IMPACT OF SEAFLOOR TOPOGRAPHY ON DISTRIBUTION OF CLAY MINERALS IN THE EAST PHILIPPINES SEA
-
摘要: 对东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆南部的125个表层沉积物样品的黏土矿物组成、含量及其矿物学特征进行了分析。研究结果表明,研究区黏土矿物组成以蒙脱石为主,平均含量为49%;其次是伊利石,平均含量为35%;绿泥石平均含量为11%;高岭石含量最少,平均含量为5%。通过将研究区黏土矿物组合特征与潜在物源区进行对比,并结合主要黏土矿物的结晶学特征,认为蒙脱石主要来源于帕里西维拉海盆周边的海山或海脊物质的风化和蚀变,其分布可能主要受控于底层洋流;伊利石和绿泥石主要来自于亚洲大陆,风力吹扬为其主要输运方式。黏土矿物表层分布显示伊利石主要富集于地势较低处,蒙脱石在靠近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊等地势较高处呈现高值。由于较少受到周边海山或海脊物质稀释和底层洋流侵蚀作用的影响,东菲律宾海深水区沉积物中风尘组分通量最能代表亚洲大陆风尘对研究区的实际贡献量,这一研究将对从东菲律宾海沉积物中提取亚洲大陆风尘物质输入信号进而追溯亚洲大陆的古气候演化历史具有重要意义。Abstract: We analyzed the clay mineral assemblages, contents and mineralogical characteristics for the 125 surface sediments recovered from the Parece Vela Basin. It is found that the clay minerals are mainly composed of smectite (average 49%), illite (average 35%) and chlorite (average 11%) with minor kaolinite(average 5%).Comparing the clay mineral assemblages and their crystallographic characters with the potential provenances, we suggest that smectite is mainly from the volcanic arc materials around the Parece Vela Basin and its distribution pattern may be mainly controlled by deep currents. Illite and chlorite are mainly derived from the Asian eolian deposits transported by wind. The spatial distribution of clay minerals indicates that illite dominates the lower terrain, while smectite is concentrated in the higher places near the Palau ridge and the Yap ridge. With the minimal effects of the volcanic material dilution and the influence of deep current erosion, the eolian flux in the deep East Philippine Sea can represent the actual contribution of Asian wind dust to the study area. It will be of great significance to extract the wind dust from the East Philippine Sea sediments for the further study of the paleoclimate evolution in the Asian continent.
-
Keywords:
- clay mineralsl /
- provenance /
- seafloor topography /
- East Philippines Sea /
- Parece Vela basin
-
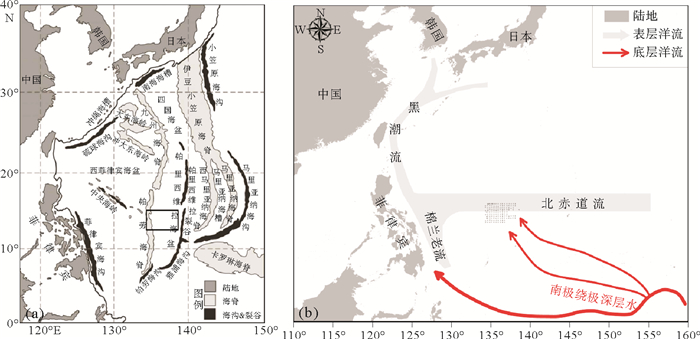
菲律宾海为西太平洋的一个边缘海。其地理位置特殊,北靠日本岛和琉球群岛,西临菲律宾群岛,东部和南部被卡罗琳洋脊及马里亚纳岛弧体系等所包围,海底地形地貌复杂多样,总体水深较大(平均超过6 000 m)。海盆内分布有众多岛弧、海沟及海盆等地质单元,主要有:南北向展布的岛弧和海脊(如九州-帕劳海脊、伊豆小笠原海脊等)、海沟和海槽(主要位于菲律宾海边缘,如菲律宾海沟、马里亚纳海沟、琉球海沟、南海海槽等)以及大面积分布的海盆(如西菲律宾海盆、四国海盆、帕里西维拉海盆等)(图 1)。迄今为止,对该海区海陆相互作用、沉积物源汇过程和古气候学的研究主要集中在西菲律宾海盆[1-7]。而位于西太平洋东部的四国海盆和帕里西维拉海盆的相关研究则相对薄弱[8-14],近年来在该海区发现的成席硅藻对探讨热带碳循环的驱动机制和硅藻席沉积的形成机制具有重要的意义[15, 16]。
黏土矿物和地球化学研究结果表明东菲律宾海表层沉积物基本上符合二端元混合模型特征,即其主要来自于当地火山物质的风化蚀变,而陆源风尘物质(中国黄土)也具有一定贡献[8-10, 12-14, 17-19],并且陆源风尘物质对研究区表层沉积物的贡献程度随远离亚洲大陆距离的增加呈现降低的趋势[8, 13, 14]。显然,东菲律宾海相较于宽广平坦的西菲律宾海要更加狭窄,海底地形和水深变化较大,海底地形的变化及其引起的底层洋流的变化可能会对沉积物的分布产生重要的影响[20],进而反映在影响沉积物的矿物和化学组成上,最为典型的实例即为跨越巴士海峡的太平洋深层水(巴士海峡深水“瀑布”)经吕宋海槽和马尼拉海沟汇入南海,对南海海盆的沉积过程及深海碳循环产生了重要的影响[21]。考虑到风力吹扬和洋流搬运是东菲律宾海沉积物输运的主要动力,其输运模式相对简单且不同输运模式均能携带不同组成的沉积物到研究区,这为利用研究区沉积物的组成来探讨不同物源区沉积物的贡献程度提供了有效的契机,然而先前的研究多集中于探讨陆源风尘物质对研究区的贡献情况,殊不知海底地形的变化也可能会对研究区沉积物的分布产生重要的影响,然而却少有研究予以涉及。本文拟通过对海底地形变化较大的东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆南部表层沉积物中黏土矿物的分布特征进行研究,结合前人的研究成果,细化研究东菲律宾海沉积物的物质来源及其输运机制,进而揭示控制东菲律宾海表层沉积物分布的关键因素,以便为加深理解边缘海盆沉积物的物质来源、输运过程及其对气候变化的响应等提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
本文所使用样品是由中国科学院海洋研究所“科学号”海洋调查船于2014—2015年期间在东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆南部取得,研究区表层沉积物粒度组成主要以粉砂和黏土为主(>96%)。本次研究主要对125个表层沉积物样品进行X射线衍射(XRD)分析(图 2)。
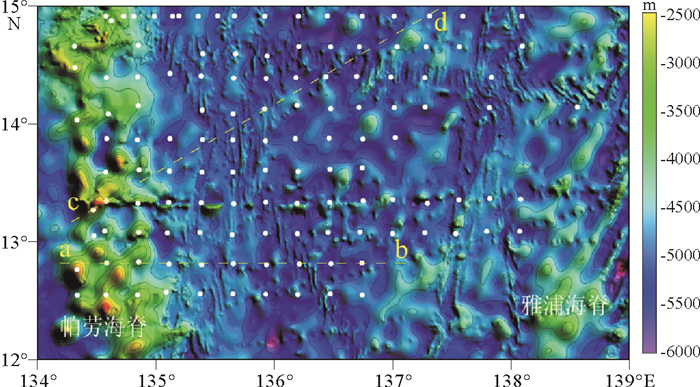
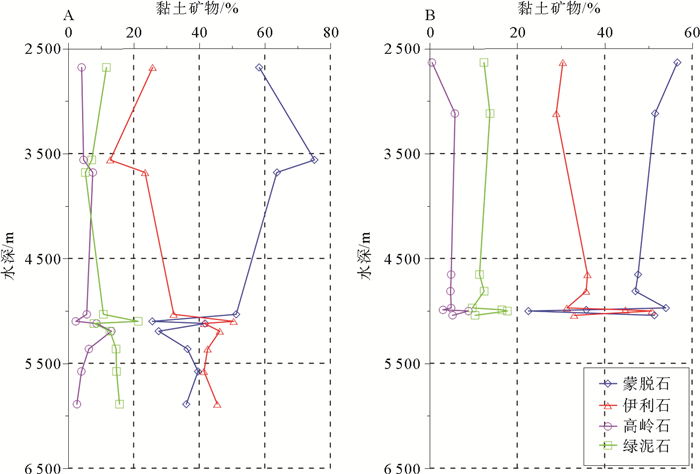
![]() 图 2 研究区站位分布图(ab和cd横断面在图中以虚线显示)Figure 2. Distribution of surface sediment stations in the study area (positions of transects ab and cd for clay mineral distribution (Fig. 6) are indicated by dotted lines)
图 2 研究区站位分布图(ab和cd横断面在图中以虚线显示)Figure 2. Distribution of surface sediment stations in the study area (positions of transects ab and cd for clay mineral distribution (Fig. 6) are indicated by dotted lines)取沉积物原样1~2 cm3,先后用15% H2O2和25% HAC反应去除有机质和碳酸盐,加去离子水离心清洗两次,使样品的抗絮凝作用发生。按Stoke原理制成定向薄片,自然风干。XRD分析采用德国产D8 Advance衍射仪:CuKα辐射,管压40 kV,管流40 mA,分别对自然条件、乙二醇蒸气饱和、加热条件(490 ℃,2 h)的样品薄片进行测试,扫描角度3°~30°2θ,步长0.02°。黏土矿物的鉴定和解释主要依据3种测试条件下获得的XRD叠加图谱的综合对比,部分样品中含有极少量的伊利石/蒙脱石混层矿物,由于峰型太弱很难准确定量,实际计算中将其归到17Å蒙脱石。波峰参数的半定量计算使用Topas2p软件在乙二醇曲线上进行,黏土矿物的相对含量主要使用(001)晶面衍射峰的面积比。4种黏土矿物蒙脱石(含少量伊利石/蒙脱石混层矿物)、伊利石、高岭石和绿泥石的相对含量计算按Biscaye[25]的方法,17Å衍射峰面积×1为蒙脱石的权重强度;10Å衍射峰面积×4为伊利石的权重强度;7Å衍射峰面积×2为高岭石和绿泥石合计的权重强度,两者的含量比例从绿泥石的(004)(3.54Å)和高岭石的(002)(3.58Å)的衍射峰面积求出,四者强度最后校正为含量100%。同时,利用乙二醇曲线计算伊利石的化学指数,即5Å/10Å峰面积比,比值小于0.5为富Fe-Mg伊利石,代表未风化的云母和伊利石;比值大于0.5为富A1伊利石,代表高度风化的伊利石。伊利石化学指数相对大小可以指示其风化程度,从而可以用来指示物源和气候变化[26]。黏土矿物晶格的有序度和晶体颗粒的大小通常用“结晶度”来衡量。伊利石的结晶度以10Å的半峰宽(FWHM)来表示,低值代表结晶度高,指示陆地物源区水解作用弱,为干冷的气候条件[27],这个参数也可用于示踪物源和搬运路径[28]。蒙皂石的结晶度用乙二醇曲线上17Å衍射峰的半峰宽(FWHM)予以表示,值越小,指示结晶度越好。
2. 结果
2.1 黏土矿物的XRD分析
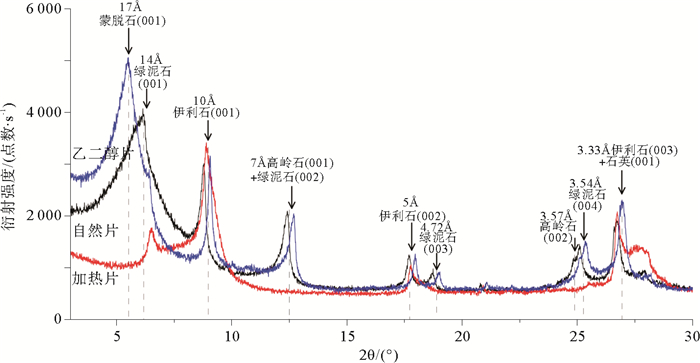
通过XRD测试分析,得到表层沉积物样品D7黏土矿物的自然片、乙二醇饱和片和加热片的典型X-射线图谱(图 3)。根据3种不同衍射图谱识别出蒙脱石、伊利石、绿泥石和高岭石4种黏土矿物。伊利石在10Å和5Å处分别为001和002衍射峰,在图 3自然片中,10Å和5Å处衍射峰显示明显,乙二醇饱和后衍射峰位置和强度基本上没有变化,证明了伊利石的存在。蒙脱石001衍射峰一般位于12~15Å之间,而绿泥石的001衍射峰在14Å附近,在自然定向片中,可以看到14Å附近的衍射峰为双峰,说明该双峰为两种黏土矿物的叠加峰,经乙二醇饱和后叠加峰分异为17Å和14Å两个特征峰,表明蒙脱石经乙二醇饱和后特征峰移至17Å的特征,由此证实了蒙脱石的存在。蒙脱石经490 ℃加热会脱水变为伊利石,其001衍射峰消失。高岭石和绿泥石在自然片衍射图谱的7Å和3.5Å附近都存在衍射峰,3.5Å附近的特征峰为两峰叠加的双峰,说明这两种矿物同时存在。高岭石和绿泥石都不具有膨胀性,在经乙二醇试剂饱和后,衍射峰的位置和强度基本没有发生改变,经高温加热后,自然片中的高岭石矿物晶格被破坏,变为非晶质,因而衍射峰消失,绿泥石的衍射峰变弱甚至消失。由衍射图谱可以看出,与二、四级基面衍射相比,大多数样品中绿泥石的一、三级基面衍射较弱,由此说明绿泥石较富铁[29]。
2.2 黏土矿物含量的分布特征
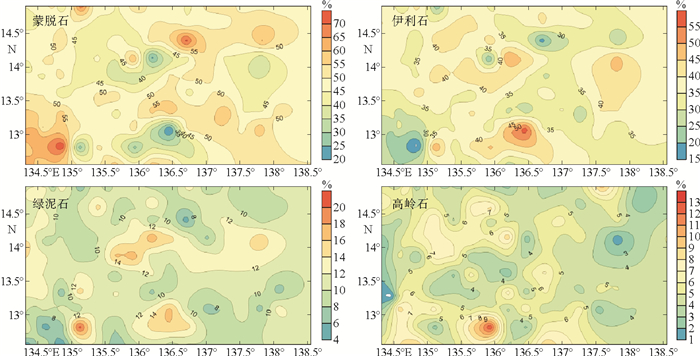
研究海区沉积物黏土矿物主要由蒙脱石、伊利石、绿泥石和高岭石4种黏土矿物组成。其中,蒙脱石(平均含量49%)和伊利石(平均含量35%)构成沉积物黏土矿物的主要成分,绿泥石(平均含量11%)和高岭石(平均含量5%)为次要成分。
研究海区蒙脱石含量平均值最高,其变化范围为18%~75%,含量值集中分布在40%~62%之间,蒙脱石总体分布规律是在靠近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊处呈现高值,蒙脱石含量大于50%,中部地势较低处则呈现低值。伊利石含量的平均值稍低于蒙脱石,且其总体分布趋势与蒙脱石正好相反,平均值为35%,变化范围较大为13%~58%,含量值集中分布在26%~44%之间,高值区主要分布在中部地势较低处,近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊处则呈现低值。绿泥石分布规律与伊利石大体相似,其平均值为11%,含量变化范围为4%~21%,含量值集中分布在7%~15%之间。高岭石分布规律则不明显,大致呈斑块状分布,其平均值为5%,含量变化范围为1%~13%(图 4)。
根据黏土矿物含量半定量计算结果,本区蒙脱石含量总体高于伊利石含量,但个别站位出现相反现象。表层黏土矿物的总体分布趋势是在地形较低处,即水深处,伊利石含量高而蒙脱石含量较低,在靠近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊处,蒙脱石含量呈现明显高值。绿泥石和伊利石具有相同的分布规律,高岭石含量最低且分布规律不明显。
3. 讨论
3.1 黏土矿物的物源分析
海洋沉积中黏土矿物的古气候解释要求了解每种矿物的潜在物源区及其输运方式[30]。前人利用黏土矿物和元素地球化学等示踪方法对研究区北部邻近海区沉积物的来源进行了研究[8-10, 12-14],研究结果表明,伊利石主要来源于研究区以西的陆地及周边岛屿,且风力的吹扬是研究区伊利石物质来源的主要输送方式;蒙脱石则主要来自于周边海山或海脊物质的蚀变,且洋流搬运对蒙脱石的分布具有一定影响。鉴于前人已在周边海区获得了较好的结果,因此本文仅进一步探讨两种主要黏土矿物组分即伊利石和蒙脱石的主要来源,其相应代表了两种黏土矿物在研究区的输运模式,即风力吹扬和洋流搬运。
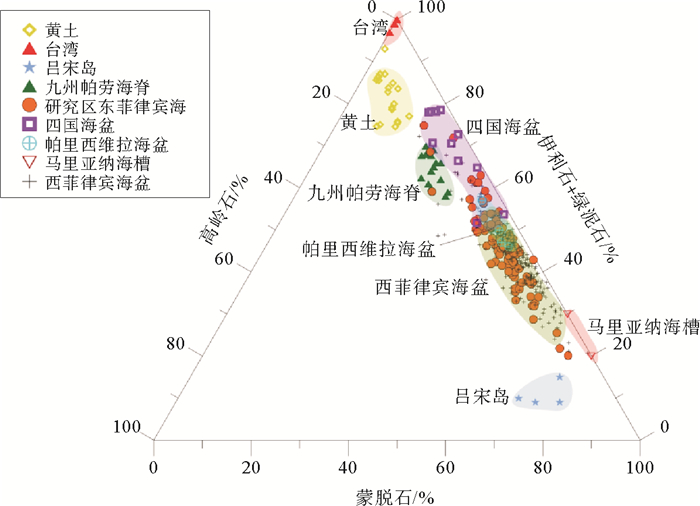
黏土矿物组成的三角图解显示东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆南部的黏土矿物来源与东菲律宾海其他区域类似(图 5),基本上符合亚洲大陆物质与周边海山或海脊物质的二端元混合模型特征。研究区蒙脱石含量平均为49%,最高达到75%,远高于以陆源物质输入为主的长江、黄河、黄海及东海的蒙脱石含量[31-33],且台湾河流中几乎不含蒙脱石,因此,研究区北部的长江、黄河、黄海、东海和台湾不可能是研究海区蒙脱石的主要来源。研究区西部的吕宋岛河流沉积物中含有大量的蒙脱石(>60%)[34],但是考虑到吕宋岛来源的蒙脱石结晶度为1.13°~2.55°Δ2θ,平均为1.66°Δ2θ[2, 35],总体上要高于研究区蒙脱石的结晶度1.40°Δ2θ,同时吕宋岛河流入海沉积物由于受到了自东向西的北赤道流的阻隔(图 1),很难大量的输送到研究海区,因此,我们认为吕宋岛河流输入不是东菲律宾海沉积物中蒙脱石的主要贡献者。同样由于受到黑潮扩散流和琉球岛弧的阻挡,来自北部、西北部日本岛来源的蒙脱石也很难进入研究区大量的沉降下来[36]。帕里西维拉海盆被九州-帕劳海脊、卡罗琳海脊和马里亚纳海脊所包围,并且黏土矿物三角图显示研究区黏土矿物组成主要位于九州-帕劳海脊和马里亚纳海槽之间(图 5),表现为亚洲大陆和海山或海脊蚀变物质的混合。且从蒙脱石的表层分布图中也可看出(图 4),在靠近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊处,蒙脱石含量均呈现出高值。因此,我们认为研究区蒙脱石主要来自于周边的海山或海脊物质的风化和蚀变,帕里西维拉海盆周围区域在渐新世之前的火山活动中形成了大量的玄武岩和安山岩[37],这些火山岩经化学风化和蚀变作用可以形成大量的蒙脱石,同时由于受到海底地形和底层洋流的影响(如南极绕极深层水,图 1b),这些海山或海脊蚀变物质进入研究区后将会再次重新分布。
研究区伊利石结晶度平均为0.26°Δ2θ,最高达0.43°Δ2θ,与中国内陆黄土和古土壤的伊利石结晶度(0.22°~0.42°Δ2θ[38])相似,且伊利石化学指数较低(平均为0.27),这说明伊利石主要是在干冷气候条件下由物理风化作用所形成,表明伊利石来源与中国黄土强烈关联。吕宋岛河流沉积物含少量或几乎不含有伊利石[34],因此,研究区高含量的伊利石(平均含量为35%)不可能由包括吕宋岛在内的菲律宾群岛所提供。值得注意的是,尽管台湾河流沉积物中含有高含量的伊利石(>65%)[39],但是考虑到台湾河流沉积物中的伊利石结晶度值一般都较低(<0.23°Δ2θ)[30, 40],研究海区伊利石结晶度要普遍高于台湾海区,且台湾河流伊利石的化学指数平均值为0.49[39],远高于研究区的0.27,因此,尽管台湾每年向海输运大量富含伊利石的沉积物[41],但是它却不是研究海区伊利石的主要贡献者。同时由于受到黑潮以及深水海槽和琉球岛弧的阻隔,东海、黄海以及日本南部的沉积物也很难大量向菲律宾海扩散[36]。稀土元素的二端元混合模型揭示陆源风尘物质对东菲律宾海表层沉积物的贡献量最高达到了72%[14];最近锶钕同位素定量研究结果也表明,研究区西北的亚洲大陆向西菲律宾海沉积物贡献了10%~50%的风尘物质[4, 6],这些都表明研究区的伊利石完全可以由充足物源的风尘携带而来。综上所述,我们认为研究海区沉积物中的伊利石主要来自于亚洲大陆,风力吹扬为其主要的输运方式。
3.2 海底地形特征对黏土矿物分布的影响
相较于西菲律宾海盆,研究区东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆南部海底地形变化较大,水深变化范围为2 600~6 000 m(图 2)。靳宁等[8]对研究区北部表层沉积物进行了黏土矿物分析,研究结果表明代表风尘物质主要成分的伊利石含量具有随远离亚洲大陆而逐渐降低的趋势。徐兆凯等[14]根据稀土元素二端元混合模型也得出了类似的结论,并且定量计算了所研究沉积物中陆源风尘物质和当地火山物质的贡献。明洁等[13]对帕里西维拉海盆的两个重力柱状样进行了黏土矿物研究,研究结果同样显示北部岩心的伊利石平均含量高于南部岩心。以上研究结果均证明了亚洲风尘对帕里西维拉海盆的重要贡献,但是同时我们必须考虑到风尘物质入海后又受到了表层和底层洋流的影响,将会在海底重新分布沉降下来,进而在利用黏土矿物分布趋势和定量计算贡献量来讨论沉积物的物质来源时,势必要将由海底地形变化引起的洋流变化考虑在内。
从图 4和图 6可以看出,与靳宁等[8]的研究结果不同,研究区表层沉积物伊利石和蒙脱石的分布并不具有自西北向东南方向逐渐降低或增加的趋势,反而与水深分布具有密切的关系,伊利石主要富集在深水区,蒙脱石含量在靠近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊等地势较高处呈现高值,可见海底地形的变化对黏土矿物的分布具有重要的影响。陆源风尘抵达研究区后,地势较高处由于受到海山或海脊蚀变物质的稀释和底层洋流的侵蚀作用,代表风尘组分的伊利石将会在海底进一步重新分布,相反地势低洼处由于周边较高地形的阻挡和富含高密度的水体,因此受到周边海山或海脊物质稀释和底流侵蚀的影响较弱,使得亚洲大陆的风尘物质能较好地保存下来。徐兆凯等[14]利用稀土元素二端元混合模型计算得出研究区北部陆源风尘贡献量为11%~72%,并且从其分布图中可以看出,研究海区纬度相差1°左右时,计算得出的陆源风尘贡献量差别高达30%,显然风力吹扬不足以造成小范围内如此大的变化,进一步证实了海底地形和底层洋流分布对研究区表层沉积物的物质组成具有重要作用。根据全球沉积物厚度分布图[42]并结合科学号考察船取样发现,研究区东西两侧海脊的沉积物(厚度 < 50 m)相对深海盆(50~250 m)明显薄,有些地方甚至基岩裸露,显示海底地形和底流对沉积物分布的影响。因此,从我们的研究结果可以看出,如果不考虑沉积物在海水中的沉降时间,研究区东菲律宾海深水区沉积物中风尘组分通量是最能代表亚洲大陆风尘实际贡献量,即受后期洋流改变较小,这一研究结果将对从东菲律宾海沉积物中提取亚洲大陆风尘物质输入信号进而追溯亚洲大陆的古气候演化历史具有重要的意义。
4. 结论
(1) 东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆南部表层沉积物黏土矿物组合以蒙脱石为主,平均含量为49%,伊利石含量次之,平均为35%,绿泥石平均含量为11%,含少量高岭石,平均含量为5%。
(2) 研究区蒙脱石主要来自于帕里西维拉海盆周边的海山或海脊物质的风化和蚀变,其分布可能主要受控于底层洋流,伊利石和绿泥石主要来自于亚洲大陆,风力吹扬为其主要的输运方式。
(3) 研究区伊利石含量在地势较低处呈现低值,蒙脱石含量在靠近帕劳海脊和雅浦海脊等地势较高处呈现高值。由于较少受到周边海山或海脊物质稀释和底流侵蚀的影响,东菲律宾海深水区沉积物中风尘组分通量最能代表亚洲大陆风尘对研究区的实际贡献量。
致谢: 本项研究使用样品由中国科学院海洋研究所2014—2015年西太地质调查航次中获得,感谢“科学号”考察船全体队员和船员为调查付出的艰辛,感谢中国科学院海洋研究所赵德博博士和张晋博士在实验及数据分析过程中给予的帮助,感谢中国科学院科技创新交叉与合作团队“海山成因、演化及深部物质循环”的支持。 -
图 2 研究区站位分布图(ab和cd横断面在图中以虚线显示)
Figure 2. Distribution of surface sediment stations in the study area (positions of transects ab and cd for clay mineral distribution (Fig. 6) are indicated by dotted lines)
图 5 研究区与潜在物源区蒙皂石-伊利石+绿泥石-高岭石三角图解
(台湾[35, 39, 43],西菲律宾海盆[35],黄土[3, 43-47],吕宋岛[34],九州-帕劳海脊[5],帕里西维拉海盆[8, 13],四国海盆[22],马里亚纳海槽[48])
Figure 5. Ternary diagram of the major clay mineral smectite-illite+chlorite-smectite in the study area and the potential provenances
(Taiwan[35, 39, 43]; West Philippine Basin[35]; Loess[3, 43-47]; Luzon Island[34]; Kyushu-Palau ridge[5]; Parece Vela Basin[8, 13]; Shikoku Basin[22]; Mariana Trough[48])
-
[1] 石学法, 陈丽蓉, 李坤业, 等.西菲律宾海西部海域黏土沉积物的成因矿物学研究[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(2): 61-71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ502.007.htm SHI Xuefa, CHEN Lirong, LI Kunye, et al. Study on mineralogy of the clay sediment in the west of Philippine Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology. 1995, 15(2): 61-71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ502.007.htm
[2] 池野, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.吕宋岛东部海域黏土矿物组合特征及物源分析[J].海洋科学, 2009, 33: 80-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200909016 CHI Ye, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. Assemblage and provenance of clay minerals of the east of Luzon Island[J]. Marine Science, 2009, 33: 80-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200909016
[3] Wan S M, Yu Z J, Clift P D, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 326: 152-159. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8574156
[4] Jiang F Q, Frank M, Li T G, et al. Asian dust input in the western Philippine Sea: Evidence from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(5): 1538-1551. doi: 10.1002/ggge.20116
[5] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(19): 11, 492-11, 504. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022025
[6] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Quantitative estimates of Asian dust input to the western Philippine Sea in the mid-late Quaternary and its potential significance for paleoenvironment[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005929
[7] Yu Z J, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Co-evolution of monsoonal precipitation in East Asia and the tropical Pacific ENSO system since 2.36 Ma: New insights from high-resolution clay mineral records in the West Philippine Sea[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 446: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.04.022
[8] 靳宁, 李安春, 刘海志, 等.帕里西维拉海盆西北部表层沉积物中黏土矿物的分布特征及物源分析[J].海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(6): 504-511. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004 JIN Ning, LI Anchun, LIU Haizhi, et al. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the northwest Parece Vela basin: distribution and provenance[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38: 504-511. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004
[9] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.东菲律宾海深水铁锰结壳发育站位沉积物的粒度及黏土矿物学特征[J].海洋学报, 2007, 29(2): 150-155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2007.02.019 XU Zhaokai, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. Grain-size and clay mineral characteristics of sediments under deep water ferromanganese crusts in the eastern Philippine Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2007, 29(2): 150-155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2007.02.019
[10] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.东菲律宾海沉积物的地球化学特征与物质来源[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(6): 695-702. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.06.013 XU Zhaokai, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. The geochemical characteristics and material sources in the eastern Philippine Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(6): 695-702. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.06.013
[11] 孟庆勇, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等.近2 Ma来东菲律宾海地球磁场相对强度变化的沉积记录[J].海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(4): 606-613. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201004021 MENG Qingyong, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. A geomagnetic paleointensity record over the last 2Ma from the east Philippine Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(4): 606-613. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201004021
[12] 熊志方, 李铁刚, 翟滨, 等.低纬度西太平洋末次冰期Ethmodiscus rex硅藻席黏土矿物特征及形成机制启示[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010 (4): 551-562. XIONG Zhifang, LI Tiegang, ZHAI Bin, et al. Clay Mineral Characteristics of Ethmodiscus rex Diatom Mats from Low-Latitude Western Pacific during the Last Glacial and Implications for Their Formation[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010 (4): 551-562.
[13] 明洁, 李安春, 孟庆勇, 等.东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆第四纪黏土矿物组合特征及物源分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4): 139-148. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201204017 MING Jie, LI Anchun, MENG Qingyong, et al. Quaternary assemblage characteristic and provenance of clay minerals in the Parecevela Basin of the east Philippine Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 139-148. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201204017
[14] 徐兆凯, 李铁刚, 李安春.东菲律宾海表层沉积物来源的稀土证据[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(2): 1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201302001 XU Zhaokai, LI Tiegang, LI Anchun. Provenance of surficial sediments of the east Philippine Sea: evidence from rare earth elements[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(2): 1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201302001
[15] Xiong Z F, Li T G, Crosta X, et al. Potential role of giant marine diatoms in sequestration of atmospheric CO2 during the Last Glacial Maximum: δ13C evidence from laminated Ethmodiscus rex mats in tropical West Pacific[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2013, 108: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.06.003
[16] Xiong Z F, Li T G, Algeo T, et al. The silicon isotope composition of Ethmodiscus rex laminated diatom mats from the tropical West Pacific: Implications for silicate cycling during the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Paleoceanography, 2015, 30(7): 803-823. doi: 10.1002/2015PA002793
[17] Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Kamioka H, et al. Asian continental nature of 87Sr/86Sr ratios in north central Pacific sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 133(1): 105-116.
[18] 秦蕴珊, 陈丽蓉, 石学法.西菲律宾海风成沉积物的研究[J].科学通报, 1995, 40(17): 1595-1597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.17.017 QIN Yunshan, CHEN Lirong, SHI Xuefa. Research on the eolian sediment in the West Philippine Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(17): 1595-1597. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.17.017
[19] Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Kamioka H, et al. Provenance of the north Pacific sediments and process of source material transport as derived from Rb-Sr isotopic systematic[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 158(3): 271-291. doi: 10.1007%2Fs11430-007-0052-6
[20] Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A, Van Loon A J. Contourite research: a field in full development[M]. In: Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A. (Eds.), Contourites. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2008:3-10.
[21] 田纪伟, 曲堂栋.南海深海环流研究进展[J].科学通报, 2012, 57(20): 1827-1832. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201220002 TIAN Jiwei, QU Tangdong. Advances in research on the deep South China Sea circulation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(20): 1827-1832. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201220002
[22] Nagel U, Muller G, Schumann D. Mineralogy of sediments cored during Deep Sea Project Leg 58-60 in the North and South Philippine Sea: results of x-ray diffraction analyses[C]// In: Hussong D M, Uyeda S, Blanchet R, et al. eds. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project. 1981, 60: 415-435.
[23] Qiu B. Kuroshio and Oyashio currents[M]. Academic Press, New York, 2001: 1413-1425. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279614392_Kuroshio_And_Oyashio_Currents
[24] Kawabe M, Fujio S. Pacific Ocean circulation based on observation[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2010, 66(3): 389-403. doi: 10.1007/s10872-010-0034-8
[25] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803-832. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2
[26] Ehrmann W. Implications of late Eocene to early Miocene clay mineral assemblages in McMurdo Sound (Ross Sea, Antarctica) on paleoclimate and ice dynamics[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1998, 139(3): 213-231. doi: 10.1016-S0031-0182(97)00138-7/
[27] Chamley H. Clay Sedimentology[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag. 1989. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=56492df065aa48837f1c7d74b393bc53&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[28] Petschick R, Kuhn G, Gingele F. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the South Atlantic: sources, transport, and relation to oceanography[J]. Marine Geology, 1996, 130(3): 203-229. doi: 10.1016-0025-3227(95)00148-4/
[29] 杨雅秀, 张乃娴, 苏昭冰, 等.中国黏土矿物[M].北京:地质出版社, 1994: 143-150. YANG Yaxiu, ZHANG Naixian, SU Zhaobing, et al. Clay Minerals in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 1994: 143-150.
[30] Liu Z, Colin C, Li X, et al. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the northeastern South China Sea and surrounding fluvial drainage basins: Source and transport[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 277(1): 48-60. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=51e3ac19a036ceb401b4c0030fb95262&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[31] Wan S, Li A, Clift P D, et al. Development of the East Asian monsoon: mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 254(3): 561-582. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=69b0d1afbfe10b3f9b0ca393b5a6a5cb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[32] Yang S, Jung H S, Lim D I, et al. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2003, 63(1): 93-120. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9692c64055ede8f886a2a97ba93984b3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[33] Lu J, Li A, Huang P, et al. Mineral distributions in surface sediments of the western South Yellow Sea: implications for sediment provenance and transportation[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015, 33(2):510-524. doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4106-x
[34] Liu Z, Zhao Y, Colin C, et al. Chemical weathering in Luzon, Philippines from clay mineralogy and major-element geochemistry of river sediments[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(11): 2195-2205. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.09.025
[35] 于兆杰.近百万年以来西菲律宾海风尘沉积研究[D].中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2013. YU Zhaojie. Research on Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology), 2013.
[36] 刘华华, 蒋富清, 周烨, 等.晚更新世以来奄美三角盆地黏土矿物的来源及其对古气候的指示[J].地球科学进展, 2016, 31(3): 286-297. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201603007 LIU Huahua, JIANG Fuqing, ZHOU Ye, et al. Provenance of clay minerals in the Amami Sankaku Basin and their paleoclimate implications since late Pleistocene[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2016, 31(3): 286-297. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201603007
[37] Honza E, Fujioka K. Formation of arcs and backarc basins inferred from the tectonic evolution of Southeast Asia since the Late Cretaceous[J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 384(1): 23-53. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c3488168eb8f7fc8f8ab68f379f6695f
[38] Ji J, Chen J, Lu H. Origin of illite in the loess from the Luochuan area, Loess Plateau, Central China[J]. Clay Minerals, 1999, 34(4): 525-525. doi: 10.1180/000985599546398
[39] Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Clay mineral composition and their sources for the fluvial sediments of Taiwanese rivers[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(6): 673-681. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4824-1
[40] Liu Z, Tuo S, Colin C, et al. Detrital fine-grained sediment contribution from Taiwan to the northern South China Sea and its relation to regional ocean circulation[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 255(3): 149-155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3c70f15b2d54be4783aa8b6db264f74b
[41] Dadson S J, Hovius N, Chen H, et al. Links between erosion, runoff variability and seismicity in the Taiwan orogen[J]. Nature, 2003, 426: 648-651. doi: 10.1038/nature02150
[42] Divins D L, Total Sediment Thickness of the World's Oceans and Marginal Seas[J], NOAA National Geophysical Data Center, Boulder, CO, 2003.
[43] Wan S, Li A, Clift P D, et al. Development of the East Asian monsoon: mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 254(3): 561-582. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=69b0d1afbfe10b3f9b0ca393b5a6a5cb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[44] 师育新, 戴雪荣, 李节通, 等.末次间冰期兰州黄土记录中的黏土矿物及其环境意义探讨[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1997, 17(1): 87-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ701.012.htm SHI Yuxin, DAI Xuerong, LI Jietong. Origin and significance of clay minerals in the Last Interglacial loess in Lanzhou area, North Central China[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1997, 17(1): 87-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ701.012.htm
[45] 师育新, 戴雪荣, 宋之光, 等.我国不同气候带黄土中黏土矿物组合特性分析[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(4): 690-695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.019 SHI Yuxin, DAI Xuerong, SONG Zhiguang, et al. Characteristics of Clay Mineral Assemblages and Their Spatial Distribution of Chinese Loess in Different Clmiatic Zones[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(4): 690-695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.019
[46] 郑洪汉, 顾雄飞, 韩家懋, 等.中国黄土中的黏土矿物及其在地层剖面中的变化趋势——洛川和陇西黄土剖面的初步研究[J].第四纪研究, 1985(1): 158-165. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DSJJ198501019.htm ZHENG Honghan, GU Xiongfei, HAN Jiamao, et al. Clay Minerals in Loess of China and Their Tendency in Loess Section[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1985(1): 158-165. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DSJJ198501019.htm
[47] 唐诵六, 顾新运, 罗家贤.豫北第四纪沉积物的矿物特征[J].土壤学报, 1979, 16(2): 157-163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRXB197902006.htm TANG Songliu, GU Xinyun, LUO Jiaxian. Mineralogical Prooerties of the Quaternary Sedients in Northern Henan[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1979, 16(2): 157-163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRXB197902006.htm
[48] 张德玉.马里亚纳海槽区黏土矿物组成及分布特征[J].黄渤海海洋, 1994, 12(2): 32-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH402.004.htm ZHANG Deyu. Clay Mineral Composition and Distribution in the Mariana Trough[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai and Bohai Seas, 1994, 12(2): 32-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH402.004.htm
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 丁雪,胡邦琦,赵京涛,王飞飞,黄威,李攀峰,刘佳,郭建卫,崔汝勇. 九州-帕劳海脊南段及邻近海域表层沉积物元素地球化学特征及其地质意义. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2023(01): 61-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 邓韬,许冬,肖婷露,叶黎明,章伟艳. 西太平洋海山盆地沉积物黏土矿物特征及其指示意义. 海洋学研究. 2023(03): 56-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 方中华,李攀峰,杨源,杨慧良,陆凯,杨佳佳,单瑞. 菲律宾海深水环境下浅地层沉积特征分析. 海洋学报. 2022(03): 53-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 肖春晖,王永红,林间. 近1 Ma以来帕里西维拉海盆沉积物物源和古气候:粒度和黏土矿物特征的指示. 沉积学报. 2022(02): 508-524 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 肖春晖,王永红,林间,田纪伟. 马里亚纳“沟-盆”深水沉积环境稀土元素特征与物源约束. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2021(01): 102-114 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 丁雪,胡邦琦,徐方建,郭建卫,崔汝勇,易亮. 晚上新世以来菲律宾海盆XT4孔黏土矿物特征及其古环境意义. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2021(01): 42-51 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 胡邦琦,易亮,赵京涛,郭建卫,丁雪,王飞飞,谌微微. 西菲律宾海盆XT06孔第四纪磁性地层与深海沉积动力过程. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2021(01): 61-74 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 王银,吕士辉,苏新,李嘉盈,李怀明,任向文. 西北太平洋多金属结核区沉积物黏土矿物特征. 中国有色金属学报. 2021(10): 2696-2712 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: