Oil and gas geochemical exploration in the southern part of East China Sea Shelf Basin—Hydrocarbon anomalies and integrated evaluation of oil-gas potentials
-
摘要: 通过对东海陆架盆地南部海域油气地球化学样品采集、酸解烃类气体和芳烃类指标的分析测试,以及地球化学异常提取,揭示了烃类地球化学指标的异常分布特征,分析了烃类气体的成因类型和深部油气属性,进行了综合地球化学异常分区和含油气性评价。烃类地球化学指标,包括酸解甲烷、酸解乙烷、芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm和稠环芳烃总量360 nm的异常,主要集中分布在研究区的西部和东部,分别与瓯江凹陷和闽江凹陷相对应。酸解烃类气体组合及甲烷碳同位素组成指示酸解烃类气体异常主要为热成因并遭受了表层氧化,深部油气属性属于干气至凝析油气,以干气为主。根据综合地球化学异常特征,划分了西部综合地球化学异常区和东部综合地球化学异常区。酸解甲烷、酸解乙烷、芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm和稠环芳烃总量360 nm指标异常在西部综合地球化学异常区均有明显显示,而东部综合地球化学异常区则以酸解烃类气体异常为主,稠环芳烃总量360 nm异常部分分布,芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm异常只有零星分布。综合评价结果表明,西部综合地球化学异常区含油气性明显优于东部综合地球化学异常区,也就是瓯江凹陷的含油气性好于闽江凹陷。Abstract: Geochemical samples are collected from the southern part of East China Sea Shelf Basin and analyzed for oil and gas geochemical indices by the authors. Geochemical indices, such as acidolysis hydrocarbon gases and aromatic hydrocarbons are analyzed. From the analysis results, geochemical anomalies are extracted, and the distribution patterns of anomalous hydrocarbon geochemical indicators revealed, in addition to the genetic types of hydrocarbon gases and deep hydrocarbon attributes. Based upon the work, integrated geochemical anomaly areas are defined and their hydrocarbon-bearing capacity evaluated for the southern area of the East China Sea Shelf Basin. The indicators of the hydrocarbon geochemical anomalies include acidolysis methane and acidolysis ethane. The anomalies with total aromatics and their derivatives over 260 nm and the total polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons above 360 nm, are mainly distributed in the eastern and western parts of the study area, corresponding to the Oujiang Sag and Minjiang Sag, respectively. Acidolysis hydrocarbon gas assemblages and methane carbon isotope compositions suggest that the anomalies of acidolysis hydrocarbon gas are mainly thermogenic type and have suffered surface oxidation. Deep hydrocarbon attributes suggest a source of dry gas to condensate oil -gas, dominated by dry gas. According to the distribution pattern of geochemical anomalies, the western comprehensive geochemical anomaly area and the eastern comprehensive geochemical anomaly areas are divided. The anomalies of acidolysis methane, acidolysis ethane, total aromatics and their derivatives over 260 nm and total polycyclic aromatics over 360 nm are evident in the western comprehensive geochemical anomaly area, while the eastern comprehensive geochemical anomaly area is dominated by acidolysis hydrocarbon gas anomalies. The total polycyclic aromatics at 360 nm are locally observed, the total aromatics and their derivatives at 260 nm are only sporadically observed in the east comprehensive geochemical anomaly area. Therefore, the western comprehensive geochemical anomaly area is obviously better than that of the eastern comprehensive geochemical anomaly area, that is, the oil and gas-bearing capacity of the Oujiang Sag is better than that of the Minjiang Sag.
-
海洋油气地球化学探测的理论基础是海底油气渗漏,主要表现为深部储层的油气向海底表层环境的渗漏。在海底表层环境,这些渗漏烃类以不同形式,如游离、吸附等赋存状态存在海底表层沉积物内,形成各类与深部油气渗漏有关的表面地球化学异常[1-6]。根据烃类气体分子组成和碳同位素组成特征可以识别地球化学异常成因类型[7-9],判别深部油气属性[10-11],获取深部含油气系统信息[12-13]。
自20世纪80年代以来,前人已在东海海域进行了一系列油气地球化学探测工作,主要集中在西湖凹陷、瓯江凹陷西部和海礁凸起等地,取得了一系列成果[14-20]。本文主要介绍东海陆架盆地南部海域油气地球化学探测研究成果。通过200个站位的地球化学样品采集、分析测试和数据处理,分析了烃类指标,包括酸解烃类气体和芳烃类指标数值特征和异常分布特征,探讨了异常成因和可能的油气属性,进行了综合地球化学异常分区和含油气性综合评价。
1. 地质背景
东海陆架盆地位于中国东部大陆边缘的东海大陆架,西邻闽浙隆起,东到钓鱼岛隆褶带,为一个发育在克拉通基底之上的中—新生代复合断陷盆地,构造单元上可以进一步分为西部坳陷带、中部隆起带和东部坳陷带[21]。盆地从西至东呈现凹-凸-凹的构造格局,南北差异性明显,具有东西分带,南北分块的特点[22-24]。盆地面积达26.7×104 km2。东西宽250 km,南北长1 500 km,有效勘探面积24×104 km2,最大沉积厚度约15 000 m,油气资源较为丰富[25]。
东海陆架盆地是东海陆架上最主要的油气储藏和生产区[22]。新生界主要烃源岩为暗色泥岩和煤,自下而上分别有古新统、始新统、渐新统—中新统等3套油气组合的有利烃源岩,整体具有较好的油气资源前景[26]。
钻井证实,瓯江凹陷内发育有月桂峰组、灵峰组以及明月峰组等3套烃源岩[27],月桂峰组与灵峰组为其中发育较好的有利烃源岩,为岩性油气藏的形成发育提供了有利条件[28],在瓯江凹陷已发现有LS36-1-1工业油气井[22,26]。
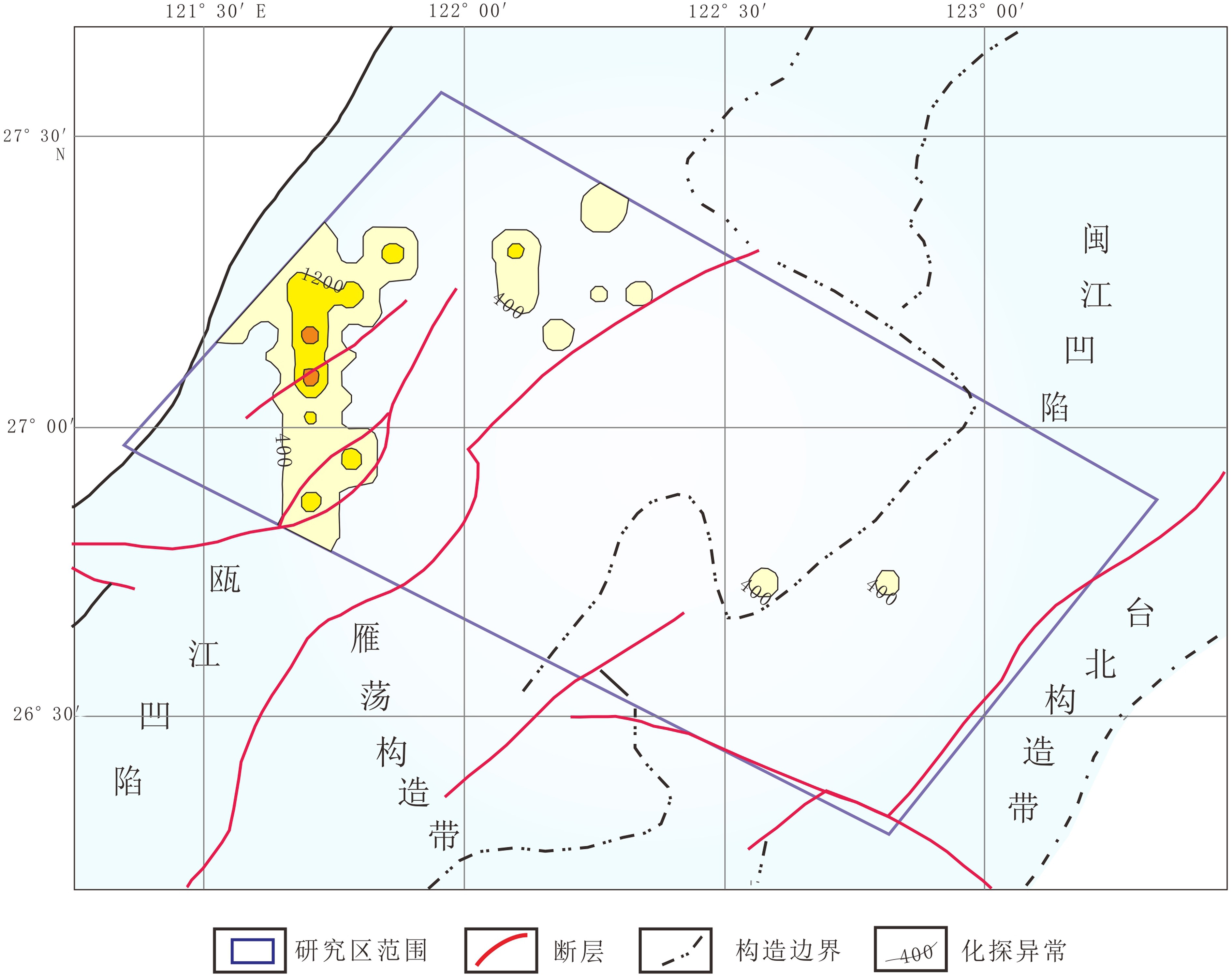
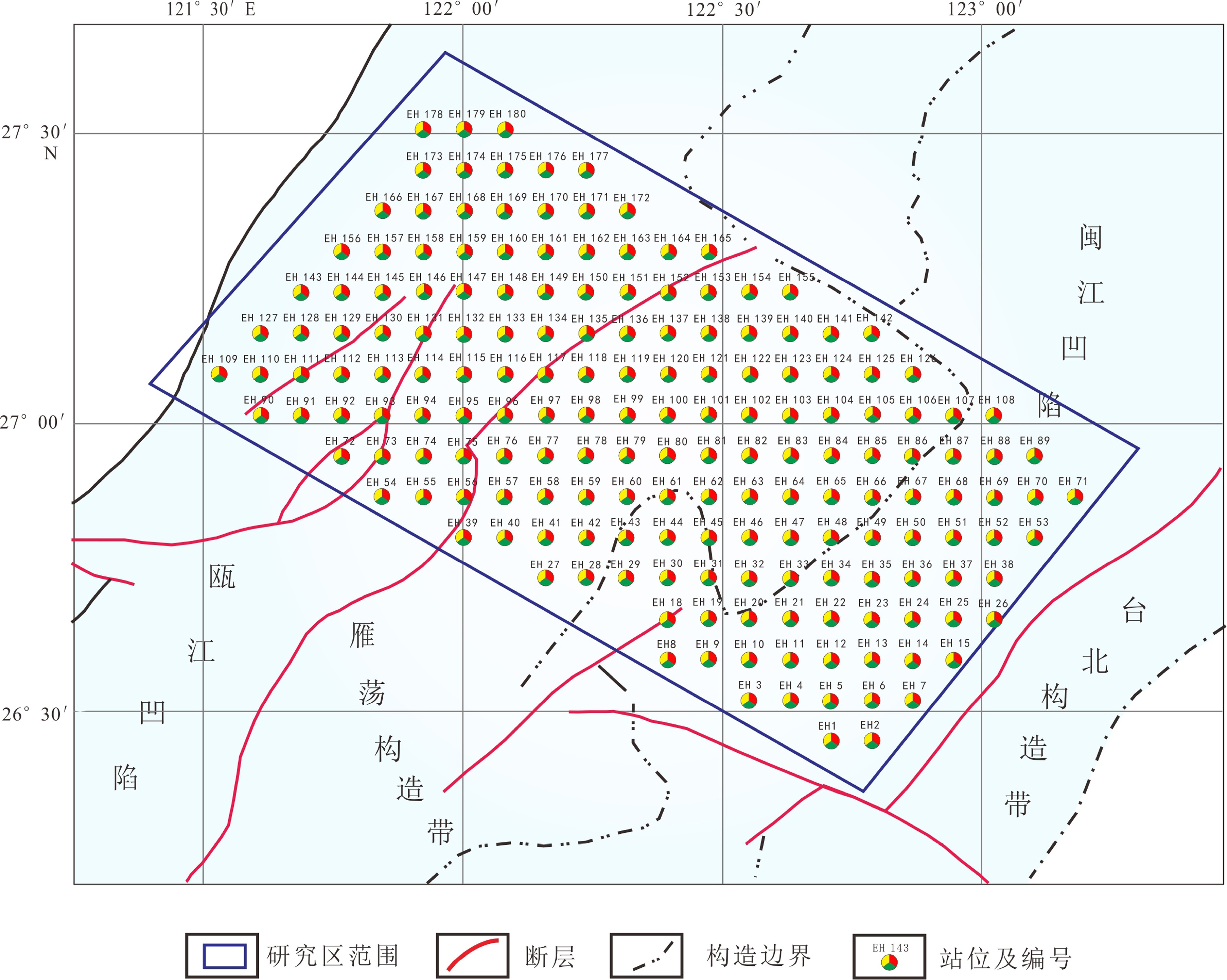
本次油气地球化学探测以东海陆架盆地南部海域的瓯江凹陷、雁荡构造带和闽江凹陷为主要探测区(图1)。该区无论是新生代还是中生代均具有较好的油气资源潜力,且勘探程度相对较低,同时以海底地势平坦、宽度广,水深小于150 m,海底沉积物主要是砂和粉砂质沉积为特点,开展海域油气地球化学探测干扰因素少,能够获得客观真实的地球化学探测结果。
2. 样品采集与分析测试
2.1 样品采集
研究区位于东海陆架盆地南部海域,水深范围为50~150 m。地球化学探测区由西向东穿过了瓯江凹陷、雁荡构造带、闽江凹陷等不同构造单元。地球化学站位布设呈北西向展布,垂直穿过上述几个主要构造单元。取样网格密度为8 km×8 km,共布设200个取样站位(图1)。
样品采集由上海海洋石油局第一海洋地质大队承担。外业调查船为“勘407”号地质调查船,导航采用中海达公司导航软件Haida海洋测量系统,定位采用美国Trimble公司产DSM132 型DGPS系统,海底沉积物柱状取样采用DDC-Z-2型振动取样器。经过2013年5月10日至6月24日和2013年9月1日至9月13日2个航段,历时59天完成了全部200个站位的海底沉积物样品采集。
2.2 分析测试
2.2.1 酸解烃类气体和酸解甲烷碳同位素
酸解烃类气体的分析测试流程为:称取粒径为0.419 mm试样50 g置于磨口烧瓶中,接到脱气系统上。磨口烧瓶置于40 ℃的水浴锅中,缓慢滴加盐酸溶液,同时摇动烧瓶,至不再产生气泡时,停止加盐酸,平衡20 min。用玻璃注射器抽取脱出气体,记录脱出气体的体积。用微量注射器准确抽取适量气体,迅速注入气相色谱仪,启动程序,采集数据,自动进行定性和定量计算。方法测定指标主要包括C1—C5轻烃类组分,测定范围(以甲烷计)≥0.05 μL/kg。
甲烷碳同位素组成分析使用的仪器为美国Thermo Finnigan公司生产的同位素质谱仪Mat253。分析流程是将气相色谱仪分离的烃类气体,转化成二氧化碳和水后进入稳定碳同位素质谱仪进行甲烷碳同位素测定。
2.2.2 芳烃及其衍生物总量
芳烃及其衍生物总量测定采用紫外吸收光谱测量法。将样品用适当的有机试剂浸泡、振荡萃取,其溶液在紫外分度计上λ200 nm~λ300 nm范围进行扫描,并记录各特征波长的吸光度值,应用标准曲线法计算含量。检测指标为220、260和275 nm波长处的芳烃含量,测定范围为ω(萘)=0.2×10−9~100×10−9。
2.2.3 稠环芳烃总量
稠环芳烃总量测量主要采用荧光光谱法。将海底沉积物样品用合适的试剂萃取后,利用荧光分光光度计,选择合适的固定激发波长,检测萃取液中可以反映油气信息的稠环芳烃荧光光谱特征及其特征峰强度。检测指标为320、360和405 nm波长处的稠环芳烃含量,测定范围为ω(萘)=0.2×10−9~100×10−9。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 结果
本次研究获得了200个站位样品的酸解烃类气体(C1—C5)、芳烃及其衍生物总量(220、260和275 nm)和稠环芳烃总量(320、360和405 nm)地球化学指标的分析结果和24个样品的酸解甲烷碳同位素分析结果。表1给出了各类地球化学指标的最大值、最小值、均值、标准偏差和变异系数。24个酸解甲烷碳同位素组成范围为−34.8‰~−32.4‰,数据较为集中,变化范围不大。
表 1 地球化学指标数值特征Table 1. Data of geochemical indicators指标及数值参数 最小值 最大值 均值 标准偏差 变异系数 酸解甲烷(μL/kg) 28.34 1 106.38 310.13 181.71 0.59 酸解乙烷(μL/kg) 0.62 16.95 5.91 3.32 0.56 酸解丙烷(μL/kg) 0.15 4.63 1.76 0.93 0.53 酸解异丁烷(μL/kg) 0.03 1.15 0.47 0.26 0.55 酸解正丁烷(μL/kg) 0.04 1.53 0.57 0.32 0.56 酸解异戊烷(μL/kg) 0.05 0.97 0.34 0.21 0.62 酸解正戊烷(μL/kg) 0.02 0.67 0.23 0.13 0.57 芳烃及其衍生物220 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 2.90 2 615.70 218.47 489.21 2.24 芳烃及其衍生物260 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 1.00 2 502.10 154.82 404.14 2.61 芳烃及其衍生物275 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 0.60 2 520.60 149.97 400.90 2.67 稠环芳烃320 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 5.90 75.00 18.61 7.87 0.43 稠环芳烃360 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 6.40 79.00 21.59 12.44 0.58 稠环芳烃405 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 1.20 46.00 7.01 6.46 0.92 3.2 讨论
3.2.1 地球化学异常分布特征
(1)地球化学指标优选和异常下限确定
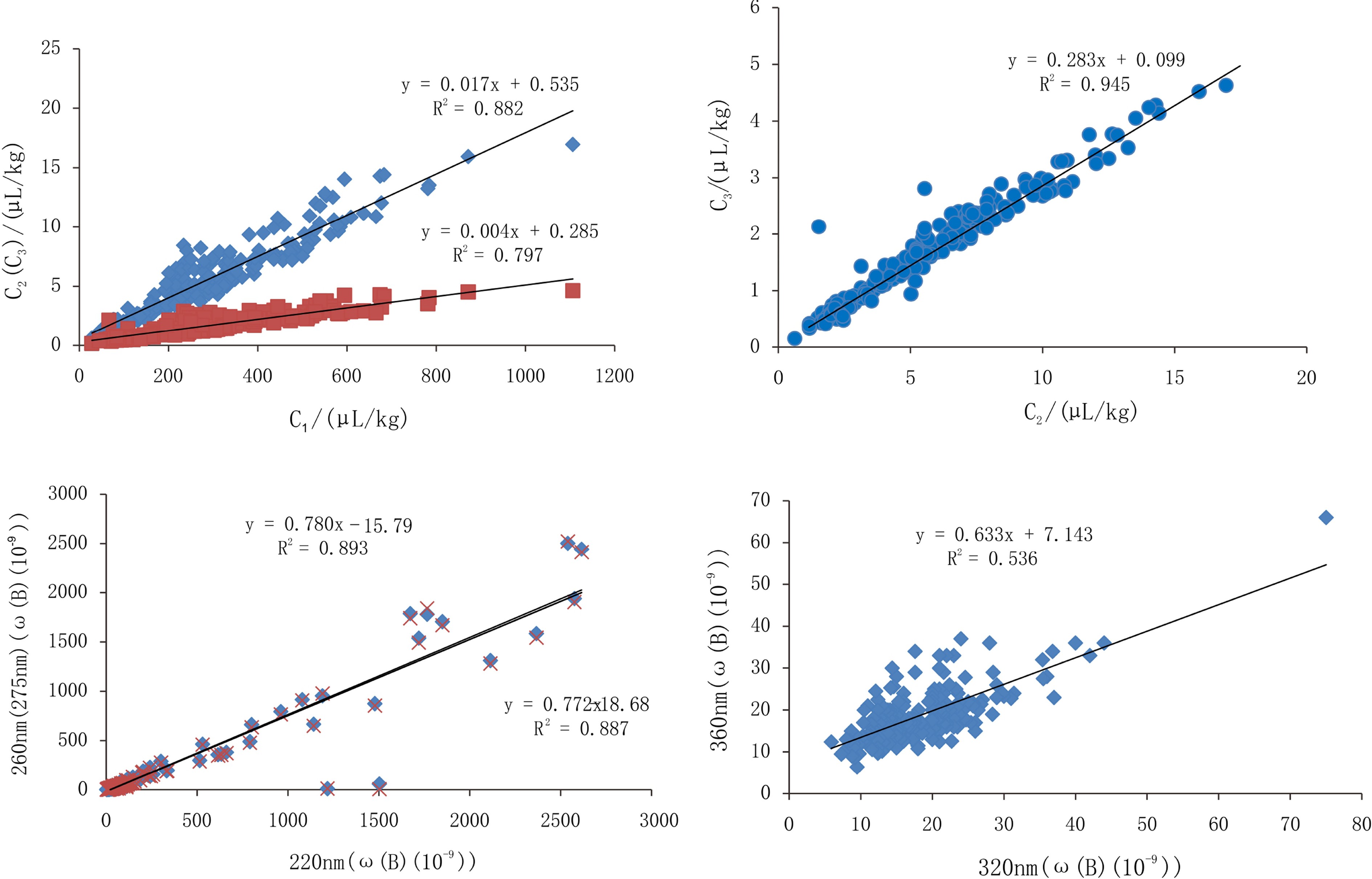
地球化学指标的优选是从众多指标中选取有代表性指标进行地球化学异常特征分析。酸解烃类气体指标相关分析结果显示,酸解甲烷与酸解乙烷和酸解丙烷之间均为正相关关系,相关系数分别为0.882和0.797,酸解乙烷和酸解丙烷为正相关关系,相关系数为0.945,明显高于酸解甲烷与酸解乙烷和丙烷的相关系数(图2)。酸解丙烷以上的酸解烃类气体,包括丁烷和戊烷含量低,一些站位的含量接近或低于检出限,在相关分析中没有考虑。现有研究表明甲烷与乙烷及以上的重烃气体组分在成因上可能存在差异,甲烷可以是生物成因,也可以是热成因,而乙烷以上的重烃气体组分主要是热成因[7-9]。为此,在酸解烃类气体指标中选择酸解甲烷和酸解乙烷2个指标进行异常特征分析。
芳烃及其衍生物总量220与260和275 nm之间相关系数分别为0.893和0.887(图2),表现为明显的正相关关系,因此,用260 nm能够代表芳烃及其衍生物总量所有指标的异常分布特征。
稠环芳烃总量在研究区海底沉积物中总体偏低,多数结果处于检出限附近,会影响这些指标之间的相关性,320与360 nm的相关系数为0.536(图2),具有一定的正相关关系,考虑到405 nm含量低,因此,从指标含量和相关性综合考虑,选择360 nm来代表稠环芳烃总量进行异常特征分析。
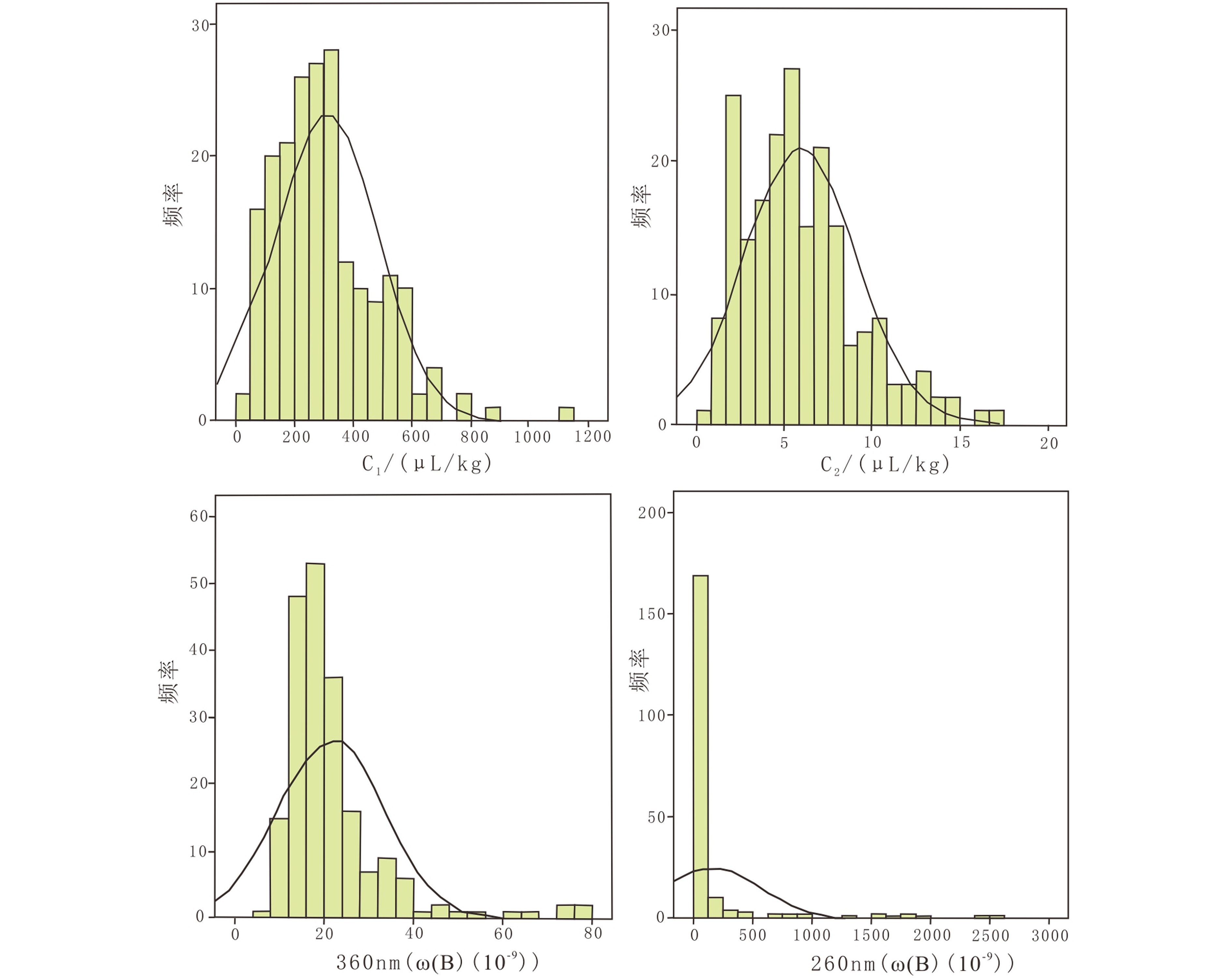
地球化学异常下限的确定有多种方法,包括图解法、计算法,以及趋势分析法等。对研究区海底沉积物主要地球化学指标的异常下限的确定主要考虑了各指标的频率分布特征并结合了计算法给出的结果。从各指标的频率分布图可见(图3),酸解甲烷的主峰范围为200~400 μL/kg,另一个次峰范围为500~600 μL/kg,2个峰的正态分布曲线的交点在300 μL/kg附近,结合计算结果确定的异常下限值为300 μL/kg。酸解乙烷的主峰范围为4~8 μL/kg,另一个次峰范围为9~12 μL/kg,2个峰的正态分布曲线的交点在6 μL/kg附近,结合计算结果确定的异常下限值为6 μL/kg。稠环芳烃总量360 nm的主峰范围为12~24ω(B)(10−9),另一个次峰范围为28~40ω(B)(10−9),2个峰的正态分布曲线的交点在23ω(B)(10−9)附近,结合计算结果确定的异常下限值为23ω(B)(10−9)。芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm的主峰范围为0~250ω(B)(10−9),另一个次峰范围为600~1100ω(B)(10−9),2个峰的正态分布曲线的交点在400ω(B)(10−9)附近,结合计算结果确定的异常下限值为400ω(B)(10−9)。
(2)酸解烃类气体地球化学异常特征
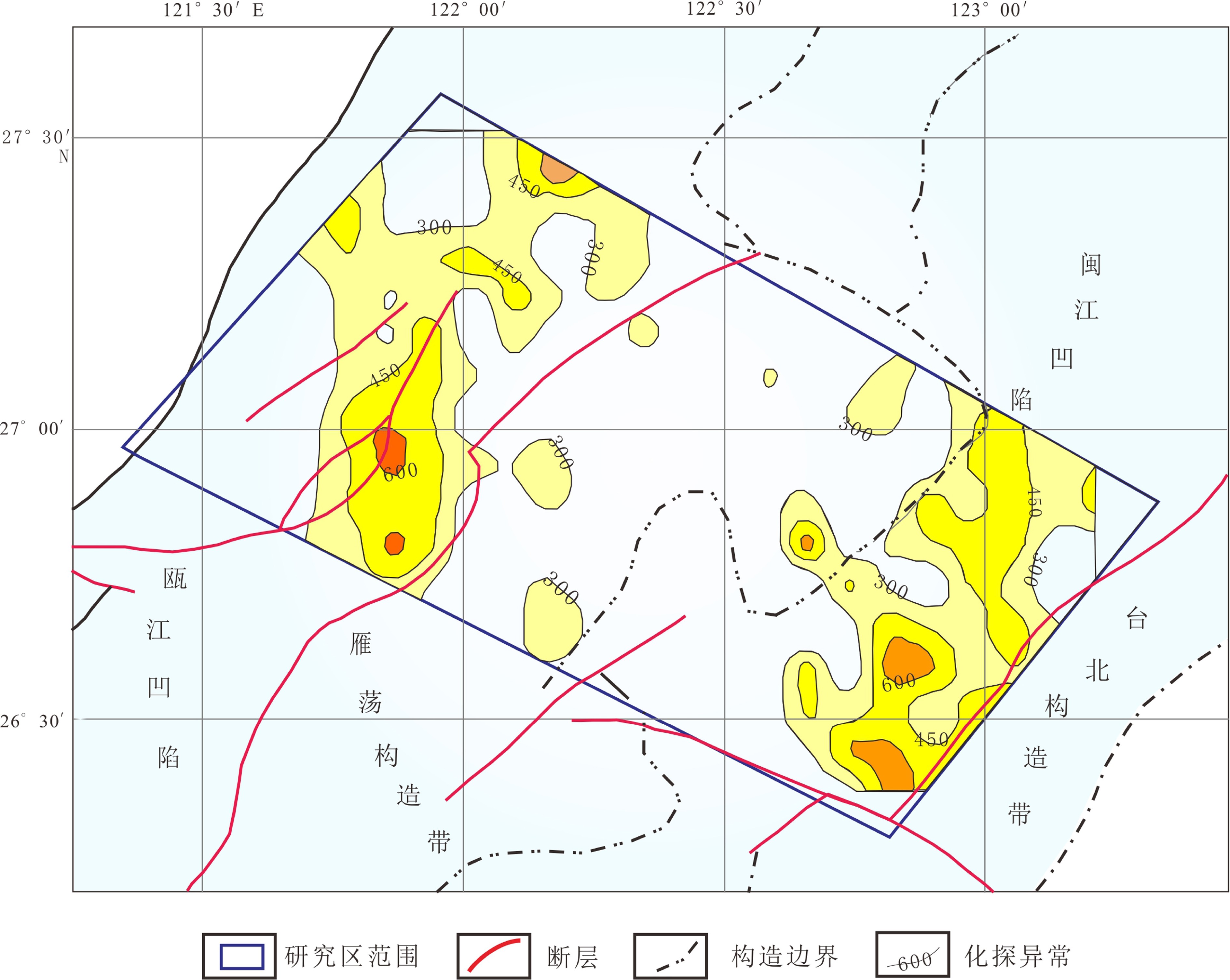
酸解甲烷地球化学异常集中分布在研究区的东部和西部,中部只有零星小异常分布且强度低,在构造单元上西部异常主要分布在瓯江凹陷范围内,而东部异常则主要分布在闽江凹陷范围内(图4)。
酸解乙烷异常分布总体上与酸解甲烷一致,也主要集中在研究区的东部和西部,但西部异常有明显分解,可进一步分解为西北部和东南部异常,在构造上酸解乙烷异常主要受瓯江凹陷和闽江凹陷的控制(图5)。
(3)芳烃类地球化学异常特征
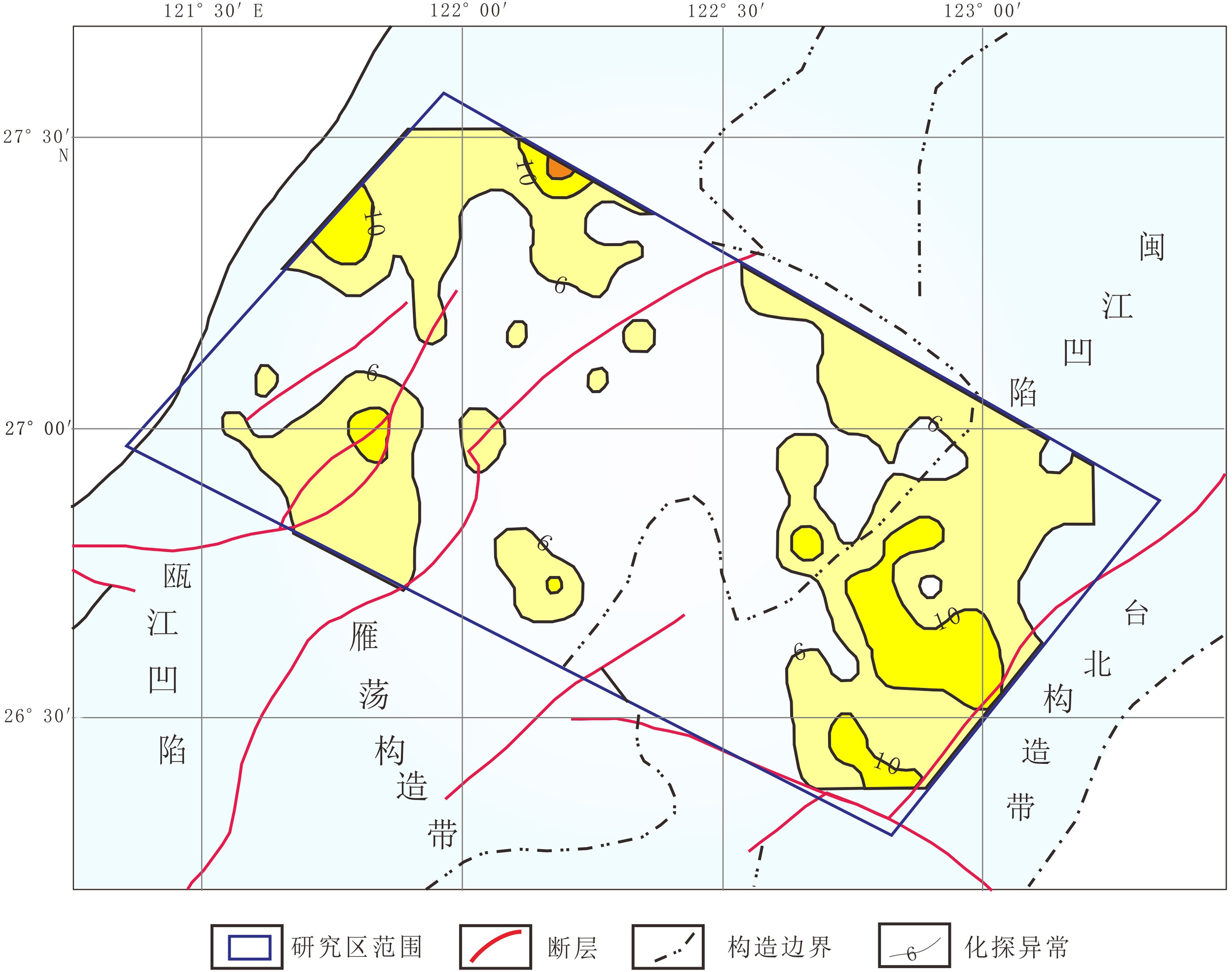
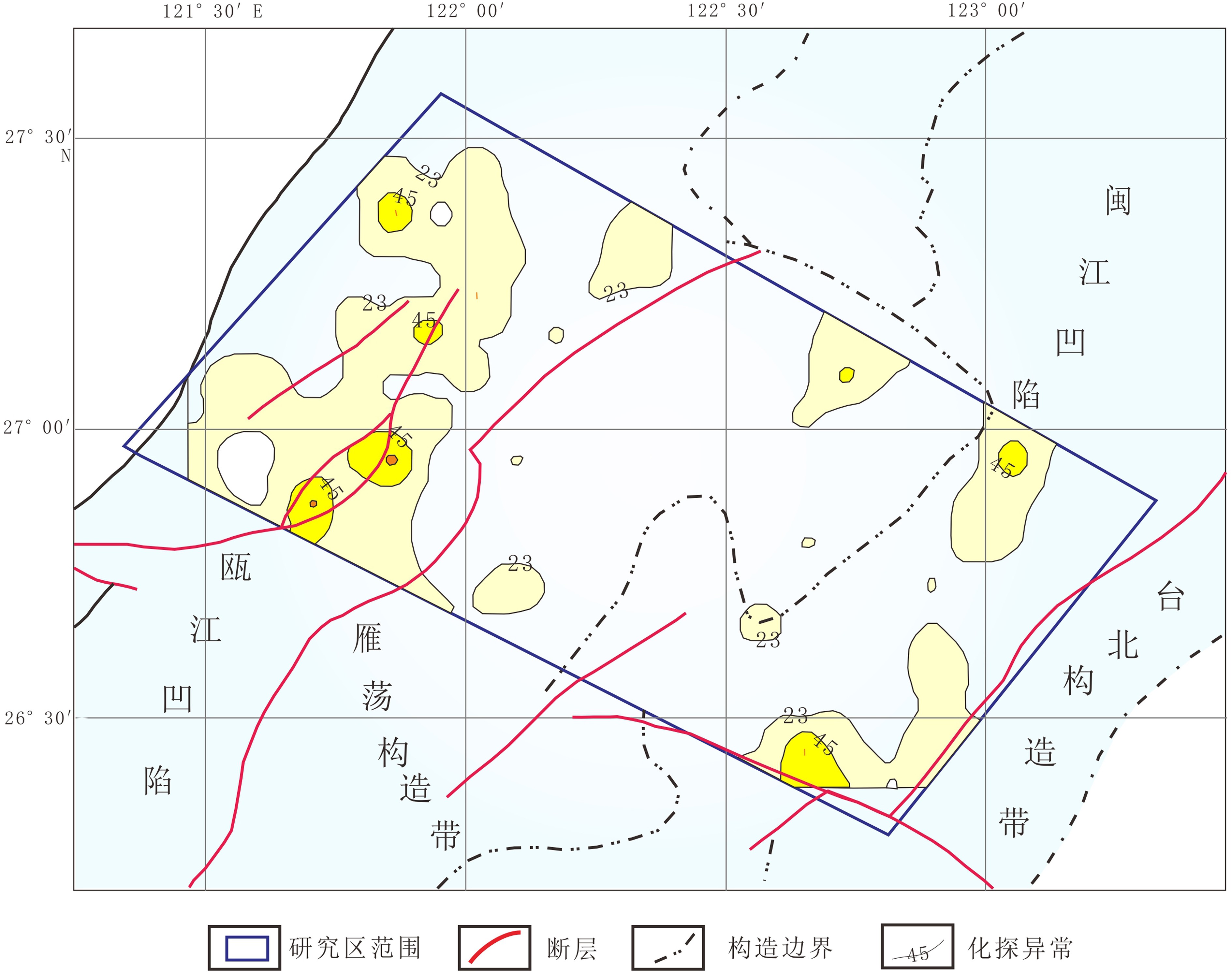
芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm地球化学异常主要分布在研究区的西部,中部无明显异常,东部只有零星的2处小规模异常存在。在构造上,西部异常位于瓯江凹陷范围内,其中大规模异常明显与瓯江凹陷内的断裂构造在空间上对应(图6)。
稠环芳烃总量360 nm地球化学异常主要分布在研究区的西部和东部,中部只有零星的小规模异常存在。相比较而言,西部异常更为集中,连续性好,异常强度和规模均较大,东部异常则较为分散,由3处规模不等的异常构成。在构造上东部异常位于闽江凹陷范围内,西部异常位于瓯江凹陷范围内且异常分布与瓯江凹陷内的断裂构造在空间上一致(图7)。
3.2.2 地球化学异常成因与油气属性分析
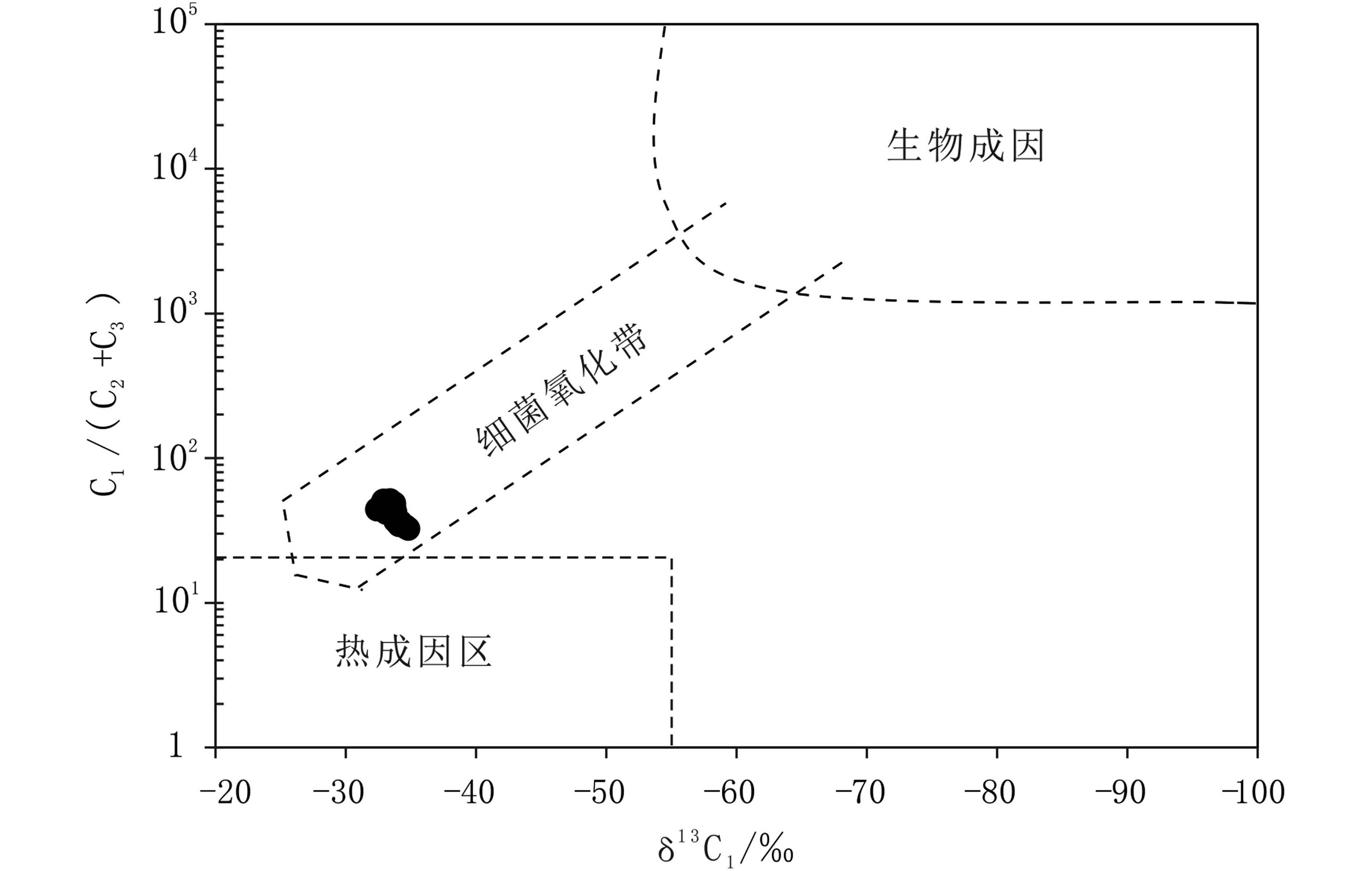
目前用于判别烃类气体地球化学异常成因类型主要指标有烃类气体分子组成及甲烷碳同位素特征。Bernard等对墨西哥湾沉积物烃类气体渗漏区一些样品的分析结果表明,细菌气比热成气同位素更轻。细菌产生的甲烷典型的碳同位素δ13C值小于−50‰,而热成甲烷典型的碳同位素δ13C值大于−50‰。细菌气的C1/(C2+C3)比值大于1 000,而热成因气其比值小于50,利用样品的C1/(C2+C3)比值与甲烷碳同位素δ13C值的关系,建立了判别热成因和生物成因的Bernard图解[7]。
东海陆架盆地南部海底沉积物酸解烃类气体组合指标的分析结果表明(表2),酸解烃类气体异常站位的C1/(C2+C3)和C1/C2比值范围分别是29.80~54.98和39.78~72.07,均属于或接近热成因范围。海底沉积物甲烷碳同位素组成变化范围为−32.4‰~−34.8‰,较生物成因烃类明显偏重,属于热成因烃范围。在Bernard图解上,所有投点均靠近热成因区,落入细菌氧化带内(图8),表明深部来源的热成因气在海底表面受到表层细菌氧化作用导致甲烷氧化和碳同位素分异[29,30]。
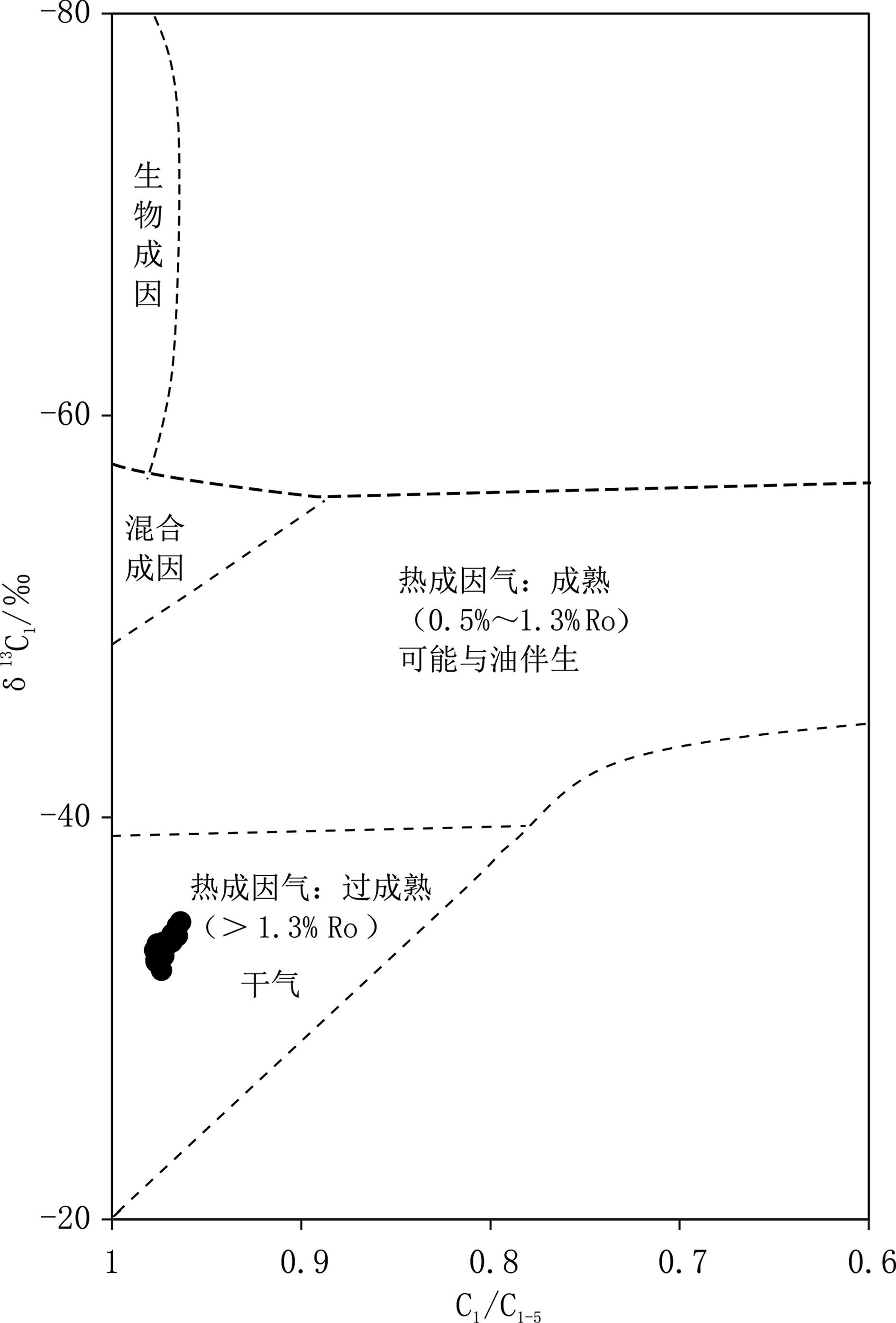
在δ13C1(‰)与C1/C1-5关系图中,样品投点明显落入热成因区,并且指示深部烃类属于过成熟的热成因干气(图9)[10]。
利用海底沉积物酸解烃类气体C1/C2+C3与C2/(C3+C4)图解[11]对研究区深部油气属性的判别结果表明,样品投点非常集中分布在“干气”区,指示深部的油气属性为干气(图10)。另外,利用海底沉积物酸解烃类气体C1/C2频率分布对深部油气类型的判别结果可以看出,研究区深部油气类型属于气藏和凝析油气藏重叠范围内,并且以气藏为主(图11),与前人在东海其他海域的判别结果相似[20]。
3.2.3 综合地球化学异常分区及含油气性评价
在单指标地球化学异常分析的基础上,通过各类指标地球化学异常的叠合,进行综合地球化学异常分区,划分了西部和东部2个综合地球化学异常区(图12)。
西部综合地球化学异常区在构造上位于瓯江凹陷范围内,酸解烃类气体、芳烃及其衍生物和稠环芳烃等指标的异常均有分布且强度较高。
东部综合地球化学异常区在构造上位于闽江凹陷范围内,酸解烃类气体异常明显且较为集中,而稠环芳烃异常存在但较为分散,芳烃及其衍生物异常不发育,只有零星异常存在。
为进一步认识东海陆架盆地南部海域油气资源潜力,参照作者在其他海域的评价经验[31],对2个综合地球化学异常区含油气性进行了综合评价,具体步骤如下:
(1)选取酸解甲烷、酸解乙烷、芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm和稠环芳烃总量360 nm共4个地球化学指标;
(2)根据各地球化学指标特征,选择异常规模、异常强度、异常和构造的符合程度和油气显示情况4个评价因子,分别给出相应得分,其中按照异常规模大小分为3级,得分分别是大规模异常2分,小规模异常1分,无异常0分;按照异常强度分为2级,高强度为2分,低强度为1分;按照异常与构造的符合程度分为2级,符合1分,不符合0分;按照是否存在油气显示分为2级,有油气显示1分,无油气显示0分;
(3)按照4个地球化学指标对应的异常规模、异常强度、异常与构造符合程度和油气显示情况计算2个综合地球化学异常区的累积得分,给出2个综合地球化学异常区含油气性对比结果(表3)。
表 3 东海陆架盆地南部海域综合地球化学异常区累积得分及评价结果Table 3. Accumulative score and evaluation results of comprehensive geochemical areas in the southern part of the East China Sea shelf basin综合地球化学异常区 评价因子 异常指标 累积得分 酸解甲烷 酸解乙烷 芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm 稠环芳烃总量360 nm 西部综合地球化学异常区(A) 异常规模 2 2 2 2 25 异常强度 2 2 2 2 构造符合 2 2 2 2 油气显示 1 东部综合地球化学异常区(B) 异常规模 2 2 0 1 15 异常强度 2 2 0 1 构造符合 2 2 0 1 油气显示 0 西部综合地球化学异常区(A):位于研究区西部的瓯江凹陷范围内,区域上处于有利的构造部位,区内有LS-36-1-1气田,酸解烃类气体、芳烃及其衍生物和稠环芳烃地球化学指标异常规模大、强度高。综合4个因子的累积得分为25分,属于好的油气远景区。
东部综合地球化学异常区(B):位于研究区东部的闽江凹陷范围内,区域上处于有利的构造部位,未见有明显的油气显示,酸解烃类气体甲烷异常规模大、强度高,其他指标也显示中等或弱异常。综合4个因子的累积得分为15分,属于中等油气远景区。
上述综合评价结果表明,东部综合地球化学异常区的含油性明显优于西部综合地球化学异常区,也就是瓯江凹陷的含油性优于闽江凹陷。应该指出的是,以上对2个综合地球化学异常区含油气性的评价结果受研究区勘探和地质认识程度的限制,只是阶段性认识,随着调查区勘探程度的提高和认识的深化,上述认识可能发生变化。
4. 结论
(1)烃类地球化学指标,包括酸解甲烷、酸解乙烷、芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm和稠环芳烃总量360 nm的异常分布主要集中在研究区的西部和东部,分别与瓯江凹陷和闽江凹陷相对应。
(2)酸解烃类气体组合及甲烷碳同位素组成指示酸解烃类气体异常主要为热成因并遭受了表层氧化,深部油气属性属于干气至凝析油气,以干气为主。
(3)西部综合地球化学异常区和东部综合地球化学异常区综合评价结果表明,西部综合地球化学异常区含油气性明显优于东部综合地球化学异常区,也就是瓯江凹陷的含油气性优于闽江凹陷。
-
表 1 地球化学指标数值特征
Table 1 Data of geochemical indicators
指标及数值参数 最小值 最大值 均值 标准偏差 变异系数 酸解甲烷(μL/kg) 28.34 1 106.38 310.13 181.71 0.59 酸解乙烷(μL/kg) 0.62 16.95 5.91 3.32 0.56 酸解丙烷(μL/kg) 0.15 4.63 1.76 0.93 0.53 酸解异丁烷(μL/kg) 0.03 1.15 0.47 0.26 0.55 酸解正丁烷(μL/kg) 0.04 1.53 0.57 0.32 0.56 酸解异戊烷(μL/kg) 0.05 0.97 0.34 0.21 0.62 酸解正戊烷(μL/kg) 0.02 0.67 0.23 0.13 0.57 芳烃及其衍生物220 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 2.90 2 615.70 218.47 489.21 2.24 芳烃及其衍生物260 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 1.00 2 502.10 154.82 404.14 2.61 芳烃及其衍生物275 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 0.60 2 520.60 149.97 400.90 2.67 稠环芳烃320 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 5.90 75.00 18.61 7.87 0.43 稠环芳烃360 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 6.40 79.00 21.59 12.44 0.58 稠环芳烃405 nm(ω(B)(10−9)) 1.20 46.00 7.01 6.46 0.92 Table 2 Discriminant index of anomaly attributes of acidolysis hydrocarbon gases from seabed sediments[7-8]
C1/C2+C3 C1/C2 δ13C1/‰ 判别标准 生物构成 >1 000 <−54 热成因 <50 4~100 −20~−54 研究区酸解烃类气体 29.80~54.98 39.78~72.07 −32.4~−34.8 表 3 东海陆架盆地南部海域综合地球化学异常区累积得分及评价结果
Table 3 Accumulative score and evaluation results of comprehensive geochemical areas in the southern part of the East China Sea shelf basin
综合地球化学异常区 评价因子 异常指标 累积得分 酸解甲烷 酸解乙烷 芳烃及其衍生物总量260 nm 稠环芳烃总量360 nm 西部综合地球化学异常区(A) 异常规模 2 2 2 2 25 异常强度 2 2 2 2 构造符合 2 2 2 2 油气显示 1 东部综合地球化学异常区(B) 异常规模 2 2 0 1 15 异常强度 2 2 0 1 构造符合 2 2 0 1 油气显示 0 -
[1] Horvitz L. Geochemical exploration for petroleum [J]. Science, 1985, 229(4716): 812-827.
[2] Brooks J M, Kennicott M C, Carey B D. Offshore surface geochemical exploration [J]. Oil and Gas Journal, 1986, 84(42): 66-72.
[3] Abrams M A. Geophysical and geochemical evidence for subsurface hydrocarbon leakage in the Bering Sea, Alaska [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1992, 9(2): 208-221. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(92)90092-S
[4] Abrams M A. Interpretation of Methane Carbon Isotopes Extracted from Surficial Marine Sediments for Detection of Subsurface Hydrocarbons[M]//Schumacher D, Abrams M A. Hydrocarbon Migration and Its Near-Surface Expression. Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA: AAPG, 1996, 66: 309-318.
[5] Klusman R W, Saeed M A. Comparison of Light Hydrocarbon Microseepage Mechanism[M]//Schumacher D, Abrams M A. Hydrocarbon Migration and Its Near-Surface Expression. Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA: AAPG, 1996, 66: 157-168.
[6] Faber E, Stahl W. Geochemical surface exploration for hydrocarbons in North Sea [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1984, 68(3): 363-386.
[7] Bernard B B, Brooks J M, Sackett W M. Light hydrocarbons in recent Texas continental shelf and slope sediments [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1978, 83(C8): 4053-4061. doi: 10.1029/JC083iC08p04053
[8] Bernard B, Brooks J M, Zumberge J. Determining the Origin of Gases in Near Surface Sediments[M]//Near-Surface Hydrocarbon Migration:Mechanisms and Seepage Rates. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American Association of Petroleum Geologist, 2002,7-10.
[9] Whiticar M J, Suess E, Wehner H. Thermogenic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the Bransfield Strait, Antarctic Peninsula [J]. Nature, 1985, 314(6006): 87-90. doi: 10.1038/314087a0
[10] Tissot B P, Welte D H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1984: 207-224.
[11] Jones V T, Matthews M D, Richers D M. Light hydrocarbons for petroleum and gas prospecting [J]. Handbook of Exploration Geochemistry, 2000, 7: 133-212. doi: 10.1016/S0168-6275(00)80029-X
[12] Abrams M A, Dahdah N F, Geršlová E. Evaluating petroleum systems in frontier exploration areas using seabed geochemistry [J]. World Oil, 2004, 225(6): 53-60.
[13] Abrams M A. Significance of hydrocarbon seepage relative to petroleum generation and entrapment [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2005, 22(4): 457-477. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.08.003
[14] 李维显, 刘峻, 黄招莲. 东海油气表层地球化学勘查指标的讨论[J]. 物探与化探, 1993, 17(2):98-101. [LI Weixian, LIU Jun, HUANG Zhaolian. A discussion on indices of surface geochemical exploration for oil and gas in the East Sea [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1993, 17(2): 98-101. [15] 朱炳球, 孙忠军, 余慧. 浅海油气地球化学勘查前景[J]. 物探与化探, 1996, 20(3):161-172. [ZHU Bingqiu, SUN Zhongjun, YU Hui. The prospects of shallow-sea oil and gas geochemical exploration [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1996, 20(3): 161-172. [16] 张建培, 王飞. 海洋油气地球化学勘探-以东海某研究区为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 1997, 19(4):332-336. [ZHANG Jianpei, WANG Fei. Marine hydrocarbon geochemical prospecting -with a study area in East China Sea as a example [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 1997, 19(4): 332-336. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199704332 [17] 席敏红, 须雪豪. 西湖凹陷保俶斜坡油气化探资料连片处理与解释[J]. 海洋石油, 1998, 18(3):44-48. [XI Minhong, XU Xuehao. The processing and explaining of hydrocarbon geochemical data in the Baochu slope of the Xihu Sag [J]. Offshore Oil, 1998, 18(3): 44-48. [18] 张建培, 须雪豪. 东海海礁凸起地球化学特征及含油气性分析[J]. 海洋石油, 2001, 21(2):1-6. [ZHANG Jianpei, XU Xuehao. Geochemical processing characters & analysis of hydrocarbon potential in the Haijiao Uplift, the East China Sea [J]. Offshore Oil, 2001, 21(2): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2001.02.001 [19] 李维显. 东海海礁凸起及邻近海区油气表层地球化学勘查[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(2):190-196. [LI Weixian. Oil and gas surface geochemical exploration in the Haijiao Uplift and its neighbouring of the East China Sea [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2003, 25(2): 190-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.02.016 [20] 杨文达, 崔征科, 张异彪. 东海地质与矿产[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2010. YANG Wenda, CUI Zhengke, ZHANG Yibiao. Geology and Mineral of East China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2010.
[21] 张锦伟, 赵汗青, 傅志飞. 东海陆架盆地南部构造演化及对油气的控制作用[J]. 海洋石油, 2011, 31(2):8-12. [ZHANG Jinwei, ZHAO Hanqing, FU Zhifei. Tectonic evolution of the southern East China Sea Shelf Basin and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation [J]. Offshore Oil, 2011, 31(2): 8-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.02.008 [22] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等. 东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J]. 上海地质, 2003(3):1-6. [LIU Jinshui, LIAO Zongting, JIA Jianyi, et al. The geological structure and tectonic evolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Shanghai Geology, 2003(3): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2003.03.001 [23] 王国纯. 东海盆地油气勘探焦点问题探讨[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):29-32. [WANG Guochun. A discussion on some focal problems of petroleum exploration in East China Sea Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 2003, 17(1): 29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2003.01.007 [24] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 李刚, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代构造演化与原型盆地性质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):105-111. [YANG Changqing, YANG Chuansheng, LI Gang, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution and prototype basin characters in the southern East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 105-111. [25] 姜亮. 东海陆架盆地油气资源勘探现状及含油气远景[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1):1-5. [JIANG Liang. Exploration status and perspective of petroleum resources in East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 2003, 17(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2003.01.001 [26] 冯晓杰, 蔡东升. 东海陆架盆地中新生代构造演化对烃源岩分布的控制作用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2006, 18(6):372-375. [FENG Xiaojie, CAI Dongsheng. Controls of Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution on source rock distribution in East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2006, 18(6): 372-375. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.06.003 [27] 郝乐伟, 王琪, 梁建设, 等. 东海陆架盆地瓯江凹陷烃源岩评价及资源量预测[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(6):1054-1059. [HAO Lewei, WANG Qi, LIANG Jianshe, et al. Evaluation of source rock and petroleum resource estimation in the Oujiang Sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(6): 1054-1059. [28] 杨传胜, 杨长清, 李刚, 等. 东海陆架盆地中-新生界油气勘探研究进展与前景分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2):136-147. [YANG Chuansheng, YANG Changqing, LI Gang, et al. Prospecting of Meso-Cenozoic hydrocarbon in the East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(2): 136-147. [29] Barker J F, Fritz P. Carbon isotope fractionation during microbial methane oxidation [J]. Nature, 1981, 293(5830): 289-291. doi: 10.1038/293289a0
[30] Whiticar M J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 161(1-3): 291-314. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00092-3
[31] 李双林, 董贺平, 赵青芳, 等. 北黄海盆地烃类地球化学场与综合异常分区[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(5):91-99. [LI Shuanglin, DONG Heping, ZHAO Qingfang, et al. Hydrocarbon geochemical fields and anomalies regions in the North Yellow Sea Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(5): 91-99.



 下载:
下载: