UNDRAINED SHEAR STRENGTH ESTIMATION OF THE COVER LAYER OF HYDRATE AT SITE W18/19 OF SHENHU AREA
-
摘要: 天然气水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度是水合物试采过程中导管喷射设计、地层沉降和井壁稳定性分析的关键参数。孔压静力触探(CPTU)为地层强度参数纵向分布规律研究提供了有效途径。本文基于南海北部神狐海域W18/19站位水合物上覆层的CPTU测试结果和室内实验数据,建立了该区经验锥头系数的确定方法,并基于确定的经验锥头系数求解上覆层不排水抗剪强度。结果表明:W18/19站位水合物上覆层由上至下为强度逐渐增大的钙质黏土,基于总锥尖阻力、有效锥尖阻力、超孔隙压力求解钙质黏土不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数分别为13.8、4.2、14.4。水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度随着深度的增加逐渐增大。基于CPTU建立的不排水抗剪强度计算方法能反映钙质黏土不排水抗剪强度的纵向分布规律。Abstract: Undrained shear strength of the cover layer of hydrate is the most important engineering parameter for conductor jetting design, strata settlement and well stability analysis during gas hydrate production test. The piezocone penetration test (CPTU) could provide effective data to understand the vertical change of undrained shear strength from seabed to hydrate bearing layer. In this paper, we conducted CPTU and corresponding laboratory test at site W18/19 of the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea. Based on the data, the estimation method of cone factor was developed to calculate the undrained shear strength. The result shows that the cover layer of hydrate is mainly consist of calcareous clay and the soil strength becomes harder with the increase in depth. The cone factors calculated from total cone tip resistance, effective cone tip resistance and excess pore pressure is 13.8, 4.2 and 14.4 respectively. Based on the CPTU data, the developed method was used to calculate the vertical change in undrained shear strength, which increases with depth within the W18/19 cover layer of hydrate.
-
天然气水合物广泛分布于陆地永久冻土带与大陆边缘海底,其中海洋水合物资源量保守估计高于陆地永久冻土带两个数量级[1]。2007年和2015年,我国在南海北部陆坡神狐海域开展天然气水合物钻探,发现了超过1 500亿m3天然气当量的水合物矿藏[2, 3]。了解该区工程地质特征,准确预测天然气水合物储层的上覆地层(简称:水合物上覆层)不排水抗剪强度参数对于井口稳定性、井壁稳定性、喷射隔水管承载力分析等至关重要[4]。
目前,确定岩土不排水抗剪强度的方法大致可分为室内实验和现场原位测试两大类[5-12]。利用孔压静力触探(CPTU)测试可以实时记录探头在岩土中静力压入时的锥尖阻力、侧摩阻力、孔隙水压力等参数,进而计算岩土的不排水抗剪强度,可为深海工程评价提供简单、经济的评价手段。国内外以往研究提出了大量基于CPTU测试结果的不排水抗剪强度计算方法,主要可分为理论方法和经验方法两类[9-16]。其中理论方法为经验公式的建立提供了依据,但它们一般基于一定的假设条件提出,在模拟不同应力历史条件下的土性、土的各向异性、灵敏度、地质年代等方面具有较大的局限性[13-16]。经验公式法是利用数理统计的方法建立锥尖阻力、侧摩阻力或孔隙水压力与不排水抗剪强度之间的各种相关关系。目前,文献中可见的基于CPTU数据估算不排水抗剪强度的经验方法主要包括根据总锥尖阻力估算、有效锥尖阻力估算和超孔隙压力值估算等3种,3种方法估算不排水抗剪强度的基本表达式分别为式(1)—式(3)[17-20]:
$$ {{S}_{u1}}=\frac{{{q}_{t}}-{{\sigma }_{v0}}}{{{N}_{kt}}} $$ (1) $$ {{S}_{u2}}=\frac{{{q}_{t}}-{{u}_{2}}}{{{N}_{kt}}} $$ (2) $$ {{S}_{u3}}=\frac{{{u}_{2}}-{{u}_{0}}}{{{N}_{\Delta u}}} $$ (3) 式中,Su1、Su2、Su3分别为根据总锥尖阻力、有效锥尖阻力和超孔隙压力值计算得到的土层不排水抗剪强度值(kPa);qt是校准后的锥尖阻力(kPa);σv0为总的上覆压力(包括水压)(kPa);u2是锥面测得的孔隙水压(kPa);u0为静水压力(kPa)。Nkt、Nke、NΔu分别为根据总锥尖阻力、有效锥尖阻力和超孔隙压力值计算不排水抗剪强度值时的锥头经验系数。
经验公式法的特点是简单易行,但不同经验公式中的经验系数具有很强的区域特性。国内陆域静力触探大多以单桥静力触探、双桥静力触探为主,不同文献中对各锥头经验系数进行了大量的反算,也得到了部分研究区锥头经验系数的推荐值。但由于各研究区差异较大,少见专门针对深海地层尤其是针对南海北部水合物赋存区孔压静力触探经验参数的研究[21-22],已有陆域的研究经验系数对海域天然气水合物试采区岩土不排水抗剪强度的适应性无法得到保障。
针对海域天然气水合物试采工程需求,利用井下孔压静力触探(Down-hole CPTU)测试仪对南海北部神狐W18/19站位水合物上覆层进行了系统测试。本文将根据W18/19站位的CPTU实测数据,并结合电动十字板、微型手动十字板、袖珍贯入仪和不固结不排水剪切等室内实验手段,拟合得到基于CPTU数据测算土层不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数,并利用拟合结果分析W18/19站位的土层不排水抗剪强度纵向分布规律。
1. 区域地质背景
神狐海域位于南海北部陆缘的中段(西沙海槽与东沙群岛之间海域),是欧亚板块、太平洋板块和印度-澳大利亚板块交汇处的一部分,经历了由板内裂陷演变为边缘坳陷的过程[23, 24]。新生代沉积厚度达1 000~7 000 m,沉积速率为40~120 cm/ka[24],有机碳含量为0.46%~1.9%[25, 26],具有较大的生烃潜力和有利的天然气水合物形成条件[27, 28]。由于受到北东、北东东、东西、北西方向的断裂控制,南海北部陆坡的海底地形呈阶梯状逐级下降,在陆坡上发育有深海槽、海底高原、陆坡台地、海底陡崖、陡坡和海谷海丘等各种特殊构造地貌或地质体。
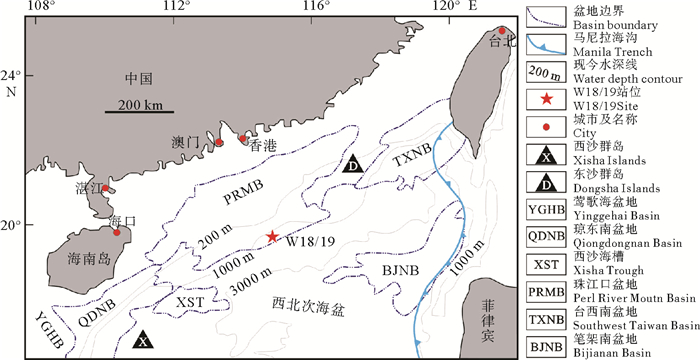
W18/19站位位于珠江口盆地珠二坳陷白云凹陷(图 1),该区处于南海北部陆坡的前端,海底地形起伏变化较大,总体趋势表现为由北西向南东倾斜,以700和1 500 m左右水深线为界,水深线700 m以北和水深线1 500 m以南地区,海底等深线相对稀疏,地形较为平缓;水深线700~1 500 m之间的区域,地形较陡。W18/19站位水深约1 272 m,水合物埋深为133~162 m,富集层段厚度为20~30 m,水合物饱和度可达64%[2]。该站位主要发育两种类型的沉积相,一种是浅层的半远洋沉积,以细粒的黏土或粉砂质黏土为主;另一种为天然堤沉积,以细粒的粉砂质黏土为主,可见黏土质粉砂或粉砂岩层。
2. 水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度估算
2.1 CPTU测试曲线及基本地质特征
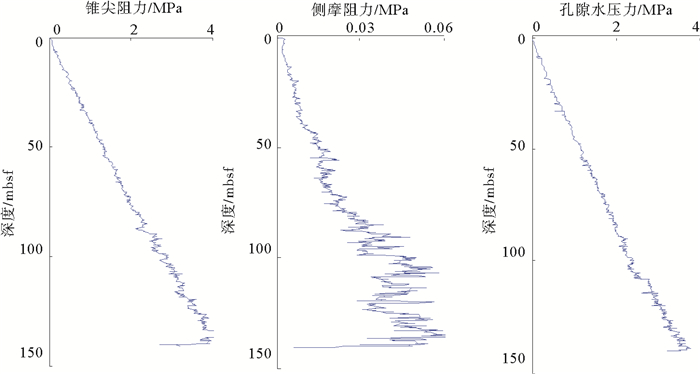
本次测试采用荷兰Fugro公司设计的WISON®(EP)系统。该系统采用10 cm2截面积、60°锥头和150 cm2摩擦筒组成的Fugro标准探头,该探头可测锥尖阻力qc、侧摩阻力fs和孔隙水压力u。测试过程中,首先用钻机清除孔内泥屑,然后以20 mm/sec的速度将探头压入地层,单次探头行程为3 m。本次在W18/19站位进行一个全井段井下CPTU测试和临近井的全井段地质取样工作。CPTU测试深度达141 mbsf。典型CPTU测试结果如图 2所示。
由图 2可知,W18/19站位CPTU测试过程中全井段锥尖阻力、孔隙压力线性规律比较明显,说明该站位纵向上土类分布较为一致,侧摩阻力在深度小于50 mbsf范围内波动较小,当深度大于50 mbsf后,波动明显增大,说明虽然该站位土类别一致,但自上而下土层压实程度不同,尤其是下部地层可能存在严重的软-硬层交互,随着深度的加深,土层强度呈现“迂回上升”现象。根据美国试验及材料协会规范2000版中对土类的判别,实际临井地质取样结果证实,W18/19站位水合物上覆层从上到下依次分布为非常软的钙质黏土、软钙质黏土、稍硬的钙质黏土、硬钙质黏土、非常硬的钙质黏土,但这些层之间并不存在特别明显的土层转化界面,而是逐渐的由软质向硬质过渡,且下部层位呈现出明显的硬-非常硬层的交互。
2.2 经验锥头系数的确定
由于土层的不排水抗剪强度不是一个固定的单值参数,主要取决于土的破坏模式、土的各向异性、应变速率和应力历史[19],因此,不同的实验方法获取到的不排水抗剪强度间存在一定的差异,在估算锥头系数时,需说明是基于哪种类型的室内实验结果进行估算。本次测试主要应用室内袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板、和不固结不排水剪切实验对W18/19站位的样品进行力学参数分析。以下将基于袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板、和不固结不排水剪切室内实验结果,分别反演利用总锥尖阻力、有效锥尖阻力和超孔隙压力值计算不排水抗剪强度值时的锥头经验系数,然后用该反演结果计算水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度。
2.2.1 根据总锥尖阻力计算强度参数的锥头系数
由式(1)可知,基于总锥尖阻力求解土层不排水抗剪强度,首先需要确定上覆土压力。本文根据土比重的测量结果按深度积分求解上覆土应力:
$$ {{\sigma }_{v0}}=\int\limits_{0}^{H}{\gamma }\centerdot {\rm d}h $$ (4) 式中,H为当前计算深度(mbsf);γ是室内测量得到的土样湿容重(kN/m3)。
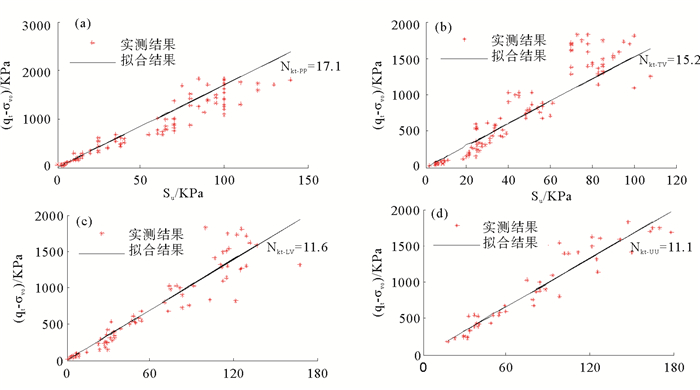
结合式(1)与室内实验结果,若按照深度统一原则,在以室内实验得到的不排水抗剪强度Su1为横坐标、以CPTU测试结果(qt-σv0)为纵坐标的坐标系中绘制Su1-(qt-σv0)散点,过原点进行线性拟合,则拟合结果的斜率可作为按照总锥尖阻力进行强度参数估算的锥头经验系数。分别对袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验结果进行过原点线性拟合,拟合结果如图 3a—3d所示。
图 3中,Nkt-PP、Nkt-TV、Nkt-LV、Nkt-UU分别表示基于袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验确定土层不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数。
由图 3可知,基于总锥尖阻力求解地层不排水抗剪强度时,根据袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验得到的W18/ 19站位水合物上覆层经验锥头系数分别为Nkt-PP =17.1,Nkt-TV=15.2,Nkt-LV=11.6,Nkt-UU=11.1。
2.2.2 根据有效锥尖阻力计算强度参数的锥头系数
同理,若按照深度统一原则,在以室内测试得到的不排水抗剪强度Su2为横坐标、以CPTU测试结果(qt-u2)为纵坐标的坐标系中绘制Su2-(qt-u2)散点,过原点进行线性拟合,则拟合结果的斜率可作为按照有效锥尖阻力进行强度参数估算的锥头经验系数。分别对袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验结果进行过原点线性拟合,拟合结果如图 4a—4d所示。
图 4中,Nke-PP、Nke-TV、Nke-LV、Nke-UU分别表示基于袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验确定土层不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数。
由图 4可知,基于有效锥端阻力求解地层不排水抗剪强度时,根据袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验得到的W18/19站位上覆层经验锥头系数分别为Nke-PP =5.07,Nke-TV=4.64,Nke-LV=4.0,Nke-UU=3.11。
2.2.3 根据超孔隙压力计算强度参数的锥头系数
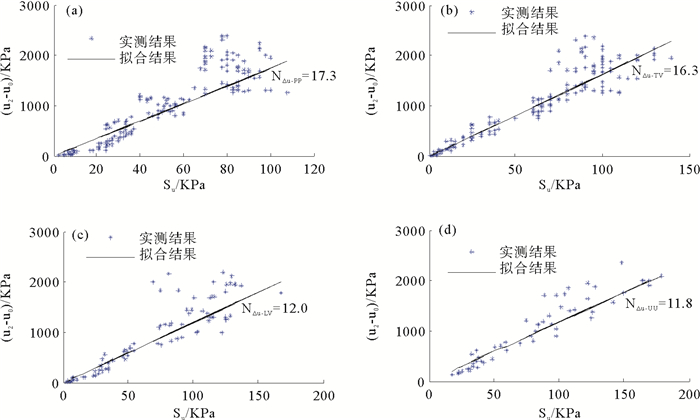
实际工程地质调查实测W18/19站位水深1 272 m,海底泥面静水压力12.84 MPa,海水平均密度取1.029 6 g/cm3,则将海水密度按深度积分可得到地层静水压力u0。然后在以室内测试得到的不排水抗剪强度Su3为横坐标、以CPTU测试结果(u2-u0)为纵坐标的坐标系中绘制Su3-(u2-u0)散点,过原点进行线性拟合,则拟合结果的斜率可作为按照超孔隙压力进行强度参数估算的锥头经验系数。分别对袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验结果进行过原点线性拟合,拟合结果如图 5a—5d所示。
图 5中,N△u-PP、N△u -TV、N△u -LV、N△u -UU分别表示基于袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验确定土层不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数。
由图 5可知,基于超孔隙压力求解地层不排水抗剪强度时,根据袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验得到的W18/19站位上覆层经验锥头系数分别为N△u-PP =17.3,N△u-TV=16.3,N△u-LV=12.0,N△u-UU=11.8。
3. 不同条件下的抗剪强度对比分析
由上述可知,不同的CPTU测试数据、不同的室内实验校准手段,得到的经验锥头系数不同。为了更直观地比较经验锥头系数对水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度的影响,将上述经验锥头系数拟合结果汇总如表 1所示。
表 1 不同实验手段得到的W18/19站位经验锥头系数Table 1. Empirical cone factors for site W18/19 based on the different test methods超孔隙
压力总锥尖
阻力有效锥
尖阻力袖珍贯入仪 17.3 17.1 5.07 手动十字板 16.3 15.2 4.64 微型电动十字板 12.0 11.6 4.0 三轴不排水不固结剪切实验 11.8 11.1 3.11 由表 1可知,对于相同的CPTU测试数据(超孔隙压力、总锥尖阻力、有效锥尖阻力),应用袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验得到的经验锥头系数总是存在如下关系:
$$ {{N}_{\text{m-pp}}}>{{N}_{\text{m-TV}}}>{{N}_{\text{m-LV}}}>{{N}_{\text{m-UU}}} $$ (5) 则由式(1)—(3)可得:
$$ {{S}_{\mathit{ui-pp}}}\le {{S}_{\mathit{ui-TV}}}\le {{S}_{ui-\mathit{LV}}}\le {{S}_{ui-\mathit{UU}}} $$ (6) 式中,i =1,2,3;m= ke,kt,△u。
由此可知,基于袖珍贯入仪确定的上覆层不排水抗剪强度偏保守,而基于三轴不排水不固结剪切实验得到的不排水抗剪强度值则偏高。为了综合评价室内实验结果与CPTU获得的强度参数之间的相关关系,可以取NPP、NTV、NLV、NUU的平均值作为相应的锥头经验系数。即:对于W18/19站位,上覆层经验锥头系数的取值为:
$$ \begin{align} & \ \ {{N}_{\Delta u}}= \\ & \text{average }\!\!\{\!\!\text{ }{{\mathit{N}}_{\Delta u-PP}}, {{N}_{\Delta u-TV}}, {{N}_{\Delta u-LV}}, {{N}_{\Delta u-UU}}\}=14.4 \\ & \ \ \ {{N}_{kt}}= \\ & \text{average }\!\!\{\!\!\text{ }{{\mathit{N}}_{kt-PP}}, {{N}_{kt-TV}}, {{N}_{kt-LV}}, {{N}_{kt-UU}}\}=13.8 \\ & \ \ {{N}_{ke}}= \\ & \text{average }\!\!\{\!\!\text{ }{{\mathit{N}}_{ke-PP}}, {{N}_{ke-TV}}, {{N}_{ke-LV}}, {{N}_{ke-UU}}\}=4.2 \\ \end{align} $$ (7) 另外,由表 1和式(5)可知,对于相同的室内实验方法,不同CPTU数据预测抗剪强度参数得到的锥头系数则存在如下关系:
$$ {{N}_{\Delta \text{u-n}}}>{{N}_{\text{kt-n}}}>{{N}_{\text{ke-n}}} $$ (8) 式中,n=PP,TV,LV,UU。
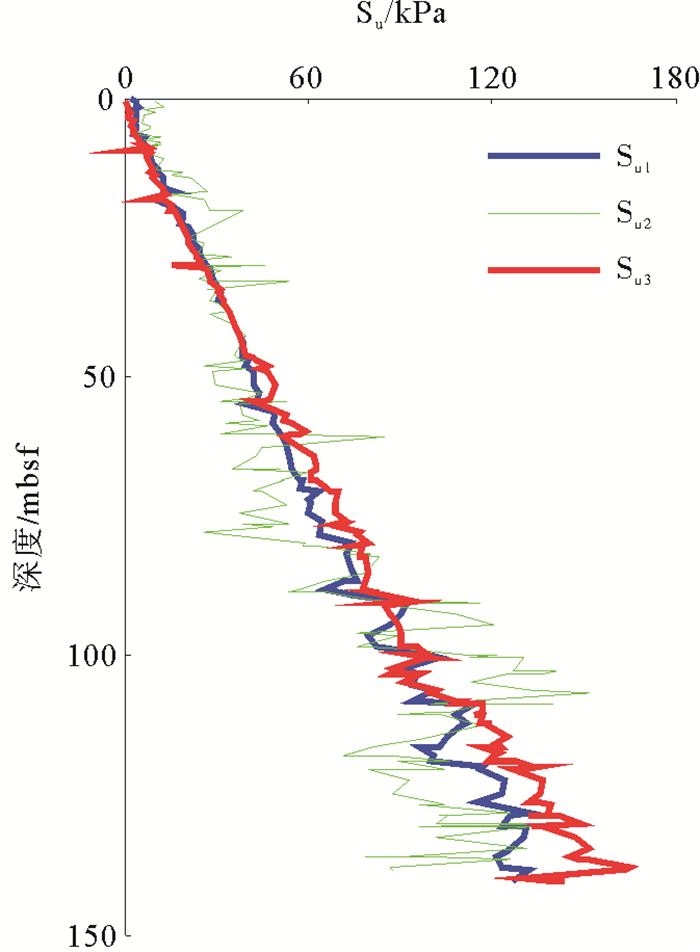
为了对比不同CPTU获取的强度参数之间的相对关系,取(7)式的计算结果,分别用式(1)—(3)计算W18/19站位水合物上覆层抗剪强度参数,如图 6所示。
由图 5可知,W18/19站位水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度随着深度的增加逐渐增大,从0.75增加至165.9 kPa,其中浅表层结果(0.75~39.05 kPa)与利用落锥试验计算的南海北部陆坡深水海域不排水抗剪强度(10~40 kPa)基本一致[21]。本文获取的0~141 mbsf水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度的纵向变化规律在南海北部神狐海域水合物赋存区尚属首次。基于3种CPTU实测参数组合计算得到的不排水抗剪强度再现性较好,能够反映水合物上覆层的基本强度参数变化规律。
总体而言,基于总锥尖阻力求解得到的土层不排水抗剪强度略小于基于超孔隙压力求解得到的土层不排水抗剪强度值。基于有效锥尖阻力计算得到的土层不排水抗剪强度参数值离散性大于基于总锥尖阻力和超孔隙水压力计算得到的不排水抗剪强度值,这是由于基于有效锥尖阻力求解不排水抗剪强度的计算模型中同时含有总锥尖阻力、超孔隙压力两个CPTU参数,造成不排水抗剪强度值的波动幅度实际上是上述两者波动幅度的叠加。特别地,以土层埋深50 mbsf为界,当深度小于50 mbsf时,基于总锥尖阻力和超孔隙压力计算模型预测得到的不排水抗剪强度再现率高达95%,且预测结果偏保守(图 5),基于有效锥尖阻力模型预测得到的不排水抗剪强度值偏“冒险”;当深度大于50 mbsf后,3种模型的预测结果离散性略微增大,基于总锥尖阻力的抗剪强度预测结果基本上可以反映3种模型预测结果的平均值,因此,在进行50 mbsf以深地层的井壁稳定性和喷射参数设计过程中,建议使用基于总锥尖阻力的抗剪强度预测结果。
通过以上分析,在南海北部陆坡神狐海域水合物赋存区域,CPTU能较好反映地层的不排水抗剪强度,可为桩基础设计、管线路由、水下基础等海上工程提供可靠的岩土设计参数,对水合物试采工程设计具有基础支撑作用。
4. 结论与建议
(1) 水合物上覆层由上至下为强度逐渐增大的钙质黏土,利用统计得到基于总锥尖阻力求解钙质黏土不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数范围为11.1~17.1,基于有效锥尖阻力求解钙质黏土不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数范围为3.11~5.07,基于超孔隙压力求解钙质黏土不排水抗剪强度的经验锥头系数范围为11.8~17.3。
(2) 同一类CPTU测试数据(超孔隙压力、总锥尖阻力、有效锥尖阻力),应用袖珍贯入仪、手动十字板、微型电动十字板和三轴不排水不固结剪切实验校准得到的经验锥头系数存在如下关系:Nm-PP>Nm-TV>Nm-LV>Nm-UU;对于相同的室内实验方法,不同类的CPTU数据预测抗剪强度参数得到的锥头系数则存在如下关系:N△u-n>Nkt-n>Nke-n。
(3) 水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度随着深度的增加逐渐增大,基于总锥尖阻力求解得到的土层不排水抗剪强度略小于基于超孔隙压力求解得到的土层不排水抗剪强度值。基于有效锥尖阻力计算得到的土层不排水抗剪强度参数值离散性大于基于总锥尖阻力和超孔隙水压力计算得到的不排水抗剪强度值。
(4) 基于CPTU测试结果能获得水合物上覆层抗剪强度参数的纵向分布规律,对深海水合物开采安全评价具有重要作用。但由于不同区块沉积特征的差异性,仍需要开展大量的针对不同区块的CPTU测试,才能建立完整的南海北部水合物赋存区上覆土层强度参数三维分布规律。
-
表 1 不同实验手段得到的W18/19站位经验锥头系数
Table 1 Empirical cone factors for site W18/19 based on the different test methods
超孔隙
压力总锥尖
阻力有效锥
尖阻力袖珍贯入仪 17.3 17.1 5.07 手动十字板 16.3 15.2 4.64 微型电动十字板 12.0 11.6 4.0 三轴不排水不固结剪切实验 11.8 11.1 3.11 -
[1] Kvenvolden K A. A primer on the geological occurrence of gas hydrate[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1998, 137(1): 9-30. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1998.137.01.02
[2] Yang S, Zhang M, Liang J, et al. Preliminary results of China's third gas hydrate drilling expedition: a critical step from discovery to development in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, 2015, 15(2): 1-5.
[3] 梁金强, 张光学, 陆敬安, 等.南海东北部陆坡天然气水合物富集特征及成因模式[J].天然气工业, 2016, 36(10): 157-162. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.10.020 LIANG Jinqiang, ZHANG Guangxue, LU Jing'an, et al. Accumulation characteristics and genetic models of natural gas hydrate reservoirs in the NE slope of the South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(10): 157-162. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.10.020
[4] 李彦龙, 刘昌岭, 刘乐乐, 等.水合物沉积物三轴试验存在的关键问题分析[J].新能源进展, 2016, 4(4): 279-285. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnyjz201604004 LI Yanlong, LIU Changling, LIU Lele, et al. Key issues for triaxial test of hydrate-bearing sediment[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 2016, 4(4): 279-285. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnyjz201604004
[5] 杨溢军, 童立元, 朱宁, 等.基坑中基于CPTU软土不排水强度确定及应用[J].地下空间与工程学报, 2016, 12(4): 1095-1101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxkj201604036 YANG Yijun, TONG Liyuan, ZHU Ning, et al. Evaluation and Application of undrained shear strength in excavation from piezocone tests (CPTU)[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2016, 12(4): 1095-1101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxkj201604036
[6] 王淑云, 楼志刚.海洋粉质黏土在波浪荷载作用后的不排水抗剪强度衰化特性[J].海洋工程, 2000, 18(1): 38-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2000.01.007 WANG Shuyun, LOU Zhigang. Degradation of undrained shear strength of marine silty clay after undrained cyclic loading[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2000, 18(1): 38-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2000.01.007
[7] Strózyk J, Tankiewicz M. The undrained shear strength of overconsolidated clays[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 91: 317-321. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.067
[8] Westerberg B, Müller R, Larsson S. Evaluation of undrained shear strength of Swedish fine-grained sulphide soils[J]. Engineering Geology, 2015, 188: 77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.01.007
[9] Grozic J L H, Nadim F, Kvalstad T J. On the undrained shear strength of gassy clays[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2005, 32(7): 483-490. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2005.10.002
[10] Juang C H, Liu C N, Chen C H, et al. Calibration of liquefaction potential index: a re-visit focusing on a new CPTU model[J]. Engineering Geology, 2008, 102(1-2): 19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.06.005
[11] Sivrikaya O, Togrol E. Determination of undrained strength of fine-grained soils by means of SPT and its application in Turkey[J]. Engineering Geology, 2006, 86(1): 52-69. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.05.002
[12] Ebrahimian B, Movahed V, Pasha A Y. Evaluation of undrained shear strength of marine clay using cone penetration resistance at South Pars field in Iran[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2012, 54: 182-195. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2012.07.018
[13] 储团结, 黄俊杰, 王中华.静力触探试验确定软黏性土不排水抗剪强度研究[J].路基工程, 2005(6): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2005.06.001 CHU Tuanjie, HUANG Junjie, WANG Zhonghua. Research on determination for undrainage shear strength of soft cohesive soil using the cone penetration test[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2005(6): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2005.06.001
[14] 季福东, 贾永刚, 刘晓磊, 等.海底沉积物工程力学性质原位测量方法[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(3): 191-200. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201603023 JI Fudong, JIA Yonggang, LIU Xiaolei, et al. In situ measurement of the engineering mechanical properties of seafloor sediment[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(3): 191-200. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201603023
[15] 马海鹏, 陈祖煜, 于沭.上海地区土体抗剪强度与静力触探比贯入阻力相关关系研究[J].岩土力学, 2014, 35(2): 536-542. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201402034 MA Haipeng, CHEN Zuyu, YU Shu. Correlations of soil shear strength with specific penetration resistance of CPT in Shanghai area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(2): 536-542. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201402034
[16] 刘维正, 石名磊, 徐林荣.考虑软黏土结构性损伤的圆柱孔扩张弹塑性分析[J].岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(3): 487-494. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytgcxb201303011 LIU Weizheng, SHI Minglei, XU Linrong. Elastoplastic analysis of cylindrical cavity expansion in natural sedimentary soft clay with structure damage[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(3): 487-494. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytgcxb201303011
[17] Lunne T, Christoffersen H P, Tjelta T I. Engineering use of piezocone data in North Sea clays[C]//Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Oslo, Norwegian: Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, 1985.
[18] Senneset K, Janbu N, Svano G. Strength and deformation parameters from cone penetration tests[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd European Symposium on Penetration Testing. Amsterdam, Netherlands: ESOPT Ⅱ, 1982.
[19] Tong L Y, Wang Q, Du G Y, et al. Determination of undrained shear strength using piezocone penetration test in clayey soil for bridge foundation[J]. Journal of Southeast University (English Edition), 2011, 27(2): 201-205.
[20] 安彦勇, 郭燕沫, 李向凤.孔压静力触探确定软黏土地基强度方法分析[J].勘察科学技术, 2009(3): 8-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2009.03.002 AN Yanyong, GUO Yanmo, LI Xiangfeng. Analysis of pore pressure static cone penetration test to determine soft clay strength[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 2009(3): 8-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2009.03.002
[21] 王虎刚, 周松望.利用落锥试验确定深水软黏土的不排水抗剪强度[J].海岸工程, 2016, 35(2): 25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2016.02.004 WANG Hugang, ZHOU Songwang. Determination of undrained shear strength of Deepwater soft clays through fall cone test[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2016.02.004
[22] 周杨锐, 王建华, 李书兆.南海荔湾深水重塑沉积物的静、动力特性[J].海洋通报, 2013, 32(5): 521-526. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hytb201305007 ZHOU Yangrui, WANG Jianhua, LI Shuzhao. Static and cyclic behaviors of Remoulded Deepwater sediments of Liwan in South China Sea[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2013, 32(5): 521-526. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hytb201305007
[23] 张毅, 何丽娟, 徐行, 等.南海北部神狐海域甲烷水合物BHSZ与BSR的比较研究[J].地球物理学进展, 2009, 24(1): 183-194. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz200901024 ZHANG Yi, HE Lijuan, XU Xing, et al. The disagreement between BSRs and the base of methane hydrate stability zones in the Shenhu area North of the South China Sea[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2009, 24(1): 183-194. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz200901024
[24] 梁劲, 王明君, 王宏斌, 等.南海神狐海域天然气水合物声波测井速度与饱和度关系分析[J].现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 217-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.02.004 LIANG Jin, WANG Mingjun, WANG Hongbin, et al. Relationship between the sonic logging velocity and saturation of gas hydrate in Shenhu Area, northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(2): 217-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.02.004
[25] McDonnell S L, Max M D, Cherkis N Z, et al. Tectono-sedimentary controls on the likelihood of gas hydrate occurrence near Taiwan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(8): 929-936. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(00)00023-4
[26] Wang P X, Prell W L, Blum P. Ocean Drilling Program Leg 184 Scientific Prospectus South China Sea, Site 1144[M]//Wang P, Prell W L, Blum P. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports. TX, USA: Ocean Drilling Program, College Station, 2000, 184: 1-97.
[27] 王宏语, 孙春岩, 张洪波, 等.西沙海槽潜在天然气水合物成因及形成地质模式[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(4): 85-91. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200504014 WANG Hongyu, SUN Chunyan, ZHANG Hongbo, et al. Origin and genetic model of potential gas hydrates in Xisha trough, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(4): 85-91. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200504014
[28] 傅宁, 米立军, 张功成.珠江口盆地白云凹陷烃源岩及北部油气成因[J].石油学报, 2007, 28(3): 32-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb200703007 FU Ning, MI Lijun, ZHANG Gongcheng. Source rocks and origin of oil and gas in the northern Baiyun Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(3): 32-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb200703007
[29] 苏明, 杨睿, 吴能友, 等.南海北部陆坡区神狐海域构造特征及对水合物的控制[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(3): 318-326. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201403002 SU Ming, YANG Rui, WU Nengyou, et al. Structural characteristics in the Shenhu Area, northern continental slope of South China Sea, and their influences on gas hydrate[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(3): 318-326. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201403002
-
期刊类型引用(18)
1. 李彦龙,吴能友,王宏斌,纪云开,綦民辉,刘昌岭,万义钊,陈明涛. 海域天然气水合物储层的多场耦合模式及研究进展. 工程地质学报. 2024(04): 1355-1366 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. Jiapeng JIN,Xiujuan WANG,Zhenyu ZHU,Pibo SU,Lixia LI,Qingping LI,Yiqun GUO,Jin QIAN,Zhendong LUAN,Jilin ZHOU. Physical characteristics of high concentrated gas hydrate reservoir in the Shenhu production test area, South China Sea. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology. 2023(02): 694-709 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 韩泽龙,宋刚,牛庆磊,邵玉涛,崔淑英,朱嵘华,李博,陈根龙. 深海井口吸力锚安装分析与实践. 钻探工程. 2023(05): 109-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 吴学震,叶鸿宇,蒋宇静,李大勇,姜杰,王刚,公彬. 海域天然气水合物自入式开采装置及其可行性研究. 中南大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(03): 1012-1022 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵小龙,王增林,赵益忠,左家强,李鹏,梁伟,王冰,陈雪,雷宏武,金光荣. 天然气水合物水平井降压开采多相渗流—传热—力学耦合数值模拟:方法和南海场地应用. 天然气工业. 2022(03): 138-149 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王辉,修宗祥,孙永福,刘绍文,宋玉鹏,董立峰,宋丙辉. 考虑天然气水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度深度变化的海底斜坡稳定性影响分析. 高校地质学报. 2022(05): 747-757 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘乐乐,刘昌岭,吴能友,阮海龙,张永超,郝锡荦,卜庆涛. 天然气水合物储层岩心保压转移与测试进展. 地质通报. 2021(Z1): 408-422 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘建辉,李占东,赵佳彬. 神狐海域天然气水合物研究新进展. 矿产与地质. 2021(03): 596-602 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘昌岭,孙运宝. 海洋天然气水合物储层特性及其资源量评价方法. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2021(05): 44-57 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 秦源康,刘康,陈国明,张爱霞,朱敬宇,夏开朗. 海洋水合物地层导管吸力锚贯入安装负压窗口分析. 石油钻采工艺. 2021(06): 737-743 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李彦龙,刘昌岭,廖华林,董林,卜庆涛,刘志超. 泥质粉砂沉积物—天然气水合物混合体系的力学特性. 天然气工业. 2020(08): 159-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 宁伏龙,梁金强,吴能友,祝有海,吴时国,刘昌岭,韦昌富,王冬冬,张准,徐猛,刘志超,李晶,孙嘉鑫,欧文佳. 中国天然气水合物赋存特征. 天然气工业. 2020(08): 1-24+203 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 董林,廖华林,李彦龙,刘昌岭. 天然气水合物沉积物力学性质测试与评价. 海洋地质前沿. 2020(09): 34-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 李彦龙,陈强,刘昌岭,吴能友,孙建业,申志聪,张民生,胡高伟. 水合物储层工程地质参数评价系统研发与功能验证. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2020(05): 192-200 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. Yanlong Li,Gaowei Hu,Nengyou Wu,Changling Liu,Qiang Chen,Chen'an Li. Undrained shear strength evaluation for hydrate-bearing sediment overlying strata in the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica. 2019(03): 114-123 .  必应学术
必应学术
16. 宋本健,程远方,李庆超,韩忠英,吕亚慧. 水合物分解对海底边坡稳定影响的数值模拟分析. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2019(03): 182-192 .  本站查看
本站查看
17. 张峰,刘丽华,吴能友,吴起,金光荣. 细砂质含水合物沉积介质的非线性弹性力学模型. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2019(03): 193-198 .  本站查看
本站查看
18. 吴景鑫,郭秀军,贾永刚,孙翔,李宁. 天然气水合物开采过程甲烷气泄漏海床基高密度电阻率法监测效果模拟与分析. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2018(06): 1854-1864 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: