东半岛蓬莱群地质考察和对比,认为朝鲜半岛临津群和山东半岛蓬莱群具有可比性,胶东地块属于下扬子地块一部分,改变原来胶东地块属于中朝地块的传统认识[5],建立了中国东部与朝鲜大地构造单元对应关系[6](表1)。
(2)海域深部地壳结构控制盆地构造及其演化。大陆架深部地壳结构控制和影响了地壳表层的构造特征和演化,从而控制了中国海域含油气盆地形成与演化。古近纪和新近纪盆地发育变质基底和未变质基底,渤海盆地基底属中朝准地台,南黄海盆地基底为扬子准地台,东海盆地基底的构造单元推测属于东南沿海褶皱系,南海陆架各盆地的基底构造单元可能为华南准地台向海域延伸部分[4]。盆地一般都经历断陷、拗陷、区域沉降三个阶段[7]
(3)中国海域古近纪和新近纪的海相夹层是地层对比的重要标志层,海侵时期是重要的烃源岩形成期[8-9] 。中国东部古近纪和新近纪经历了5次主要的海侵,由早至晚分别为白垩纪晚期—古新世早期、古新世晚期—始新世早期、始新世晚期—渐新世早期、渐新世晚期—中新世早期、上新世晚期—下更新世早期。陆相沉积盆地形成的海相生物层是在海侵期高峰时海洋生物进入陆盆后发育的,海相夹层可作为地层对比的重要标志层。海侵时期,近海盆地由于海平面变化或构造升降形成了半封闭的滨海湖或冩湖,生物大量繁殖,在生物死亡之后快速埋藏进入还原环境中,有机质经过一定埋藏,在适当的温度、压力作用下向烃类转化,逐渐形成丰富的油气源。
(4)中国近海新生代沉积盆地主要生油层发育于断陷期,受控于盆地演化[10]。中国近海新生代沉积盆地主要生油层位于盆地沉积下部,有腐泥型、腐质型和混合型3种类型,主要是由古陆至海的变迁和盆地由断陷到拗陷的演化历史所决定的。
(5)海域第三纪富含油气盆地具有“盆地面积大、沉积厚度大、生烃期次多、圈闭类型多、运移距离短”特点。中国海域富含油气盆地面积一般在5×104 km2以上,沉积厚度(1~2)×104 m,第三纪有4次生油期,形成了包括背斜、断块、古潜山、披覆构造和岩性圈闭等多种油气藏类型,油气聚集紧邻生油中心或深凹,尤其处于“凹中隆”或“凹围隆”背景下的构造或岩性圈闭[11]。
(6)创新形成了中国海域油气资源区域快速评价技术[12-14],评价了中国海域含油气盆地的油气资源。充分利用二维地震资料,以层序地层为指导,揭示盆地地质结构和沉积充填历史,构建模型库和知识库,形成盆地模拟基础上的海域油气资源区域快速评价技术,并采用该方法开展了海域低勘探程度盆地油气资源评价[15]。
(7)编制了首幅中国海域油气勘探开发形势图(1∶200万)。1984年,彭世福等主持编制了第一幅中国海域油气勘探开发形势图(1∶200万)[16],郭振轩编制首幅海域新生代盆地分布图(1∶500万)[17],此后利用GIS技术构建了海域油气勘探开发数据库[18-19],并于1994年开始每年动态编制中国海域油气勘探开发形势图2幅(东部海域和南部海域各1幅,1∶200万),为国家相关决策部署提供了第一手资料。
(8)明确提出中国海域油气资源战略性调查的重点方向。鉴于中国海域总体勘探程度较低、油气资源探明程度低的特点,在分析第三纪盆地油气勘探开发形势的同时,开展了战略研究,提出了中国海域油气资源战略性调查的九大重点方向[20],分别为北黄海和南黄海北部的陆相中生界、南黄海海域中-古生界、东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带的古新统及中生界、东海陆架盆地的第三系煤层气、南海陆坡深水油气、渤海海域晚第三纪晚期油气藏、南沙海域生物礁相油气藏、中国近海的海相中生界、中国近海的天然气勘探。蔡乾忠还提出南海北部残留特提斯[21-22]及东海“灵峰海”概念[23]。
(9)在1996—1999年,通过参与CCOP/CPGDP国际合作项目(“东南亚地质单元对比”),共享了CCOP/CPGDP数据库,为我国海洋油气地质工作“辐射全球海”奠定了初步的资料基础[4]。
1.2 中国东部新区新层系调查评价阶段(2005—2018年)
中国东部新区新层系调查评价阶段以全国油气资源战略选区调查评价与研究国家专项“南黄海前第三系油气前景研究”为启动标志[4],全面开展了以北黄海、南黄海、东海前新生界为目标层系的油气资源调查。
1.2.1 北黄海油气资源调查
该阶段由中国地质调查局组织实施,针对北黄海开展二维多道地震、三维多道地震、重力磁力和油气化探调查,并实施探井钻探。对地质结构、地层发育与分布、油气地质条件和油气资源潜力等进行研究与评价,取得以下主要成果:查明了北黄海东部重点海域中—新生界地质结构[4,24];明确了上侏罗统和中侏罗统两套主力烃源岩,以上侏罗统为主[25-27];发育多套有利生储盖组合[25,28],综合研究认为北黄海具有一定的勘探前景[28]。
1.2.2 南黄海油气资源调查
2005年,全国油气资源战略选区调查评价国家专项“南黄海前第三系油气前景研究”项目的启动正式拉开了南黄海中—古生代海相盆地油气调查的序幕[29-31]。2005年依托“南通幅”调查项目采集的区域二维多道地震资料,以崂山隆起为主,开展南黄海海相中—古生界地震探测技术攻关。2006年在理论模拟的基础上,进行震源容量、枪/缆沉放组合、电缆长度、覆盖次数、接收道数等攻关实验,以及地震资料采集与处理技术攻关,在XQ06-4地震测线中部深层发现了有效内幕地震反射,推测为古生代的地层反射[32-33],并显示为挤压褶皱构造特征。2007年,进一步增加电缆排列长度和覆盖次数,电缆长度达到5 700 m,覆盖次数达到76次,在XQ07-3地震测线T2波之下发现厚度大的地震反射层,存在3套较为清晰的反射标志层组,进一步推测为古生代的地层地震反射[34-36],更进一步坚定了海相中—古生界油气勘探的信心。
2008—2016年依托国家专项项目,进一步进行地震探测技术攻关[29,37-39],增加震源容量和排列长度,不断优化采集参数,尤其是2015年针对崂山隆起重点地区,采集参数设计从“高覆盖次数、富低频信号、强震源能量”3个方面进行重点攻关,取得了突破性进展,获得了崂山隆起5 000 km海相中—古生界高品质地震资料,总结形成了“高覆盖次数、富低频信号、强震源能量”地震探测技术(简称“高富强”地震探测技术)。2015年在崂山隆起重点区开展了油气地球化学勘查,进行了综合地球化学异常分区与含油气性评价,圈定了油气化探异常区。在2008—2016年,立足技术攻关,开展综合研究,实现了南黄海海相中—古生界的战略选区、选带,综合评价认为南黄海具有较大的油气勘探前景,具有形成与上扬子四川盆地相似的大型油气田的物质基础[4,40-42]。2016年进一步应用“高富强”地震探测技术,针对崂山隆起有利区带的重点构造开展三维地震调查,首次获得了深层海相中—古生界较好的三维地震资料。2016年完成科探井CSDP-2钻探,在志留系、泥盆系、石炭系、二叠系和下三叠统中发现多层油气显示[43-45]。2016—2018年,以前期地震资料为基础,开展综合研究,优选了有利区带,圈定了多个有利构造圈闭[4,46-48] 。
1.2.3 东海油气资源调查
2005-2007年,青岛所承担了国土资源部地质大调查专项,以中生界为主要目的层开展二维地震资料采集,获得部分深层不连续反射。2009-2014年,青岛所先后承担了国土资源部油气资源战略研究中心下属调查项目及国家专项项目,进一步针对深层进行技术攻关,采用长排列大震源的新技术,开展二维地震资料采集,获得了深层较好的常规二维多道地震资料和宽线多道地震资料。在闽江凹陷南部完成了380个站位海底沉积物柱状样品采集,并进行了海底沉积物顶空气、低空大气和海底底层水的样品采集。2016—2018年,青岛所依托国家地质调查专项,厘定了中生代地层层序,分析了地质结构,提出了东海南部与南海北部在中生代曾连为一体的“大东海”新认识[49],评价了资源潜力,优选了油气勘探远景区,认为东海中生界具有较大的油气勘探潜力。
1.3 管辖内与管辖外海域调查研究阶段(2019至今)
2019年至今,青岛所一方面开展东部海域油气资源调查,另一方面在北印度洋印度扇近海盆地与巴基斯坦开展联合科学考查与研究。依托国家海洋地质调查专项在南黄海崂山隆起继续开展地震探测技术攻关和补充调查,并针对重点构造开展OBS调查,获取了海相中—古生界地震速度,建立了地质速度模型,圈定了崂山隆起西部边界及其2个NW向构造带,进一步优选了崂山隆起有利构造带和南部地区有利区带。在东海进一步开展地震调查,取得了深层更好的地震成像资料,解析了盆地结构特征,评价了油气资源潜力。取得了以下主要成果:构建了东海陆架盆地中生代原型盆地,确认了东海及邻域中生代两次海侵事件的时间[50-51];优选出闽江斜坡为东海陆架盆地中生代油气勘探有利区带,圈定了闽江斜坡和台北转折带为有利区带[52-55]。
在中国和巴基斯坦印度洋联合科考与研究中,取得了突破性进展,获得了北印度洋印度扇近海盆地深层中生界有效地震反射,明确了印度扇近海盆地地质结构,探讨了油气资源潜力,研究认为印度扇近海盆地发育白垩系、古新统—始新统以及中新统3套有利烃源岩[56];发育下白垩统砂岩、渐新统—中新统砂岩及古新统—始新统碳酸盐岩3套储层,具有分布广、厚度大的特点;形成3套油气成藏组合:第1组合以下白垩统泥岩为烃源岩,白垩系砂岩为储层,上白垩统厚层泥页岩为盖层,该组合在陆域印度河盆地和邻近的海域库奇盆地获得油气发现;第2组合以古新统—始新统为烃源岩,古新统—始新统碳酸盐岩为储层,下中新统泥岩为盖层,该组合在陆域和库奇盆地KD-1井获得油气发现;第3组合以下中新统泥岩为烃源岩,以中中新统水道砂岩为储层,以上新统—中新统及以上泥岩为盖层,该组合在海域浅水区PakCan-1井获得油气发现。由此可见,印度扇近海盆地具有形成大中型油气田的地质条件[57-58]。
2. 研究进展
2.1 海域新区新层系油气资源调查技术探索与应用
2.1.1 “高富强”地震探测技术
海陆对比认为,南黄海中—古生界发育3套区域性烃源岩和2类规模性储层,具有形成大中型油气田的物质基础,但是,由于中—古生界上下地层之间巨大的速度差造成的屏蔽作用,南黄海深部中、古生代地层常常得不到有效反射,在地震剖面上表现为空白,严重阻碍了南黄海油气的勘探突破。针对这一问题,青岛所陈建文研究团队联合国内多家单位,依托南黄海多个油气资源调查项目,历经十多年科技攻关,探索出以“高覆盖次数、富低频成分、强能量震源”为主要特色的南黄海盆地深部海相中—古生界油气资源地震探测技术,突破了南黄海深部油气勘探的技术瓶颈。利用该技术在崂山隆起上获得中—古生界有效反射(图1)[29,34-39] ,剖面上显示为3套标志层[34-36,59],最大探测深度超过15 000 m。
![]() 图 1 南黄海海相中—古生界地震层序及地质属性标定图据参考文献[39]修改。S1—S7为海相中—古生界地震层序,T2相当于新近系底界,B1—B3为三套典型地震反射标志层组.Figure 1. Paleozoic-Mesozoic seismic sequence and geological attributes correlation in the South Yellow SeaModified from reference [39]. S1 to S7 are the seismic sequences of marine Paleozoic-Mesozoic. T2 is the bottom boundary of Neogene. The B1 to B3 are the three typical seismic marker layers.
图 1 南黄海海相中—古生界地震层序及地质属性标定图据参考文献[39]修改。S1—S7为海相中—古生界地震层序,T2相当于新近系底界,B1—B3为三套典型地震反射标志层组.Figure 1. Paleozoic-Mesozoic seismic sequence and geological attributes correlation in the South Yellow SeaModified from reference [39]. S1 to S7 are the seismic sequences of marine Paleozoic-Mesozoic. T2 is the bottom boundary of Neogene. The B1 to B3 are the three typical seismic marker layers.2.1.2 地球化学探测技术
海洋油气地球化学勘查是以海底烃类渗漏理论为指导,针对海底沉积物、底层海水、海水表面油膜、近海面低空大气等多种介质,通过烃类和非烃类、微生物等多种指标的分析测试和鉴定、识别地球化学异常,再结合地质、地球物理资料,进行综合解释和评价,获取海底油气渗漏、深部油气存在和属性等信息的技术方法。
自2000年以来,青岛所先后在南黄海、北黄海、渤海、东海南部,以及南海北部湾海域等开展了海洋油气地球化学勘查工作,通过区域地球化学勘查、目标地球化学勘查、井中地球化学勘查3个层次的海洋油气地球化学勘查工作,形成了完善的海洋油气地球化学勘查技术体系,取得了一系列地质成果,提高了海洋油气化学勘查技术的应用效果,为我国海洋油气资源勘探提供了资料积累和技术支撑。
青岛所油气地球化学勘查取得的主要技术与成果体现在5个方面:①研发了海面低空大气、底层海水和海底沉积物不同介质样品的采集与保真技术装备;②规范了包括烃类气体、中等分子烃类和高分子量烃类等直接指标和微生物与蚀变碳酸盐等间接指标的海洋油气地球化学勘查指标体系,建立了各类地球化学指标分析测试技术流程;③形成了海洋油气地球化学勘查异常提取技术,包括数据预处理、异常背景分析和异常分析,异常下限确定方法;④建立了地球化学异常成因分析技术,利用烃类气体分子及其碳、氢同位素组成识别热成因烃和生物烃,利用三维荧光图谱和相关参数判别深部原油类型,利用饱和烃及生物标志物图谱和参数判别原油的沉积环境、沉积相、热成熟度和时代等;⑤开展了综合地球化学异常分区与含油气性评价,通过异常叠合分析方法圈定综合地球化学异常区,通过选定参数及其累积得分进行综合地球化学异常区含油气性排序,圈定了南黄海崂山隆起综合地球化学异常区3个、北黄海综合地球化学异常区8个和东海综合地球化学异常区2个,优选了南黄海崂山隆起局部构造。建立了围绕高石3构造的油-气双环状表面地球化学异常模式[60-62]。
2.1.3 重磁震联合反演技术
重磁震联合反演是盆地构造单元和盆地结构早期研究的重要技术手段。青岛所针对在我国东部海域获取的二维多道地震、重力和磁力数据,通过一系列的数据处理得到地震、重力和磁力成果数据。利用东部海域周边露头、陆域和海域钻井资料,获得岩石的地球物理性质参数,包括岩石密度、磁性、弹性和导电性等。根据地震解释,进行重力和磁力设置初始几何模型,并依据地层物理性质参数进行密度和磁化率赋值,观察实测曲线、理论曲线拟合情况,并进行修正,直至实测曲线、理论曲线具有较好的拟合关系[45]。以南黄海为例,南北向重磁震联合反演剖面揭示了南黄海盆地的基底结构、磁性基底埋深、海相中-古生界厚度及火山岩分布。反演结果表明(图2),南黄海崂山隆起上广泛发育了震旦—早二叠世地层,崂山隆起存在较大磁异常幅值,主要为变质基底以及结晶基底引起的上隆,同时可能存在基性火山岩的叠加。北部烟台坳陷古近系之下应发育有厚度较大的中、古生界。南部勿南沙隆起和青岛坳陷中,上古生界和中生界青龙组分布广泛,根据密度反演推测下部也有广泛的下古生界分布,这与区域海陆对比相一致[45]。重磁震联合反演技术同样揭示了东海陆架盆地的基底结构、中生界厚度以及中生界残留盆地的隆坳格局。
根据地震提供的层位进行反演时,可以取长补短,发挥综合优势,重、磁反演与其他地质、地球物理方法结合,在进行资料解释时可以起到降低其多解性的作用。
2.1.4 区域油气资源快速评价技术
2000年,青岛所主持完成了国家高技术发展计划(“863”计划)海洋领域“820”主题中“海上油气资源区域快速综合评价技术(820-03-03)”课题[12]。研制了一套针对海上无钻井或钻井很少的沉积盆地的早期快速综合评价技术和软件系统。该技术包括综合地球物理盆地描述、层序地层学盆地描述两大技术和以油气运聚为主的盆地模拟技术及相应的3个软件系统。该技术主要开展盆地的沉降史、热史、生排烃史及油气运移聚集历史的动态模拟[12-13]。
该技术在海域盆地油气资源早期快速评价应用中成效显著,例如,采用该技术在只进行了地球物理概查和普查但尚未开展钻探的南海某盆地预测了27个大型构造带,其中14个构造钻获油气,成功率达71.4%[12-13]。所研制的二维盆地模拟技术在渤海、南黄海、东海和南海北部得到了广泛应用,迈出了高新技术产业化的第一步[12-13]。
2.2 东部海域新区新层系油气地质新认识
2.2.1 北黄海中生界油气地质新认识
(1)查明了盆地油气地球化学异常立体分布特征、成因及其主控因素
通过化探样品分析和综合研究,优选出7类有效化探指标,其中荧光光谱、紫外吸收光谱、酸解烃、顶空气和热释烃为主要指标,三维荧光和蚀变碳酸盐为辅助指标。
平面上双环带结构的油气地球化学异常表明形成异常的烃类可能存在2种来源(侏罗系烃源岩和断裂构造的宏渗漏)或由2期油气运移事件形成;垂向上烃类地球化学异常受深度、岩性和成熟度等多种因素控制,总体表现为由浅向深各烃类指标含量(或异常幅度)和干燥系数随深度增加逐渐增大,反映了成熟度和生烃能力的变化特征[60]。化探分析研究的结果也被钻井和后续的测试结果所印证。
(2)探明了盆地东部油气地质条件与主要成藏组合
钻探证实东部坳陷中—晚侏罗世发育湖泊-三角洲相沉积体系,发育中侏罗统和上侏罗统2套暗色泥岩[26-27]。中侏罗统暗色泥岩总体属“中等”烃源岩;上侏罗统暗色泥岩总体属“中等—好”、局部达到“优质”烃源岩。上侏罗统烃源岩成为坳陷油气成藏组合的主力供烃源,侏罗系有效烃源岩的分布范围控制了油藏的空间展布[23,27]。上侏罗—下白垩统的“下生上储上盖式”是最重要的成藏组合,其次是侏罗系内部的“自生自储自盖式”或“上生下储上盖式”组合[27]。
2.2.2 南黄海海相中—古生界油气地质新认识
(1)南黄海地块与周边地块经历了3次拼合和6期沉积盆地演化过程
南黄海地块作为下扬子一部分,它与周缘板块的作用及形成演化是在区域大地构造背景下形成的。下扬子-南黄海地块与周缘存在3期拼合模式:①扬子和华夏地块新元古代汇聚模式,扬子和华夏在西缘的拼合时间发生在1.0 Ga左右,最后的拼合时间为825 Ma左右[63],同时在扬子和华夏拼合过程中发生过大规模的陆壳生长,伏川弧后盆地蛇绿岩代表了扬子与华夏地块的缝合带[64-65];②加里东期的碰撞造山拼合模式,主要发生于晚奥陶世至晚志留世华夏与扬子挤压拼合前陆造山,表现强烈的花岗岩岩浆活动及高压变质作用[66],同时华夏造山带经历了俯冲、碰撞及造山后伸展这样一个完整的造山过程;③印支期华南远程效应拼合模式,形成于西冈瓦那大陆与劳亚大陆的汇聚和古特提斯洋消减以及新特提斯洋的打开背景下的晚三叠世至早侏罗世,华北、华南与印支地块等地块发生拼合,最终于三叠纪形成了统一的Pangea大陆[67],在这个过程中,扬子板块俯冲于华北板块之下,华北板块向扬子板块强烈逆冲推覆,在南黄海南部青岛坳陷至勿南沙隆起表现为远程效应推覆。
南黄海盆地是在前南华纪褶皱变质结晶基底之上,经历了中、元古代末四堡运动和新元古代晋宁运动的固结回返后,形成变质岩结晶的基底结构,之后做为扬子地台的一部分,经历了地台、断陷和坳陷3个主要发育时期[68],以及6个发育阶段,即震旦纪—中奥陶世稳定克拉通沉积阶段、晚奥陶世—志留纪俯冲碰撞前陆盆地发育阶段、晚泥盆世—早三叠世为伸展-裂陷盆地发育阶段、印支期陆内俯冲挤压对冲阶段、早白垩世—始新世伸展断陷阶段、古近纪—第四纪拗陷阶段。
(2)南黄海海相中—古生界发育有利油气成藏组合
海陆对比表明,南黄海发育与扬子区陆域类似的新元古代—中生代海相沉积建造和形成演化历史。在地震剖面上(图1),具有上震旦统至下三叠统清晰的反射特征,地震上下志留统高家边组上段以上地层已经为钻井资料所证实[69-71]。南黄海上震旦统至下三叠统发育3套区域性烃源岩及碳酸盐岩和碎屑岩两大储集体系,三套有利烃源岩包括下寒武统幕府山组、上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统高家边组、二叠系(栖霞组和龙潭—大隆组);碳酸盐岩储层主要发育于上震旦统、寒武系、奥陶系、石炭系和下三叠统,碎屑岩储层主要发育于志留系、泥盆系和上二叠统龙潭组[69-73]。综合评价认为烃源岩以下寒武统幕府山组和上奥陶统五峰组-下志留统高家边组为主,其次为二叠系栖霞组和龙潭—大隆组;储层以碳酸盐岩储层为主,其次为碎屑岩储层。地震资料综合解释和区域对比表明,南黄海上震旦统至下三叠统发育4套完整的生储盖组合[74]。第1组合烃源岩为下寒武统幕府山组泥页岩,储层为上震旦统灯影组白云岩,幕府山组泥页岩为盖层,形成上生下储油气成藏组合;第2组合烃源岩为下寒武统幕府山组泥页岩,储层为中寒武统—奥陶系白云岩和灰岩,盖层为上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统高家边组泥页岩,形成下生上储油气成藏组合;第3组合烃源岩为上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统高家边组下段泥页岩,储层为志留系至上泥盆统五通组砂岩以及石炭系灰岩,盖层主要为下二叠统栖霞组泥质灰岩与灰质泥岩、上二叠统龙潭—大隆组泥页岩,形成下生上储油气成藏组合;第4组合烃源岩主要为下二叠统栖霞组灰岩、上二叠统龙潭—大隆组泥页岩,储层主要为上二叠统龙潭组砂岩和下三叠统青龙组碳酸盐岩,盖层主要为上二叠统龙潭—大隆组厚层泥岩及三叠系青龙组泥灰岩、膏盐层,形成自生自储、下生上储油气成藏组合。这4种油气成藏组合在四川盆地均发现了大型、特大型气田,如威远、安岳、普光气田等[75-79],因此也表明与上扬子四川盆地具有相似沉积建造的南黄海海相中—古生界具有较大的油气勘探前景。
(3)四期运动造就多源多期成藏模式
南黄海自晚震旦世以来主要经历了四期构造运动,其中,印支运动对古生界油气藏的影响最大,主要表现在对早期油气藏的破坏、重新调整聚集以及对晚古生代烃源岩生成的油气聚集成藏和油气散失,其次是燕山运动和喜山运动对古生界油气藏的改造和破坏。CSDP-2井包裹体显微荧光、测温和测年分析表明,无论是封存于中上志留统砂岩、上二叠统砂岩中的流体包裹体,还是封存于石炭系灰岩中的流体包裹体均存在多期油气充注现象,通常表现为至少两期油气充注[46-48]。
下寒武统幕府山组烃源岩品质好,分布广,具有形成大规模油气藏的基础,该套烃源岩生成的油气贯穿了从上震旦统至下三叠统油气成藏过程。该套烃源岩主要生油阶段在晚志留世—泥盆纪,在中二叠世达到生气高峰。生成的油气沿着断裂和储集层优先运移聚集到崂山隆起的构造圈闭中。晚印支之后的各期构造运动,对早先形成聚集的油气进行了调整和改造,早期原生油气藏发生调整,一部分保留在圈闭中,一部分通过断层向上运移到上部储层中。
上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统高家边组烃源岩品质中等—好,分布范围较大,生油阶段主要集中在晚泥盆世—二叠纪,中三叠世达到生气高峰。下志留统高家边组烃源岩生成的天然气通过断层进入圈闭形成气藏。二叠系烃源岩在中三叠世开始生油,中白垩世达到生油高峰,由于受燕山期和喜山期构造抬升影响,下三叠统遭受强烈剥蚀,下二叠统也遭受不同程度剥蚀,因此浅部下三叠统和上二叠统油气藏破坏性较大,而石炭系至下二叠统栖霞组保留完整,其灰岩储层紧邻烃源岩,易形成浅层油藏。同时受印支晚期和燕山期构造改造作用,前期下志留统高家边组生成的气藏经过构造调整后在浅层圈闭重新聚集成藏,并与来自二叠系的原油形成油气同藏。由此可见,从晚震旦纪到二叠纪,四期构造运动的叠加最终形成了南黄海崂山隆起多源多期复式油气成藏模式(图3)。
2.2.3 东海陆架盆地中生界油气地质新认识
(1) 不同类型的2期盆地叠置造就了中生代“大东海”盆地
根据与东海邻区浙江及福建地层对比、地震资料解释以及重、磁资料反演认为,东海南部中生代地层不仅分布广、厚度大,而且与南海北部很可能处于同一构造背景(图4),构成了一个面积约20万km2,厚度在3 000~8 000 m的巨大沉积体。这个沉积体的范围超出了传统意义的东海盆地,我们姑且称之为“大东海”中生代盆地[49]。目前,东海南部中生代残留厚度为4 000~8 000 m,东海盆地FZ10-1-1和FZ13-2-1井揭示了2套中生界烃源岩,分别是侏罗系福州组和白垩系渔山组,初步分析认为具有较大生烃潜力[80-81]。而南海北部也发育了较厚的中生界侏罗系和白垩系,残留厚度为3 000~7 000 m,其沉积环境为深海-海陆过渡相,同样具有较好的生油潜力[81]。据区域构造展布、构造演化、沉积环境特征综合分析认为,东海陆架盆地南部与南海北部陆架盆地在中生代可能连为一体,组成了一个“大东海”盆地。可以预见,将南海北部和东海南部作为整体研究,东海中生界油气勘探必将有新的发现。
(2)中生代盆地具有“北东分带”的结构特点和两期演化过程
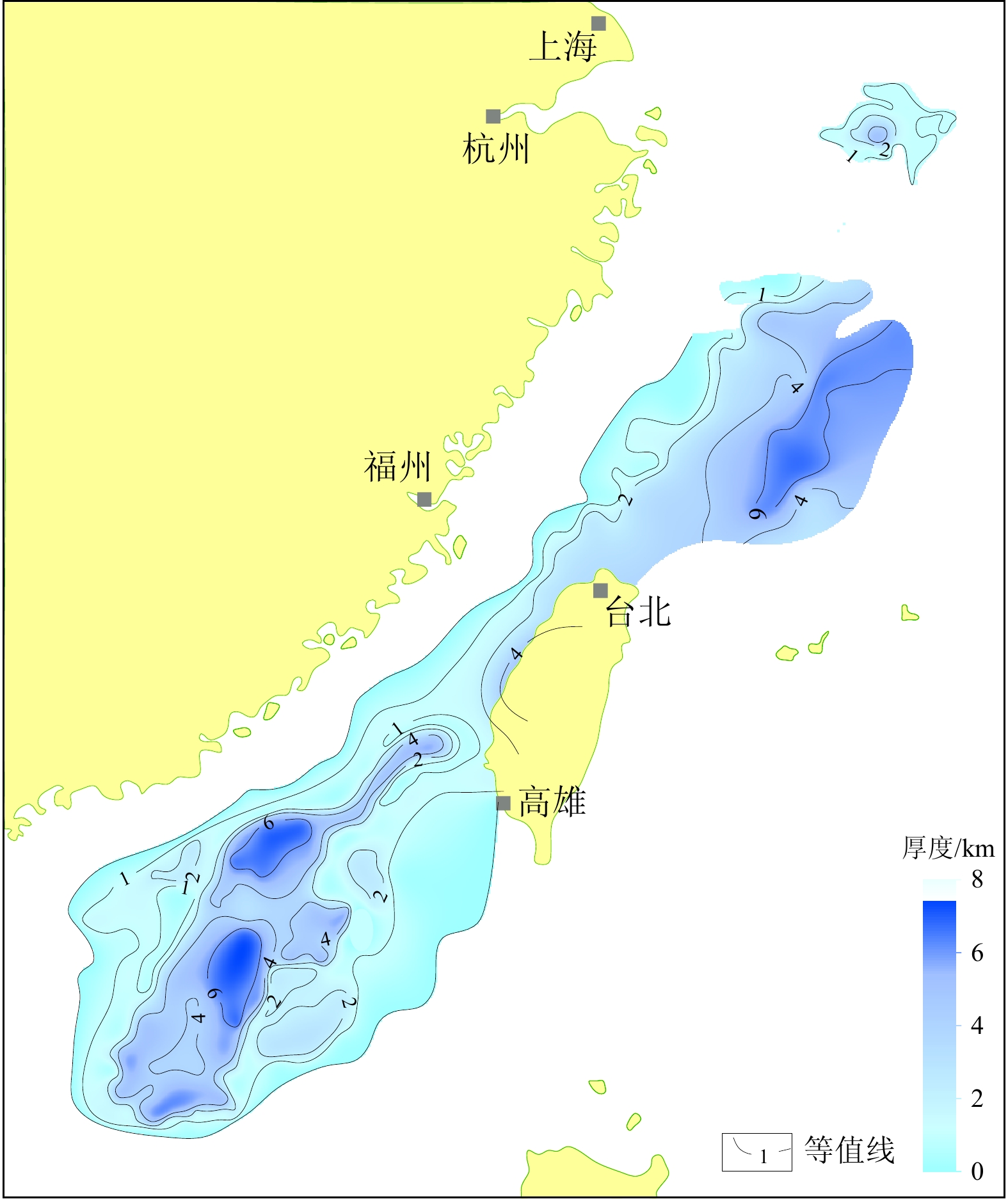
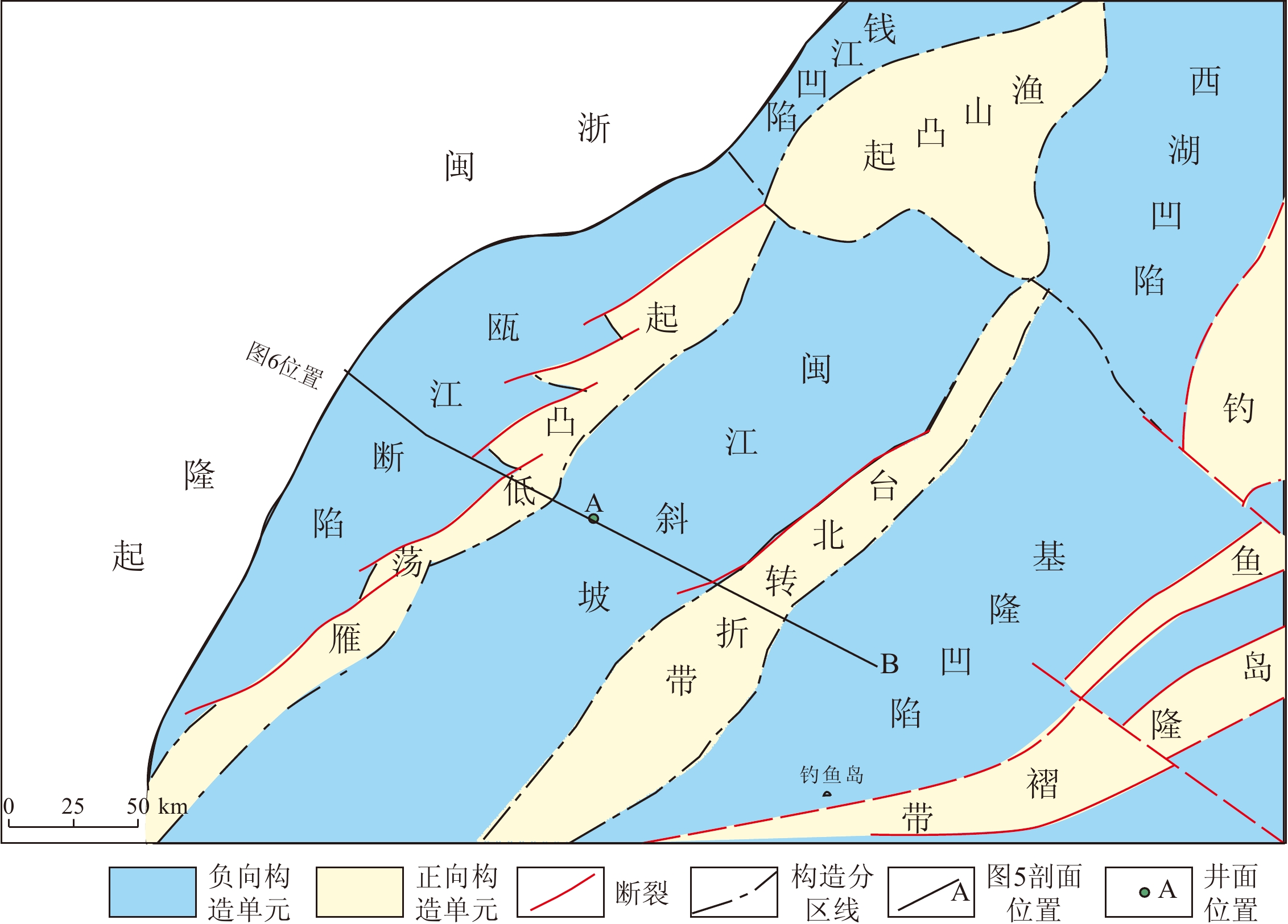
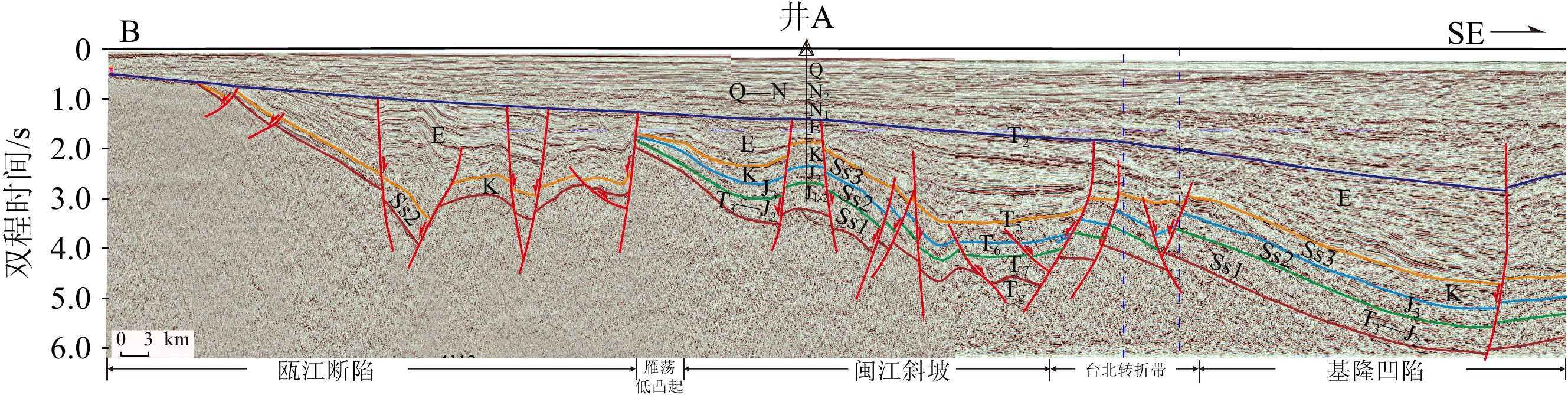
东海盆地南部深部主要发育NE-NNE和NW向2组断裂系统,控制盆地中、新生界的平面结构具有“东西分带、南北分块”的格局,自西向东分别为瓯江断陷、雁荡凸起、闽江斜坡、台北转折带和基隆凹陷(图5)[87];垂向剖面结构上整体表现为中生界和新生界叠置的三层楼结构——坳陷、箕状断陷与坳陷结构叠置(图6)。
![]() 图 5 东海盆地南部中生代构造单元[87]Figure 5. Mesozoic tectonic units in the southern part of the East China Sea Basin
图 5 东海盆地南部中生代构造单元[87]Figure 5. Mesozoic tectonic units in the southern part of the East China Sea Basin![]() 图 6 东海盆地南部地震解释剖面[87]Figure 6. Seismic interpretation profile of the southern part of the East China Sea Basin
图 6 东海盆地南部地震解释剖面[87]Figure 6. Seismic interpretation profile of the southern part of the East China Sea Basin东海陆架盆地主要受太平洋构造域和特提斯构造域影响,经历了多期次改造,导致盆地中生代变形复杂,华南中生代主体表现为古大陆边缘再造至陆内构造变形。海西期—印支中晚期华南主要为克拉通盆地,东海陆架是一个与扬子—华南克拉通毗邻的大陆边缘盆地;印支晚期中国东部受南北向挤压结束了克拉通边缘盆地演化;晚三叠—中侏罗世,东海陆架盆地进入古太平洋活动大陆边缘发展阶段;晚侏罗—早白垩世华南东部是燕山运动的高潮期,发育大规模的火山喷发和火山碎屑堆积,表明东亚大陆边缘进入俯冲活动型大陆边缘阶段。
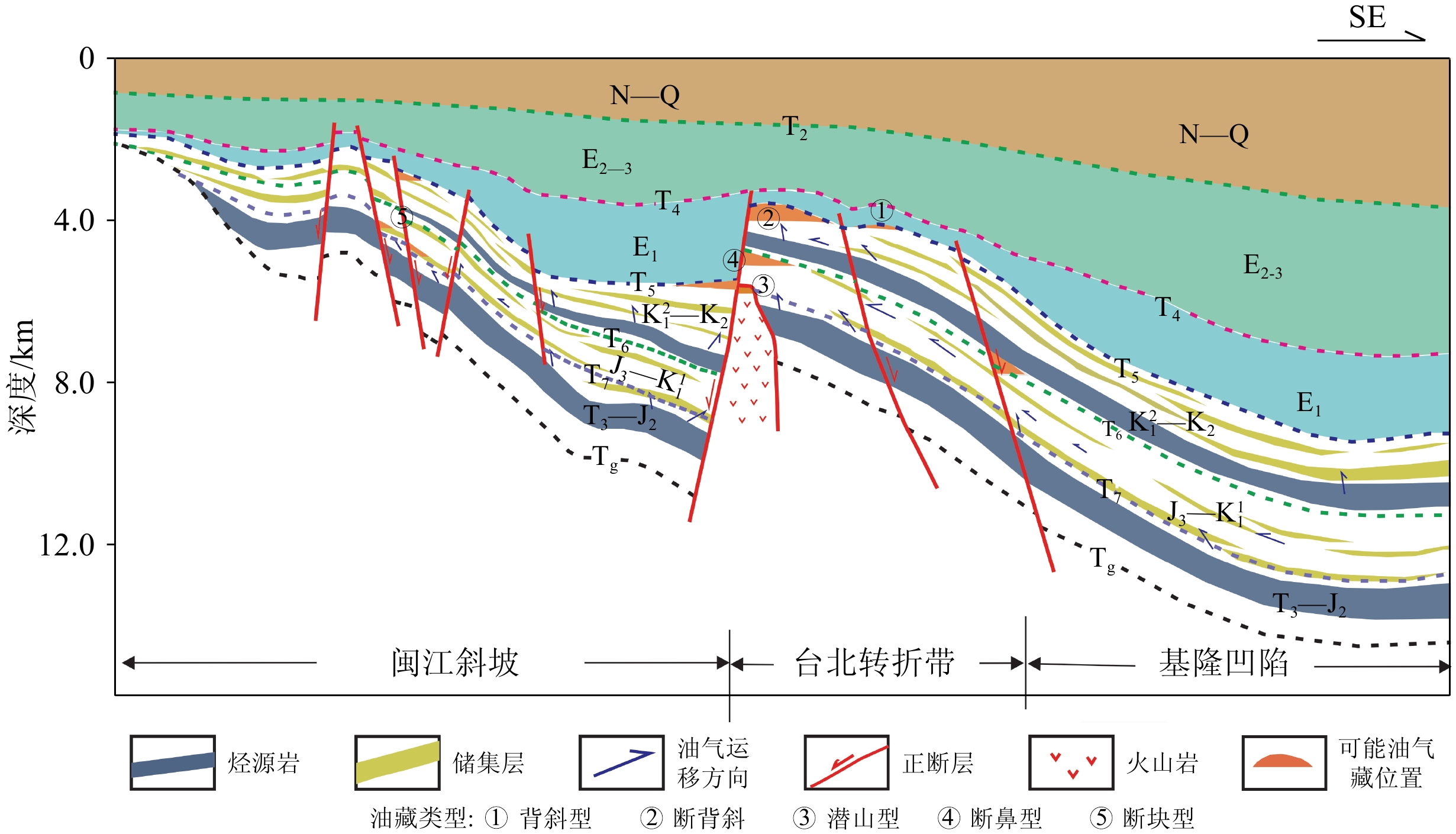
(3)“复式成藏模式”助力东海中生界油气勘探
钻井及地震资料解释认为,东海盆地南部中生界发育2套烃源岩,其生储盖组合主要有3套:①上三叠统—下侏罗统暗色泥岩和煤层作为烃源岩,中上侏罗统砂岩作为储层,下白垩统厚层泥岩作为盖层;②上三叠统—下侏罗统暗色泥岩和煤层作为烃源岩,上白垩统砂岩作为储层,古近系厚层泥岩作为盖层;③下白垩统厚层暗色泥岩作为烃源岩,上白垩统砂岩作为储层,古近系厚层泥岩作为盖层。构造分析认为[51],在晚三叠世到中侏罗世期间,东海盆地南部构造变形微弱,断层不发育,主要形成自生自储型油气藏。在这个时期,下侏罗统烃源岩生成的油气主要聚集在生烃中心附近,这类“自生自储型”油气藏主要分布在盆地南部。在晚侏罗世到白垩纪期间,东海盆地南部构造变形强烈,断层沟通了源岩同时破坏了前期形成的油气藏,中生界烃源岩生成的油气沿着断层、凹陷边缘渗透性的砂体、不整合面等向上运移,在砂体尖灭时或断层封闭时期,油气主要受断裂、不整合面和砂体的控制,这类“古生新储型”油气藏主要分布在斜坡带和断层附近[88],或沿断层输导到厦门组或闽江组形成“古生新储”油气藏,该类油气藏主要发育在斜坡带以及切穿中生界烃源岩的断层上倾方向。在始新世末到渐新世期间,新一期的断裂活动产生了大量新的张性断层或老断层复活,原有的油气在明月峰组区域盖层下重新运移,重新聚集成藏,进而形成了东海盆地南部中生界早期成藏、晚期调整的复式成藏模式(图7)。综合分析认为,台北转折带和闽江斜坡构造带为中生界有利勘探方向,台北转折带和基隆凹陷西部形成近源陡坡-断层型成藏模式,而闽江斜坡则发育远源缓坡-断层型成藏模式[88]。
2.3 印度扇盆地的科学考查发现与认识
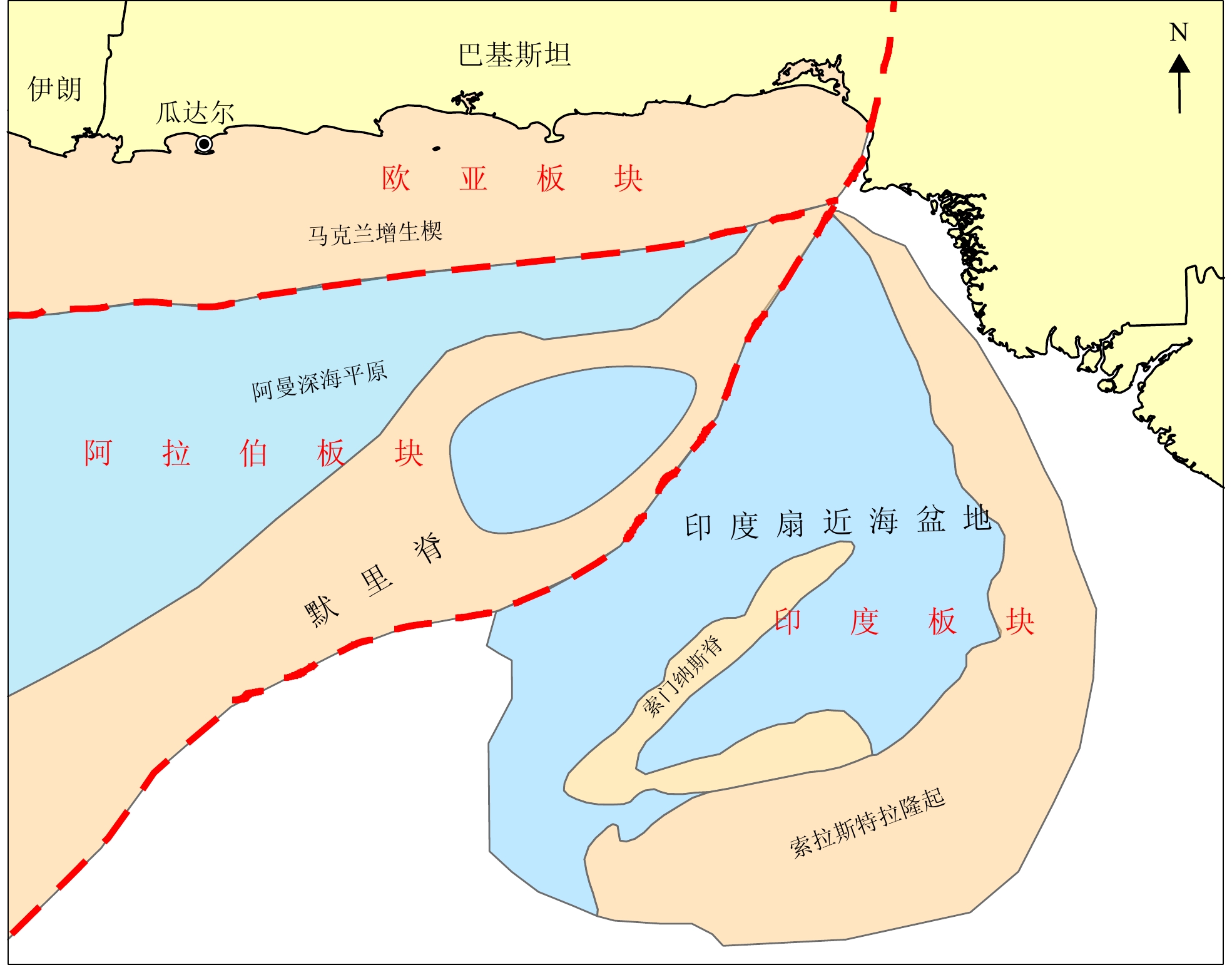
2019—2021年,中国-巴基斯坦联合科学考查海域位于印度洋阿拉伯海的北部,东邻印度西海岸、北靠巴基斯坦南部海岸线、西接霍尔木兹海峡,南为广阔的印度洋,调查区大致位于印度扇上端,面积约为21×104 km2[56-57],其构造单元自北向南包括马克兰增生楔、阿曼深海平原、默里脊和印度扇近海盆地4个构造单元(图8)。在印度扇近海盆地的中巴联合科学考查取得了三大重要发现,获得了对该海域油气新区新层系的新认识,认为该盆地具有形成大中型油气田的地质条件,拓展了巴基斯坦海域油气勘探领域。
2.3.1 印度扇近海盆地广泛发育中生界
印度扇近海盆地新生界沉积巨厚,最厚处超过一万米,新生界基底为晚白垩世德干火成岩时期形成的溢流玄武岩[89-92],地震反射波难以穿透这套火山岩,多年来未获得清晰的中生界反射。陆架和深海虽有多口钻井,但均未揭示盆地中生界,学者对该区中生代地层发育一直存在较大争议,限制了盆地油气勘探活动的开展。
新采集的高品质二维地震剖面突破了火成岩层的屏蔽效应,通过开展地震反射界面追踪、波组特征分析和速度分析,揭示了中生代地层在印度扇近海盆地广泛分布,其受控于盆地早期裂陷作用,整体厚度800~10 000 m(图9),表现为东南厚、西北薄,向北和向西超覆,最大沉积厚度位于研究区东南和西北两个区域,该套地层在陆域的下印度河盆地已证实为重要烃源岩层和油气产层[93]。
中生代地层在近陆棚区和索拉斯特拉隆起分布面积广而厚,裂陷期断裂基本没有断穿该玄武岩,玄武岩的覆盖对下部油气可能起到了很好的圈闭作用,因此,印度扇近海盆地中生界将是重要勘探层系,具有较大的油气勘探前景。
2.3.2 盆地西部发育大型重力滑动构造
印度扇近海盆地在新生代进入被动大陆边缘盆地阶段,盆地以热沉降为主,断层不发育。2019—2021年中巴联合科学考查首次在盆地西部发现了一套大型重力滑动构造[94]。该构造具有如下特征:平面上根据应力状态和变形特征可分为伸展区、过渡区及挤压区,其中,伸展区长度约35 km,过渡区长度约15 km,挤压区长度约50 km(图9)。纵向上,剖面自下而上可分为3套层序:构造层Ⅰ(T0-O50)、构造层Ⅱ(O50-P55)、构造层Ⅲ(O50-海底),分别对应重力滑动前层序、重力滑动期层序、重力滑动期后层序。
伸展区位于陆架坡折以北,以发育大断距向南倾的生长断层和滚动背斜为典型特征(图10),发育4条大型生长断层,主断面接近铲式,切穿构造层Ⅰ及构造层Ⅱ,断层倾角约25°,向下逐渐收敛于滑脱面,4条生长断层之间呈多米诺式,次级断层与之呈“Y”形或反“Y”形等。滚动背斜(逆牵引构造)是标志性的伴生构造,形态不对称,背斜顶部产状平缓,翼部随深度增加产状逐渐变陡,由于生长断层的活动,构造层I发生旋转翘倾,伸展区构造层Ⅰ均向北倾,倾角10°~20°,当断层在构造层Ⅱ沉积时持续活动,最终发育为顶薄翼厚的滚动背斜。
挤压区以超压泥岩强烈变形、发育小断距逆冲断层、泥底辟、断层相关褶皱、背驮式盆地及同沉积背斜为主要特征。根据反射特征,构造层Ⅰ可分为4组,自下而上分别为:底部强烈流动变形泥岩、中下部弱变形砂泥岩互层、中上部弱流动变形泥岩、上部弱变形砂泥岩互层。由于滑脱面位于超压泥岩层下部,因此该套泥岩吸收了大部分应变,导致强烈流变,向上刺穿形成4排泥底辟。中构造层Ⅱ由南往北依次发育同沉积背斜、背驮式盆地及滚动背斜。北部发育浅层正断层。同沉积背斜主要位于泥底辟之上,为下伏地层隆起同期形成,具有顶薄翼厚特征。背驮式盆地沉积厚度变化较大,在背斜顶部该构造层较薄。浅构造层Ⅲ几乎无构造变形,以平行层序为主。
该重力滑动构造受控于印度扇的时空演化[95],伸展区滚动背斜及挤压区断层相关褶皱可能是油气聚集的理想场所。
2.3.3 浅水区碳酸盐岩台地
联合科学考查证实巴基斯坦海域浅水陆架区发育大规模古新统—始新统碳酸盐岩缓坡台地,水深小于200 m,靠近中新统烃源岩生烃中心(图11)。古新统—始新统碳酸盐岩台地生物礁滩储层,主要发育于浅水区陆架边缘台地,可以识别出地震反射呈丘状的外形,内部杂乱、同相轴振幅较强的台地边缘相,平行强振幅较连续反射的台地内冩湖相,以及弱振幅、连续性较差的滩体等多种沉积类型。海陆对比研究发现,该套储层在陆域是重要的储层,超过40%油气产于该套储层。
前人研究发现下印度河盆地及邻近海域古新统—始新统存在多套生储盖组合,其中始新统发育多套碳酸盐岩储层并成藏。陆架区Dabbo Creek-1井钻遇始新统碳酸盐岩台地,含大量藻类及有孔虫,岩性以颗粒灰岩、礁灰岩等为主,储层物性优异。多套区域泥岩既可充当烃源岩,也可充当盖层,与碳酸盐岩储层空间上毗邻,时空配置条件优越。因此,浅水陆架区发育的碳酸盐岩缓坡台地具有较好油气储集潜力,是下一步调查的重要方向。
2.4 海域油气资源勘探开发形势与战略性方向
2.4.1 中国海域油气资源勘探开发形势
中国海域常规剩余油气资源较为丰富,其中常规石油剩余地质资源量主要集中在构造与深水岩性两大领域,构造领域剩余石油地质资源量137.40×108 t,深水岩性领域剩余石油地质资源量29.79×108 t,两者合计167.19×108 t,占中国海域剩余石油资源的86%[97]。常规天然气剩余地质资源量集中于构造、生物礁、深水岩性三大领域,其中构造领域剩余天然气地质资源量14.57×1012 m3,生物礁领域7.04×1012 m3,深水岩性领域6.35×1012 m3,三者合计27.97×1012 m3,占海域剩余天然气资源量的97%[98]。
中国近海油气资源较丰富,但探明程度较低,油气资源分布不均,勘探程度存在差异[99]。但是,自十三五以来,我国海域坚持以寻找大中型油气田为目标,积极探索深层、深水、高温高压领域,发现了5个亿吨级油田、4个5 000亿m3级油田群、2个千亿方级规模气田,油气探明地质储量呈快速增长态势,海洋石油增产量连续4年占全国石油总增产量的60%以上,成为我国能源上产的主力军。目前,石油资源主要分布在渤海、珠江口、北部湾3个盆地,占总资源量的91%,探明地质储量占总探明地质储量的99%,探明程度相对比较低,分别为30%、38%、22%[100]。天然气资源主要集中在东海、珠江口、琼东南、莺歌海4个盆地,占总资源量的86%[100],探明地质储量占总探明地质储量的76%。其他盆地勘探风险高,成功率低,探明程度也很低。
随着中国海上成熟领域勘探程度的不断加深,勘探发现的难度越来越大,海上油气勘探从简单的构造油气藏向复杂的地层—岩性油气藏拓展,从浅层向中深层、潜山拓展,从浅水区向深水区拓展,从常温常压区向高温高压区拓展,从常规油气藏向低渗油气藏拓展。近年来勘探理论及关键技术攻关,在渤海海域潜山、环渤中凹陷岩性、琼东南盆地深水深层、珠江口盆地惠州凹陷、涠西南页岩油等多个区域不同地质类型层段取得重大勘探突破,发现大中型油气田的探明储量占总储量的67%,为我国海域增储上产奠定了坚实的基础[101-103]。
2.4.2 中国海域油气资源勘查战略性方向
我国海域油气勘探应关注新地区、新层系、新领域、新类型等4大战略方向,应加大渤海深层潜山及中浅层岩性、北黄海及南黄海北部陆相中生界、南黄海中—古生界碳酸盐岩油气藏、东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带古新统及中生界、东海陆架盆地煤层气、南海陆坡深水油气、中国近海海相中生界、南沙海域生物礁相油气藏等八大领域的勘探力度。尤其近年来,在南海北部陆坡深水区发现了荔湾3-1、陵水17-2等深水油气田,在渤海发现了蓬莱9-1、渤中19-6大型基岩油气田及渤海垦利6-1新近系大型岩性油气田,在东海陆架盆地发现了4千亿m3储量的煤层气田[104-106],这些重大发现证实了海域油气勘探突破方向。南黄海中—古生界、东海陆架盆地中生界已成为公益性海洋油气调查主要方向,认为随着投入加大和科技水平提升,海域前新生界新层系必将取得突破,并成为未来油气储量的重要增长点。
2.4.3 全球海域油气资源勘探开发形势
近10年来,全球海域共发现油气田1 223处,其中环印度洋沿岸发现256处,累计探明油气可采储量68.77亿t[107],海域油气勘探主要经历3个阶段:超深水天然气勘探发现活跃、探明储量大幅增长阶段(2010—2011年);超深水向浅水转移、油气发现低迷、新增储量大幅下滑阶段(2011—2016年);油气零星发现、新增储量低位波动阶段(2016年至今)。近年来,全球海域钻探逐渐从浅水向深水、超深水以及极地海域转变,在波斯湾、莫桑比克、澳大利亚西北陆缘等传统海域钻探活动依然活跃。天然气发现依然维持在六成以上的较高水平,主要包括东非的鲁伍马盆地、西北非塞内加尔盆地和黑海盆地等,这些盆地是新增的主要富天然气盆地[108]。近10年全球新增储量海域占比64%,海域中深水/超深水的占比77%,年度新增储量海域占比多数超六成,其中2012 、2018 年海域占比均为77%。鲁伍马盆地、圭亚那盆地、桑托斯盆地、塞内加尔盆地、墨西哥湾盆地是深水、超深水储量新的增长点[108]。其中,鲁伍马盆地主要在古近系重力流中获得发现,圭亚那盆地主要在下白垩统生物礁、上白垩统重力流砂岩、中新统重力流砂岩中获得发现,塞内加尔盆地主要在上白垩统重力流砂体中获得发现,埃拉托色尼盆地上白垩统—中新统生物礁和黑海盆地渐新统—中新统重力流是深水新证实的油气成藏组合,这些盆地储量的增长成为持续引领近几年最为重要的储量增长点[108-109]。
2.4.4 海丝路共建国家海洋油气勘探方向
海丝路共建国家海洋油气调查工作应该关注五大领域。①通过开展中巴联合海洋地质联合科学考查,在巴基斯坦海域获得中生界新发现,认为巴基斯坦东部海域派肯坳陷中生界分布广,资源前景好,提出以陆架区中新统河道砂岩和深水区始新统礁灰岩为主要勘探目标层[110]。②孟加拉湾是南亚地区开展油气开发合作的重要区域[111-112]。自20世纪90年代起,在孟加拉湾近海浅水区相继发现了一系列气田,近年来又持续加强了深水油气勘探力度,预计该区天然气剩余可采储量约26亿t。中资企业已在该区获得实质性勘探突破(缅甸深水区AD-1/8区块),可继续加强该区的投资合作力度。③自2006年以来东非海域油气勘探取得多个重大突破,已成为全球油气勘探新的热点。中资企业已进入该区进行实质性合作(鲁武马盆地4区块)。④巴新海域是值得关注的热点合作区域。巴新油气资源丰富,投资财税政策优越,目前该区海洋油气勘探活动主要集中在巴布亚湾,总体勘探程度非常低[112]。中海油目前持有该国4个油气勘探区块。⑤东南亚海域是我国油气勘探潜在的合作海域。东南亚海域油气资源潜力大,中国和东盟国家开展海域油气开发合作呈现良好前景。
3. 面临的挑战
青岛所公益性油气调查主要集中在黄、东海海域。随着深层、深水、深海油气勘探的不断推进,海域油气勘探的难度日益加大,南黄海至今尚未实现商业性油气突破,东海中生界油气勘探难以深入推进等问题进一步凸显。同时,还面临着海域油气勘探理论和技术方法的创新等诸多挑战。新区、新层系、新领域、新类型的公益性油气调查要获得成功并进一步引领商业性油气勘探,急需解决以下重大技术与基础地质问题。
3.1 浅水区及构造复杂区深层地震成像技术攻关
目前南黄海深层海相中—古生界成像效果最好地区主要集中在崂山隆起区,而北部烟台坳陷、南部勿南沙隆起及西部浅水区地震成像总体较差,主要原因在于北部烟台坳陷构造较为复杂,地震波绕射和散射较强,深部地震成像较差;西部浅水区一方面受新近系与下伏地层之间由密度差形成的反射层对深层地震能量穿透的强屏蔽作用,造成深部地震成像效果相对较差,另一方面由于水浅,地震震源容量不足及地震采集电缆长度受限等造成深层较难获取有效地震资料;而南部勿南沙隆起深部地震成像效果差的原因还不明确,有待进一步分析。因此需要在已有以崂山隆起为基础建立起来的“高富强”地震技术基础上,进一步开展技术攻关,获取深层有效地震反射资料,实现对南黄海海相中—古生界整体评价。
3.2 黄、东海前新生代原型盆地恢复
黄、东海海域新生代盆地之下发育大型前新生代沉积盆地,因埋藏深、地震资料品质较差以及盆地经历了多期叠加改造等原因导致前新生代原型盆地恢复较为困难。建议在“高富强”技术基础上加密地震调查和技术攻关,进一步刻画南黄海和东海陆架两大叠合盆地的地质结构,分析华夏、扬子、华北板块之间相互作用背景下的盆地形成演化过程,进而恢复原型盆地,为黄东海海域油气发现指明方向。
3.3 前新生代盆地有效烃源岩、规模储层成因及分布预测
如前所述,南黄海海相中—古生界发育3套区域性烃源岩及碳酸盐岩和碎屑岩两大储集体系,烃源岩总体具有较高有机质丰度和热演化程度,储层发育具有多层系、多类型的特点。但是,目前南黄存在于勘探程度低、钻井揭示少的问题,对下寒武统、上奥陶统—下志留统和二叠系烃源岩发育受哪些主控因素影响及有效性烃源岩分布规律缺乏清晰的认识。在四川盆地所发现的大、中型油气田均具有较好的储集条件,并且也具有相当大的规模[77-79,113]。对南黄海海相中—古生界储层特征还未进行系统的研究,对于规模性储层的发育特点、成因和分布规律缺乏深入研究。对南黄海海相中—古生界有效烃源岩、规模性储层的成因及分布规律认识不清将制约有利勘探靶区的评价和优选,从而影响油气勘探的发现和突破。因此,下一步应充分利用海陆资料,深入开展南黄海海相中—古生界有效烃源岩、规模性储层的成因及分布规律研究。
3.4. 中生代“大东海”原型盆地地质结构分析
前已述及,东海南部与南海北部在中生代时期可能连为一体,称之为“大东海”[49],初步研究认为蕴含着丰富的油气资源。迄今东海南部中生界高品质的地震资料较少,钻遇中生界烃源岩的钻井只有2口,因此,对于中生代“大东海”原型盆地的南北边界、结构特征、地层层序、构造演化及石油地质条件还是缺乏清晰的认识。建议加大“大东海”盆地中生界地震调查,开展“大东海”及其周边陆域中生代地层对比,深入开展油气地质综合研究和油气资源潜力评价,优选有利勘探目标,建立“大东海”盆地中生界油气成藏模式,为实现油气重大突破奠定基础。
4. 未来展望
4.1 海域油气资源调查前景广阔
中国近海油气勘探发现屡创历史新高,中型规模以上油气田的发现占比持续提升。随着渤中19-6、渤中13-2、渤中29-6、乐东10-1、惠州26-6、垦利6-1、涠页-1等多个大中型优质整装油气田的勘探发现[1,8-116],以及东海西湖凹陷新生界油气勘探发现,标志着我国在深水、深层、岩性勘探、潜山、非常规等领域取得了重大突破,也证实了中国海域天然气勘探处于早期阶段,剩余油气资源比较丰富,新区、新层系、新领域资源潜力巨大。南黄海具有与上扬子四川盆地相似海相中—古生界沉积建造,形成了良好的石油地质条件[40-45];东海中生代形成“大东海”沉积盆地,沉积厚层的三叠系至白垩系,具有较好的油气地质条件[49]。因此,我国海域油气资源调查前景广阔。
4.2 南黄海崂山隆起实现海域新区新层系突破的现实地区
前期研究表明,南黄海崂山隆起不仅发育构造稳定的海相下古生界,而且具有形成大型油气田的物质基础[40,117],形成了3点重要认识:①崂山隆起具有强磁性基底, 呈古隆起结构特征,古隆起为大型油气田分布的主要地区;②崂山隆起下油气成藏组合成为油气勘探的重点目标,尤其是有望形成以下寒武统为主要烃源岩、上震旦统灯影组为储层的上生下储规模性油气藏;③南黄海二叠系和三叠系以近源 “自生自储” 和 “下生上储” 型油气藏为主。 综合研究认为, 南黄海海相中—古生界是中国东部海域实现重大突破的首要新层系,油气勘探的突破区域重点在崂山隆起,可望发现威远型、安岳型大气田[75-79]。
4.3 非常规油气是值得重视的领域
非常规油气主要指页岩油、页岩气、致密砂岩油、致密气和煤层气等。近年来,中国在非常规油气勘探方面不断取得发现和突破,如四川、鄂尔多斯、准噶尔、松辽、渤海湾、柴达木等盆地。2020年中国非常规油气年产量接近7 000万t油当量,其中致密油和页岩油超过300万t,页岩气突破200亿m3,致密气超450亿m3,预计2030年非常规油气将占原油总产量的20%,非常规油气将是产量增长的主力[118]。东部海域具备形成非常规油气的地质条件,重点是致密油、致密气和页岩气,并获得了一定的油气发现。在北黄海盆地白垩系和侏罗系已获得低产油流,并在上侏罗统页岩岩芯中发现原油;在南黄海二叠系、泥盆系和志留系致密砂岩中见油气显示和气测异常,砂岩中富含油气包裹体,并且在白垩系泰州组页岩中发现原油。东部海域不同盆地不同地层非常规油气勘探类型有所差异。在北黄海盆地非常规油气勘探主要是白垩系和侏罗系致密油勘探,其次兼顾上侏罗统的页岩油。在南黄海盆地主要是古生界致密气勘探,同时在下古生界高家边组和下寒武统幕府山组烃源岩中有望获得与中上扬子相似的页岩气勘探重大发现和突破;中生界砂岩储层致密油和白垩系与古近系阜宁组页岩油勘探也将是进一步勘探的方向,目前在与南黄盆地具有相同沉积演化历史的苏北盆地阜宁组获得了页岩油勘探重大突破,实现了页岩油的经济开采。在东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷仍将是持续推进古近系始新统致密气勘探,同时兼顾致密油;闽江凹陷以中生界的致密油和致密气勘探为主;东部基隆凹陷存在与西湖凹陷古近系类似的致密油气勘探前景,同时深层的中生界发育,其致密油气也将是下一步勘探方向。
4.4 深水深层是发展方向
近年来,中国逐步取得渤中26-6亿吨级深层油田、宝岛21-1深水深层气田等规模油气发现[101,114-115]。开平南亿吨级油田的发现,进一步揭示了我国深水深层领域巨大的勘探潜力。中国海域潜在深水深层新生界和中生界、古生界残余盆地的富烃凹陷是未来油气勘探和增储重点,具备加大勘探开发力度的资源基础。深水深层新生界和中生界以南海为代表,深层新生界以东海西湖为代表,深层古生界以南黄海为代表。深水深层油气资源丰富,油气藏类型多样,是寻找大中型油气田、实现油气可持续发展的重要领域。与浅层及中浅层传统勘探领域相比,中国深水深层油气勘探程度总体较低,是未来油气增储增产的重要接替领域。
4.5 拓展海丝路海域联合科学考查
持续开展东南亚、环印度洋等海丝路共建国家联合科学考查工作,以与巴基斯坦联合地质科学考查为典范,推动与东南亚、环印度洋等海丝路共建国家合作,重点是推动北印度洋地区、东非海域、巴新海域和东南亚重点海洋新区新层系的联合地质科学考查,提高地质认识,同时探索南美洲周边海域的联合科学考查,以期获得新的认识和重大发现,促进地区发展。
青岛所重建45年来,在油气资源调查工作中一直践行基础性、公益性和战略性定位,取得了重要调查数据和研究成果。二轮油气选区中,提出了南黄海中—古生界和东海中生界为今后油气勘探目标区的创新性认识,得到了石油公司的认可并应用于勘探实践。通过海域地震资料采集、处理、解释一体化综合分析,提出了能较好识别南黄海深层反射结构的“高富强”深部探测技术。在印度洋海域开展联合科学考查,开启了海丝路共建国家海洋油气与天然气水合物的勘探合作,油气调查从近海延伸到深海,从蔚蓝走向了深蓝,从国内走向国外,探索出了一条公益性联合科考的创新性模式。
机遇与挑战并存。青岛所将以服务国家能源战略和实现海洋强国为己任,持续开展油气调查与研究工作,力争早日实现南黄海中—古生界和东海中生界油气突破,成为引领商业性油气勘探的排头兵,同时深化与海丝路共建国家海洋联合科学考查合作。
-
图 1 南黄海海相中—古生界地震层序及地质属性标定图
据参考文献[39]修改。S1—S7为海相中—古生界地震层序,T2相当于新近系底界,B1—B3为三套典型地震反射标志层组.
Figure 1. Paleozoic-Mesozoic seismic sequence and geological attributes correlation in the South Yellow Sea
Modified from reference [39]. S1 to S7 are the seismic sequences of marine Paleozoic-Mesozoic. T2 is the bottom boundary of Neogene. The B1 to B3 are the three typical seismic marker layers.
图 5 东海盆地南部中生代构造单元[87]
Figure 5. Mesozoic tectonic units in the southern part of the East China Sea Basin
图 6 东海盆地南部地震解释剖面[87]
Figure 6. Seismic interpretation profile of the southern part of the East China Sea Basin
-
[1] 杨有星, 高永进, 周新桂, 等. 新疆地区公益性油气调查进展与主要成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2023, 10(3):1-15 YANG Youxing, GAO Yongjin, ZHOU Xingui, et al. Progress and main achievements of public welfare oil and gas survey in Xinjiang[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2023, 10(3):1-15.]
[2] 姜亭, 周俊林, 牛亚卓, 等. 西北公益性油气地质调查进展和展望[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3):64-80 JIANG Ting, ZHOU Junlin, NIU Yazhuo, et al. Progress and prospect of public petroleum geological survey in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3):64-80.]
[3] 王海明. 全球海洋油气勘探开发特征及前景[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2022(12):212-213,167 WANG Haiming. Characteristics and prospects of global offshore oil and gas exploration and development[J]. Chemical Engineering & Equipment, 2022(12):212-213,167.]
[4] 陈建文, 梁杰, 张银国, 等. 中国海域油气资源潜力分析与黄东海海域油气资源调查进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(6):1-29 CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Regional evaluation of oil and gas resources in offshore China and exploration of marine Paleo-Mesozoic oil and gas in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(6):1-29.]
[5] 蔡乾忠. 论鲁东地体的形成机制及其归属[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1989, 9(1):5-15 CAI Qianzhong. Formation mechanism of Ludong (eastern Shandong province) terrane and its actual subordinativeness[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1989, 9(1):5-15.]
[6] 蔡乾忠. 中国东部与朝鲜大地构造单元对应划分[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(1):7-24 CAI Qianzhong. Corresponding division of geotectonic units of eastern China and Korea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(1):7-24.]
[7] 陈国威. 中国海域含油气盆地的基本特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1986, 6(4):31-36 CHEN Guowei. Main characteristics of hydrocarbon-bearing basins in China seas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1986, 6(4):31-36.]
[8] 彭世福. 中国近海早第三纪海侵层序及地层对比[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1992, 12(1):41-56 PENG Shifu. Tertiary transgressive sequences and stratigraphic correlation in China offshore area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1992, 12(1):41-56.]
[9] 彭世福. 浅析中国近海第三纪海侵及其与油气关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1986, 6(4):67-78 PENG Shifu. Preliminary study on relation between tertiary transgression and hydrocarbon in China offshore[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1986, 6(4):67-78.]
[10] 郭振轩. 中国近海新生代沉积盆地生油层发育特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1986, 6(4):79-85 GUO Zhenxuan. Characteristics of source beds for the major Cenozoic sedimentary basin in China offshore[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1986, 6(4):79-85.]
[11] 蔡乾忠. 中国海域及邻区主要含油气盆地与成藏地质条件[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1998, 18(4):1-10 CAI Qianzhong. Primary hydrocarbon bearing basins and the pool forming conditions in China seas and adjacent regions[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1998, 18(4):1-10.]
[12] 戴春山. 中国海域含油气盆地群和早期评价技术[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2011 DAI Chunshan. Oil Gas Basin Group of China Seas and Early Resource Assessment Techniques[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2011.]
[13] 戴春山, 刘伊克, 陈建文, 等. 海上油气资源区域快速综合评价技术[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(4):79-82 DAI Chunshan, LIU Yike, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Fast comprehensive assessment techniques for offshore hydrocarbon resources[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(4):79-82.]
[14] Dai C S, Lin F, Chen J W, et al. Techniques for Quick, Comprehensive Assessment of Offshore Petroleum Resources, in Offshore Geology of China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2003: 173-178.
[15] 陈建文. 南黄海北部油气资源评价研究[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2004 CHEN Jianwen. Petroleum and gas evaluation of northern South Yellow Sea basin[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2004.]
[16] 彭世福, 郭振轩. 中国海域油气勘探开发形势图说明书[R]. 青岛: 地质矿产部海洋地质研究所, 1984 PENG Shifu, GUO Zhenxuan. Specification of situation map of oil and gas exploration and development in the China sea[R]. Qingdao: Institute of Marine geology, Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, 1984.]
[17] 郭振轩. 新生代盆地图[M]//刘光鼎. 中国海区及邻域地质地球物理图集. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993: 74-75 GUO Zhenxuan. Cenozoic basin maps[M]//LIU Guangding. Geological and Geophysical Maps in China Sea and around Area. Beijing: Science Press, 1993: 74-75.]
[18] 肖国林. 应用GIS建立中国海域油气资源地理信息系统的思路[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1999(4):1-3,5 XIAO Guolin. The thinking of geographic information system of oil and gas resources with GIS in China seas[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 1999(4):1-3,5.]
[19] 肖国林. 基于GIS技术的中国海域油气资源可视化数据库的设计与实现: 以黄海盆地油气勘查可视化数据库为例[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2002, 18(11):39-42 XIAO Guolin. Design and realization of visualized dataset of China sea area petroleum resources on the basis of GIS technique[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2002, 18(11):39-42.]
[20] 陈建文, 肖国林, 刘守全, 等. 中国海域油气资源勘查战略研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(4):77-82 CHEN Jianwen, XIAO Guolin, LIU Shouquan, et al. Strategy of oil and gas resources explorations in China seas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(4):77-82.]
[21] 蔡乾忠, 刘守全, 莫杰. 寻找海相油气新领域: 从南海北部“残留特提斯”谈起[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(3):157-162 CAI Qianzhong, LIU Shouquan, MO Jie, et al. Search for new domains of marine-origin petroleum: "remained Tethys" in the northern South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2000, 14(3):157-162.]
[22] 蔡乾忠. 特提斯与海相油气: 开拓我国海域油气新领域[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1999(7):1-7 CAI Qianzhong. Tethys and marine oil and gas-opening up a new area of oil and gas in China's sea area[J]. Marine Geological Performance, 1999(7):1-7.]
[23] 蔡乾忠. “残留特提斯”的猜想: 从中国近海域发现海相中生界: 古新统谈起[J]. 中国地质, 1998(4):39-41 CAI Qianzhong. The conjecture of "residual Tethys" begins with the discovery of the Mesozoic Paleocene Series in the waters near China[J]. Geology of China, 1998(4):39-41.]
[24] 简晓玲, 刘金萍, 王改云. 北黄海东部次盆地中新生代原型盆地分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2019, 31(1):22-31 JIAN Xiaoling, LIU Jinping, WANG Gaiyun. Analysis of Meso-Cenozoic prototype basins in the East Sub-basin, northern Yellow Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019, 31(1):22-31.]
[25] 刘金萍, 王改云, 王嘹亮, 等. 北黄海东部次盆地油气成藏主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(6):888-896 LIU Jinping, WANG Gaiyun, WANG Liaoliang, et al. Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern Sub-basin, North Yellow Sea[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(6):888-896.]
[26] 蔡来星, 肖国林, 董贺平, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷中生界烃源岩特征及其指示的油气勘探方向[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(2):583-601 CAI Laixing, XIAO Guolin, DONG Heping, et al. Characteristics of Mesozoic source rocks and exploration direction of oil and gas in the eastern depression, North Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(2):583-601.]
[27] 肖国林, 蔡来星, 郭兴伟, 等. 北黄海盆地东部坳陷勘探突破对我国近海残留“黑色侏罗系”油气勘探的启示[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2019, 49(1):115-130 XIAO Guolin, CAI Laixing, GUO Xingwei, et al. Exploration enlightenment on residual “black Jurassic” in Chinese offshore from exploration breakthrough in eastern sag of the North Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2019, 49(1):115-130.]
[28] 王改云, 刘金萍, 简晓玲, 等. 北黄海盆地中生界沉积充填及有利生储盖组合[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(1):191-198 WANG Gaiyun, LIU Jinping, JIAN Xiaoling, et al. Sedimentary filling and favorable source-reservoir-seal rock assemblage of Mesozoic in the North Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2016, 52(1):191-198.]
[29] 陈建文, 张异彪, 刘俊, 等. 南黄海“高富强”地震勘查技术及其应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(10):9-17 CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yibiao, LIU Jun, et al. The “HRS” seismic exploration technology and its application in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(10):9-17.]
[30] 张敏强, 漆滨汶, 高顺莉, 等. 南黄海中古生界勘探进展及油气潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(3):7-15 ZHANG Minqiang, QI Binwen, GAO Shunli, et al. New exploration progress and hydrocarbon potential of the Meso-Paleozoic systems in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(3):7-15.]
[31] 陈建文. 南黄海前第三系油气前景研究项目设计书(2005年)[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2005 CHEN Jianwen. Project design document of oil and gas prospects of Pre-Tertiary in South Yellow Sea (2005)[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2005.]
[32] 陈建文, 吴志强, 李慧君, 等. 南黄海前第三系油气前景研究2006年工作总结[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2007 CHEN Jianwen, WU Zhiqiang, LI Huijun, et al. 2006 work summary of oil and gas prospects of Pre-tertiary in South Yellow Sea[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2007.]
[33] 雷宝华, 陈建文, 梁杰, 等. 印支运动以来南黄海盆地的构造变形与演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):45-54 LEI Baohua, CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, et al. Tectonic deformation and evolution of the South Yellow Sea basin since Indosinian movement[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3):45-54.]
[34] 陈建文, 吴志强, 李慧君, 等. 南黄海前第三系油气前景研究2007年工作总结[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2008 CHEN Jianwen, WU Zhiqiang, LI Huijun, et al. 2007 work summary of oil and gas prospects of Pre-tertiary in South Yellow Sea[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2008.]
[35] 陈春峰, 施剑, 徐东浩, 等. 南黄海崂山隆起形成演化及对油气成藏的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):55-65 CHEN Chunfeng, SHI Jian, XU Donghao, et al. Formation and tectonic evolution of Laoshan uplift of South Yellow Sea basin and its effect on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3):55-65.]
[36] 张海啟, 陈建文, 李刚, 等. 地震调查在南黄海崂山隆起的发现及其石油地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(3):107-113 ZHANG Haiqi, CHEN Jianwen, LI Gang, et al. Discovery from seismic survey in Laoshan uplift of the south Yellow Sea and the significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(3):107-113.]
[37] 陈建文, 梁杰, 施剑, 等. 南黄海海相中-古生界地震探测技术突破技术瓶颈[J]. 中国地质调查成果快讯, 2016, 3(4):18-21 CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, SHI Jian, et al. Breakthrough of the seismic exploration technology of the marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Results Express of China Geological Survey, 2016, 3(4):18-21.]
[38] 陈建文, 施剑, 张异彪, 等. 地震调查技术突破南黄海海相中—古生界成像技术瓶颈[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(6):847-858 CHEN Jianwen, SHI Jian, ZHANG Yibiao, et al. The application of “HRS” seismic exploration technology to making breakthrough of the seismic imaging “Bottleneck” of the marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(6):847-858.]
[39] 陈建文, 雷宝华, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海盆地油气资源调查新进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3):1-23 CHEN Jianwen, LEI Baohua, LIANG Jie, et al. New progress of petroleum resources survey in South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(3):1-23.]
[40] 陈建文. 南黄海海相中生界—古生界具有形成大型油气田的物质基础[J]. 中国地质调查成果快讯, 2016, 2(12):6-10 CHEN Jianwen. Material base of great resources in marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Results Express of China Geological Survey, 2016, 2(12):6-10.]
[41] 陈建文, 龚建明, 李刚, 等. 南黄海盆地海相中—古生界油气资源潜力巨大[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):1-7 CHEN Jianwen, GONG Jianming, LI Gang, et al. Great resources potential of the marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1):1-7.]
[42] 陈建文, 何玉华, 肖国林, 等. 南黄海海域油气资源普查成果报告[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2017 CHEN Jianwen, HE Yuhua, XIAO Guolin, et al. Oil and gas resource general survey of the South Yellow Sea[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2017.]
[43] 陈建文. 南黄海崂山隆起海相中—古生界发现多个大型圈闭构造[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(4):69-70 CHEN Jianwen. Many large trap structures develop in the marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(4):69-70.]
[44] 陈建文, 何玉华, 肖国林, 等. 南黄海海域油气资源调查成果报告[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2017 CHEN Jianwen, HE Yuhua, XIAO Guolin, et al. Oil and gas resource survey of the South Yellow Sea[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2017.]
[45] 陈建文, 何玉华, 肖国林, 等. 南黄海海域油气资源调查成果报告[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2019 CHEN Jianwen, HE Yuhua, XIAO Guolin, et al. Oil and gas resource survey of the South Yellow Sea[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2019.]
[46] 陈建文, 张银国, 欧光习, 等. 南黄海古生界油气多期成藏的包体证据[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(2):69-70 CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, OU Guangxi, et al. The inclusion evidences of multi-accumulation of Paleozoic in South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(2):69-70.]
[47] 陈建文, 张银国, 欧光习. 南黄海崂山隆起志留系古油藏的深部烃源证据[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(1):74-76 CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, OU Guangxi. Evidence of deep hydrocarbon sources from the Silurian Paleo-reservoir in the Laoshan uplift of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(1):74-76.]
[48] Zhang Y G, Chen J W, Liang J, et al. Evidence of the existence of paleo reservoirs in Laoshan Uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. China Geology, 2018, 1(4):566-567. doi: 10.31035/cg2018067
[49] 李刚, 龚建明, 杨长清, 等. “大东海”中生代地层分布: 值得关注的新领域[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):97-104 LI Gang, GONG Jianming, YANG Changqing, et al. Stratigraphic features of the Mesozoic “great East China Sea”: a new exploration field[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3):97-104.]
[50] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 孙晶, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代演化与动力学转换过程[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2019, 49(1):139-153 YANG Changqing, YANG Chuansheng, SUN Jing, et al. Mesozoic evolution and dynamics transition in southern Shelf Basin of the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2019, 49(1):139-153.]
[51] 金春爽, 乔德武, 须雪豪, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部油气资源前景与选区[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(5):1601-1609 JIN Chunshuang, QIAO Dewu, XU Xuehao, et al. Oil and gas potential and target selection in southern East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(5):1601-1609.]
[52] 龚建明, 李刚, 杨传胜, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生界分布特征与油气勘探前景[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2013, 43(1):20-27 GONG Jianming, LI Gang, YANG Chuansheng, et al. Hydrocarbon prospecting of Mesozoic Strata in southern East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2013, 43(1):20-27.]
[53] 杨长清, 李刚, 龚建明, 等. 中国东南海域中生界油气地质条件与勘探前景[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2015, 45(1):1-12 YANG Changqing, LI Gang, GONG Jianming, et al. Petroleum geological conditions and exploration prospect of the Mesozoic in southeast China sea area[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(1):1-12.]
[54] 杨长清, 韩宝富, 杨艳秋, 等. 东海陆架盆地中生界油气调查进展与面临的挑战[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(4):1-8 YANG Changqing, HAN Baofu, YANG Yanqiu, et al. Oil and gas exploration in the Mesozoic of East China Sea Shelf Basin: progress and challenges[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(4):1-8.]
[55] 杨传胜, 杨长清, 李刚, 等. 东海陆架盆地中—新生界油气勘探研究进展与前景分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2):136-147 YANG Chuansheng, YANG Changqing, LI Gang, et al. Prospecting of Meso-Cenozoic hydrocarbon in the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(2):136-147.]
[56] 江凯禧, 姚长华, 郭清正, 等. 印度扇深水区古—始新统烃源岩特征及发育模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(4):785-793 JIANG Kaixi, YAO Changhua, GUO Qingzheng, et al. Characteristics and depositional model of Paleocene and Eocene Source Rocks in Deepwater Area of Indus Fan[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(4):785-793.]
[57] Gong J M, Liao J, Liang J, et al. Exploration prospects of oil and gas in the northwestern part of the Offshore Indus Basin, Pakistan[J]. China Geology, 2020, 3(4):633-642. doi: 10.31035/cg2020051
[58] 龚建明, 廖晶, Khalid M, 等. 巴基斯坦海域油气勘探方向探讨[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(11):1-6 GONG Jianming, LIAO Jing, Khalid M, et al. Preliminary study on the oil and gas exploration targets in offshore pakistan[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(11):1-6.]
[59] Chen J W, Xu M, Lei B H, et al. Prospective prediction and exploration situation of marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic oil and gas in the South Yellow Sea[J]. China Geology, 2019, 2(1):67-84. doi: 10.31035/cg2018072
[60] 李双林, 董贺平, 赵青芳, 等. 海洋油气地球化学勘查技术及其应用实践[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2022 LI Shuanglin, DONG Heping, ZHAO Qingfang, et al. Offshore Oil and Gas Geochemical Exploration Technology and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2022.]
[61] 李双林, 赵青芳, 王建强, 等. 南黄海盆地崂山隆起中南部海底沉积物饱和烃类地球化学特征于热成因烃类输入[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(5):669-679 LI Shuanglin, ZHAO Qingfang, WANG Jianqiang, et al. Geochemistry of saturated hydrocarbons and thermogenic hydrocarbon input in seabed sediments from the south central Laoshan Uplift in South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(5):669-679.]
[62] 李双林, 赵青芳, 董贺平, 等. 南黄海盆地崂山隆起CSDP-2井中—古生界海相地层吸附烃类气体成因类型与源区特征[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2-3):209-218 LI Shuanglin, ZHAO Qingfang, DONG Heping, et al. Genetic types and source characteristics of hydrocarbon gases adsorbed by Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine strata in well CSDP- 2, Laoshan uplift, South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(2-3):209-218.]
[63] Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X, et al. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China: constraints from SHRIMP U–Pb zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd–Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 174(1-2):117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.07.004
[64] 周新民, 邹海波, 杨杰东, 等. 安徽歙县伏川蛇绿岩套的Sm-Nd等时线年龄及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 1989(16):1243-1245 ZHOU Xinmin, ZOU Haibo, YANG Jiedong, et al. Sm-Nd isochron age and its geological significance of the Fuchuan ophiolite suite in Shexian County, Anhui Province[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1989(16):1243-1245.]
[65] 王存智, 黄志忠, 邢光福, 等. 赣东北蛇绿岩地幔橄榄岩岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4):1178-1188 WANG Cunzhi, HUANG Zhizhong, XING Guangfu, et al. The origin of the mantle peridotite from ophiolitite in northeast Jiangxi and its geological implications[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(4):1178-1188.]
[66] 邢光福, 姜杨, 陈志洪, 等. 钦杭结合带首次发现加里东期榴闪岩[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2013, 34(4):208 XING Guangfu, JIANG Yang, CHEN Zhihong, et al. Caledonian eclogite amphibolite was discovered for the first time in the Qinhang joint belt[J]. Resources Survey & Environment, 2013, 34(4):208.]
[67] Zhao G C, Wang Y J, Huang B C, et al. Geological reconstructions of the East Asian blocks: from the breakup of Rodinia to the assembly of Pangea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186:262-286. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.10.003
[68] 张银国, 梁杰. 南黄海盆地二叠系至三叠系沉积体系特征及其沉积演化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2014, 44(5):1406-1418 ZHANG Yinguo, LIANG Jie. Sedimentary system characteristics and their sedimentary evolution from the Permian to Triassic in the southern Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(5):1406-1418.]
[69] 郭兴伟, 朱晓青, 牟林, 等. 南黄海中部隆起二叠纪-三叠纪菊石的发现及其意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):121-128 GUO Xingwei, ZHU Xiaoqing, MU Lin, et al. Discovery of Permian-Triassic ammonites in the central uplift of the South Yellow Sea and its geological implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3):121-128.]
[70] 蔡来星, 王蛟, 郭兴伟, 等. 南黄海中部隆起中-古生界沉积相及烃源岩特征: 以CSDP-2井为例[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2017, 47(4):1030-1046 CAI Laixing, WANG Jiao, GUO Xingwei, et al. Characteristics of sedimentary facies and source rocks of Mesozoic-Paleozoic in central uplift of south Yellow Sea: a case study of CSDP-2 coring well[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2017, 47(4):1030-1046.]
[71] 肖国林, 蔡来星, 郭兴伟, 等. 南黄海中部隆起CSDP-2井中—古生界烃源岩精细评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(12):24-36 XIAO Guolin, CAI Laixing, GUO Xingwei, et al. Detailed assessment of Meso-Paleozoic hydrocarbon source rocks: implications from well Csdp-2 on the central uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(12):24-36.]
[72] 张银国, 陈清华, 陈建文, 等. 下扬子海相中—古生界烃源岩发育的控制因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):8-12 ZHANG Yinguo, CHEN Qinghua, CHEN Jianwen, et al. Controlling factors on the Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine source rocks in the Lower Yangtze platform[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(1):8-12.]
[73] 贾东, 胡文瑄, 姚素平, 等. 江苏省下志留统黑色页岩浅井钻探及其页岩气潜力分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2016, 22(1):127-137 JIA Dong, HU Wenxuan, YAO Suping, et al. Shallow borehole drilling of the lower Silurian black shale in Jiangsu Province and the Shale Gas potential analysis[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2016, 22(1):127-137.]
[74] 袁勇, 陈建文, 梁杰, 等. 海陆对比看南黄海海相中—古生界的生储盖组合特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2):195-202,212 YUAN Yong, CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, et al. Source-reservoir-seal assemblage of marine Mesozoic-Paleozoic in South Yellow Sea Basin by land-ocean comparison[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2):195-202,212.]
[75] 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3):278-293 ZOU Caineng, DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3):278-293.]
[76] 罗志立, 韩建辉, 罗超, 等. 四川盆地工业性油气层的发现、成藏特征及远景[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2013, 34(5):504-514,495 LUO Zhili, HAN Jianhui, LUO Chao, et al. The discovery, characteristics and prospects of commercial oil and gas layers/reservoirs in Sichuan Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2013, 34(5):504-514,495.]
[77] 马新华, 杨雨, 文龙, 等. 四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩大中型气田分布规律及勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1):1-13 doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)30001-1 MA Xinhua, YANG Yu, WEN Long, et al. Distribution and exploration direction of medium- and large-sized Marine carbonate gas fields in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1):1-13.] doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)30001-1
[78] 刘辉, 韩嵩, 叶茂, 等. 四川盆地大中型气田分布特征及勘探前景[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2018, 41(2):55-62 LIU Hui, HAN Song, YE Mao, et al. Medium to large gas fields in Sichuan Basin: distribution characteristics and exploration prospects[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2018, 41(2):55-62.]
[79] 韩克猷, 孙玮. 四川盆地海相大气田和气田群成藏条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(1):10-18 doi: 10.11743/ogg20140102 HAN Keyou, SUN Wei. Conditions for the formation of large Marine gas fields and gas field clusters in Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(1):10-18.] doi: 10.11743/ogg20140102
[80] 杨长清, 杨艳秋, 孙晶, 等. 东海陆架盆地西部和东南部油气资源调查[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2019 YANG Changqing, YANG Yanqiu, SUN Jing, et al. Oil and gas resources survey in the west and southeast of East China Sea Shelf basin[R]. Qingdao: Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2019.]
[81] 龚建明, 徐立明, 杨艳秋, 等. 从海陆对比探讨东海南部中生代油气勘探前景[J]. 世界地质, 2014, 33(1):171-177,189 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2014.01.018 GONG Jianming, XU Liming, YANG Yanqiu, et al. Discussion on Mesozoic hydrocarbon potential of sourthern East China Sea based on comparision between offshore and onshore areas[J]. Global Geology, 2014, 33(1):171-177,189.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2014.01.018
[82] 陈建文, 杨长清, 张莉, 等. 中国海域前新生代地层分布及其油气勘查方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1):1-25 CHEN Jianwen, YANG Changqing, ZHANG Li, et al. Distribution of Pre-Cenozoic strata and petroleum prospecting directions in China Seas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1):1-25.]
[83] 刘建华, 黎明碧, 方银霞. 东海陆架盆地海相中生界及其与邻近古海洋关系探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(2):1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.001 LIU Jianhua, LI Mingbi, FANG Yinxia. Mesozoic strata in East China Sea Shelf Basin and their relationship with adjacent Palaeo-seas[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(2):1-7.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.02.001
[84] 唐建. 东海及邻近地区中生代沉积地层展布研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2007 TANG Jian. Study on the Mesozoic sedimentary strata distribution of East China and adjacent areas[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2007.]
[85] Shu L S, Zhou X M, Deng P, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Southeast China block: new insights from basin analysis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3):376-391. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.06.004
[86] 杨艳秋, 李刚, 戴春山. 东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带中生界分布特征及其有利区探讨[J]. 世界地质, 2011, 30(3):396-403 YANG Yanqiu, LI Gang, DAI Chunshan. Characteristics of Mesozoic distribution and discussion on its favourable area in western depression zone of East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Global Geology, 2011, 30(3):396-403.]
[87] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 杨艳秋, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部深部地层格架与油气资源潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(5):158-171 YANG Changqing, YANG Chuansheng, YANG Yanqiu, et al. Deep stratigraphic framework and hydrocarbon resource potential in the Southern East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(5):158-171.]
[88] 杨长清, 孙晶, 杨传胜, 等. 东海盆地南部中生界油气成藏模式[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(8):89-92 YANG Changqing, SUN Jing, YANG Chuansheng, et al. The Mesozoic hydrocarbon accumulation model in the southern East China Sea basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(8):89-92.]
[89] Calvès G, Schwab A M, Huuse M, et al. Thermal regime of the northwest Indian rifted margin – comparison with predictions[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(5):1133-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.02.010
[90] Calvès G, Schwab A M, Huuse M, et al. Seismic volcanostratigraphy of the western Indian rifted margin: the pre-Deccan igneous province[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2011, 116(B1):B01101.
[91] Carmichael S M, Akhter S, Bennett J K, et al. Geology and hydrocarbon potential of the offshore Indus Basin, Pakistan[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2009, 15(2):107-116. doi: 10.1144/1354-079309-826
[92] 刘金萍, 王改云, 简晓玲, 等. 巴基斯坦印度扇近海盆地油气地质条件分析[J]. 地质学刊, 2022, 46(4):351-357 LIU Jinping, WANG Gaiyun, JIAN Xiaoling, et al. Analysis of petroleum geological condition in offshore Indus Basin, Pakistan[J]. Journal of Geology, 2022, 46(4):351-357.]
[93] 陈旭, 刘彩芹, 王红梅, 等. 印度河盆地T区块构造特征与油气成藏[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2017, 52(6):1305-1314 CHEN Xu, LIU Caiqin, WANG Hongmei, et al. Tectonic characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Block T, Indus River Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2017, 52(6):1305-1314.]
[94] 廖晶, 龚建明, 陈建文, 等. 印度扇近海盆地重力滑动构造新发现[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(6):76-79 LIAO Jing, GONG Jianming, CHEN Jianwen, et al. New discovery of gravity slip structure in India Fan offshore basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(6):76-79.]
[95] Rodriguez M, Chamot-Rooke N, Huchon P, et al. The Owen Ridge uplift in the Arabian Sea: implications for the sedimentary record of Indian monsoon in Late Miocene[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 394:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.03.011
[96] Shahzad K, Betzler C, Qayyum F. Controls on the Paleogene carbonate platform growth under greenhouse climate conditions (Offshore Indus Basin)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101:519-539. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.025
[97] 郑民, 李建忠, 吴晓智, 等. 我国主要含油气盆地油气资源潜力及未来重点勘探领域[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3):833-847 ZHENG Min, LI Jianzhong, WU Xiaozhi, et al. Potential of oil and gas resources of main Hydrocarbon-Bearing basins and key exploration fields in China[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3):833-847.]
[98] 吴晓智, 柳庄小雪, 王建, 等. 我国油气资源潜力、分布及重点勘探领域[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(6):146-155 WU Xiaozhi, LIU Zhuangxiaoxue, WANG Jian, et al. Petroleum resource potential, distribution and key exploration fields in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(6):146-155.]
[99] 何家雄, 姚永坚, 于俊峰, 等. 中国近海盆地油气地质特征及勘探开发进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(11):1-17 HE Jiaxiong, YAO Yongjian, YU Junfeng, et al. Petroleum geological characteristics and progress of exploration and development in offshore basins of China[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(11):1-17.]
[100] 谢玉洪. 中国海洋石油总公司油气勘探新进展及展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(1):26-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.01.003 XIE Yuhong. New progress and prospect of oil and gas exploration of China national offshore oil corporation[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(1):26-35.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.01.003
[101] 徐长贵, 赖维成, 张新涛, 等. 中国海油油气勘探新进展与未来勘探思考[J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(2):1-12 XU Changgui, LAI Weicheng, ZHANG Xintao, et al. New progress and future exploration thinking of CNOOC oil and gas exploration[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(2):1-12.]
[102] 谢玉洪, 高阳东. 中国海油近期国内勘探进展与勘探方向[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1):20-30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.003 XIE Yuhong, GAO Yangdong. Recent domestic exploration progress and direction of CNOOC[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1):20-30.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.003
[103] 谢玉洪. 中国海油“十三五”油气勘探重大成果与“十四五”前景展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(1):43-54 XIE Yuhong. Major achievements in oil and gas exploration of CNOOC in the 13th Five-Year Plan period and prospects in the 14th Five-Year Plan period[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(1):43-54.]
[104] 米立军, 周守为, 谢玉洪, 等. 南海北部深水区油气勘探进展与未来展望[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(3):58-65 doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.007 MI Lijun, ZHOU Shouwei, XIE Yuhong, et al. Deep-Water oil and gas exploration in northern South China Sea: progress and outlook[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24(3):58-65.] doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.007
[105] 杨海风, 牛成民, 柳永军, 等. 渤海垦利6-1新近系大型岩性油藏勘探发现与关键技术[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(3):24-32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.003 YANG Haifeng, NIU Chengmin, LIU Yongjun, et al. Discovery and key exploration technology of KL6-1 large lithologic oil reservoir of Neogene in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(3):24-32.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.003
[106] 王昕, 周心怀, 徐国胜, 等. 渤海海域蓬莱9-1花岗岩潜山大型油气田储层发育特征与主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(2):262-270 doi: 10.11743/ogg20150211 WANG Xin, ZHOU Xinhuai, XU Guosheng, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of reservoirs in Penglai 9-1 large-scale oilfield in buried granite hills, Bohai Sea[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(2):262-270.] doi: 10.11743/ogg20150211
[107] IHS Markit. IHS energy: EDIN[EB/OL]. (2023-01-01)[2023-04-31].
[108] 王兆明, 温志新, 贺正军, 等. 全球近10年油气勘探新进展特点与启示[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(2):27-37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2022.02.003 WANG Zhaoming, WEN Zhixin, HE Zhengjun, et al. Characteristics and enlightenment of new progress in global oil and gas exploration in recent ten years[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(2):27-37.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2022.02.003
[109] 张功成, 屈红军, 张凤廉, 等. 全球深水油气重大新发现及启示[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(1):1-34,55 doi: 10.7623/syxb201901001 ZHANG Gongcheng, QU Hongjun, ZHANG Fenglian, et al. Major new discoveries of oil and gas in global deepwaters and enlightenment[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(1):1-34,55.] doi: 10.7623/syxb201901001
[110] 叶德燎. 东南亚石油资源与勘探潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2005, 10(1):55-60,64 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2005.01.008 YE Deliao. Petroleum resources and exploration potential in Southeast Asia[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2005, 10(1):55-60,64.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2005.01.008
[111] 王建强, 赵青芳, 梁杰, 等. 海上丝绸之路沿线深水油气资源勘探方向[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2):219-232 WANG Jianqiang, ZHAO Qingfang, LIANG Jie, et al. Exploration guide of deepwater oil and gas resources along the Maritime Silk Road[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(2):219-232.]
[112] 张义娜, 蔡文杰, 杨松岭, 等. 巴布亚盆地侏罗系陆架边缘三角洲沉积特征及其油气勘探方向[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(1):167-176 ZHANG Yina, CAI Wenjie, YANG Songling, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the Jurassic shelf-edge delta and oil and gas exploration in the Papuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(1):167-176.]
[113] 康玉柱. 中国古生代海相大油气田形成条件及勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2007, 28(3):263-265 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2007.03.001 KANG Yuzhu. Conditions and explorative directions of marine giant oil-gas fields of Paleozoic in China[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2007, 28(3):263-265.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2007.03.001
[114] 徐长贵, 周家雄, 杨海风, 等. 渤海海域油气勘探新领域、新类型及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(1):163-182 doi: 10.7623/syxb202401010 XU Changgui, ZHOU Jiaxiong, YANG Haifeng, et al. New fields, new types and resource potentials of oil-gas exploration in Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(1):163-182.] doi: 10.7623/syxb202401010
[115] 李威, 李友川. 渤海海域渤中19-6构造带油气纵向连续分布形成机理研究[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(1):74-83 doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.01.009 LI Wei, LI Youchuan. Study on formation mechanism of oil and gas longitudinal continuous distribution of BZ19-6 structural belt, Bohai Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(1):74-83.] doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.01.009
[116] 薛永安. 认识创新推动渤海海域油气勘探取得新突破: 渤海海域近年主要勘探进展回顾[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(2):1-8 XUE Yongan. New breakthroughs in hydrocarbon exploration in the Bohai Sea area driven by understanding innovation: a review of major exploration progresses of Bohai Sea are in recent year[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(2):1-8.]
[117] 陈建文, 龚建明, 张银国, 等. 扬子陆域地质考察及其对南黄海油气勘探的启示[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2023: 143-170 CHEN Jianwen, GONG Jianming, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Geological Survey of Yangtze Land Area and Its Inspiration to Oil and Gas Exploration in South Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2023: 143-170.]
[118] 邹才能, 邱振. 中国非常规油气沉积学新进展: “非常规油气沉积学”专辑前言[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(1):1-9 ZOU Caineng, QIU Zhen. Preface: new advances in unconventional petroleum sedimentology in China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(1):1-9.]
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杨艳秋,李森,梁杰,孙晶. 南黄海盆地南部海相构造层研究新进展. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(02): 12-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 袁勇,陈建文,骆迪,李清,梁杰,蓝天宇,王建强,曹珂,赵化淋. 南黄海盆地烟台坳陷新生界二氧化碳封存地质条件与封存前景. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(03): 35-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: