Forms of sedimentary phosphorus in the South Yellow Sea and the implication to regional eutrophication trend
-
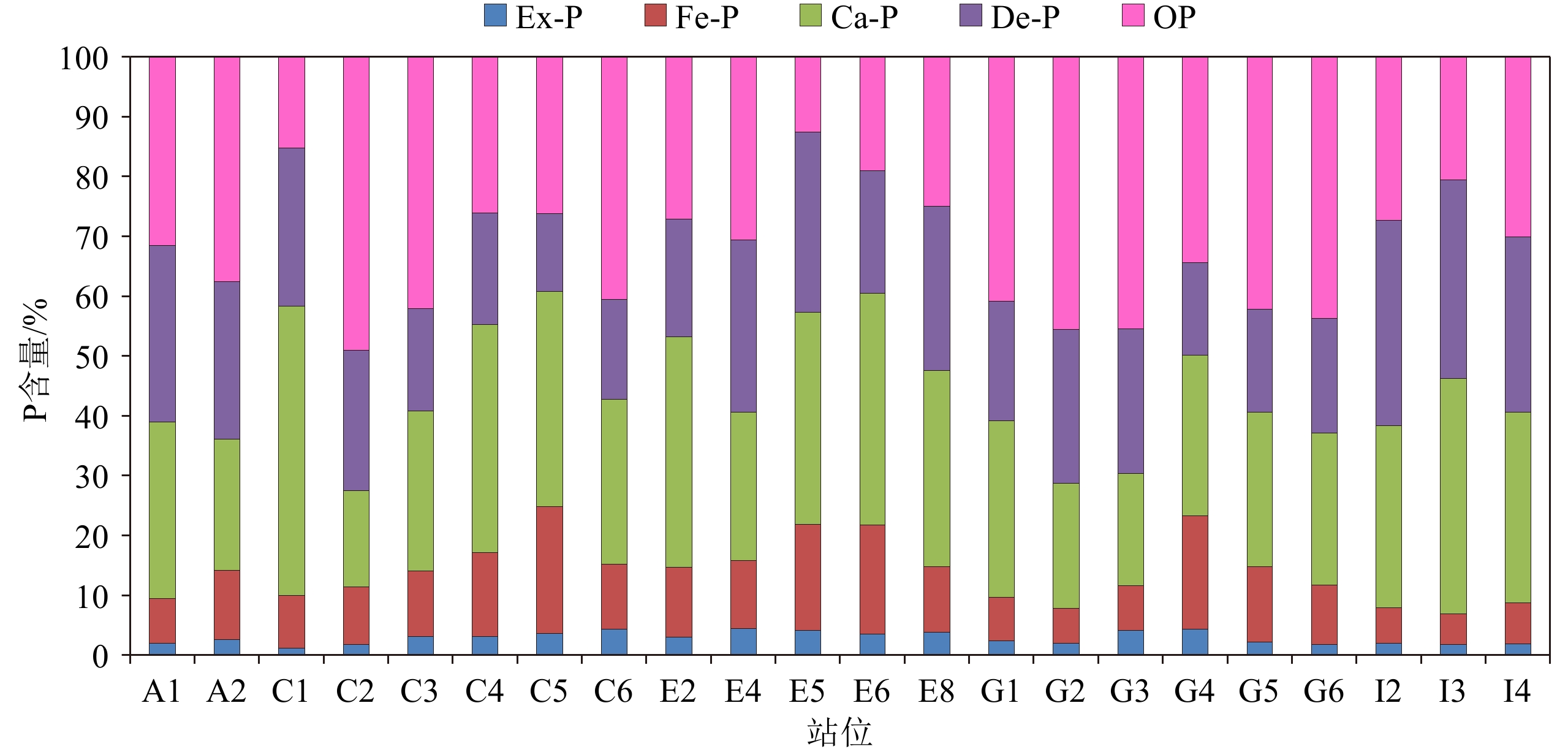
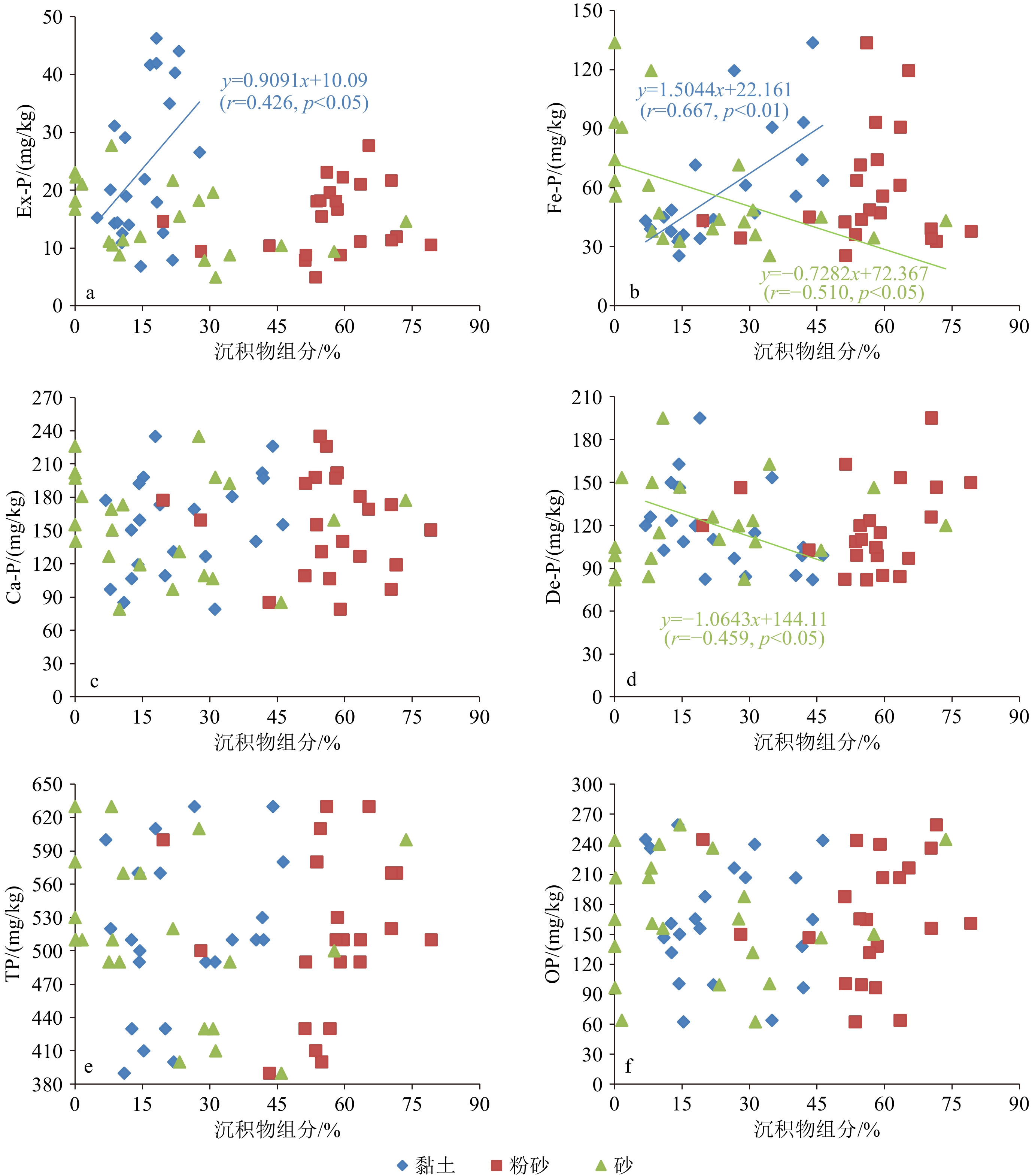
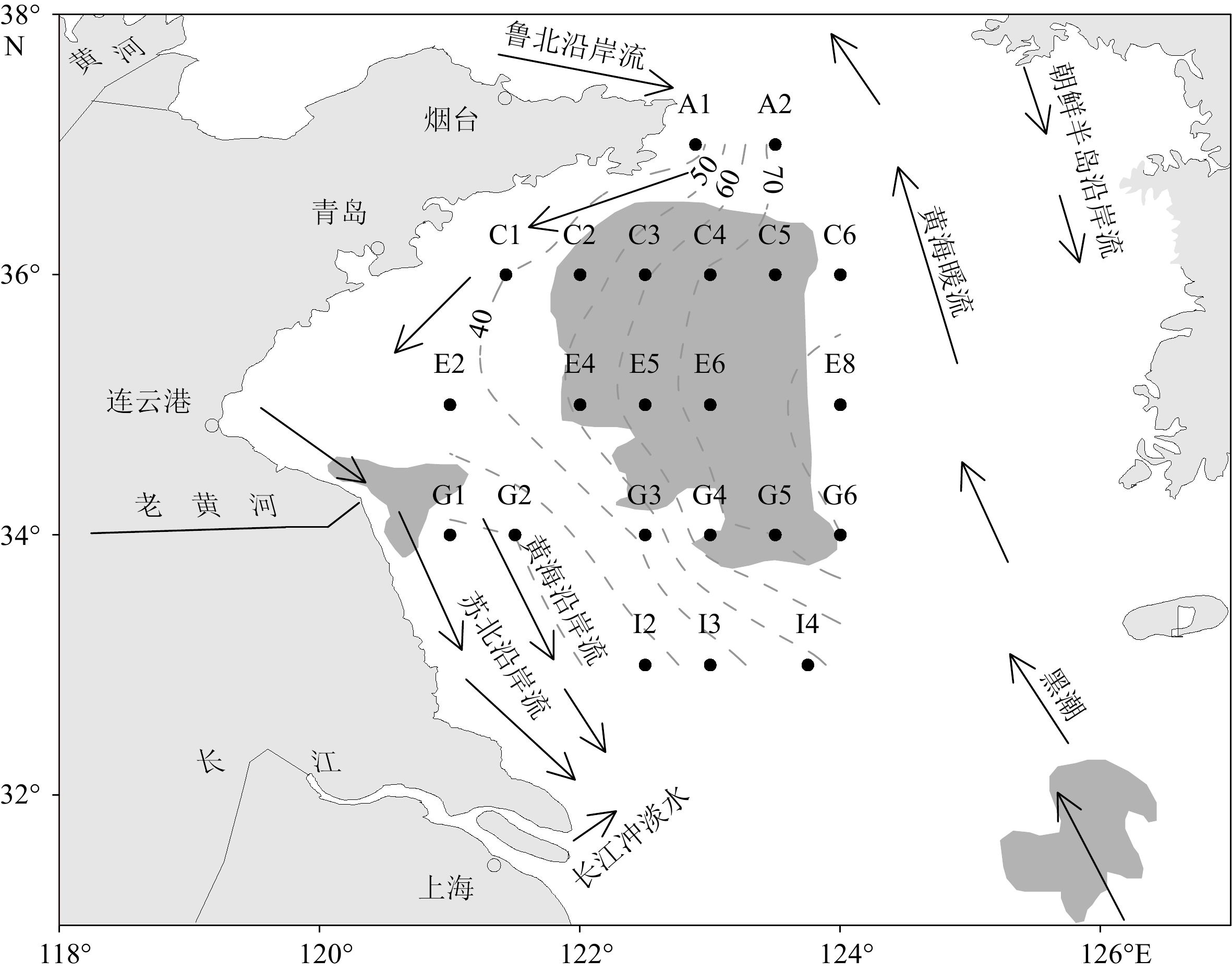
摘要: 南黄海水体富营养化日益加剧,作为我国绿潮孕育和暴发的主要场所,其水体富营养化的形成演变机制仍未完全清楚。为解析该区沉积物中营养元素磷(P)的释放特征和对水体富营养化的潜在贡献,采用改进的连续浸取法(SEDEX)分析了表层沉积中磷的含量水平和赋存形态,探讨了其生物有效性和对水体富营养化态势的影响。研究表明:总磷(TP)平均值为514 mg/kg,处于轻度污染,以无机磷(IP)为主要赋存形态(76.39%),有机磷(OP)次之,IP又以Ca-P为主(30.17%)。各形态磷平均贡献依次为OP>Ca-P>De-P>Fe-P>Ex-P。Ca-P和De-P属于生物不可利用磷,在沉积物中稳定性较强,在较粗粒径沉积物中含量较高。Ex-P和Fe-P易吸附于细颗粒沉积物表面,pH、温度、水体动力和氧化还原条件等是影响其吸附-释放的主要因素,南黄海海水酸化将促进Ex-P和Fe-P向海水释放,加剧海水富营养化程度。OP变化趋势显示,近岸以陆源输入为主,远岸生物过程具有重要贡献。南黄海生物有效磷(BAP:Ex-P + Fe-P + OP)平均值为240.1 mg/kg,占TP的46.4%,表明研究区沉积磷生物可利用性较强,释放到水体的风险较高,对该区富营养化具有重要长期潜在贡献。Abstract: Eutrophication has been increasingly occurred in the South Yellow Sea (SYS), the main region of outbreak of green tide. However, the mechanism and evolution of eutrophication in this area remains not fully resolved. Concentrations and forms of the surface sediment phosphorus (P) in the SYS were determined by the modified sequential extraction method (SEDEX) to examine the bioavailability and potential contribution to the eutrophication. Results show that the mean value of total phosphorus (TP) in surface sediments was 514 mg/kg, being generally in a mildly contaminated condition. Inorganic phosphorus (IP) was the main form (76.39%), of which 30.17% was Ca-P. The average contribution of each P form was in the order of OP (organic P) > Ca-P (Ca bound P) > De-P (detritus P) > Fe-P (Fe bound P > Ex-P (exchangeable P). Ca-P and De-P are not bioavailable species, which are less easily released under normal hydrodynamic disturbance in sediments, and are generally enriched in coarse-grained sediments. Ex-P and Fe-P are easily adsorbed into fine-grained sediments, for which pH, temperature, hydrodynamics, and redox conditions are important environmental factors. Acidification of seawater in the SYS will elevate the release of Ex-P and Fe-P into seawater and worsen the degree of eutrophication. Distribution of OP indicated the contribution of biological processes in the open sea in addition to the terrestrial input in the nearshore. The mean value of bioavailable phosphorus including Ex-P, Fe-P and OP was 240.1 mg/kg, which accounted for 46.4% of TP, suggesting that sedimentary P in SYS is more bioavailable, showing a higher risk of P release into the water column, and an important long-term potential contributor to local eutrophication.
-
Keywords:
- sedimentary phosphorus /
- bioavailable phosphorus /
- nutrients /
- eutrophication /
- South Yellow Sea
-
-
步骤 提取试剂和条件 磷形态 1 1 mol/L MgCl2 (pH=8), 2h Ex-P 2 CDB (pH=7.6), 8h Fe-P 3 1 mol/L NaAc-Hac (pH=4), 6h Ca-P 4 1 mol/L HCl, 24h De-P 表 2 南黄海表层沉积物中各形态磷相关性
Table 2 Correlation among various phosphorus forms in the surface sediments of South Yellow Sea
参数 TP IP OP Ex-P Fe-P Ca-P De-P TP 1 IP 0.639** 1 OP 0.480* −0.368 1 Ex-P 0.526* 0.423 0.154 1 Fe-P 0.512* 0.595** −0.059 0.727** 1 Ca-P 0.519* 0.907** −0.408 0.222 0.470* 1 De-P 0.085 0.271 −0.207 −0.271 −0.457* 0.082 1 注:**:p<0.01,*:p<0.05。 表 3 南黄海表层沉积物中形态磷与环境参数相关性
Table 3 Correlation among various phosphorus forms and environmental parameters in the surface sediments of South Yellow Sea
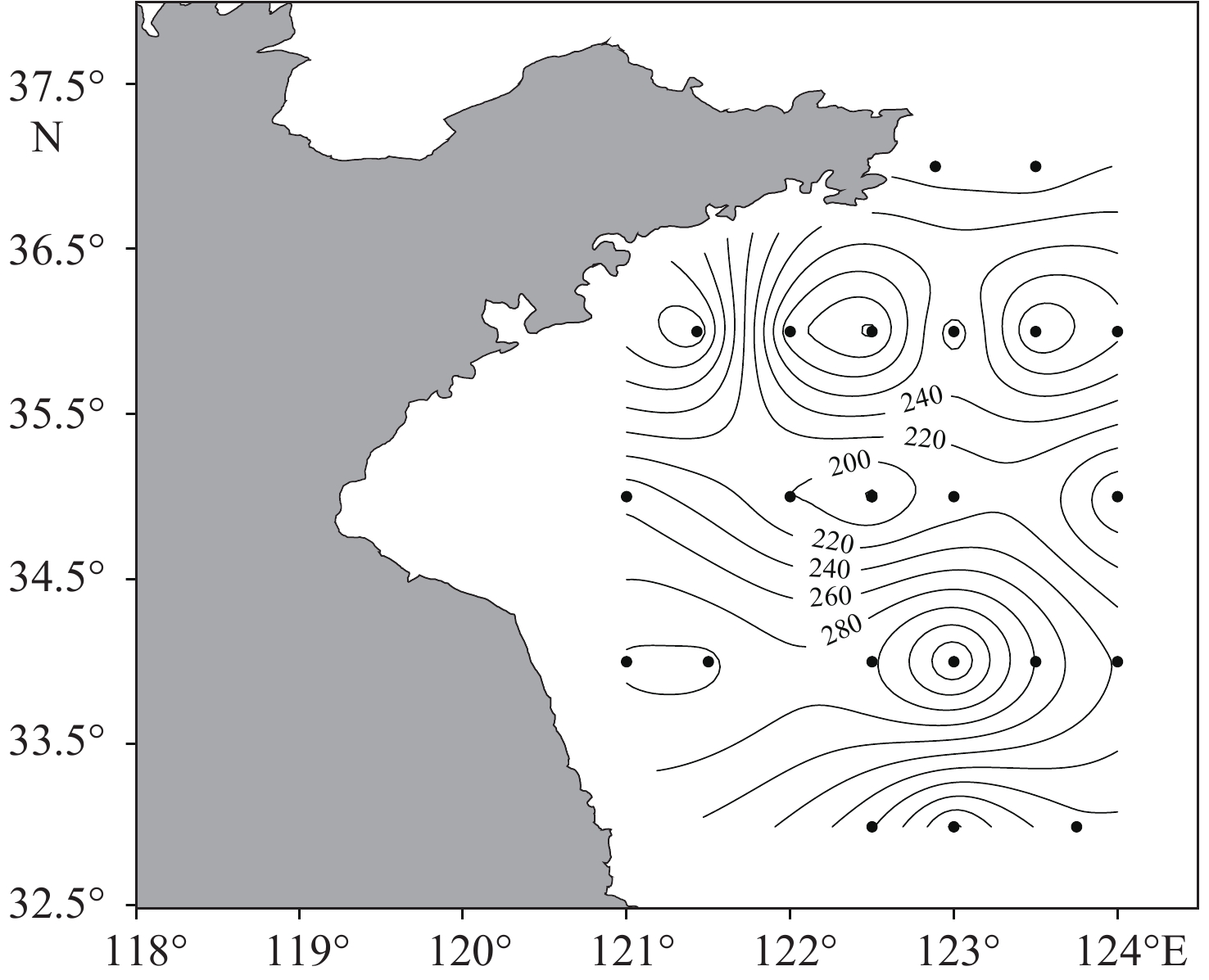
参数 TP IP OP Ex-P Fe-P Ca-P De-P 水深 −0.317 −0.107 −0.261 0.320 0.503* −0.087 −0.682** 表层海水硫化物 0.368 0.148 0.273 0.029 0.092 0.025 0.208 底层海水硫化物 0.223 0.228 −0.003 0.342 0.535* 0.133 −0.256 表层海水温度 0.280 0.124 0.196 0.121 0.050 0.071 0.106 底层海水温度 0.349 0.206 0.188 −0.041 −0.134 0.171 0.354 表层海水盐度 −0.192 0.023 −0.258 0.209 0.359 −0.051 −0.260 底层海水盐度 −0.192 0.001 −0.233 0.271 0.415 −0.071 −0.347 表层海水pH值 −0.079 −0.055 −0.033 0.564** 0.602** −0.092 −0.687** 底层海水pH值 −0.049 −0.168 0.133 0.053 0.020 −0.274 −0.006 注:**:p<0.01; *:p<0.05。 -
[1] Wang B D, Xin M, Wei Q S, et al. A historical overview of coastal eutrophication in the China Seas[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 136:394-400. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.044
[2] 黎慧, 万夕和, 王李宝, 等. 南黄海辐射沙脊群海域氮磷的季节变化及潜在性富营养化分析[J]. 生态科学, 2016, 35(2):75-80 LI Hui, WAN Xihe, WANG Libao, et al. Seasonal change of nitrogen and phosphorus and analysis of potential eutrophication in radial sand ridge group region of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Ecological Science, 2016, 35(2):75-80.
[3] 杨庶, 杨茜, 曲克明, 等. 南黄海近海富营养化长期演变的沉积记录[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(1):22-28 YANG Shu, YANG Qian, QU Keming, et al. Sedimental records of eutrophication in coastal waters of the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(1):22-28.
[4] 颜天, 于仁成, 周名江, 等. 黄海海域大规模绿潮成因与应对策略: “鳌山计划”研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5):950-958 YAN Tian, YU Rencheng, ZHOU Mingjiang, et al. Mechanism of massive formation and prevention strategy against large-scale green tides in the south yellow sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5):950-958.
[5] 韦钦胜, 王保栋, 姚庆祯, 等. 海水增温和富营养化驱动下的黄海水体脱氧和酸化[C]//中国海洋学会2017年学术年会论文集. 青岛: 中国海洋学会, 2017: 83-97 WEI Qinsheng, WANG Baodong, YAO Qingzhen, et al. Deoxygenation and acidification of Yellow Sea waters driven by seawater warming and eutrophication[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 Annual Academic Conference of the Oceanic Society of China. Qingdao, 2017: 83-97.
[6] Wei Q S, Yao Q Z, Wang B D, et al. Long-term variation of nutrients in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2015, 111:184-196. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2015.08.003
[7] 宋金明, 李学刚, 邵君波, 等. 南黄海沉积物中氮、磷的生物地球化学行为[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2006, 37(4):370-376 SONG Jinming, LI Xuegang, SHAO Junbo, et al. Biogeochemical characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in the south Yellow Sea sediments[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2006, 37(4):370-376.
[8] Meng J, Yu Z G, Yao Q Z, et al. Distribution, mixing behavior, and transformation of dissolved inorganic phosphorus and suspended particulate phosphorus along a salinity gradient in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 168:124-134. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.09.016
[9] Barik S K, Bramha S, Bastia T K, et al. Characteristics of geochemical fractions of phosphorus and its bioavailability in sediments of a largest brackish water lake, South Asia[J]. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 2019, 19(3):370-382.
[10] Ruttenberg K C, Berner R A. Authigenic apatite formation and burial in sediments from non-upwelling, continental margin environments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(5):991-1007. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90035-U
[11] Li C L, Yang D Z, Zhai W D. Effects of warming, eutrophication and climate variability on acidification of the seasonally stratified North Yellow Sea over the past 40 years[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815:152935. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.152935
[12] Sun Y Q, Yao L L, Liu J L, et al. Prevention strategies for green tides at source in the Southern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 178:113646. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113646
[13] Li D X, Gao Z Q, Wang Z C. Analysis of the reasons for the outbreak of Yellow Sea green tide in 2021 based on long-term multi-source data[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2022, 178:105649. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2022.105649
[14] Wang J J, Beusen A H W, Liu X C, et al. Spatially explicit inventory of sources of nitrogen inputs to the Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea for the period 1970-2010[J]. Earth’s Future, 2020, 8(10):e2020EF001516. doi: 10.1029/2020EF001516
[15] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 黄海地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989 QIN Yunshan, ZHAO Yiyang, CHEN Lirong, et al. Yellow Sea Geology[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1989.
[16] 苏纪兰, 袁业立. 中国近海水文[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005 SU Jilan, YUAN Yeli. Modern Hydrology in China[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2005.
[17] 石学法, 刘焱光, 乔淑卿, 等. 渤海、黄海和东海沉积物类型图[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021 SHI Xuefa, LIU Yanguang, QIAO Shuqing, et al. Sediment Type Map of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021.
[18] Aydin I, Aydin F, Saydut A, et al. A sequential extraction to determine the distribution of phosphorus in the seawater and marine surface sediment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 168(2-3):664-669. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.095
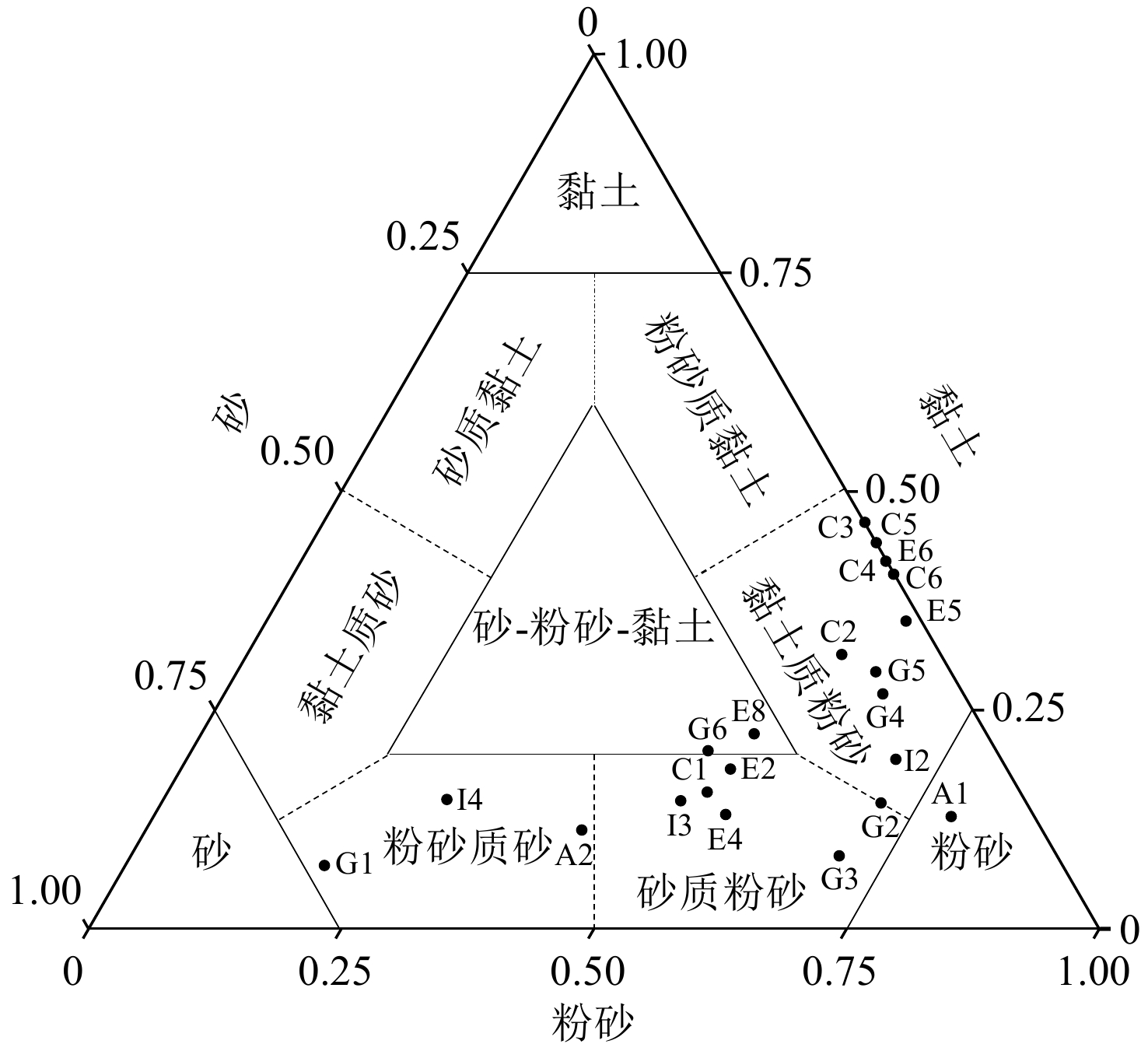
[19] Shepard F P. Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1954, 24(3):151-158.
[20] Fu Z H, Hong Z J, Wei J L, et al. Phosphorus fractionation and adsorption characteristics in drinking water reservoir inlet river sediments under human disturbance[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2022, 22(9):2530-2547. doi: 10.1007/s11368-022-03257-1
[21] 黎睿, 王圣瑞, 肖尚斌, 等. 长江中下游与云南高原湖泊沉积物磷形态及内源磷负荷[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(6):1831-1839 LI Rui, WANG Shengrui, XIAO Shangbin, et al. Sediments phosphorus forms and loading in the lakes of the mid-lower reaches of the Yangtze River and Yunnan Plateau, China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(6):1831-1839.
[22] Luo C Y, Wen S L, Lu Y H, et al. Coprecipitation of humic acid and phosphate with Fe(III) enhances the sequestration of carbon and phosphorus in sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 2022, 588:120645. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120645
[23] Ding S, Liu Y, Dan S F, et al. Historical changes of sedimentary P-binding forms and their ecological driving mechanism in a typical "grass-algae" eutrophic lake[J]. Water Research, 2021, 204:117604. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117604
[24] Cheng X L, Huang Y N, Li R, et al. Impacts of water temperature on phosphorus release of sediments under flowing overlying water[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2020, 235:103717. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103717
[25] Ding S M, Sun Q, Chen X, et al. Synergistic adsorption of phosphorus by iron in lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock®): New insight into sediment phosphorus immobilization[J]. Water Research, 2018, 134:32-43. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.055
[26] Chen X M, Zhang W, Yin Y P, et al. Seasonal variation characteristics and release potential of phosphorus in sediments: a case study of the Qiuxi River, a typical diffuse source pollution river in southwestern China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2021, 21(1):575-591. doi: 10.1007/s11368-020-02805-x
[27] Liu Y Q, Cao X Y, Li H, et al. Distribution of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria in relation to fractionation and sorption behaviors of phosphorus in sediment of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(21):17679-17687. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9339-0
[28] Kaiserli A, Voutsa D, Samara C. Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments - lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece[J]. Chemosphere, 2002, 46(8):1147-1155. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00242-9
[29] Chen H J. Surface-flow constructed treatment wetlands for pollutant removal: applications and perspectives[J]. Wetlands, 2011, 31(4):805-814. doi: 10.1007/s13157-011-0186-3
[30] 周帆琦, 沙茜, 张维昊, 等. 武汉东湖和南湖沉积物中磷形态分布特征与相关分析[J]. 湖泊科学, 2014, 26(3):401-409 doi: 10.18307/2014.0310 ZHOU Fanqi, SHA Qian, ZHANG Weihao, et al. Distribution and correlation analysis of phosphorus fractions in the sediments from the Lake Nanhu and Lake Donghu in Wuhan[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2014, 26(3):401-409. doi: 10.18307/2014.0310
[31] Andrieux-Loyer F, Aminot A. Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemical characteristics in French coastal areas[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2001, 52(5):617-629. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2001.0766
[32] 魏俊峰, 陈洪涛, 刘月良, 等. 2008年调水调沙期间黄河下游悬浮颗粒物中磷的赋存形态[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(2):368-374 WEI Junfeng, CHEN Hongtao, LIU Yueliang, et al. Phosphorus forms of the suspended particulate matter in the Yellow Rive downstream during water and sediment regulation 2008[J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(2):368-374.
[33] 于子洋, 杜俊涛, 姚庆祯, 等. 黄河口湿地表层沉积物中磷赋存形态的分析[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(3):942-950 YU Ziyang, DU Juntao, YAO Qingzhen, et al. Distribution of phosphorus in surface sediments from the Yellow River Estuary wetland[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(3):942-950.
[34] 于佳真, 王晓昌, 薛涛, 等. 不同温度下西安汉城湖沉积物吸附、释放特性和磷形态[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(11):6275-6282 YU Jiazhen, WANG Xiaochang, XUE Tao, et al. Phosphorus sorption, release characteristic under different temperature and phosphorus fractions in sediments of Hancheng Lake in Xi’an[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(11):6275-6282.
[35] 岳维忠, 黄小平, 孙翠慈. 珠江口表层沉积物中氮、磷的形态分布特征及污染评价[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(2):111-117 YUE Weizhong, HUANG Xiaoping, SUN Cuici. Distribution and pollution of nitrogen and phosphorus in surface sediments from the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38(2):111-117.
[36] 周爱民, 王东升, 汤鸿霄. 磷(P)在天然沉积物水界面上的吸附[J]. 环境科学学报, 2005, 25(1):64-69 ZHOU Aimin, WANG Dongsheng, TANG Hongxiao. Adsorption of phosphorus on sediment-water interface[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2005, 25(1):64-69.
[37] Sutula M, Bianchi T S, McKee B A. Effect of seasonal sediment storage in the lower Mississippi River on the flux of reactive particulate phosphorus to the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2004, 49(6):2223-2235. doi: 10.4319/lo.2004.49.6.2223
[38] Meng J, Yao P, Yu Z G, et al. Speciation, bioavailability and preservation of phosphorus in surface sediments of the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent East China Sea inner shelf[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 144:27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.04.015
[39] Baken S, Moens C, Van Der Grift B, et al. Phosphate binding by natural iron-rich colloids in streams[J]. Water Research, 2016, 98:326-333. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.04.032
[40] Sekula-Wood E, Benitez-Nelson C R, Bennett M A, et al. Magnitude and composition of sinking particulate phosphorus fluxes in Santa Barbara Basin, California[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2012, 26(2):GB2023.
[41] 乔永民, 郭佳, 杨骏, 等. 洱海湖滨带与湖中心带表层沉积物磷的形态对比分析与环境学意义[J]. 生态科学, 2017, 36(4):38-45 QIAO Yongmin, GUO Jia, YANG Jun, et al. Comparative analysis of phosphorus fraction in surface sediment between lakeside and middle zone of Erhai Lake and its environmental significance[J]. Ecological Science, 2017, 36(4):38-45.
[42] Bańkowska-Sobczak A, Blazejczyk A, Eiche E, et al. Phosphorus inactivation in lake sediments using calcite materials and controlled resuspension-mechanism and efficiency[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(3):223. doi: 10.3390/min10030223
[43] 孟佳, 姚庆祯, 陈洪涛, 等. 北黄海表层沉积物中颗粒态磷的形态分布[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(10):3361-3367 MENG Jia, YAO Qingzhen, CHEN Hongtao, et al. Forms and distributions of particulate phosphorus in the surface sediments of North Yellow Sea[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(10):3361-3367.
[44] 江雪, 文帅龙, 姚书春, 等. 天津于桥水库沉积物磷赋存特征及其环境意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(3):628-639 doi: 10.18307/2018.0305 JIANG Xue, WEN Shuailong, YAO Shuchun, et al. Environmental significance of phosphorus existing forms in the sediments of Yuqiao Reservoir in Tianjin[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(3):628-639. doi: 10.18307/2018.0305
[45] Yang B, Song G D, Liu S M, et al. Phosphorus recycling and burial in core sediments of the East China Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2017, 192:59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2017.04.001
[46] Liu S M, Zhang J, Chen H T, et al. Benthic nutrient recycling in shallow coastal waters of the Bohai Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2004, 22(4):365-372. doi: 10.1007/BF02843630
[47] Bastami K D, Neyestani M R, Raeisi H, et al. Bioavailability and geochemical speciation of phosphorus in surface sediments of the Southern Caspian Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 126:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.095
[48] 向速林, 吴涛哲, 龚聪远, 等. 去除有机质对城市浅水湖泊氮磷释放特征的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(5):9-14,74 XIANG Sulin, WU Taozhe, GONG Congyuan, et al. Effects of organic matter removal on nitrogen and phosphorus release characteristics from surface sediments in urban shallow lakes[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 41(5):9-14,74.
[49] Zhuang W, Gao X L, Zhang Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of phosphorus in surface sediments of two major Chinese mariculture areas: The Laizhou Bay and the coastal waters of the Zhangzi Island[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 83(1):343-351. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.03.040
[50] 潘成荣, 汪家权, 郑志侠, 等. 巢湖沉积物中氮与磷赋存形态研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2007, 23(1):43-47 PAN Chengrong, WANG Jiaquan, ZHENG Zhixia, et al. Forms of phosphorus and nitrogen existing in sediments in Chaohu Lake[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2007, 23(1):43-47.
[51] Rydin E, Malmaeus J M, Karlsson O M, et al. Phosphorus release from coastal Baltic Sea sediments as estimated from sediment profiles[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 92(1):111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.12.020
[52] Mort H P, Slomp C P, Gustafsson B G, et al. Phosphorus recycling and burial in Baltic Sea sediments with contrasting redox conditions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(4):1350-1362. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.11.016
[53] Lukkari K, Leivuori M, Vallius H, et al. The chemical character and burial of phosphorus in shallow coastal sediments in the northeastern Baltic Sea[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2009, 94(2):141-162. doi: 10.1007/s10533-009-9315-y
[54] Redfield A C, Ketchum B H, Richards F A. The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater[M]//Hill M N. The Sea. New York: Wiley InterScience, 1963.
[55] Coelho J P, Flindt M R, Jensen H S, et al. Phosphorus speciation and availability in intertidal sediments of a temperate estuary: relation to eutrophication and annual P-fluxes[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 61(4):583-590. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2004.07.001
[56] Prasad M B K, Ramanathan A L. Dissolved organic nutrients in the Pichavaram mangrove waters of east coast of India[J]. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 2008, 37(2):141-145.



 下载:
下载: