Triassic Subduction Polarity and Orogenic Process of the Sulu Orogen, East China
-
摘要: 中国东部的苏鲁造山带印支期先后经历了大洋消减俯冲、大陆碰撞、陆壳深俯冲、陆内造山等复杂过程。综合苏鲁造山带的构造地质学、岩石学、岩相古地理学、年代学进展,发现以下事实用传统的华南向华北俯冲难以解释:(1)徐淮地区形成了明显的朝北西拓展的逆冲构造变形,此外,苏鲁造山带中还存在大量的北西向逆冲推覆构造;(2)苏鲁造山带中出露的白垩纪花岗岩中来自古元古代的继承锆石,以及Sr、Nd、Pb同位素示踪结果都显示与华北地块南缘地质体更为相似;(3)苏鲁造山带北侧的胶莱盆地以及胶北隆起缺乏晚古生代到中生代的弧后火山岩证据;(4)华北南缘三叠纪时期的古地理环境更接近被动大陆边缘。基于这些事实,本文认为,晚古生代-早三叠世早期苏鲁段的商丹洋可能向南东俯冲,不同于秦岭-大别段的商丹洋向北俯冲,消减到秦岭-大别微陆块苏鲁段之下,发生华北地块与该微陆块的拼合,华北地块整体向南东楔入秦岭-大别微陆块,导致大别-苏鲁超高压岩石垂向折返剥露;中三叠世-晚三叠世,勉略洋自东向西的剪刀式闭合,华南地块向北秦岭-大别微陆块俯冲拼合,并逐渐将华南地块与华北地块之间的秦岭-大别微陆块向西、向北侧向挤出,到了中生代华北地块持续向南东俯冲并楔入华南地块,将苏鲁-大别造山带沿郯庐断裂错断并最终形成该区总体构造格局。Abstract: The Sulu Orogen, located in East China, has experienced a series of complex Indosinian tectonic processes including subduction of oceanic crust, continent-continent collision, deep continent subduction and intracontinental orogenism. After synthesis of recent researches on tectonics, petrology and paleogeography in the Sulu Orogen, this paper reached the following conclusions that are different from the traditional tectonic models of subduction of the South China Block under the North China Block. 1) In addition to the NW thrusts in the Xu-Huai area, a large number of northwestward thrusts occur in the orogen. 2) The existence of inherited Early Pterozoic zircon and the Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic tracers in the Cretaceous granites in the Sulu Orogen sugest the affinity of the orogen to the North China Block. 3) In the Jiaolai Basin and the Jiaobei Uplift, there is no arc magmatism was recorded from Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic. 4) The southern margin of the North China Block was a passive margin in Triassic. The Shangdan Ocean was subductd southeastward under the Qinling-Dabie Microplate in the Sulu segment, but northward in the Qinling-Dabie segment from Late Paleozoic to Early Triassic, which resuted in the collision of the North China Block and the Qinling-Dabie Microplate. The North China Block indented into the Qinling-Dabie Microplate and thus caused the vertical exhumation of the high-pressure and ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks. During the Middle-Late Triassic, the northward scissors-type closure of the Mianlue Ocean resulted in an assembly of the South China Block to the Qinling-Dabie Microplate from west to east. The Qinling-Dabie Microplate between the North China and South China blocks was laterally extruded to the west and the north respectively. In the Mesozoic, together with the intracontinental subduction of the North China Block to the South China Block, the Sulu-Dabie Orogen was indented southeastwards by the North China Block. The tectonic setting in the Sulu Orogen and adjacent region was basically formed then.
-
Keywords:
- Sulu Orogen /
- subduction polarity /
- orogenic process /
- Indosinian /
- scissors-type closure
-
苏鲁造山带地跨安徽、江苏、山东三省,构造上位于中国华北地块与华南地块之间碰撞带的东段。从全球板块构造格局来看,该地区属于印支期古特提斯闭合的产物,而现今又处于太平洋板块-欧亚板块之间的洋陆过渡带,受太平洋板块俯冲、印度-澳大利亚板块和欧亚板块碰撞的影响。
印支期是东亚现今大地构造格局初步成型的阶段,随着商丹洋和勉略洋的最终闭合,华北地块与华南地块最终拼合,形成了中国东部的近东西向的复合型造山带——秦岭-大别-苏鲁造山带形成,发育了世界上著名的大别-苏鲁高压-超高压变质带,该变质带一直是国内外的热点[1-12]。现阶段关于苏鲁造山带高压超高压变质带研究的观点,已就深俯冲折返形成了一种“共识”:高压-超高压岩石的形成与折返都是华南向华北之下俯冲的产物。国内外研究对高压超高压变质岩的折返研究提出了很多构造模式,例如,逆冲挤压作用、走滑断裂、造山逃逸等[13-17]。Maruyama et al.[18]基于东大别的研究,认为垂向挤出是超高压岩石同造山折返的重要过程。Wang等[19]则进一步指出这种折返始于早三叠世,并通过南北地块之间的强大挤压,导致高压-超高压岩片平行造山带的侧向挤出。Ratschbacher等[20, 21]认为,大别造山带向东构造逃逸时代不是同造山的,而应在造山后的白垩纪到新生代,并认为与太平洋板块白垩纪中期启动的俯冲有关。Li等[22-24]基于西大别的研究提出了一种印支期同造山两阶段的挤出模式,其中第一阶段为垂向挤出,从地壳深部挤出到30 km左右的深度,第二阶段为侧向挤出,逐渐从中地壳挤出至地表,但是并没有解决苏鲁造山带高压-超高压岩石的挤出过程。可见,对苏鲁-大别造山带的高压-超高压岩石剥露机制、折返挤出时间、挤出背景都还存在不同认识。
本文拟结合近5年来苏鲁-大别造山带及周边的构造地质学、岩石学、古地理学的研究进展,对苏鲁造山带的印支期俯冲极性和高压-超高压岩石剥露等问题重新讨论,系统的将华北地块的印支期地质事件与苏鲁造山带的高压-超高压岩石折返过程相结合,并以此为出发点建立一个新的造山模型,重建印支期中国东部碰撞造山过程,这对古太平洋板块俯冲启动时间的探讨也必将起到约束作用。
1. 苏鲁造山带的基本特征
苏鲁造山带向西与秦岭-大别造山带相连接(图 1),向东横穿黄海,与朝鲜半岛的临津江造山带和洪城杂岩相连接[25-31];向西,秦岭-大别造山带继续与祁连、昆仑造山带连接,统称为中国中央造山带。
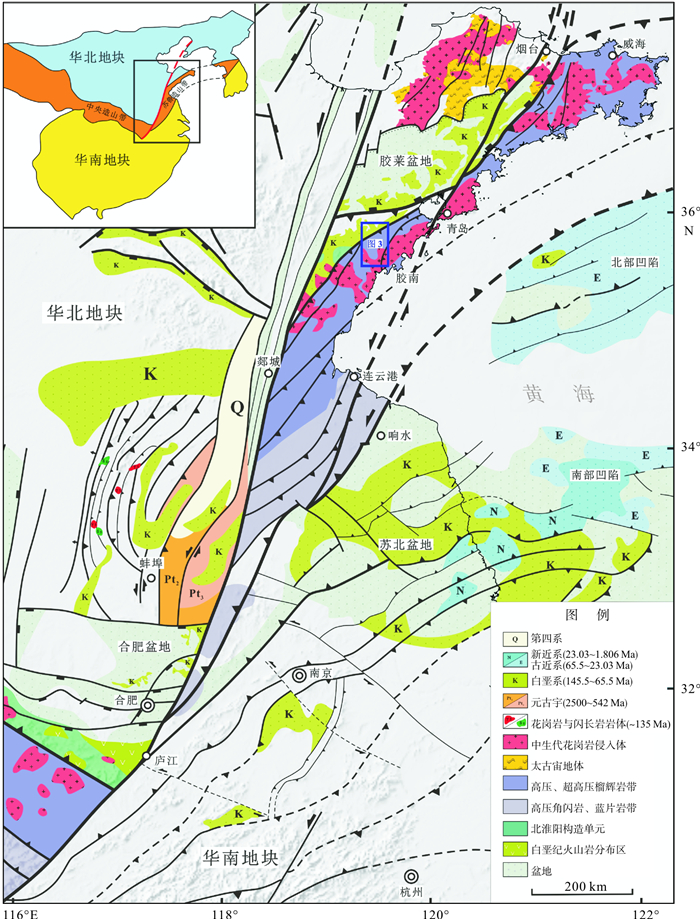
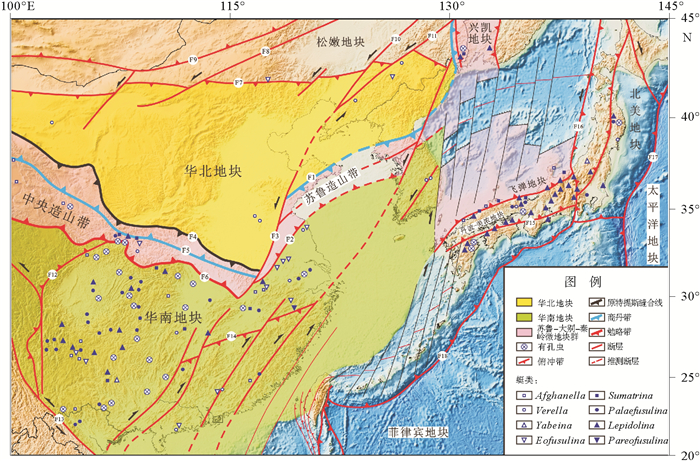
![]() 图 1 中国东部晚古生代—中生代大地构造单元及有孔虫、蜓类分布(据文献[25-33]编制)断裂名称:F1.五莲-青岛-牟平断裂;F2.嘉山-响水断裂;F3.郯庐断裂;F4.洛南-栾川断裂;F5.商丹带;F6.勉略带;F7.索伦断裂;F8.西拉木伦断裂;F9.贺根山断裂;F10.依兰-伊通断裂;F11.敦化-密山断裂;F12.龙门山断裂;F13.哀牢山-红河断裂;F14.江绍断裂;F15.日本中央断裂;F16.千岛俯冲带;F17.日本俯冲带;F18.琉球俯冲带Figure 1. Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic tectonic map of East Asia showing the tectonic units and distribution of the foraminifera and the fusulinids(compiled after [25-33])Faults, sutures and subduction zones: F1.Wulian-Qingdao-Yantai Fault; F2.Jiashan-Xiangshui Fault; F3.Tanlu Fault; F4.Luonan-Luanchuan Fault; F5.Sangdan Suture; F6.Mianlue Suture; F7.Solonker Suture; F8.Xilamulun Fault; F9.Hegenshan Suture; F10.Yilan-Yitong-Fault; F11.Dunhua-Mishan Fault; F12.Longmenshan Fault; F13.Ailaoshan-Red River Fault; F14.Jiangshan-Shaoxing Fault; F15.Central Japan Fault; F16.Kuril Subduction Zone; F17.Japan Subduction Zone; F18.Rykyu Subduction Zone
图 1 中国东部晚古生代—中生代大地构造单元及有孔虫、蜓类分布(据文献[25-33]编制)断裂名称:F1.五莲-青岛-牟平断裂;F2.嘉山-响水断裂;F3.郯庐断裂;F4.洛南-栾川断裂;F5.商丹带;F6.勉略带;F7.索伦断裂;F8.西拉木伦断裂;F9.贺根山断裂;F10.依兰-伊通断裂;F11.敦化-密山断裂;F12.龙门山断裂;F13.哀牢山-红河断裂;F14.江绍断裂;F15.日本中央断裂;F16.千岛俯冲带;F17.日本俯冲带;F18.琉球俯冲带Figure 1. Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic tectonic map of East Asia showing the tectonic units and distribution of the foraminifera and the fusulinids(compiled after [25-33])Faults, sutures and subduction zones: F1.Wulian-Qingdao-Yantai Fault; F2.Jiashan-Xiangshui Fault; F3.Tanlu Fault; F4.Luonan-Luanchuan Fault; F5.Sangdan Suture; F6.Mianlue Suture; F7.Solonker Suture; F8.Xilamulun Fault; F9.Hegenshan Suture; F10.Yilan-Yitong-Fault; F11.Dunhua-Mishan Fault; F12.Longmenshan Fault; F13.Ailaoshan-Red River Fault; F14.Jiangshan-Shaoxing Fault; F15.Central Japan Fault; F16.Kuril Subduction Zone; F17.Japan Subduction Zone; F18.Rykyu Subduction Zone苏鲁造山带地区的岩浆岩(图 2)主要形成于中生代的晚三叠世、晚侏罗世和早白垩世。空间上来看,晚三叠世的碱性岩以及晚侏罗世的花岗岩仅出露苏鲁造山带的东部地区,而早白垩世的岩浆岩则广泛分布于整个苏鲁-大别造山带[37-42]。印支期高压-超高压岩石出露在五莲-青岛-烟台断裂以东,东侧在海域的千里岩岛尚有出露,威海一带可见部分属于典型华北地块的古元古代荆山群卷入高压-超高压变质带。
江苏省北部连云港地区,高压-超高压变质岩带、岩浆带等都呈北东走向展布,与苏鲁造山带的延伸方向相一致。据朱光等[34]和胡红雷等[35],苏北盆地于印支期形成大量前陆褶皱带,这些前陆褶皱的轴向也大多为北东向。可见,苏鲁造山带的在印支期的演化主要受华北地块、华南地块两大地块碰撞造山作用控制。
前人研究都认为,苏鲁造山带与秦岭-大别造山带的地质构造总体是三地块沿两条缝合带相互作用的结果(图 1):华北地块、华南地块、苏鲁-大别-南秦岭微陆块(可分为苏鲁段和秦岭-大别段)。苏鲁-大别-南秦岭微陆块通过商丹带和勉略带先后与华南、华北地块最终缝合。最近的研究表明,古生代中期,随着原特提斯洋的消减,华北地块经过远距离漂移最终向南与北秦岭块体碰撞拼合;随后,约400 Ma古特提斯洋打开,华北与北秦岭共同向北漂移,并最终与华南地块成为现今的南北向关系;古生代期间始终处于被动陆缘的华南地块北部的商丹洋向华北地块下俯冲,同时,华南地块北缘也发生裂解,于泥盆纪之后出现勉略洋;最终,商丹洋和勉略洋于印支期闭合,勉略洋闭合则相对较晚一点,直到中晚三叠世华南地块、秦岭-大别微陆块才与华北地块和加里东期变成其组成部分的北秦岭块体碰撞[54-63]。
三叠纪晚期,勉略洋闭合的同时,古太平洋向西的俯冲消减则逐渐启动,位于西太平洋地区的整个中国东部的各个构造单元才一致受到古太平洋板块俯冲作用影响,在华北、华南地块东部形成了广泛的NNE向印支末期的褶皱-逆冲变形。在对东亚大陆边缘的重建中认为,中生代早三叠世之前,东亚大陆边缘仍处在被动陆缘阶段,之后,晚三叠世-早白垩世,东亚大陆边缘才转变为大陆岩浆弧发育的安第斯型活动陆缘阶段;晚白垩世以后直到渐新世,东亚大陆边缘逐渐进入了走滑拉分盆地发育的NNE向安第斯型大陆边缘阶段;之后NNE向安第斯型大陆边缘可能由于俯冲后撤,发生伸展垮塌,形成西太平洋型活动大陆边缘[64]。
2. 苏鲁造山带北部与南部变形特征
苏鲁造山带的南、北界线的厘定是苏鲁造山带的重要研究内容。前人基于对苏鲁造山带高压超高压变质岩分布,以及印支期、燕山期花岗岩的岩石学、地球化学的研究,对苏鲁造山带的范围虽已基本达成共识(图 2),但是现今分析表明,这个地带非常复杂,华北与华南不同属性的、大小不同的岩片出露具有复杂性。
2.1 苏鲁造山带北界
主要依据是高压-超高压变质岩石现今出露分布的西界、北界,确定苏鲁造山带的北部边界应以五莲-青岛-烟台断裂带为界。而且,该断裂带两侧基底分别具有明显华北地块属性和具有扬子地块属性,该断裂南部、东部大量分布印支期榴辉岩[7, 65, 66],而在该断裂北部西部的胶北隆起则主要分布古元古代胶辽吉带的高压麻粒岩。高压-超高压环境下形成的印支早期榴辉岩,可以作为苏鲁造山带的标志,故五莲-青岛-烟台断裂带向西延伸应与商丹带相连接,而向东则延伸至朝鲜半岛(图 1),进而连接兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地体西侧的牡丹江断裂带,该界限同时也是古特提斯洋的北部界限[25-31]。但是,刘利双等[67]在海阳所发现,海阳所地区片麻岩和变基性岩的原岩形成时代主要为古元古代,部分为太古代,与胶北早前寒武纪变质基底或古元古造山带杂岩原岩年龄具有一定的相似性,而明显不同于苏鲁超高压变质带新元古代原岩年龄(850 ~ 750 Ma)。海阳所地区变基性岩及其围岩均来自于华北克拉通东南缘胶北地体的古老变质基底,并经历了古元古代(~1 850 Ma)和中-晚三叠世(235~220 Ma)两期变质热事件的改造。此前,也有人提出华北地块作为印支期深俯冲带的上盘,不可能有相关上盘的岩片卷入到俯冲盘的苏鲁造山带中,因而提出侏罗纪-早白垩世陆内俯冲阶段华北地块向华南地块或苏鲁造山带之下俯冲,进而卷入苏鲁造山带。然而,刘利双等[67]的结果表明,海阳所的基性麻粒岩除了古元古代变质外,只有晚三叠世变质叠加,因而基本上还是同造山或造山后的变形导致这些岩片卷入苏鲁造山带。
五莲-青岛-烟台断裂带可进一步划分为NEE向的五莲-青岛段和NE向的青岛-牟平段[68]。其中沿五莲-青岛段,石门-薛家庄韧性变形带与之伴生(图 3),变形带内构造岩主要有糜棱岩、变余糜棱岩、超糜棱岩、构造片岩等,其中糜棱岩面理主要倾向NNW,拉伸线理则较为复杂,倾伏向主要集中在NWW向、NE向和NNE向,依据面理和线理可以看出,该韧性剪切带至少受到了三期剪切变形的影响[68, 69]。第一期表现为左行走滑运动,从矿物共生组合的角度看,该期变形环境属于角闪岩相;第二期表现为右行走滑运动,由于伸展剥露作用,在岩石中这一期变形显示为退变质事件,该期变形环境属于绿片岩相;第三期变形表现为左行走滑运动,呈带状展布,变形叠加在前两期变形之上,变形环境属于低绿片岩相[68]。从构造变形和变质相特征来看,应与苏鲁造山带复杂的侧向挤出和剥露过程相关。青岛-牟平段,又称即墨-牟平断裂,沿该断裂带,燕山期闪长玢岩脉、正长斑岩脉、煌斑岩脉、石英脉等岩脉发育,该段叠加的燕山期活动更为显著[68]。
2.2 苏鲁造山带南界
苏鲁造山带南部界线的研究主要围绕苏北地区展开,一般认为苏北盆地北部界线嘉山-响水断裂为苏鲁造山带南部界线(图 2),向西应与襄樊-广济断裂或勉略带连接,向东进入黄海北部地区,应在千里岩岛和南黄海盆地北界之间通过,可能南黄海北部坳陷的北部界线就是嘉山-响水断裂的海中延伸[43-48],再向东连接朝鲜半岛洪城杂岩附近,之后被NNE向断裂错断后,应当继续向东北延伸,可能对应在复原新生代后期打开的日本海之后日本的飞弹地块南侧的边缘构造带,那里也发育印支期榴辉岩和兰片岩,向北继续对比,可能为兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地体东侧[25-28]。
总体来说,苏鲁造山带南部变形不及北部强烈。而南部包括嘉山-响水断裂、苏北盆地内部大量的褶皱和逆冲断层的走向与北部地体中构造变形的走向较为一致。沿苏鲁造山带南部排列着数量众多的向南东逆冲的断层(图 2),这些断层呈叠瓦状排列,其走向与嘉山-响水断裂也基本平行,因而,前人认为,嘉山-响水断裂南部是苏鲁造山带碰撞过程中形成的前陆变形区,盆地内部广泛分布印支期构造变形和数量众多的推覆体(图 2)[35]。接近苏鲁造山带地区的变形区,可进一步细分出两个冲断带:苏北盆地基底的海相地层中分布数量众多向南东逆冲的断层和与之平行的褶皱[35]。
综上所述,华北地块与苏鲁造山带印支期在北部边界上呈现苏鲁造山带向华北地块逆冲推覆,而华北地块向苏鲁造山带之下俯冲的特征;而印支期在南部边界上呈现华南地块向苏鲁造山带之下俯冲。
3. 苏鲁造山带北界俯冲极性
当前,对于苏鲁造山带南界是因为华南地块向苏鲁造山带向北俯冲争议不大,但关于苏鲁造山带北界俯冲极性的研究尚存分歧,下面主要从构造变形、同位素、古地理三个角度进行分析。
3.1 构造证据
通常认为苏鲁造山带与临津江构造带是相连的[25-28],从年代学上看,和日本飞弹地体的榴辉岩带也存在关联[30, 31]。Oh[29-31]则提出,飞弹地体的榴辉岩与兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地体的兰片岩之间存在密切联系,可能属于相同的板块构造过程下形成的。李三忠等[5]提出,苏鲁-大别造山带在印支期早期是一条总体NE向的造山带。勉略带向东延伸虽然在大别段还存在争议,但至少襄樊-广济断裂是个巨大界线,属于碰撞带南界没异议,虽然没有可靠的洋壳记录,但附近发育220 Ma左右的兰片岩,向日本延伸则发现同时代的兰片岩和洋壳记录,同样恢复日本海之后,向北部延伸,表明兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块晚古生代期间可能从大华南板块“撕裂”出去。最终,印支期华北向华南下面楔入碰撞过程中,该原始NE向造山带逐渐发生弯曲,这种弯山变形影响到了整个郯庐断裂以西地区,并被后期郯庐断裂走滑错切。期间,作为下盘的胶辽吉带前寒武纪基底广泛出露的古元古代岩片也参与了这种变形,因而在海阳所、烟台地区有一些荆山群或太古代基底的岩片卷入到苏鲁造山带之内[71-75]。榴辉岩沿着北侧的商丹带俯冲隧道挤出到中部地壳,因而必然位于北侧,而兰片岩是与勉略带俯冲相关,形成时间也晚于榴辉岩挤出到中地壳的时间,因而沿着勉略带俯冲隧道剥露,必然现今分布在南侧,这种高压-超高压岩石的分布规律和相关变形特征,都证明华北地块向苏鲁造山带下面俯冲。
Xu等[17]曾经提出了一个高压超高压变质岩片逐渐向北逆冲折返的构造模型,并对苏鲁造山带中存在向北的逆冲推覆断层进行过描述。而中国大陆科学钻探计划(CCSD)在1 200米深度以上的部位也揭示出与这种构造模型相似的向西逆冲的逆冲断层[34, 35],证实了这种华北地块可能在印支期向南俯冲的合理性。因此可以认为,在苏鲁造山带的北缘,存在一个较为明显的向南东方向的俯冲。
据赵淑娟等[63]对北秦岭的研究,整个北秦岭区印支期卷入了三幕褶皱和数量众多的断裂带,主要断裂带从南向北有4条:商丹带、朱阳关-夏馆、官坡-乔端和洛南-栾川断裂,除了最南端的商丹带倾向北东以外,其余断裂带都是倾向南西,且走滑作用强烈。而北东倾向的商丹带很有可能也是一个侧向或斜向俯冲-碰撞带[2]。这可能表明是华北地块沿苏鲁造山带向东的俯冲才是正向俯冲-碰撞带。
3.2 同位素证据
传统的认识都是,华南地块向苏鲁造山带俯冲,或者华南地块沿五莲-青岛-烟台断裂向北俯冲,整个苏鲁造山带作为沿俯冲隧道折返剥露的华南属性的岩片,即高压超高压变质岩、镁铁质-超镁铁质岩都是由华南地块深俯冲之后折返地表的产物。但是,如果地质事实真是如此,那么该地区白垩纪的花岗岩、源自中深部地壳的镁铁质-超镁铁质岩石都应该与华南地块具有相似的同位素地球化学特征,然而,Sr、Nd、Pb同位素示踪分析结果却表明,苏鲁造山带中的白垩纪花岗岩、镁铁质-超镁铁质岩石与华北地块的同位素特征相近[76, 77]。这就从同位素地球化学的角度说明,苏鲁造山带中出露的白垩纪火山岩、镁铁质-超镁铁质岩石是由华北地块深俯冲熔融产生的。
另外,沿苏鲁造山带广泛分布中生代花岗岩,通过对苏鲁造山带地区白垩纪花岗岩继承锆石年龄进行统计发现,继承锆石的年龄中,古元古代占据了较大的一部分[78-87]。然而,在秦岭-大别微陆块以及华南地块靠近苏鲁-大别造山带的邻区,并不存在古元古代或古元古代变质的地质体出露,也就是说白垩纪花岗岩中继承锆石的物源区应该不是亲华南的属性。相反,在北秦岭地体和华北地块南部,大量古元古代地质体出露。因此,这里用华南地块向苏鲁造山带俯冲卷入较难解释这一现象。
3.3 古地理证据
古地理分析表明,晚古生代华北古地理环境经历了陆表海沉积相、海-陆过渡相、河流湖泊相三个阶段[88-91]。晚二叠世晚期,华北地块东南缘主要表现为浅水湖泊沉积环境。华北地块东部三叠纪至侏罗纪的残存地层记录也揭示了华北地块东南侧造山带导致的持续隆升过程,沉积相特征则揭示了自东向西的迁移,由靠近造山带向远离造山带岩相逐渐转变,晚古生代到早中生代的沉积序列与被动大陆边缘相似[88-91]。同时,在华北地块南缘缺乏华南地块向华北地块俯冲的岛弧型火山岩记录。虽然火山碎屑岩也在华北地区东部的晚古生代沉积层中有所发现[92],但分布较少,并不具有很强的说服力,依然可以认为华北地块南部很可能是一种被动大陆边缘,而这种构造环境往往是俯冲盘。
综合以上对构造地质学、岩石学以及古地理学的研究,本文认为华北地块向南俯冲更符合最近揭示的诸多地质事实,所以可以认为,华北地块的南缘印支期是向南俯冲的。
4. 苏鲁造山带造山过程
苏鲁造山带造山过程的研究最为重要也作为核心的应当是确定俯冲极性,而以往的俯冲极性的观点并不能回答现今构造地质学观察、岩石学证据以及地层学解释等,所以基于前述对苏鲁造山带俯冲极性新的认识,对苏鲁造山带的造山过程构建出了一个新模型——南向俯冲的弯山构造,并围绕以下几个问题深入探讨:(1)晚古生代华南地块、华北地块与劳俄古陆、冈瓦纳古陆之间的构造格局。(2)参与造山过程的各个大地块在晚古生代初期,也就是前造山期,所处的相对空间位置;(3)印支期造山期间,古元古代地体是如何进入苏鲁造山带。
4.1 大华南板块
板块重建与还原需要对大量的地质事实进行综合分析,并以这些地质事实为基础才能进行重建[93]。从亲缘性来看,中国南方主要地块大多源自早古生代冈瓦纳古陆的北缘[94, 95],华南地块主要位于澳大利亚西北部,并在早古生代之前,两者之间的相对位置长期保持不变。
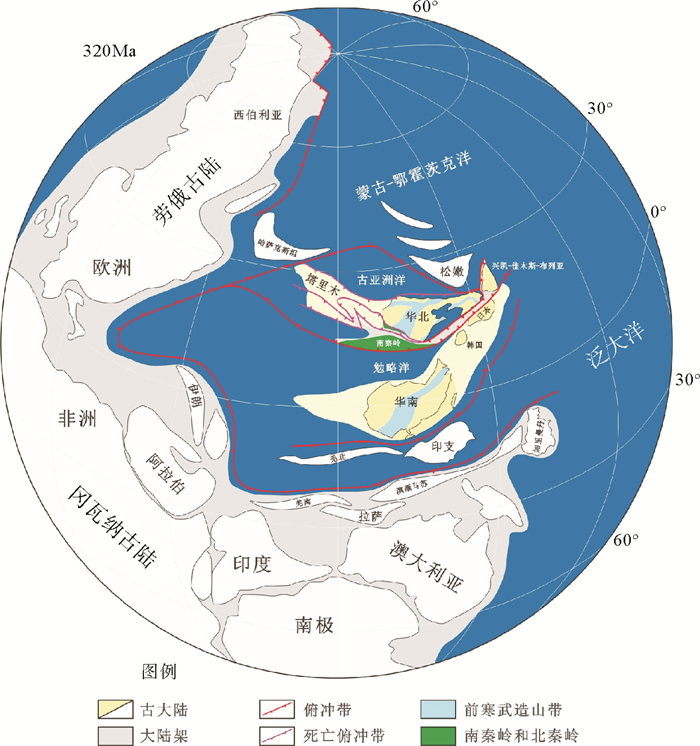
首先从古生物地层学的角度来看,有孔虫类在石炭-二叠纪进入了繁盛期,尤其蜓类的快速演化至二叠纪末全部绝迹,这些特点使得有孔虫蜓类成为指示石炭纪-二叠纪时代的标准化石。而有孔虫蜓类作为一种单细胞生物,其运动能力较差,所以不同种类的蜓其分布范围较为有限,通常来看,同一种类的蜓往往只分布在同一大陆区域相连的大陆架上,而间隔着深海盆地的不同大陆大陆架上不具有对比性,所以有孔虫蜓类的化石可以作为反映石炭纪-二叠纪热带亚热带正常浅海环境的指相化石。Kobayashi [32, 33]围绕华南大陆特有的8种蜓类的分布进行了系统全面的研究,之后还系统的研究了分布在二叠纪特提斯构造域的有孔虫。他发现,这几种蜓类的分布范围主要集中在南秦岭、华南地块、飞弹地体、丹波-美浓地体以及兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块上,这些地块当时都处于浅海陆架环境,种属都具有极强的可对比性(图 1)。
除此之外,依据兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块记录的泛非期构造变形事件与华夏地块记录的加里东期的构造变形事件总体相近[96-98],根据其泛非期构造变形的基底进行板块重建,兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块在早古生代应该位于冈瓦纳古陆靠近澳大利亚的位置,并与华南地块的位置较为接近[99-105]。之后,兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块在晚三叠世-早侏罗世因牡丹江洋的闭合,与松嫩地体发生最后碰撞,并在牡丹江断裂带附近形成了蓝片岩、云母片岩、长英质糜棱岩、超镁铁质岩与少量大理岩交替出现的地质现象[106]。特别是,一些二叠纪以来的岛弧型火山岩主要发育在兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块上,表明西侧的牡丹江洋可能向东俯冲,而不是向西俯冲,尽管还不能排除古太平洋俯冲是否在兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块东侧已经启动。
基于以上观点,可以勾勒出一个范围较传统认识上的华南板块更广泛的大华南板块,该板块的范围包括扬子地块、华夏地块、朝鲜半岛临津江造山带以南的各个地体、日本飞弹地块以及东北兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块(图 4)。
4.2 古特提斯洋的演化
东北亚的演化长期以来大多数研究都归结为两大动力系统:古亚洲洋动力系统和古太平洋动力系统。实际上,按照上述研究,古特提斯洋动力系统在中国东北地区的研究中不容忽视。根据古地磁的资料,在早古生代大华南地块与华北地块的位置都位于南半球中低纬度附近,雁列式分布于冈瓦纳古陆的北缘,空间上两者大体上呈东西向成带展布[107-109]。
依据对古洛南-栾川断裂带糜棱岩以及糜棱状片麻岩中白云母、黑云母的40Ar/39Ar年龄的研究[110],可以知道古洛南-栾川断裂带在深部起始活动的年龄早于~372 Ma。宽坪洋闭合、古洛南-栾川断裂带成为北秦岭微陆块与华北地块的主缝合带,同时开始碰撞、折返,这一系列事件发生在440~400 Ma,所以在秦岭-大别段,华北地块向南俯冲的时间可能在早古生代[111-113]。
晚泥盆世,随着古特提斯洋打开,作为其北部分支的勉略洋也随之打开,大华南地块、华北地块从冈瓦纳古陆裂离,并可能沿着转换断层向劳俄古陆移动[57-63],此时由于各个块体之间的位移,古洛南-栾川断裂、商丹带以及五莲-青岛断裂都表现为明显的右行走滑运动[63],之后华北地块向北漂移,两大地块在石炭纪才逐渐在空间上呈现出南、北展布的构造格局[109](图 4)。此时大华南地块向南秦岭微陆块俯冲,商丹洋逐渐消失,勉略洋也开始自东向西剪刀式闭合,华南与华北地块之间的秦岭-大别微陆块(或南秦岭地块)被向北或向西挤出,导致洛南-栾川断裂表现出右行走滑,而商丹带和五莲-青岛断裂带则表现出左行走滑,同时华北地块开始了向大华南地块的楔入。
4.3 苏鲁造山带碰撞造山的过程
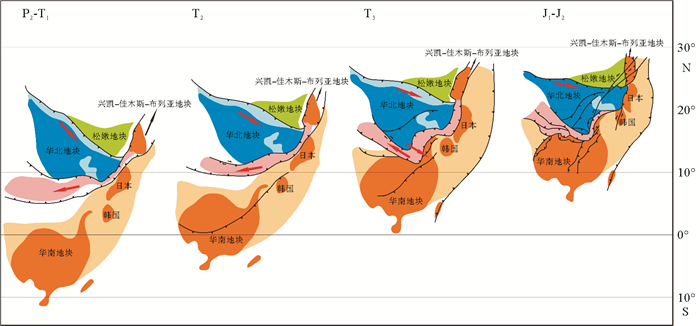
大华南地块与华北地块早古生代期间都与冈瓦纳古陆拼合,并位于其北缘[57-63, 114-120]。结合古地磁的资料[91-93],晚古生代先后裂离冈瓦纳古陆,都向北漂移,印支期秦岭段和苏鲁段分别是华北向华南、华南向华北发生俯冲,并最终拼合,俯冲-碰撞过程如下(图 5):
(1) 晚二叠世开始,随着勉略洋关闭大华南地块向南秦岭地块的俯冲,秦岭段自东向西的剪刀式拼合,秦岭段未俯冲的北秦岭微陆块向西挤出,古洛南-栾川断裂带和商丹带分别表现出右行和左行走滑;而同时随着商丹洋关闭,华北地块向秦岭-大别微陆块(苏鲁段)的俯冲,苏鲁段自南向北的剪刀式拼合,兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块向北逃逸。这期间,商丹洋和勉略洋都表现出某种程度的斜向俯冲。
(2) 早-中三叠世期间,华南地块与华北地块持续向北漂移,两个地块之间的勉略洋逐渐消亡,开始碰撞造山运动。在苏鲁段的造山过程中华北地块向南东俯冲,最终因华北地块向大华南地块的楔入,被俯冲下去的北秦岭微陆块对应岩片和华北地块南缘的古元古代胶辽吉带卷入苏鲁造山带中。
(3) 晚三叠世,随着古太平洋板块向西俯冲的启动,整个东亚地区开始受到来自古太平洋板块的强烈地质作用影响,出现该区最早的NNE向褶皱变形,例如华南的湖南中部、长江中下游等地显示最清楚。晚三叠世-早侏罗世,东北地区的松嫩地块与兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地体拼合,整个原特提斯构造域的北部边缘完全拼贴。同时,导致了向东俯冲的华北地块发生拆沉,出现后造山的花岗岩,并且拆沉的华北板片逐渐向西撕裂,从而使得240~200 Ma的岩浆作用会向西拓展并出现西向年轻化的趋势。而华南地块东侧同期岩浆作用也向西变年轻,但机制与华北不同,是低角度板块平板俯冲的结果[121]。
(4) 燕山期,华北地块再经历深俯冲熔融,在岩浆熔融过程中部分古元古代地质体也发生了熔融,并形成岩浆上涌,这也就导致白垩纪花岗岩中出现部分古元古代继承锆石和地球化学特征。
5. 结论
(1) 华南地块的范围相比传统认识的更为宽广,不仅包括传统认识中的扬子地块、华夏地块,还包含朝鲜半岛的临津江造山带以及洪城杂岩、日本北部的飞弹地体以及中国东北的兴凯-佳木斯-布列亚地块,即大华南地块。
(2) 苏鲁造山带的俯冲及碰撞造山过程,始于沿商丹带华北地块(包括北秦岭地体)印支期朝南东方向向苏鲁-大别-南秦岭微陆块之下发生深俯冲,形成超高压榴辉岩,沿向南东倾的俯冲隧道折返剥露在北部分布;中晚二叠世到早三叠世勉略洋逐渐消亡,自东向西剪刀式闭合,形成兰片岩,沿向北的俯冲隧道折返在南部剥露;之后华北地块与华南地块在苏鲁造山带强烈碰撞,伴随着南秦岭微陆块向西、佳木斯等地块向北的挤出,华北地块强烈楔入作用的同时将大别造山带与苏鲁造山带弯曲、错断,形成巨大的弯山构造。
(3) 在华北地块向南俯冲的过程中一些华北地块的古元古界岩片卷入了上盘的苏鲁造山带中,并一同折返至地表。
-
图 1 中国东部晚古生代—中生代大地构造单元及有孔虫、蜓类分布
(据文献[25-33]编制)断裂名称:F1.五莲-青岛-牟平断裂;F2.嘉山-响水断裂;F3.郯庐断裂;F4.洛南-栾川断裂;F5.商丹带;F6.勉略带;F7.索伦断裂;F8.西拉木伦断裂;F9.贺根山断裂;F10.依兰-伊通断裂;F11.敦化-密山断裂;F12.龙门山断裂;F13.哀牢山-红河断裂;F14.江绍断裂;F15.日本中央断裂;F16.千岛俯冲带;F17.日本俯冲带;F18.琉球俯冲带
Figure 1. Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic tectonic map of East Asia showing the tectonic units and distribution of the foraminifera and the fusulinids
(compiled after [25-33])Faults, sutures and subduction zones: F1.Wulian-Qingdao-Yantai Fault; F2.Jiashan-Xiangshui Fault; F3.Tanlu Fault; F4.Luonan-Luanchuan Fault; F5.Sangdan Suture; F6.Mianlue Suture; F7.Solonker Suture; F8.Xilamulun Fault; F9.Hegenshan Suture; F10.Yilan-Yitong-Fault; F11.Dunhua-Mishan Fault; F12.Longmenshan Fault; F13.Ailaoshan-Red River Fault; F14.Jiangshan-Shaoxing Fault; F15.Central Japan Fault; F16.Kuril Subduction Zone; F17.Japan Subduction Zone; F18.Rykyu Subduction Zone
-
[1] Chen R X, Zheng Y F, Gong B, et al. Origin of retrograde fluid in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks: Constraints from mineral hydrogen isotope and water content changes in eclogite-gneiss transitions in the Sulu orogeny[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(9): 2299-2325. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.02.012
[2] Li S Z, Jahn B M, Zhao S J, et al. Triassic southeastward subduction of North China Block to South China Block: insights from new geological, geophysical and geochemical data[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 166: 270-285, doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.01.009.
[3] Niu Y L, Liu Y, Xue Q Q, et al. Exotic origin of the Chinese continental shelf: new insights into the tectonic evolution of the western Pacific and eastern China since the Mesozoic[J]. Earth Sciences, 2015, 60(18): 1598-1616. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JXTW201518006.htm
[4] Wang J, Chang S C, Lin P J, et al. Evidence of Early Cretaceous transpression in the Sulu orogenic belt, eastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 687: 44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.09.005
[5] 李三忠, 刘鑫, 索艳慧, 等.华北克拉通东部地块和大别—苏鲁造山带印支期褶皱—逆冲构造与动力学背景[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(9): 2031-2049. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200909001 LI Sanzhong, LIU Xin, SUO Yanhui, et al. Triassic folding and thrusting in the Eastern Block of the North China Craton and the Dabie-Sulu orogen and its geodynamics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(9): 2031-2049. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200909001
[6] 李三忠, 王金铎, 刘建忠, 等.鲁西地块中生代构造格局及其形成背景[J].地质学报, 2005, 79(4): 487-497. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.04.006 LI Sanzhong, WANG Jinduo, LIU Jianzhong et al. Mesozoic structure and its tectonic setting in the Western Shandong Block[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(4): 487-497. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.04.006
[7] 索书田, 钟增球, 周汉文, 等.大别-苏鲁超高压和高压变质带构造演化[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 71-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.009 SUO Shutian, ZHONG Zengqiu, ZHOU Hanwen, et al. Tectonic evolution of Dabie-Sulu UHP and HP metamorphic belts, East-Central China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(3): 71-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.009
[8] 吴萍萍, 王椿镛, 丁志峰, 等.大别-苏鲁及邻区上地幔的各向异性[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(8): 2539-2550. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX201208007.htm WU Pingping, WANG Chunyong, DING Zhifeng, et al. Seismic anisotropy of upper mantle beneath the Dabie-Sulu and its adjacent areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(8): 2539-2550. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX201208007.htm
[9] 许志琴, 李源, 梁凤华, 等. "秦岭-大别-苏鲁"造山带中"古特提斯缝合带"的连接[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(4): 671-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.04.001 XV Zhiqin, LI Yuan, LIANG Fenghua, et al. A connection between of the Paleo-Tethys suture zone in the Qinling-Dabie-Sulu Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(4): 671-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.04.001
[10] 杨文采, 胡振远, 程振炎, 等.郯城—涟水综合地球物理剖面[J].地球物理学报, 1999, 42(2): 206-217. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1999.02.008 YANG Wencai, HU Zhenyuan, CHENG Zhenyan, et al. Long profile of Geophysical investigation from Tanchen to Lianshui, East-Central China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1999, 42(2): 206-217. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1999.02.008
[11] 杨文采, 杨午阳, 金振民, 等.苏鲁超高压变质带岩石圈的地震组构[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2004, 34(4): 307-319. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200404002.htm YANG Wencai, Yang Wuyang, Jin Zhenmin, et al. Lithospheric seismic fabrics of Sulu ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt[J]. Science in China: Series D: Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(5): 585-600. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200404002.htm
[12] 郑永飞.超高压变质与大陆碰撞研究进展:以大别-苏鲁造山带为例[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(18): 2129-2152. doi: 10.1016-j.fgb.2010.02.001/ ZHENG Yongfei. A perspective view on ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and continental collision in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(20): 3081-3104. doi: 10.1016-j.fgb.2010.02.001/
[13] Hynes A. Encouraging the extrusion of deep-crustal rocks in collisional zones[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2002, 66(1): 5-24. doi: 10.1180/0026461026610013
[14] Platt J P. Exhumation of high-pressure rocks: a review of concepts and processes[J]. Terra Nova, 1993, 5(2): 119-133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.1993.tb00237.x
[15] Ring U, Laws S, Bernet M. Structural analysis of a complex nappe sequence and late-orogenic basins from the Aegean Island of Samos, Greece[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1999, 21(11): 1575-1601. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(99)00108-X
[16] Ring U, Ratschbacher L, Frisch W, et al. Kinematics of the Alpine plate-margin: structural styles, strain and motion along the Penninic-Austroalpine boundary in the Swiss-Austrian alps[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1989, 146(5): 835-849. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.146.5.0835
[17] Xu Z Q, Wang Q, Tang Z M, et al. Fabric kinematics of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the main borehole of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling Project: implications for continental subduction and exhumation[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 475(2): 235-250. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.02.041
[18] Maruyama S, Liou J G, Zhang R Y. Tectonic evolution of the ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) and high-pressure (HP) metamorphic belts from central China[J]. The Island Arc, 1994, 3(2): 112-121. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.1994.tb00099.x
[19] Wang E, Meng Q R, Burchfiel B C, et al. Mesozoic large-scale lateral extrusion, rotation, and uplift of the Tongbai-Dabie Shan belt in east China[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(4): 307-310. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0307:MLSLER>2.0.CO;2
[20] Ratschbacher L, Franz L, Enkelmann E, et al. The Sino-Korean-Yangtze suture, the Huwan detachment, and the Paleozoic-Tertiary exhumation of (ultra) high-pressure rocks along the Tongbai-Xinxian-Dabie Mountains[C]//Hacker B R, McClelland W C, Liou J G. Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism: Deep Continental Subduction. Geological Society of America Special Papers. Geological Society of America, 2006, 403: 45-75.
[21] Ratschbacher L, Hacker B R, Webb L E, et al. Exhumation of the ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in east central China: cretaceous and Cenozoic unroofing and the Tan-Lu fault[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000, 105(B6): 13303-13338. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900040
[22] Li S Z, Kusky T M, Zhao G C, et al. Two-stage Triassic exhumation of HP-UHP terranes in the western Dabie orogen of China: constraints from structural geology[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 490(3-4): 267-293. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.05.010
[23] Li S Z, Kusky T M, Liu X C, et al. Two-stage collision-related extrusion of the western Dabie HP-UHP metamorphic terranes, central China: evidence from quartz c -axis fabrics and structures[J]. Gondwana Research, 2009, 16(2): 294-309. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.03.003
[24] Li S Z, Kusky T M, Zhao G C, et al. Thermochronological constraints on two-stage extrusion of HP/UHP terranes in the Dabie-Sulu orogen, east-central China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 504(1-4): 25-42. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.01.017
[25] Arakawa Y, Saito Y, Amakawa H. Crustal development of the Hida belt, Japan: Evidence from Nd-Sr isotopic and chemical characteristics of igneous and metamorphic rocks[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328(1-2): 183-204. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00183-9
[26] Wu Y D, Hou Q L. The extension of the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt in Korean Peninsula: based on 40Ar/39Ar Tectonic chronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(10): 3187-3204.
[27] Zhou J B, Wilde S A, Zhang X Z, et al. The onset of Pacific margin accretion in NE China: evidence from the Heilongjiang high-pressure metamorphic belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 478(3-4): 230-246. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.08.009
[28] 唐贤君, 於文辉, 单蕊.中国东部-朝鲜半岛中生代板块结合带划分研究现状与问题[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(5): 606-617. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201005002 TANG Xianjun, YU Wenhui, SHAN Rui. The mesozoic plate boundary in the Eastern China and Korean peninsula: present studies and problems[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(5): 606-617. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201005002
[29] Oh C W. A new concept on tectonic correlation between Korea, China and Japan: histories from the late Proterozoic to Cretaceous[J]. Gondwana Research, 2006, 9(1-2): 47-61. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2005.06.001
[30] Oh C W, Krishnan S, Kim S W, et al. Mangerite magmatism associated with a probable Late-Permian to Triassic Hongseong-Odesan collision belt in South Korea[J]. Gondwana Research, 2006, 9(1-2): 95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2005.06.005
[31] Oh C W, Kim S W, Williams I S. Spinel granulite in Odesan area, South Korea: Tectonic implications for the collision between the North and South China blocks[J]. Lithos, 2006, 92(3-4): 557-575. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.03.051
[32] Kobayashi F. Tethyan uppermost Permian (Dzhulfian and Dorashamian) foraminiferal faunas and their paleogeographic and tectonic implications[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 150(3-4): 279-307. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(99)00011-5
[33] Kobayashi F. Palaeogeographic constraints on the tectonic evolution of the Maizuru Terrane of Southwest Japan to the eastern continental margin of South China during the Permian and Triassic[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2003, 195(3-4): 299-317. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00363-8
[34] 朱光, 朴学峰, 张力, 等.合肥盆地伸展方向的演变及其动力学机制[J].地质论评, 2011, 57(2): 153-166. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201102001 ZHU Guang, PIAO Xuefeng, ZHANG Li, et al. Evolution of extensional direction in the Hefei Basin and its dynamic mechanism[J]. Geological Review, 2011, 57(2): 153-166. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201102001
[35] 胡红雷, 朱光.苏北地区前陆变形特征与形成机制[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(3): 366-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2013.03.002 HU Honglei, ZHU Guang. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the foreland deformation in the Subei region[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2013, 37(3): 366-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2013.03.002
[36] Fan W M, Guo F, Wang Y J, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the northern Huaiyang tectono-magmatic belt, central China: partial melts from a lithospheric mantle with subducted continental crust relicts beneath the Dabie orogen[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 209(1-2): 27-48. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.04.020
[37] 徐扬, 冯岩, 李日辉.胶北地块前寒武纪基底研究新进展[J].现代地质, 2011, 25(5): 965-974. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.05.017 XU Yang, FENG Yan, LI Rihui. Main progresses in the study of Precambrian Basement of Jiaobei Terrane, Eastern China[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(5): 965-974. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.05.017
[38] 孔凡梅, 刘云, 李旭平, 等.胶北地块变质基底超镁铁岩的矿物岩石地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(6): 1549-1563. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201506005 KONG Fanmei, LIU Yun, LI Xuping, et al. Mineralogical and Petrogeochemical characteristics of ultramafic rocks from the metamorphic basement of the Jiaobei terrane[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(6): 1549-1563. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201506005
[39] 刘平华, 刘福来, 王舫, 等.胶北地体多期变质事件的P-T-t轨迹及其对胶-辽-吉带形成与演化的制约[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 2889-2941. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201510005 LIU Pinghua, LIU Fulai, WANG Fang, et al. P-T-t paths of the multiple metamorphic events of the Jiaobei terrane in the southeastern segment of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt (JLJB), in the North China Craton: impication for formation and evolution of the JLJB[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(10): 2889-2941. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201510005
[40] 刘建辉, 刘福来, 丁正江, 等.胶北地体早前寒武纪重大岩浆事件、陆壳增生及演化[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 2942-2958. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201510006 LIU Jianhui, LIU Fulai, DING Zhengjiang, et al. Early Precambrian major magmatic events, and growth and evolution of continental crust in the Jiaobei terrane, North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(10): 2942-2958. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201510006
[41] 张岳桥, 李金良, 张田, 等.胶莱盆地及其邻区白垩纪-古新世沉积构造演化历史及其区域动力学意义[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(9): 1229-1257. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.09.007 ZHANG Yueqiao, LI Jinliang, ZHANG Tian, et al. Cretaceous to paleocene tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Jiaolai basin and the contiguous areas of the Shandong peninsula (North China) and its geodynamic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(9): 1229-1257. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.09.007
[42] 耿科, 王瑞江, 李洪奎, 等.山东省麻粒岩与麻粒岩相变质作用——研究现状及对前寒武纪大地构造演化的启示[J].地质论评, 2016, 62(1): 153-170. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201601014 GENG Ke, WANG Ruijiang, LI Hongkui, et al. Granulite and granulite facies metamorphism in Shandong Province——research status and implications to Precambrian geotectonic evolution[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(1): 153-170. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201601014
[43] 郝天珧, SUH M, 刘建华, 等.黄海深部结构与中朝-扬子块体结合带在海区位置的地球物理研究[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 51-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.007 HAO Tianyao, SUH M, LIU Jianhua, et al. Deep structure and boundary belt position between Sino-Korean and Yangtze blocks in Yellow Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(3): 51-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.007
[44] 李楠.南黄海盆地北部坳陷构造演化及沉积相研究[D].国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2010. LI Nan. Research on structural evolution and sedimentary facies in North Depression of South Yellow Sea Basin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2010.
[45] 王振鸿, 胡明毅, 汤济广, 等.南黄海盆地南部坳陷晚白垩世-第四纪构造演化对油气的控制[J].化工矿产地质, 2014, 36(3): 129-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2014.03.001 WANG Zhenhong, HU Mingyi, YANG Jiguang, et al. Control on petroleum by tectonic evolution of the late Cretaceous-Quaternary in the South Depression of the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2014, 36(3): 129-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2014.03.001
[46] 曾洁.南黄海盆地北部坳陷中生代沉积相研究[D].中国科学院海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2013. ZENG Jie. Research on sedimentary fades of Mesozoic in North Depression of South Yellow Sea Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of the Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013.
[47] 岳保静, 廖晶, 刘鸿, 等.中朝-扬子板块碰撞结合带东部边界及海域延伸[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1): 75-85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201401009 YU Baojing, LIAO Jing, LIU Hong, et al. East boundary of the collision belt between Sino-Korean and Yangtze Plates in Eastern China and their extension in the sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(1): 75-85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201401009
[48] 田振兴.北黄海盆地断裂特征及其深部构造研究[D].中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2005. TIAN Zhenxing. The disquisition on fracture character and deep-level Geological structure in the North Yellow Sea Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2005.
[49] Shu L S, Yin H W, Faure M, et al. Mesozoic intracontinental underthrust in the SE margin of the North China Block: insights from the Xu-Huai thrust-and-fold belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 141: 161-173, doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.08.020.
[50] 舒良树, 吴俊奇, 刘道忠.徐宿地区推覆构造[J].南京大学学报, 1994, 30(4): 638-647. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0469-5097.1994.04.001 SHU Liangshu, WU Junqi, LIU Daozhong. Thrust tectonics of Xuzhou-Suzhou Region, Eastern China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences Edition, 1994, 30(4): 638-647. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0469-5097.1994.04.001
[51] 王鹏程, 赵淑娟, 李三忠, 等.长江中下游南部逆冲变形样式及其机制[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(1): 230-244. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201501017 WANG Pengcheng, ZHAO Shujuan, LI Sanzhong, et al. The styles and dynamics of thrust in the south of the Middle-Lower Yangtze River area, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(1): 230-244. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201501017
[52] Zhou J B, Wilde S A, Zhao G C, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Wulian complex: Defining the boundary between the North and South China Cratons in the Sulu Orogenic Belt, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 162(3-4): 559-576. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.10.008
[53] Zhu G, Jiang D Z, Zhang B L, et al. Destruction of the eastern North China Craton in a backarc setting: evidence from crustal deformation kinematics[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(1): 86-103. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.08.005
[54] Liu X C, Jahn B M, Liu D Y, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of a metagabbro and eclogites from western Dabieshan (Hong'an block), China, and its tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 394(3-4): 171-192. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2004.08.004
[55] Liu X C, Wei C J, Li S Z, et al. Thermobaric structure of a traverse across western Dabieshan: implications for collision tectonics between the Sino-Korean and Yangtze cratons[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2004, 22(4): 361-379. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2004.00519.x
[56] Meng Q R, Zhang G W. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 323(3-4): 183-196. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00106-2
[57] 李三忠, 杨朝, 赵淑娟, 等.全球早古生代造山带(Ⅰ):碰撞型造山[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2016, 46(4): 945-967. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604003.htm LI Sanzhong, YANG Zhao, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Global Early Paleozoic Orogens (Ⅰ): collision-type orogeny[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(4): 945-967. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604003.htm
[58] 李三忠, 杨朝, 赵淑娟, 等.全球早古生代造山带(Ⅱ):俯冲-增生型造山[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2016, 46(4): 968-1004. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604002.htm LI Sanzhong, YANG Zhao, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Global Early Paleozoic Orogens (Ⅱ): subduction-accretionary-type orogeny[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(4): 968-1004. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604002.htm
[59] 李三忠, 李玺瑶, 赵淑娟, 等.全球早古生代造山带(Ⅲ):华南陆内造山[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2016, 46(4): 1005-1025. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604003.htm LI Sanzhong, LI Xiyao, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Global Early Paleozoic Orogens (Ⅲ): intracontinental orogen in South China[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(4): 1005-1025. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604003.htm
[60] 李三忠, 杨朝, 赵淑娟, 等.全球早古生代造山带(Ⅳ):板块重建与Carolina超大陆[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2016, 46(4): 1026-1041. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604004.htm LI Sanzhong, YANG Zhao, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Global Early Paleozoic Orogens (Ⅳ): plate reconstruction and supercontinent Carolina[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(4): 1026-1041. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201604004.htm
[61] 李三忠, 赵淑娟, 李玺瑶, 等.东亚原特提斯洋(Ⅰ):南北边界和俯冲极性[J].岩石学报, 2012, 32(9): 2609-2627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201609002.htm LI Sanzhong, ZHAO Shujuan, LI Xiyao, et al. Proto-Tehtys Ocean in East Asia (I): northern and southern border faults and subduction polarity[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 32(9): 2609-2627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201609002.htm
[62] 李三忠, 赵淑娟, 余珊, 等.东亚原特提斯洋(Ⅱ):早古生代微陆块亲缘性与聚合[J].岩石学报, 2012, 32(9): 2628-2644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201609003.htm LI Sanzhong, ZHAO Shujuan, YU Shan, et al. Proto-Tehtys Ocean in East Asia (Ⅱ): affinity and assmbly of Early Paleozoic micro-continental blocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 32(9): 2628-2644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201609003.htm
[63] 赵淑娟, 李三忠, 余珊, 等.东亚原特提斯洋(Ⅲ):北秦岭韧性剪切带构造特征[J].岩石学报, 2012, 32(9): 2645-2655. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201609004.htm ZHAO Shujuan, LI Sanzhong, YU Shan, et al. Proto-Tethys Ocean in East Asia (Ⅲ): structures of ductile shear zones in the North Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 32(9): 2645-2655. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201609004.htm
[64] 李三忠, 余珊, 赵淑娟, 等.东亚大陆边缘的板块重建与构造转换[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(3): 65-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201303008 LI Sanzhong, YU Shan, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Tectonic transition and plate reconstructions of the East Asian continental magin[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(3): 65-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201303008
[65] Liu X C, Jahn B M, Cui J J, et al. Triassic retrograded eclogites and Cretaceous gneissic granites in the Tongbai Complex, central China: implications for the architecture of the HP/UHP Tongbai-Dabie-Sulu collision zone[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(3-4): 211-237. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.06.005
[66] 徐扬, 杨坤光, 李日辉, 等.北苏鲁超高压变质带前寒武纪基底研究新进展[J].现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 248-259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.002 XU Yang, YANG Kunguang, LI Rihui, et al. Main progresses in the study of Precambrian basement of the north Sulu ultra-high pressure metamorphic belt, Eastern China[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(2): 248-259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.002
[67] 刘利双, 刘福来, 刘平华, 等.苏鲁超高压变质带中海阳所地区变基性岩的地球化学性质及变质演化特征[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 2863-2888. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201510004 LIU Lishuang, LIU Fulai, LIU Pinghua, et al. Geochemical characteristics and metamorphic evolution of meta-mafic rocks from Haiyangsuo area, Sulu ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(10): 2863-2888. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201510004
[68] 宋明春, 王沛成.山东省区域地质[M].山东:山东省地图出版社, 2003. SONG Mingchun, WANG Peicheng. Regional Geology of Shandong Province[M]. Shandong: Shandong Cartographic Publishing House, 2003.
[69] 宋明春, 马文斌.胶南隆起北缘石门-薛家庄韧性剪切带[J].山东地质, 1997, 13(1): 77-84. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDDI199701007.htm SONG Mingchun, MA Wenbin. Shimen-Xuejiazhuang ductile shear belt in the North Margin of Jiaonan uplift[J]. Shandong Geology, 1997, 13(1): 77-84. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDDI199701007.htm
[70] 顾德林, 张长厚, 陈建强, 等.胶南隆起北部地质构造特征及其演化[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996: 1-9. GU Delin, ZHANG Changhou, CHEN Jianqiang, et al. The Geological and Tectonic Evolution of the Northern of the Jiaonan Uplift, Southeastern Shandong Province[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1996: 1-9.
[71] Li S Z, Zhao G C, Dai L M, et al. Mesozoic basins in eastern China and their bearing on the deconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47: 64-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.008
[72] Liu F L, Wang F, Liou J G, et al. Mid-Late Triassic metamorphic event for Changhai meta-sedimentary rocks from the SE Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton: evidence from monazite U-Th-Pb and muscovite Ar-Ar dating[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 94: 205-225. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.05.001
[73] 李三忠, 刘建忠, 赵国春, 等.华北克拉通东部地块中生代变形的关键时限及其对构造的制约——以胶辽地区为例[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(3): 633-646. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200403027 LI Sanzhong, LIU Jianzhong, ZHAO Guochun, et al. Key geochronology of Mesozoic deformation in the eastern block of the North China Carton and its constraints on regional tectonics: a case of Jiaodong and Liaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20(3): 633-646. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200403027
[74] 李三忠, 刘永江, 杨振升.辽吉地区古元古代造山作用的大陆动力学过程及其壳内响应[J].地球物理学报, 1998, 41(S): 142-152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX1998S1015.htm LI Sanzhong, LIU Yongjiang, YANG Zhensheng. Intracrustal response to continental dynamic processes of the Paleoproterozoic orogeny in Liao-Ji area[J]. Acta Geophysica of Sinica, 1998, 41(S): 142-152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX1998S1015.htm
[75] 刘福来, 刘平华, 王舫, 等.胶-辽-吉古元古代造山/活动带巨量变沉积岩系的研究进展[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 2816-2846. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201510002 LIU Fulai, LIU Pinghua, WANG Fang, et al. Progresses and overviews of voluminous meta-sedimentary series within the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic/mobile belt, North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(10): 2816-2846. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201510002
[76] Jahn B M, Rumble D, Liou J G. Geochemistry and isotope tracer study of UHP metamorphic rocks[M]//Carswell D A, Compagnoni R. Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphism. EMU Notes in Mineralogy Series. Mineralogical Society of America, 2003: 365-414.
[77] Jahn B M, Chen B. Dabieshan UHP metamorphic terrane: Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic Constraint to Pre-metamorphic Subduction Polarity[J]. International Geology Review, 2007, 49(1): 14-29. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.49.1.14
[78] Bryant D L, Ayers J C, Gao S, et al. Geochemical, age, and isotopic constraints on the location of the Sino-Korean/Yangtze Suture and evolution of the Northern Dabie Complex, east central China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2004, 116(5): 698-717. doi: 10.1130/B25302.2
[79] Huang J, Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F, et al. Melting of subducted continent: element and isotopic evidence for a genetic relationship between Neoproterozoic and Mesozoic granitoids in the Sulu orogen[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 229(4): 227-256. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.11.007
[80] Liu S, Hu R Z, Gao S, et al. U-Pb zircon age, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of alkaline intrusions and associated mafic dikes from Sulu orogenic belt, eastern China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 106(3-4): 365-379. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2008.09.004
[81] Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. Early Cretaceous adakitic granites in the Northern Dabie Complex, central China: implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(10): 2609-2636. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.008
[82] Xu H J, Ma C Q, Ye K. Early cretaceous granitoids and their implications for the collapse of the Dabie orogen, eastern China: SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 240(3-4): 238-259. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.02.018
[83] Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure orogenic belt, east China and their relationship to lithospheric thinning[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 222(3-4): 200-231. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.07.006
[84] Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. Zircon isotope evidence for recycling of subducted continental crust in post-collisional granitoids from the Dabie terrane in China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(22): L22602. doi: 10.1029-2004GL021061/
[85] Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. Post-collisional granitoids from the Dabie orogen in China: zircon U-Pb age, element and O isotope evidence for recycling of subducted continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2007, 93(3-4): 248-272. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.03.067
[86] 郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, 等.苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞-碰撞后构造过程:锆石U-Pb年代学[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200504025 GUO Jinghui, CHEN Fukun, ZHANG Xiaoman, et al. Evolution of syn-to post-collisional magmatism from north Sulu UHP belt, eastern China: zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200504025
[87] 赵子福, 郑永飞.俯冲大陆岩石圈重熔:大别-苏鲁造山带中生代岩浆岩成因[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2009, 39(7): 888-909. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200907004.htm ZHAO Zifu, ZHENG Yongfei. Remelting of subducted continental lithosphere: Petrogenesis of Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2009, 39(7): 888-909. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200907004.htm
[88] 陈世悦, 刘焕杰.华北地台东部石炭-二叠纪岩相古地理特征[J].中国区域地质, 1997, 16(4): 379-386. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD704.005.htm CHEN Shiyue, LIU Huanjie. Carboniferous-Permian lithofacies and paleogeography in the eastern part of the North China Platform[J]. Regional Geology of China, 1997, 16(4): 379-386. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD704.005.htm
[89] 陈世悦, 刘焕杰.华北石炭-二叠纪层序地层格架及其特征[J].沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 63-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.1999.01.010 CHEN Shiyue, LIU Huanjie. Sequence stratigraphic framework and its characteristics of the carboniferous-Permian in North China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1): 63-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.1999.01.010
[90] 吕大炜, 李增学, 刘海燕, 等.华北晚古生代海平面变化及其层序地层响应[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(5): 1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.05.012 LV Dawei, LI Zengxue, LIU Haiyan, et al. The sea-level change and its response to the Late Paleozoic sequence stratigraphy in North China[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(5): 1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.05.012
[91] 邵龙义, 董大啸, 李明培, 等.华北石炭-二叠纪层序-古地理及聚煤规律[J].煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8): 1725-1734. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201408045 SHAO Longyi, DONG Daxiao, LI Mingpei, et al. Sequence-paleogeography and coal accumulation of the Carboniferous-Permian in the North China Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8): 1725-1734. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201408045
[92] 张开均.华北板块东缘晚古生代火山活动及其大地构造含义[J].中国煤田地质, 1998, 10(3): 11-12, 20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGMT803.002.htm ZHANG Kaijun. Late andesitic volcanism of Late Palacozoic era along the eastern margin of North China Plate and its tectonic implications[J]. Coal Geology of China, 1998, 10(3): 11-12, 20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGMT803.002.htm
[93] Yu S, Li S Z, Zhao S J, et al. Long history of a Grenville orogen relic-The North Qinling terrane: evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt from Rodinia to Gondwana[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 271: 98-117. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.09.020
[94] Cao H H, Li S Z, Zhao S J, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of Neoproterozoic to early Paleozoic sedimentary rocks in the North Qinling Orogenic Belt: implications for the tectonic evolution of the Kuanping Ocean[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 279: 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.04.001
[95] Sun W J, Li S Z, Liu X, et al. Deep structures and surface boundaries among Proto-Tethyan micro-blocks: Constraints from seismic tomography and aeromagnetic anomalies in the Central China Orogen[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 659: 109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.07.033
[96] Wilde S A, Dorsett-Bain H L, Liu J L. The identification of a Late Pan-African granulite facies event in northeastern China: SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Mashan Group at Liu Mao, Heilongjiang Province, China[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Geological Congress: Precambrian Geology and Metamorphic Petrology, VSP International. Vol. 17. Amsterdam: VSP International Science Publishers, 1997: 59-74.
[97] Wilde S A, Zhang X Z, Wu F Y. Extension of a newly identified 500 Ma metamorphic terrane in North East China: further U-Pb SHRIMP dating of the Mashan Complex, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328(1-2): 115-130. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00180-3
[98] Wilde S A, Wu F Y, Zhang X Z. Late Pan-African magmatism in Northeastern China: SHRIMP U-Pb zircon evidence from granitoids in the Jiamusi Massif[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122(1-4): 311-327. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00217-6
[99] Cocks L R M, Torsvik T H. The dynamic evolution of the Palaeozoic geography of eastern Asia[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 117: 40-79. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.12.001
[100] Han G Q, Liu Y J, Neubauer F, et al. Provenance analysis of Permian sandstones in the central and southern Da Xing'an Mountains, China: constraints on the evolution of the eastern segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 580: 100-113. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.08.041
[101] Shu L S, Wang B, Cawood P A, et al. Early Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic intraplate tectonic and magmatic events in the Cathaysia Block, South China[J]. Tectonics, 2015, 34(8): 1600-1621. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003835
[102] Zhou J B, Wilde S A, Zhang X Z, et al. The onset of Pacific margin accretion in NE China: Evidence from the Heilongjiang high-pressure metamorphic belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 478(3-4): 230-246. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.08.009
[103] Zhou J B, Wilde S A, Zhao G C, et al. New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages from the Heilongjiang high-pressure belt: constraints on the Mesozoic evolution of NE China[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310(9): 1024-1053. doi: 10.2475/09.2010.10
[104] 周建波, 曾维顺, 曹嘉麟, 等.中国东北地区的构造格局与演化:从500 Ma到180 Ma[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(5): 1298-1316, 1329. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz200905002 ZHOU Jianbo, ZENG Weishun, CAO Jialin, et al. The tectonic framework and evolution of the NE China: from~500 Ma to~180 Ma[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(5): 1298-1316, 1329. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz200905002
[105] 周建波, 张兴洲, WILDE S A, 等.黑龙江杂岩的碎屑锆石年代学及其大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(8): 1924-1936. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200908017 ZHOU Jianbo, ZHANG Xingzhou, WILDE S A, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of Heilongjiang complex and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(8): 1924-1936. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200908017
[106] 李伟民, 刘永江, TAKASU A, et al.黑龙江依兰地区蓝片岩的变质演化P - T - t轨迹[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(10): 3085-3099. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201410022 LI Weimin, LIU Yongjiang, TAKASU A, et al. Pressure (P)-temperature (T)-time (t) paths of the blueschists from the Yilan area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(10): 3085-3099. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201410022
[107] 黄宝春, 周秀, 朱日祥.从古地磁研究看中国大陆形成与演化过程[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(3): 348-359. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.03.031 HUANG Baochun, ZHOU Xiu, ZHU Rixiang. Discussions on Phanerozoic evolution and formation of continental China, based on paleomagnetic studies[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(3): 348-359. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.03.031
[108] 黄宝春, 朱日祥, Otofuji Y, 等.华北等中国主要地块早古生代早期古地理位置探讨[J].科学通报, 2000, 45(4): 337-345. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb200004001 HUANG Baochun, ZHU Rixiang, Otofugi Y, et al. The Early Paleozoic paleogeography of the North China block and the other major blocks of China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(12):1057-1065. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb200004001
[109] 翟永建, 周烑秀.华南和华北陆块显生宙的古地磁及构造演化[J].地球物理学报, 1989, 32(3): 292-307. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1989.03.006 ZHAI Yongjian, ZHOU Yaoxiu. Paleomagnetism and tectonic evolutions of North and South China Blocks since the Phanerozoic[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 1989, 32(3): 292-307. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1989.03.006
[110] Dong Y P, Genser J, Neubauer F, et al. U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the exhumation history of the North Qinling terrane, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(4): 881-893. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.09.007
[111] 宋传中, 张国伟, 任升莲, 等.秦岭-大别造山带中几条重要构造带的特征及其意义[J].西北大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 39(3): 368-380. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBDZ200903006.htm SONG Chuanzhong, ZHANG Guowei, REN Shenglian, et al. The research on deformation features of some structural zones in the Qinling-Dabieshan orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 39(3): 368-380. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBDZ200903006.htm
[112] 宋传中, 张国伟, 王勇生, 等.秦岭洛南-栾川构造带的变形分解与年代学制约[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2009, 39(2): 144-156. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200902002.htm SONG Chuanzhong, ZHANG Guowei, WANG Yongsheng, et al. The constraints of strain partitioning and geochronology in Luonan-Luanchuan tectonic belts on Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2009, 52(3): 300-312. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200902002.htm
[113] Zhao S J, Li S Z, Liu X, et al. 2015. The northern boundary of the Proto-Tethys Ocean: Constraints from structural analysis and U-Pb zircon geochronology of the North Qinling Terrane[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 560-574. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.09.005
[114] Xiao W J, Huang B C, Han C M, et al. A review of the western part of the Altaids: a key to understanding the architecture of accretionary orogens[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 18(2-3): 253-273. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.01.007
[115] 聂仕琪. 1050~410 Ma全球板块重建: 中国三大地块的洋陆格局及区域构造演化[D].中国科学技术大学硕士学位论文, 2015. NIE Shiqi. 1050~410 Ma Global Plate Reconstruction: ocean-continental framework and the tectonic history of the three stable blocks in China[D]. Master Dissertation of University of Science and Technology of China, 2015.
[116] 余珊.全球背景下中国华北与华南板块重建: 从Rodinia裂解到Gondwana形成[D].中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2015. YU Shan. Plate reconstruction of the North and South China blocks under the global background: from the break-up of Rodinia to the formation of Gondwana[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2015.
[117] 李三忠, 余珊, 赵淑娟, 等.超大陆旋回与全球板块重建趋势[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(1): 51-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201501006 LI Sanzhong, YU Shan, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Perspectives of supercontinent cycle and global plate reconstruction[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(1): 51-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201501006
[118] 李三忠, 余珊, 赵淑娟, 等.超大陆与全球板块重建派别[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 34(6): 97-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201406009 LI Sanzhong, YU Shan, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Schools of thought on supercontinent and global plate reconstruction[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2015, 34(6): 97-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201406009
[119] 李曙光.论华北与扬子陆块的碰撞时代——同位素年代学方法的原理及应用[J].安徽地质, 1992, 2(4): 13-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHDZ199204001.htm LI Shuguang. On the Time of Collision between the North China and Yangtze Continental segments-the principle and application of isotope chronology[J]. Geology of Anhui, 1992, 2(4): 13-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHDZ199204001.htm
[120] Li S Z, Zhao S J, Liu X, et al. Closure of the proto-Tethys ocean and early Paleozoic amalgamation of microcontinental blocks in East Asia[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.01.011.
[121] Li Z X, Li X H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: a flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(2): 179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1



 下载:
下载: