Elemental geochemical characteristics of surface sediments from the southern Kyushu-Palau Ridge and their geological significance
-
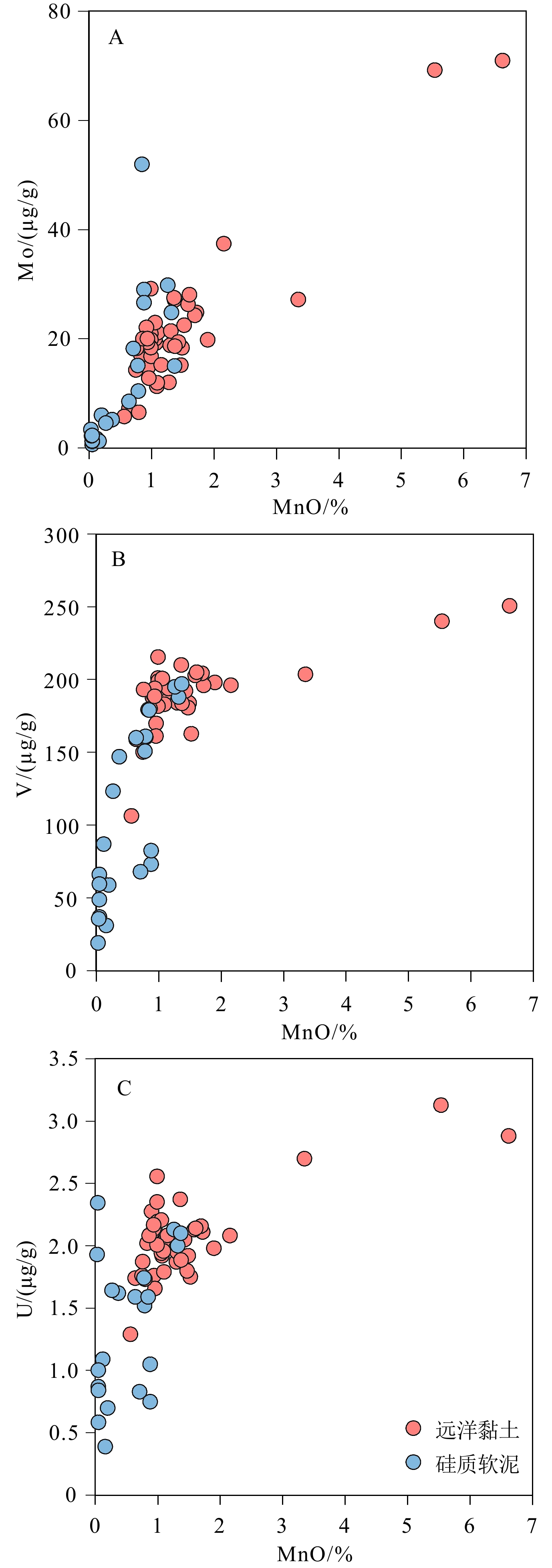
摘要: 菲律宾海地理位置特殊,蕴含着丰富的前沿地球科学问题,是研究地球多圈层相互作用的天然实验室。近年来,菲律宾海中部九州-帕劳海脊南段已成为研究热点,但对其表层沉积物物质来源和沉积环境了解尚存在不足。本文通过对采集于九州-帕劳海脊南段水深为3900~6100 m的69个站位样品开展沉积地球化学研究,旨在判别沉积物的物质来源和沉积环境空间变化特征。结果表明:研究区底质类型为远洋黏土和硅质软泥,不同类型沉积物的碎屑组分化学风化程度均较低,受分选和再循环的影响较小,是亚洲风尘物质和岛弧火山物质的混合产物,且以亚洲风尘物质为主;研究区不同类型站位的沉积环境基本一致,整体处于氧化沉积环境,底层水体氧化还原条件不是研究区沉积物中过渡金属(如Mo)元素富集的控制因素,铁锰(氢)氧化物是连接水体-沉积物中过渡金属元素源-汇过程的重要纽带。此外,底部氧化还原条件可能不是该海域硅藻席沉积保存的必要条件。Abstract: The Philippine Sea, with its special geographical location, is rich in frontier geoscience issues and is a natural laboratory for studying the Earth multi-layer interactions. In recent years, the southern section of the Kyushu-Palau Ridge in the central Philippine Sea has become a hot spot for geoscience research, but its surface sediment provenance and sedimentary environment are not yet well understood. The sediment geochemistry of 69 stations collected from the southern section of the Kyushu-Palau Ridge at water depths of 3900-6100m was studied to identify the spatial variability of sediment provenance and depositional environments. The results show that the sediment types in the study area are pelagic clay and siliceous ooze, and the clastic components of sediment are less chemically weathered, less affected by sorting and recycling, and are mixed products of Asian dust materials and island-arc volcanic materials, of which Asian dust materials are dominated; and the different types of sediment in the study area are basically in an oxidative depositional environment, and the bottom water redox conditions are not a controlling factor for the enrichment of transition metal (e.g., Mo) elements in the sediments, indicating that Fe-Mn (oxyhydr)oxides are an important link between the source-sink processes of transition metal elements at the water-sediment interface. In addition, bottom redox conditions may not be necessary for the preservation of diatom mats.
-
东海某凹陷低孔低渗储层油气资源丰富,但是主要油气层系存在砂泥岩层胶结疏松,砂泥岩层中夹煤层等现象,导致复杂的钻井情况,如何降低滤液对油气层的侵入影响,减少侵入深度,预防与控制水敏和液锁效应的发生是提高低孔低渗储层有效开发的重要手段[1-2],因此,优选了一套油包水钻井体系,井壁稳定性得到了改善,钻井周期明显缩短,储层保护取得显著成绩,但是更换泥浆体系对测井和录井也带来了新的问题,油基泥浆侵入对电阻率、中子、核磁仪器的响应与水基泥浆完全不同,此外气测录井和荧光录井资料受油基泥浆影响大[3-7]。本文通过对比水基泥浆和油基泥浆环境下测井和录井资料解释差异,探索东海地区在油基泥浆背景下的油气快速识别方法。
1. 水基泥浆与储层污染
水基泥浆的主要组成部分为水,除此之外还有少量添加剂(例如黏土剂、降滤失剂和防水锁剂等),水作为泥浆中分散相,主要以化学结构水、吸附水和自由水的形式存在,并且自由水的比重较大,一般占比70%~80%[1],因此,泥浆对地层的液相侵入严重,易造成储层污染。
东海某凹陷NBxx-5-1s井4 211~4 229 m岩心孔隙度分布范围为8%~10.7%,渗透率分布范围为0.18~5.4 mD,属于东海典型低孔低渗储层。储层的孔隙结构喉道细小,泥浆中固相颗粒侵入损害深度和程度有限,泥浆中自由水在正压差或者毛管力作用下侵入储层,驱替近井地带中天然气,侵入带水相饱和度增大,气相渗透率显著降低,水锁效应导致气井低产甚至无产[1-2]。
NBxx-5-1s井测井解释出两套气层,花港组的H6层和平湖组的P2层(图1),录井显示皆为细砂岩,H6和P2层自然伽马分布范围为40~70 API,平均为50 API,孔隙度分布范围为8%~11.2%,平均为9%,H6层电阻率分布范围为34~40 ohmm,P2层电阻率分布范围为40~61 ohmm;RCI测压显示H6层测压9个点,流度分布范围为2.3~3.3 mD/cp,平均为2.74 mD/cp,P2层测压8个点,流度分布范围为2.3~12.7 mD/cp,平均为8.89 mD/cp;经过对比,P2层的渗透性、电性特征,均优于H6层(表1),但是DST测试结果差异较大,P2层测试产气微量;H6层测试产气7.3万方/天。
表 1 NBxx-5-1s井DST2与DST3综合对比表Table 1. Comparison of DST2 and DST3 in NBxx-5-1s特征参数 DST2 DST3 P2 H6 射孔深度段(m) 4 198.0~4 220.0 4 439.4~4 470.2 4 228.1~4 237.0 4 239.8~4 248.1 4 475.3~4 493.8 4 258.1~4 261.8 4 265.2~4 277.0 射开厚度(m) 49.3 54.7 钻井泥浆比重(sg) 1.36 1.36 机械转速(m/h) 6~7.5 8~15 气测全量(%) 10~11.53 5~17.6 电阻率(Ω•m) 40~61 34~40 储层孔隙度(%) 8~11.2 8~11.2 测压流度(mD/cp) 2.3~12.7/平均8.89 2.3~3.3/平均2.74 核磁渗透率(mD)诱喷压差(Mpa) 5~1015.5 1~325.5 液垫 海水 柴油 射孔弹类型 692SD-127P-1 SDP45PYX39-3 射孔穿深(mm) 909 1 447 工作制度 二开二关 二开二关 通过对该井泥浆侵入分析,3 960~4 000 m地层在泥浆中浸泡后,复测电阻率P40H明显低于随钻电阻率P40H,复测电阻率A40H与随钻电阻率A40H无差异(图2),指示地层受到泥浆侵入明显,泥浆侵入深度大于P40H探测深度,小于A40H探测深度(地层电阻率为30 Ωm时,A40H径向探测深度为62 in(约157 cm),P40H径向探测深度为35 in(约88 cm)),推测泥浆侵入深度约1 m。H6层、P2层地层物性与3 960~4 000 m地层物性相近(孔隙度约10%,渗透率约3 mD),在相同泥浆比重背景下,推测泥浆侵入对储层的污染程度相近。
对比H6与P2地层的DST测试工艺(表1),P2层为高温地层(地层温度157 ℃),射孔采用超高温弹,超高温弹径向穿深0.9 m;H6层为常温地层(地层温度148 ℃),射孔采用普通弹药,弹药径向穿深1.5 m。根据上述对比结果,P2层射孔弹穿深有限,并且诱喷压差较小,原状地层天然气无法突破侵入带,在水锁效应下无法形成有效渗流,导致两次测试产能差异明显。
2. 油基泥浆对测井、录井的影响
为了满足东海地区低孔低渗储层保护的需要,优选了一套油包水钻井液体系,该体系的实验室基础配方如下:3#白油+3%主乳化剂+1%辅乳化剂+1%润湿剂+4%有机土+3%降滤失剂+2%碱度调节剂+2%封堵剂+2%疏水胶体封堵剂+0.5%流型调节剂+1.2%高温流变稳定剂+重晶石(油水比为80∶20)。新钻井液体系性能良好,在清洁井眼、泥浆滤失、携岩性等方面效果好,能保证井筒环境的稳定,为录井作业和测井作业提供良好环境,但是,泥浆体系的变化为测井和录井带来新的挑战。
2.1 油基泥浆对测井的影响
油基泥浆对电法测井影响较大,对放射性、声法测井影响小。水基泥浆测井仪器在油基泥浆环境中无法正常使用,目前一批油基泥浆测井仪器投入使用并推广,其中电阻率仪器在油基泥浆环境下的响应特征与水基泥浆不同,当钻遇水层时,电阻率曲线呈现分异特征。
利用泥浆滤失原理和电阻率仪器延时测井方式,观察电阻率分异特征,快速判别油气层和水层。储层流体为油气时,流体成分与油基泥浆类似均为非导电流体,泥浆滤失前后冲洗带泥浆电阻率无差异;储层流体为水时,流体成分与油基泥浆截然不同,泥浆滤失后,地层水的混入导致泥浆的油包水体系被打破,形成导电回路,泥浆滤失后冲洗带电阻率高于滤失前泥浆电阻率[7-10]。
NBxx-5-2井在油基泥浆环境下钻遇气层和水层(图3),4 449~4 474 m井段随钻与复测电阻率P16H重叠,地层流体为气,4 474~4 538 m井段随钻与复测电阻率P16H分异,且复测电阻率P16H高于随钻电阻率P16H,地层流体为水,电阻率梯度变化点为流体界面。4 471.5 m经过电缆泵抽取样(MDT仪器)(图4),泵抽至45 min时,井下流体实验室光谱分析仪得知,地层泵抽出流体为天然气和泥浆滤液,泵抽至160 min,泵抽压增大至4.13 Mpa,地层出现明显段塞流水信号,证实地层出水,与电阻率延时测井判断一致。
2.2 油基泥浆对录井的影响
研究区建立了水基泥浆环境下气测组分快速识别地层流体图版(图5),图版数据来源于研究区测试资料,并且划分3个区,分别为油区、凝析油气区、气区,根据气测组分计算组分中相对含量C1/C2+和C2+/C1+,再结合录井荧光信息,判断储层流体性质。研究区NBxx-5-1s井是水基泥浆,4 198~4 277 m井段录井无荧光显示(图1,表2),通过气测组分快速识别为气层,该井段经过测试,产气7.3万方/天,天然气为干气,甲烷含量91.61%。
表 2 NBxx-5-1s、NBxx-6-2录井荧光显示表Table 2. Logging fluorescence of NBxx-5-1s and NBxx-6-2井名 深度/m 岩性 荧光录井 直照 滴照 顶 底 颜色 面积/% 颜色 反应 NBxx-5-1s 4 198.0 4 238.0 灰白色/浅灰色细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩 无 / 无 / 4 240.0 4 248.0 浅灰色细砂岩 无 / 无 / 4 250.0 4 252.0 浅灰色细砂岩 无 / 无 / 4 258.0 4 264.0 灰色泥质细砂岩 无 / 无 / 4264.5 4 284.5 浅灰色粉砂岩、细砂岩 无 / 无 / NBxx-6-2 3 712.0 3 721.0 细砂岩 暗黄色 5 乳白色 慢 3 729.0 3 735.0 细砂岩 暗黄色 10 乳白色 慢 3 736.0 3 750.0 细砂岩 暗黄色 10 乳白色 慢 3 761.0 3 766.0 细砂岩 暗黄色 5 乳白色 慢 3 775.0 3 797.0 细砂岩 暗黄色 5 乳白色 慢 由于油基泥浆的推广,气测组分和荧光信息受到泥浆影响,导致研究区快速识别图版适用性受到限制。NBxx-6-2井3 712~3 797 m井段录井荧光暗黄色,发光面积5%~10%(图6,表2),荧光显示十分丰富。通过气测组分快速识别,3 743.5 m落点于凝析油气区,该点MDT泵抽,井下流体实验室测量得到稳定地层流体组分,计算气油比为319.2 m3/m3,测量油密度为0.61 g/m3,证实地层流体为油,并非凝析油;通过气测组分快速识别,3 760 m落点于气区,该点泵抽气油比13 523.9 m3/m3,证实地层流体为气(表3),流体性质判断正确,但与录井中荧光显示活跃矛盾。因此,认为在钻井过程中,岩石破碎气中的气体组分被油基泥浆不等比吸收,导致气测组分中的相对含量失衡,产生误判,并且油基泥浆中白油组分含少量芳香烃,存在荧光现象,导致录井过程中荧光信息丰富。
表 3 NBxx-6-2井3 743.5 m泵抽信息表Table 3. MDT pumping information, depth of 3 743.5 m, Well NBxx-6-2深度/m 探针类型 流度 泵抽时间 泵抽体积/L 取样情况 IFA流体识别结论 GOR气油比/(m3/m3) 3 743.5 椭圆形探针 83.96 73 28.6 2PVT 油层 319.2 3 760 椭圆形探针 66.7 57 11 1PVT 气层 13 523.9 3. 不同泥浆体系测录井综合对比
3.1 井筒环境对比
东海地区主要油气层层段以砂泥岩为主,砂泥岩薄互层夹煤层时常发育,钻井过程中泥岩和煤层剥落掉块、泥岩分散造浆易形成钻井卡阻、井径扩大等复杂情况,油基泥浆为油包水体系,滤失低,摩阻低,携岩性强,电稳定性好,具备良好的井筒清洁作用和储层保护能力,能改善钻井环境,缩短钻井周期。油基泥浆推广以来,在东海应用于多口井,表4为研究区油基泥浆3口井与水基泥浆1口井钻井周期对比,油基泥浆钻井周期明显缩短。图7为4口井的井径曲线对比,油基泥浆井壁更清洁,井眼环境更好。
表 4 研究区4口井钻井周期对比Table 4. Comparison of drilling cycles for the four wells from the research area井名 完钻井深/m 钻井天数 备注 NBxx-5-1s 4 850 59 水基泥浆 NBxx-7-1 4 480 20 油基泥浆 NBxx-5-2d 4 680 15 油基泥浆 NBxx-5-3 4 500 28 油基泥浆 3.2 油气水层解释对比
油基泥浆与水基泥浆在井筒环境下均会有滤失性,钻遇渗透性好的储层,不同径向探测深度电阻率呈现出分异现象。水基泥浆环境下,钻遇油气层时,由于地层流体导电性差,泥浆侵入地层后,探测深度深的电阻率一般大于探测浅的电阻率,即电阻率“低侵”现象;油基泥浆环境下,钻遇水层时,由于油基泥浆导电性差,泥浆侵入地层后,探测深度深的电阻率一般小于探测深度浅的电阻率,即电阻率“高侵”现象。对比了研究区2口井的电阻率“低侵”与“高侵”现象(图8),依图所示水基泥浆“低侵”现象明显,该现象普遍应用于渗透层的识别,并非油气水层识别,油基泥浆“高侵”现象能较好识别渗透性水层,结合延时测井,可以有效区分油气层与水层。
东海低孔低渗背景下的油层与气层识别是难点,地层中流体性质变化快,且油层与气层测井特征相似,很难快速识别。水基泥浆环境下,泥浆主要为海水和少量添加剂,组分中无荧光信息,录井过程中荧光信息主要反映地层流体荧光信息,并且气测组分中相对含量能反映地层中轻质与重质分布,利用区域经验图版结合荧光信息能较好识别储层流体性质;油基泥浆环境下,白油为主要组成部分,白油成分中含有少量的芳香烃,具有一定荧光特性,并且油基泥浆不等比吸收岩石破碎气,利用区域经验图版判断储层流体性质受到局限,需要建立油基泥浆环境下的区域经验图版,结合精度更高的三维荧光信息,综合判断储层流体性质[11-16]。
3.3 储层物性评价
油基泥浆钻井能提供状态良好、稳定的井壁环境,测井仪器记录地层信息的准确程度得到保障,像常规测井中的自然伽马、阵列声波、岩性密度等,均能得到品质为优的资料。但是对于测量地层含氢指数信息的仪器,像中子仪器、核磁仪器需要做井场环境校正(含氢校正)。
渗透性地层一般都有泥浆侵入,中子测井探测范围内的流体被认为是侵入带,油基泥浆滤液与地层流体的混合造成含氢量略低于淡水含氢量,通过对比邻井相同层位,水基泥浆环境下中子响应值,现场对油基泥浆下的中子做进场环境校正[7-10]。依据NBxx-7-1井现场测井图(图9),CNC2为油基泥浆校正后的中子,相比原始测量中子CNCF略大,在做储层定量评价计算孔隙度时使用环境校正后的中子曲线,能保证储层物性计算更准确。
核磁测井不受岩石骨架影响,广泛应用于储层评价中,特别是孔隙结构复杂的低孔低渗储层。核磁仪器的径向探测深度为井周5~10 cm,井周极易被泥浆充填,核磁测量的T2谱信息中包含泥浆信息。水基泥浆环境下,泥浆主要成分为水,T2谱的分布基本不受影响,主要反映储层中不同尺寸孔隙分布,大孔隙驰豫时间长,小孔隙驰豫时间短;油基泥浆环境下,泥浆主要成分为油,T2谱受泥浆黏度影响,出现谱峰后移现象,造成大孔隙假象。
NBxx-5-1s井为水基泥浆环境下二维核磁(MReX)测量,该层段为气水分异明显的底水气藏(图10),砂体A为气层,砂体B为含气水层,两段砂体的T2谱谱峰分布相似性较高,地层含气性的改变并未影响T2谱分布,4 212~4 230 m砂体T2谱谱峰分布与岩心物性吻合良好。近井地带水基泥浆驱替地层流体,核磁探测范围为泥浆信息,地层含气性被泥浆信息覆盖。因此,水基泥浆环境下核磁T2谱能反应低孔低渗储层孔隙结构分布。
NBxx-6-2井为油基泥浆环境下二维核磁(MReX)测量,该层段为气、油、水三相分异的油气藏(图11),核磁T2谱谱峰出现明显后移,物性好、大孔隙发育段,T2谱形态宽缓,物性差、小孔隙发育段,T2谱形态窄陡。地层流体性质变换并未影响T2谱分布,但泥浆体系变换引起T2谱谱峰后移,并存在“拖曳”现象。因此,油基泥浆环境下核磁T2谱受泥浆影响较大,T2谱谱峰相对位置关系不能直接反应低孔低渗储层孔隙结构分布,谱峰形态特征能表征孔隙发育情况。
油基泥浆会影响核磁T2谱分布,通过核磁T2谱评价储层的有效孔隙度、总孔隙、束缚水等参数时,需要进行含氢校正,目前Baker公司MReX仪器的含氢校正是针对评价参数的含氢校正,含氢校正后核磁有效孔隙度大于校正前有效孔隙度。
3.4 储层渗透性评价
电缆地层测试是一种测井作业,是目前唯一能进行动态地层测试的作业。东海常用的电缆地层测试仪器包括斯伦贝谢的MDT仪和贝壳休斯的RCI仪,本次研究不讨论公司之间仪器的工作原理和系统差异,仅从测压资料的解释上分析水基泥浆和油基泥浆给电缆地层测试带来的影响。
根据达西定律可知,储层有效渗透率为一定压力降下,地层流体流过探针的流量,压降流度定义为,地层有效渗透率除以黏度[17-20],一般用M表示(式1),压降流度是储层有效渗透率和黏度的综合反映,并且探针刺破泥饼,座封后形成冲洗带封闭环境,冲洗带流体为泥浆滤液和原装地层流体的混合液,因此,压降流度信息与泥浆黏度有密切关系。
$$ M = \frac{K}{\mu } = C\frac{q}{{2{\rm{\pi }}{r_p}*\Delta P}} $$ (1) 式中,M为测压流度,mD/cP;K为有效渗透率,μm2;μ为黏度,cP;q为压降流速,cm3/s;rp为探针半径,cm;Δp为压差Mpa;C为仪器形状系数,不同探针有不同的数值,无量纲。
一般情况下,室温条件下水基泥浆黏度为1 cp,而油基泥浆黏度为2~5 cp,鄢捷年[4]认为,油包水乳化钻井液表观黏度随温度的升高而降低,随压力的增大而增大,但是在井底条件下,表观黏度受到温度的变化大,压力的作用减小。因此推测,水基泥浆和油基泥浆在地层条件下,黏度均存在降低的现象,根据公式1推导,认为油基泥浆条件下测量得到储层流度略低于相同物性储层水基泥浆条件下流度,因此,在低孔低渗储层油基泥浆条件下,分析流度信息时,应客观估算储层的渗流能力,这对储层有效产能估算有指导意义。
图12为东海某凹陷斜坡带选取相近构造6口井的低孔低渗储层(15%>孔隙度≥10%,10 mD>渗透率≥0.1 mD)流度信息与岩心空气渗透率交会图,在低孔低渗储层背景下,油基泥浆条件下相同流度对应的岩心空气渗透率更高。水基泥浆条件下岩心的空气渗透率是流度信息的大约1~2倍关系,油基泥浆条件下岩心的空气渗透率是流度信息的大约3~5倍关系,这都与泥浆体系的黏度有关系,因此,在评估储层的渗透性时,应区分泥浆体系和泥浆黏度信息,为估算储层产能提供有效依据。
4. 结论
(1)油基钻井液具备优良的泥浆性能,保证了井筒环境清洁型,为录井作业和测井作业提供了良好的环境;
(2)油基泥浆环境下利用延时测井能较好的区分油气层与水层,油层与气层区分应建立油基泥浆环境下区域经验图版;
(3)油基泥浆环境下测井资料质量优,但是中子、核磁仪器需要做含氢校正;
(4)油基泥浆环境下,利用测压资料估算储层渗透性,需要明确泥浆体系与泥浆黏度信息。
-
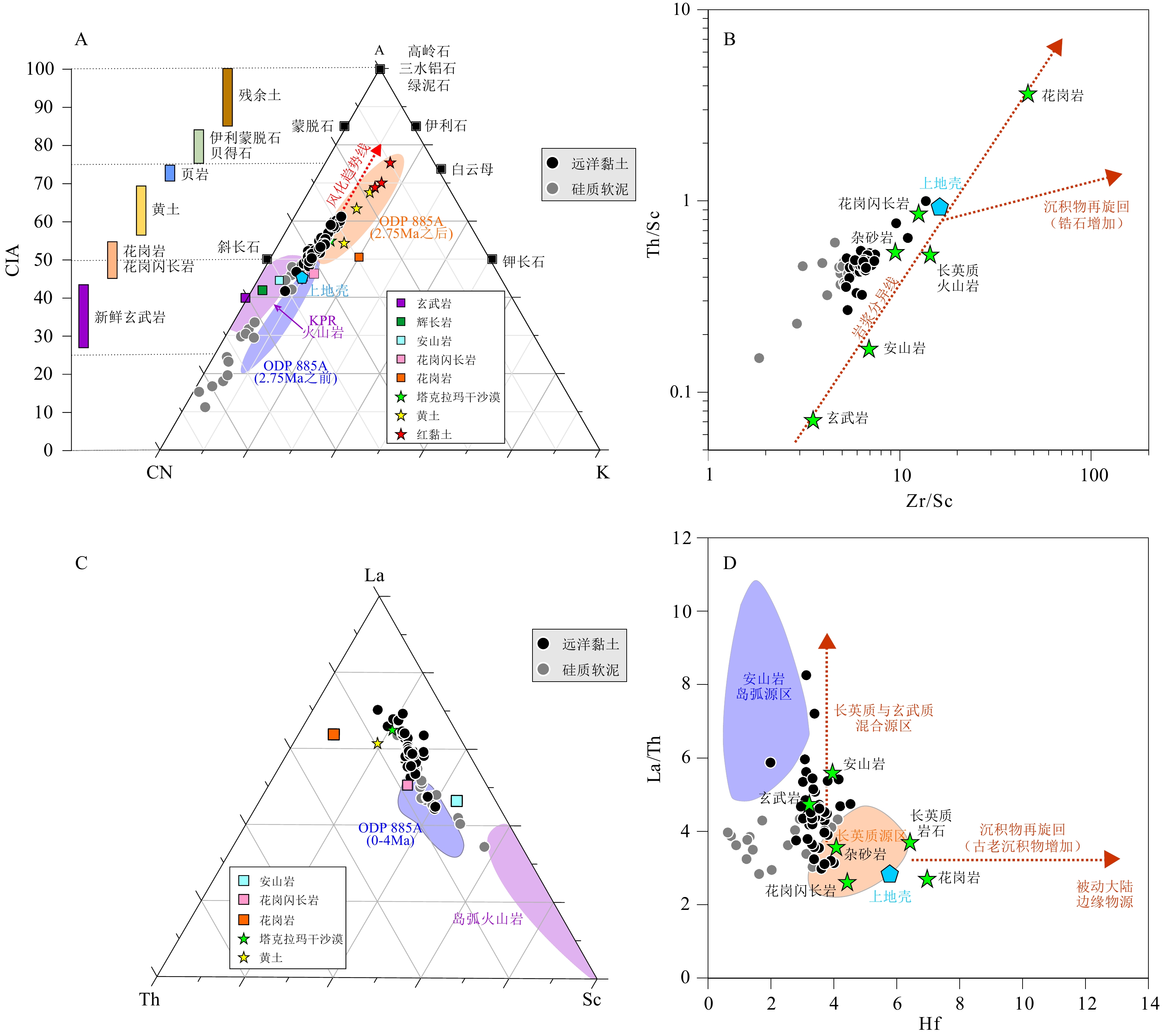
图 3 源区风化强度和沉积分选再循环评价图
A:A-CN-K图解[24],B:Th/Sc-Zr/Sc双变量图[29],C:La-Th-Sc三角图解[30],D:La/Th-Hf双变量图[31] 。底图均据引用文献重新绘制。
Figure 3. Evaluation of the weathering intensity in the source regions and the sedimentary sorting and recycling
A: A-CN-K ternary diagram [24], B: Th/Sc-Zr/Sc diagram [29], C: La-Th-Sc ternary diagram [30], D: La/Th-Hf diagram [31].
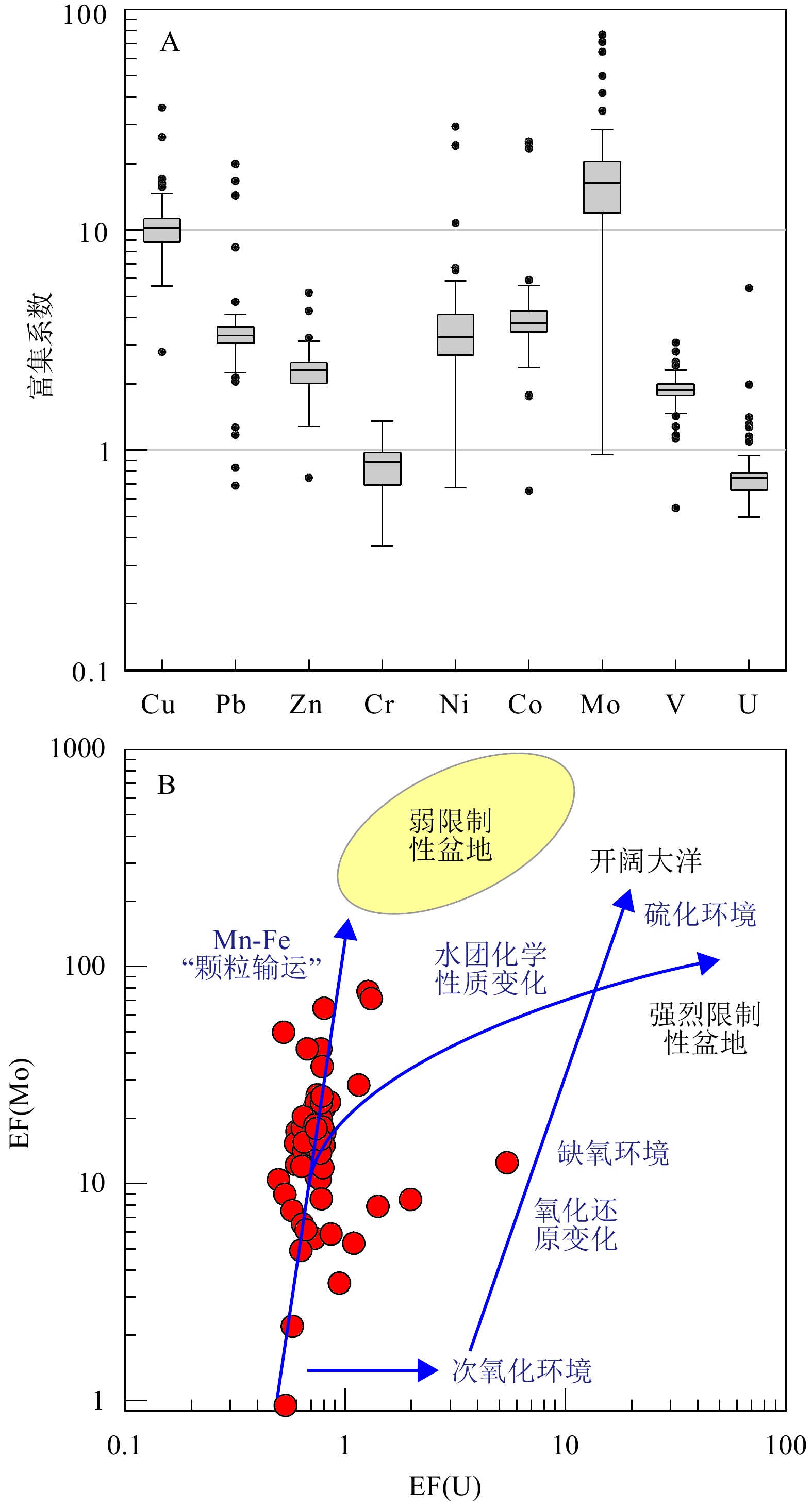
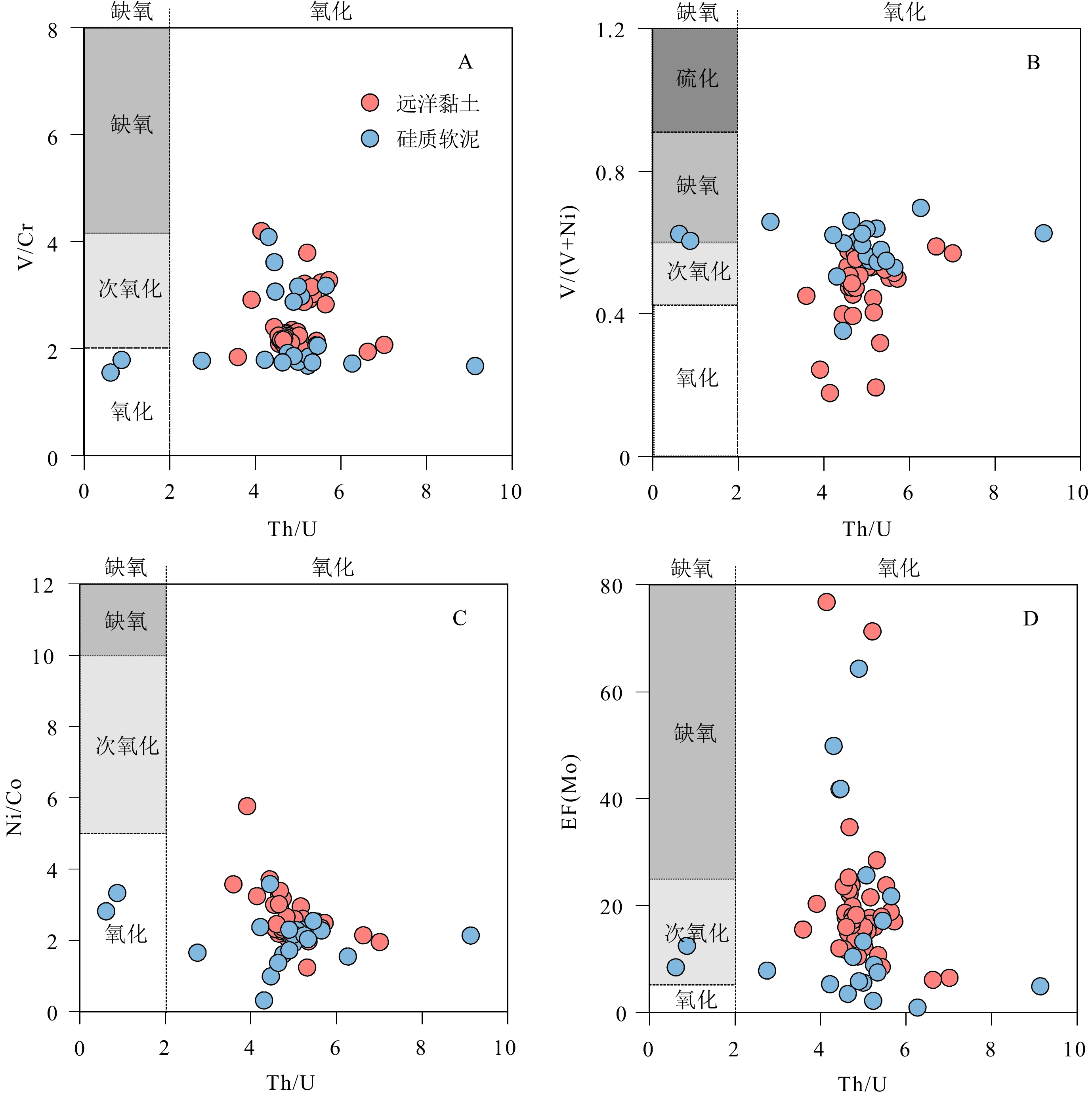
图 6 研究区底层水体氧化还原环境识别图
A:V/Cr-Th/U协变图,B:V/(V + Ni)-Th/U协变图,C:Ni/Co-Th/U协变图,D: EF(Mo)-Th/U协变图。其中V/Cr、Th/U和Ni/Co的含氧量临界值参考文献[49-50]。
Figure 6. Diagrams of redox environment of bottom water
A: V/Cr-Th/U; B: V/(V + Ni)-Th/U; C: Ni/Co-Th/U; D: EF(Mo)-Th/U. Critical oxygen content of V/Cr, Th/U, and Ni/Co ratios are from references[49-50].
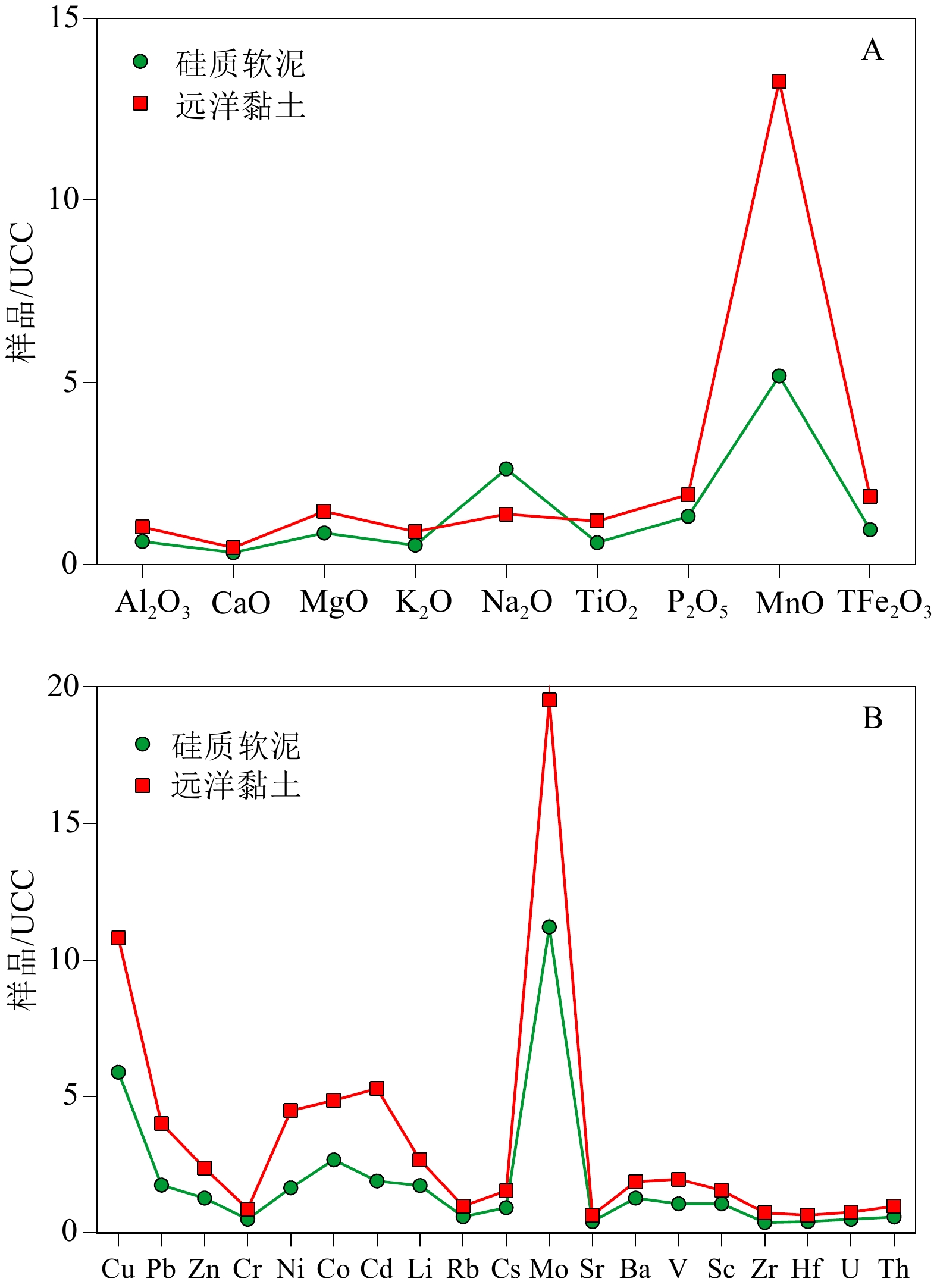
表 1 研究区表层沉积物常量元素氧化物含量和微量元素含量
Table 1 Contents of major and trace elements of the surface sediments of this study
组分 最小值 最大值 平均值 上地壳[21] 常量
元素
/%Al2O3 2.46 17.4 13.8 15.4 CaO 0.45 2.51 1.52 3.59 MgO 0.21 4.11 3.16 2.48 K2O 0.43 2.87 2.16 2.8 Na2O 3.16 16.2 5.81 3.27 TiO2 0.04 0.84 0.64 0.64 P2O5 0.04 0.56 0.26 0.15 MnO 0.03 6.62 1.14 0.1 TFe2O3 0.87 12.4 7.99 5.04 微量
元素
/(μg/g)Cu 28.2 842 268 28 Pb 5.1 299 57.7 17 Zn 18.1 292 138 67 Cr 12.3 105 69.2 92 Ni 11.5 1160 181 47 Co 4.08 384 75.3 17.3 Cd 0.03 3.31 0.42 0.09 Li 8.35 73.6 50 21 Rb 12.8 106 72 84 Cs 0.78 9.5 6.62 4.9 Mo 0.63 70.9 18.7 1.1 Sr 48.2 709 196 320 Ba 244 2280 1106 624 V 19.1 251 164 97 Sc 2.51 25.4 19.7 14 Zr 9.9 223 121 193 Hf 0.6 4.53 3.11 5.3 U 0.39 3.13 1.84 2.7 Th 1.19 16.3 9 10.5 La 5.81 77.4 39.0 31.0 -
[1] 宋维宇, 刘娅楠, 胡邦琦, 等. 基于DEM数据的菲律宾海典型区地貌类型划分[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(1):192-198 SONG Weiyu, LIU Yanan, HU Bangqi, et al. Landform classification for the Philippine Sea based on DEM data [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(1): 192-198.
[2] 张国伟, 李三忠. 西太平洋-北印度洋及其洋陆过渡带: 古今演变与论争[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(4):1-17 ZHANG Guowei, LI Sanzhong. West Pacific and North Indian Oceans and their ocean-continent connection zones: Evolution and debates [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(4): 1-17.
[3] 李春峰, 周多, 李刚, 等. 西太平洋地球动力学问题与未来大洋钻探目标[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(3):759-769 LI Chunfeng, ZHOU Duo, LI Gang, et al. Geodynamic problems in the Western Pacific and future scientific drill targets [J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(3): 759-769.
[4] 杜学鑫, 祝文君, 牟明杰, 等. 菲律宾海板块俯冲与岛弧演化的钻探靶区研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(5):199-210 DU Xuexin, ZHU Wenjun, MOU Mingjie, et al. Study on drilling target area of subduction of Philippine Sea plate and island arc evolution [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(5): 199-210.
[5] 万世明, 徐兆凯. 西太平洋风尘沉积记录研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(6):1208-1219 WAN Shiming, XU Zhaokai. Research progress on eolian dust records in the west Pacific [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(6): 1208-1219.
[6] Xu Z K, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Enhanced terrigenous organic matter input and productivity on the western margin of the Western Pacific Warm Pool during the Quaternary sea-level lowstands: Forcing mechanisms and implications for the global carbon cycle [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 232: 106211. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106211
[7] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Quantitative estimates of Asian dust input to the western Philippine Sea in the mid-late Quaternary and its potential significance for paleoenvironment [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005929
[8] Jiang F Q, Zhou Y, Nan Q Y, et al. Contribution of Asian dust and volcanic material to the western Philippine Sea over the last 220 kyr as inferred from grain size and Sr-Nd isotopes [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2016, 121(9): 6911-6928. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012000
[9] Jiang F Q, Frank M, Li T G, et al. Asian dust input in the western Philippine Sea: Evidence from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(5): 1538-1551. doi: 10.1002/ggge.20116
[10] 明洁, 李安春, 孟庆勇, 等. 东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆第四纪黏土矿物组合特征及物源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4):139-148 MING Jie, LI Anchun, MENG Qingyong, et al. Quaternary assemblage characteristic and provenance of clay minerals in the Parecevela Basin of the East Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 139-148.
[11] 靳宁, 李安春, 刘海志, 等. 帕里西维拉海盆西北部表层沉积物中黏土矿物的分布特征及物源分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(6):504-511 JIN Ning, LI Anchun, LIU Haizhi, et al. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the northwest Parece Vela Basin: distribution and provenance [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38(6): 504-511.
[12] 黄杰, 万世明, 张国良, 等. 海底地形特征对东菲律宾海表层黏土矿物分布的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1):77-85 HUANG Jie, WAN Shiming, ZHANG Guoliang, et al. Impact of seafloor topography on distribution of clay minerals in the East Philippines Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 77-85.
[13] Qin X W, Luo W D, Li P F, et al. Topographic and geomorphological features and tectogenesis of the southern section of the Kyushu-Palau Ridge (KPR) and its adjacent areas [J]. China Geology, 2021, 4(4): 571-584.
[14] Shang L N, Li P F, Du R L, et al. Structural characteristics of the KPR-CBR triple-junction inferred from gravity and magnetic interpretations, Philippine Sea Plate [J]. China Geology, 2021, 4(4): 541-552. doi: 10.31035/cg2021089
[15] 侯方辉, 秦轲, 陆凯, 等. 九州-帕劳海脊中段及两侧盆地构造沉积特征及俯冲起始: 多道反射地震综合研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(5):187-198 HOU Fanghui, QIN Ke, LU Kai, et al. Tectono-sedimentary characteristics and subduction initiation in the middle Kyushu-Palau Ridge and adjacent basins: A comprehensive study of multichannel seismic reflection profiles [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(5): 187-198.
[16] 黄威, 胡邦琦, 宋维宇, 等. 九州-帕劳海脊南部13°20′N海山铁锰结壳关键金属富集规律及制约因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(5):137-148 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2022052401 HUANG Wei, HU Bangqi, SONG Weiyu, et al. Enrichment and constraints of critical metals in ferromanganese crusts from 13°20'N seamount of the southern Kyushu-Palau Ridge [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(5): 137-148. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2022052401
[17] 黄威, 胡邦琦, 徐磊, 等. 帕里西维拉海盆西缘中段铁锰结核的地球化学特征和成因类型[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(1):199-209 HUANG Wei, HU Bangqi, XU Lei, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the ferromanganese nodules in the middle western margin of the Parece Vela Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(1): 199-209.
[18] 宋维宇, 李超, 孟祥君, 等. 九州-帕劳海脊南段共生多金属结核与富钴结壳地球化学特征及其资源意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(5):149-157 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2022061701 SONG Weiyu, LI Chao, MENG Xiangjun, et al. Geochemical characteristics and resource significance of polymetallic nodules and cobalt-rich crusts in the southern Kyushu-Palau ridge [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(5): 149-157. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2022061701
[19] Kawabe M, Fujio S. Pacific ocean circulation based on observation [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2010, 66(3): 389-403. doi: 10.1007/s10872-010-0034-8
[20] Hu D X, Wu L X, Cai W J, et al. Pacific western boundary currents and their roles in climate [J]. Nature, 2015, 522(7556): 299-308. doi: 10.1038/nature14504
[21] Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Elsevier: Oxford, 2014: 1-51.
[22] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites [J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885): 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[23] McLennan S M. Weathering and global denudation [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(2): 295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[24] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(7): 1523-1534. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3
[25] Ishizuka O, Taylor R N, Yuasa M, et al. Making and breaking an island arc: A new perspective from the Oligocene Kyushu-Palau arc, Philippine Sea [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2011, 12(5): Q05005.
[26] Sun J M, Zhu X K. Temporal variations in Pb isotopes and trace element concentrations within Chinese eolian deposits during the past 8 Ma: Implications for provenance change [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 290(3-4): 438-447. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.01.001
[27] Chen B, Yang X P, Jiang Q D, et al. Geochemistry of aeolian sand in the Taklamakan Desert and Horqin Sandy Land, northern China: Implications for weathering, recycling, and provenance [J]. CATENA, 2022, 208: 105769. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105769
[28] Zhang Q, Liu Q S, Roberts A P, et al. Mechanism for enhanced eolian dust flux recorded in North Pacific Ocean sediments since 4.0 Ma: Aridity or humidity at dust source areas in the Asian interior? [J]. Geology, 2020, 48(1): 77-81. doi: 10.1130/G46862.1
[29] McLennan S M, Hemming S R, McDaniel D K, et al. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics [J]. Special Papers-Geological Society of America, 1993, 284: 21-40.
[30] Bhatia M R, Crook K A W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92(2): 181-193. doi: 10.1007/BF00375292
[31] Floyd P A, Leveridge B E. Tectonic environment of the Devonian Gramscatho basin, south Cornwall: framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1987, 144(4): 531-542. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.144.4.0531
[32] Shao L, Li X H, Wei G J, et al. Provenance of a prominent sediment drift on the northern slope of the South China Sea [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2001, 44(10): 919-925. doi: 10.1007/BF02907084
[33] Wei G J, Liu Y, Ma J L, et al. Nd, Sr isotopes and elemental geochemistry of surface sediments from the South China Sea: Implications for Provenance Tracing [J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 319-322: 21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.05.007
[34] Olivarez A M, Owen R M, Rea D K. Geochemistry of eolian dust in Pacific pelagic sediments: Implications for paleoclimatic interpretations [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(8): 2147-2158. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90093-K
[35] 丁雪, 胡邦琦, 徐方建, 等. 晚上新世以来菲律宾海盆XT4孔黏土矿物特征及其古环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(1):42-51 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020111301 DING Xue, HU Bangqi, XU Fangjian, et al. Evolution of clay minerals assemblages since Late Pliocene and its paleoenvironmental implications: Evidence from Core XT4 of the Philippine Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(1): 42-51. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020111301
[36] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等. 东菲律宾海沉积物的地球化学特征与物质来源[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(6):923-931 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.06.013 XU Zhaokai, LI Anchun, JIANG Fuqing, et al. Geochemical character and material source of sediments in the eastern Philippine Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(6): 923-931. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.06.013
[37] 褚征, 胡宁静, 刘季花, 等. 西菲律宾海表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征及物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5):53-62 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2016.05.006 CHU Zheng, HU Ningjing, LIU Jihua, et al. Rare earth elements in sediments of west Philippine Sea and their implications for sediment provenance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(5): 53-62. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2016.05.006
[38] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2014, 119(19): 11492-11504. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022025
[39] Jiang F Q, Zhu X, Li T G, et al. Increased dust deposition in the Parece Vela Basin since the mid- Pleistocene inferred from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019, 173: 83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.12.011
[40] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update [J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1-2): 12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
[41] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Baudin F, et al. Analysis of marine environmental conditions based onmolybdenum–uranium covariation—Applications to Mesozoic paleoceanography [J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 324-325: 46-58. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.09.009
[42] Bennett W W, Canfield D E. Redox-sensitive trace metals as paleoredox proxies: A review and analysis of data from modern sediments [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 204: 103175. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103175
[43] Algeo T J, Li C. Redox classification and calibration of redox thresholds in sedimentary systems [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 287: 8-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.01.055
[44] Algeo T J, Tribovillard N. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum–uranium covariation [J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(3-4): 211-225. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.001
[45] Morford J L, Emerson S R, Breckel E J, et al. Diagenesis of oxyanions (V, U, Re, and Mo) in pore waters and sediments from a continental margin [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(21): 5021-5032. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.05.015
[46] Krishnaswami S. Authigenic transition elements in Pacific pelagic clays [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1976, 40(4): 425-434. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(76)90007-7
[47] Piper D Z. The metal oxide fraction of pelagic sediment in the equatorial North Pacific Ocean: A source of metals in ferromanganese nodules [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(8): 2127-2145. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90193-7
[48] Hatch J R, Leventhal J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U. S. A. [J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1-3): 65-82. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-Y
[49] Jones B, Manning D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones [J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1-4): 111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X
[50] Wignall P B, Twitchett R J. Oceanic anoxia and the end permian mass extinction [J]. Science, 1996, 272(5265): 1155-1158. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5265.1155
[51] Rimmer S M. Geochemical paleoredox indicators in Devonian–Mississippian black shales, Central Appalachian Basin (USA) [J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3-4): 373-391. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.029
[52] Xiong Z F, Li T G, Algeo T, et al. Paleoproductivity and paleoredox conditions during late Pleistocene accumulation of laminated diatom mats in the tropical West Pacific [J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 334: 77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.09.044
[53] Luo M, Algeo T J, Tong H P, et al. More reducing bottom-water redox conditions during the Last Glacial Maximum in the southern Challenger Deep (Mariana Trench, western Pacific) driven by enhanced productivity [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2018, 155: 70-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.01.006
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杨艳秋,李森,梁杰,孙晶. 南黄海盆地南部海相构造层研究新进展. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(02): 12-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 袁勇,陈建文,骆迪,李清,梁杰,蓝天宇,王建强,曹珂,赵化淋. 南黄海盆地烟台坳陷新生界二氧化碳封存地质条件与封存前景. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(03): 35-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: