TYPES OF SEA-BOTTOM CHANNELS AND RELATED GASHYDRATE ACCULULATIONS IN THE SHENHU AREA, SOUTH CHINA SEA (SCS)
-
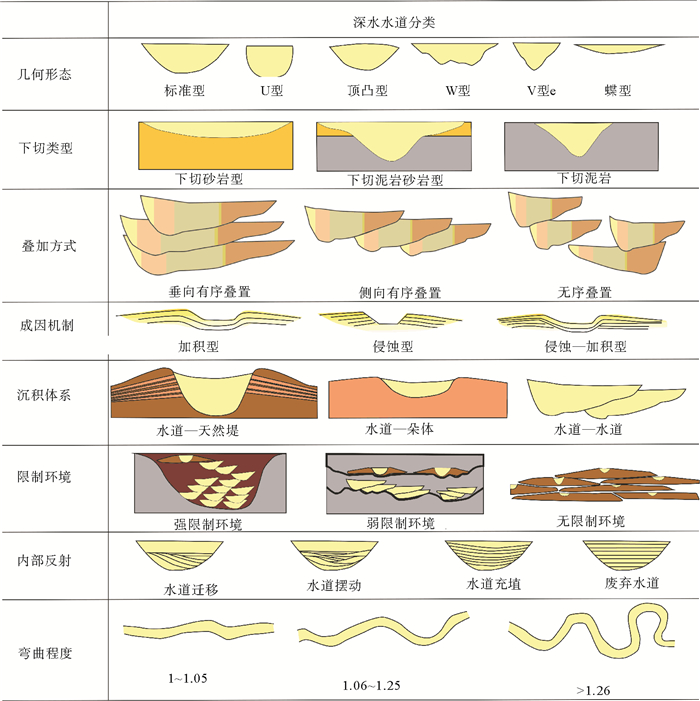
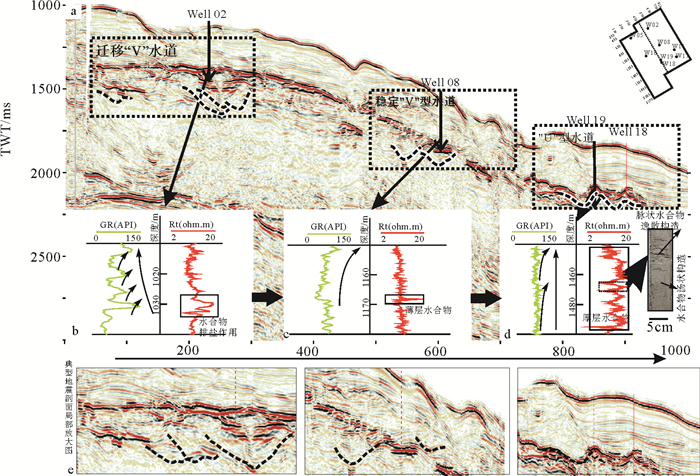
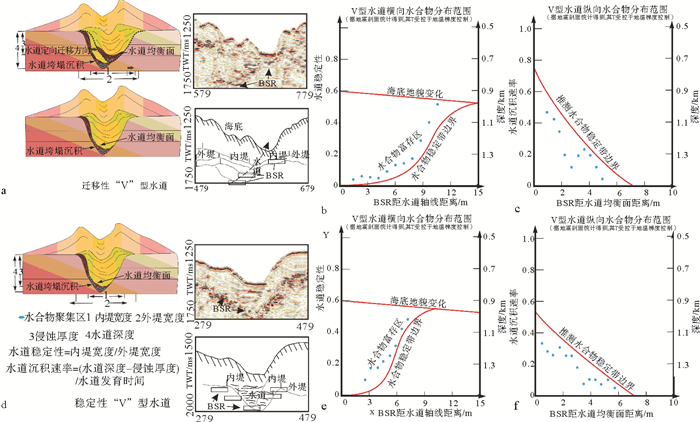
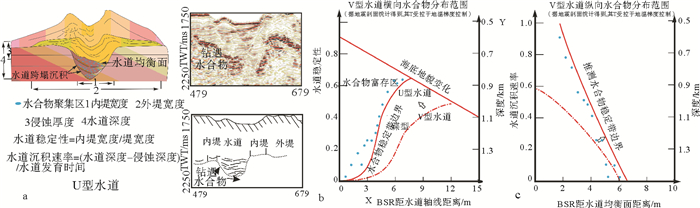
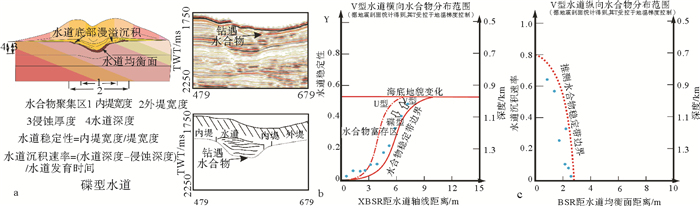
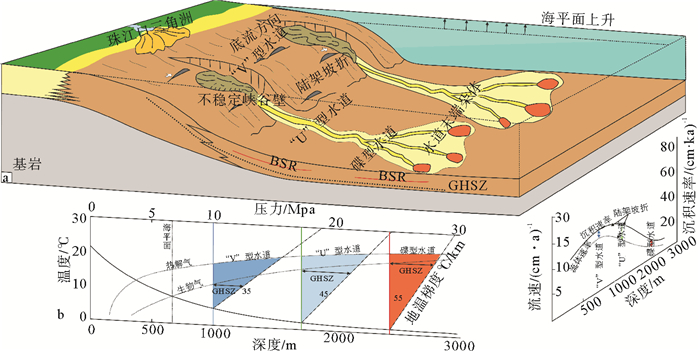
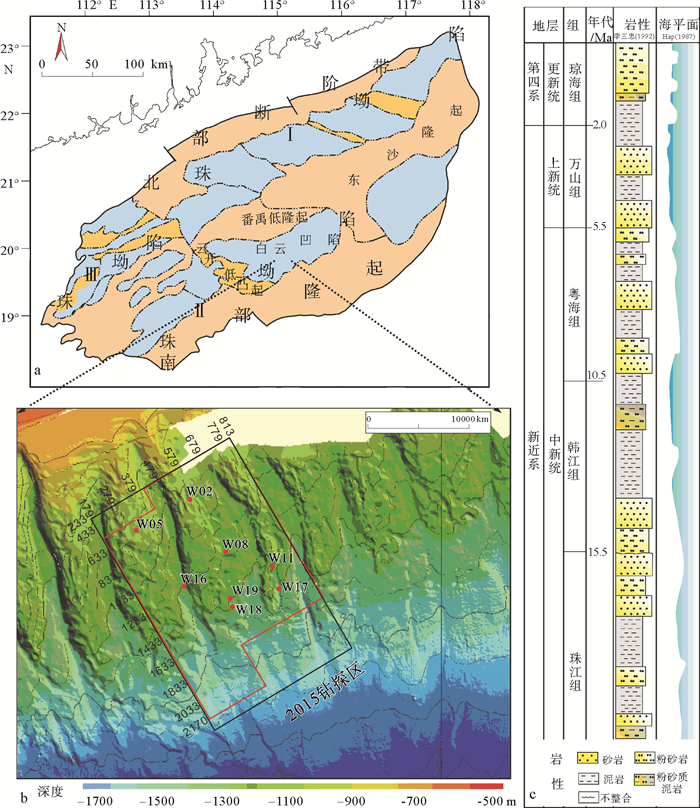
摘要: 2007年和2015年,我国在南海北部神狐海域的水合物钻探结果揭示,水合物在赋存空间上表现为不均匀性。该区域发育多种类型的深水水道,基于水道特征开展不同类型水道的描述,并分析其对水合物成藏差异性的影响,将对该区域水合物的勘探和后续开采具有重要意义。通过地震剖面的综合解释和井震心综合分析,对神狐海域的水道类型进行了划分,探讨了水合物成藏的差异。结果表明,研究区的水道可划分为“V”型、迁移“V”型、“U”型和碟型等4种类型,不同类型水道的水合物赋存特征各异。“V”型和迁移“V”型水道的水合物主要富集在峡谷壁垮塌沉积中,但富存程度较低;“U”型水道的水合物主要富集在谷底沉积和两侧天然堤中;碟型水道的水合物主要富集在水道末端朵体及越岸扇体中。综合解释认为,沉积速率和水流侵蚀速率是造成神狐海域不同类型水道中水合物成藏差异的主要因素。Abstract: The drilling data collected from the Shenhu area in the years from 2007 to 2015 reveals that the area is rich in gas hydrate, which is greatly heterogenous in spatial distribution. There are many channels of different kinds developed in the study area. It is significant to study the types of channels and its bearing on gas hydrate accumulation as well as their impacts on future exploration. Through seismic interpretation and integrated analysis of seismic, logging and coring data, we made a classification of channel types and related hydrate accumulations. According to their shape and genesis, there are four kinds of channels: the "V" shaped channel, migrating "V" shaped channel, "U" shaped channel and saucer shaped channel. The characteristics of gas hydrate accumulation depend upon to some extent the types of channels. The gas hydrate reservoir in the "V" shape or migrating "V" shape channels, which usually have low hydrate abundance, are mostly located in the collapse deposits along the canyon wall. As to the "U" shaped channel, gas hydrates are mainly accumulated in the thalweg and levee deposits. In the Saucer shape channels, however, gas hydrates are mainly deposited in the coarse grained sediments of terminal lobes and overbank fans. The sedimentation rate and flow erosion rate are the main factors to the gas hydrate accumulation in variable shape d channels.
-
致谢: 本次研究数据由广州海洋地质调查局提供,在此对为本次研究提供帮助的林霖、董亦思、单新、唐倩宇、赵晨帆等表示感谢,并且对本文提出宝贵建议的评审专家和编辑老师表示感谢。
-
-
[1] Gong C L, Wang Y M, Zheng R C, et al. Middle Miocene reworked turbidites in the Baiyun Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea margin: Processes, genesis, and implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 128: 116-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.06.025
[2] 陈泓君, 蔡观强, 罗伟东, 等.南海北部陆坡神狐海域峡谷地貌形态特征与成因[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(5): 19-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201205003 CHEN Hongjun, CAI Guanqiang, LUO Weidong, et al. Features of canyon morphology and their origin in the Shenhu area, Northern Slope of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(5): 19-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201205003
[3] Callow R H T, Mcilroy D, Kneller B, et al. Integrated ichnological and sedimentological analysis of a Late Cretaceous submarine channel-levee system: The Rosario Formation, Baja California, Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 41: 277-294. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.02.001
[4] Behseresht J, Bryant S L. Sedimentological control on saturation distribution in Arctic gas-hydrate-bearing sands[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 341-344: 114-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=007a4e59204598df4d8436b8eed856cc
[5] 于兴河, 王建忠, 梁金强, 等.南海北部陆坡天然气水合物沉积成藏特征[J].石油学报, 2014, 35(2): 253-264. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201402005 YU Xinghe, WANG Jianzhong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Depositional accumulation characteristics of gas hydrate in the northern continental slope of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolia Sinica, 2014, 35(2): 253-264. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201402005
[6] 曾小明, 于兴河, 梁金强, 等.神狐海域天然气水合物地质建模及有利区预测[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(4): 117-126. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201404014 ZENG Xiaoming, YU Xinghe, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Geological model and prediction for favorable area of natural gas hydrate in Shenhu area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(4): 117-126. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201404014
[7] 沙志彬, 郭依群, 杨木壮, 等.南海北部陆坡区沉积与天然气水合物成藏关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5): 89-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200905012 SHA Zhibin, GUO Yiqun, YANG Muzhuang, et al. Relation between sedimentation and gas hydrate reservoirs in the Northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5): 89-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200905012
[8] Milkov A V, Sassen R. Economic geology of offshore gas hydrate accumulations and provinces[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2002, 19(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(01)00047-2
[9] 苏明, 沙志彬, 匡增桂, 等.海底峡谷侵蚀-沉积作用与天然气水合物成藏[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(1): 155-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.01.019 SU Ming, SHA Zhibin, KUANG Zenggui, et al. Erosion and sedimentation of the submarine canyons and the relationship with gas hydrate accumulation[J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(1): 155-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.01.019
[10] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 刘鑫, 等.南海的盆地群与盆地动力学[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6): 55-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206006 LI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, LIU Xin, et al. Basin dynamics and basin groups of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 55-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206006
[11] 苏明, 沙志彬, 乔少华, 等.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物钻探区第四纪以来的沉积演化特征[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8): 2975-2985. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201508030 SU Ming, SHA Zhibin, QIAO Shaohua, et al. Sedimentary evolution since Quaternary in the Shenhu hydrate drilling area, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(8): 2975-2985. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201508030
[12] Haq B U, Hardenbol J, Vail P R. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the triassic.[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4793): 1156-1167. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1156
[13] Han J H, Xu G Q, Li Y Y, et al. Evolutionary history and controlling factors of the shelf breaks in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 179-189. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.06.009
[14] 陈芳, 周洋, 苏新, 等.南海神狐海域含水合物层粒度变化及与水合物饱和度的关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105014 CHEN Fang, ZHOU Yang, SU Xin, et al. Gas hydrate saturation and its relation with grain size of the hydrate-bearing sediments in the Shenhu Area of Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105014
[15] Wang X J, Collett T S, Lee M W, et al. Geological controls on the occurrence of gas hydrate from core, downhole log, and seismic data in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357: 272-292. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.09.040
[16] Stow D A V, Mayall M. Deep-water sedimentary systems: New models for the 21st century[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(2): 125-135. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00064-1
[17] Forbes D L. Morphology and sedimentology of a sinuous gravel-bed channel system: lower Babbage river, Yukon Coastal Plain, Canada[M]//Collinson J D, Lewin J. Modern & Ancient Fluvial Systems.[S.l.]: The International Association of Sedimentologists, 2009: 195-206.
[18] 王真真, 王秀娟, 郭依群, 等.白云凹陷陆坡峡谷沉积与迁移特征及其对天然气水合物成藏的影响[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(3): 105-113. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201403012 WANG Zhenzhen, WANG Xiujuan, GUO Yiqun, et al. Deposition and migration of sediments in submarine canyons of Baiyun Sag and their effects on gas hydrate accumulation[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(3): 105-113. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201403012
[19] 沙志彬, 杨木壮, 梁劲.天然气水合物成矿的沉积控制因素[J].海洋地质动态, 2003, 19(6): 16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.06.007 SHA Zhibin, YANG Muzhuang, LIANG Jin. Sedimentation-controlling factors of natural gas hydration[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2003, 19(6): 16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.06.007
[20] 黎明碧, 金翔龙, 初凤友, 等.神狐-一统暗沙隆起中部新生代地层层序划分及沉积演化[J].沉积学报, 2002, 20(4): 545-551. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.003 LI Mingbi, JIN Xianglong, CHU Fengyou, et al. Sequence division and sedimentary evolution of Cenozoic in the middle Shenhu-Yitong Ansha uplift[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(4): 545-551. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.003
[21] 栾锡武, 李晓芸.流体迁移和海底地形与天然气水合物的形成[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(2): 1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201202001 LUAN Xiwu, LI Xiaoyun. Sea floor topography of shallow gas hydrate area-data from Okhotsk Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(2): 1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201202001
[22] 钟建强, 黄慈流, 詹文欢.南海新生代沉积建造的基本特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(4): 25-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600250308 ZHONG Jianqiang, HUANG Ciliu, ZHAN Wenhuan. Basic characters of Cenozoic sedimentary formation in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1996, 16(4): 25-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600250308
[23] 陈芳, 苏新, 陆红锋, 等.南海神狐海域有孔虫与高饱和度水合物的储存关系[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(5): 907-915. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201305001 CHEN Fang, SU Xin, LU Hongfeng, et al. Relations between biogenic component (Foraminifera) and highly saturated gas hydrates distribution from Shenhu Area, Northern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(5): 907-915. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201305001
[24] Clark J D, Pickering K T. Architectural elements and growth patterns of submarine channels: Application to hydrocarbon exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 80(2): 194-221. https://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040489559910_2192.html
[25] Posamentier H W. Depositional elements associated with a basin floor channel-levee system: case study from the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(6-8): 677-690. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.01.002
[26] 李华, 王英民, 徐强, 等.深水单向迁移水道-堤岸沉积体系特征及形成过程[J].现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 653-661. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.03.017 LI Hua, WANG Yingmin, XU Qiang, et al. Characteristics and processes of deep water unidirectionally-migrating channel-levee system[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(3): 653-661. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.03.017
[27] 李磊, 王英民, 张莲美, 等.南海北部白云深水区水道与朵体沉积序列及演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(4): 71-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200904009 LI Lei, WANG Yingmin, ZHANG Lianmei, et al. Sedimentary sequence and evolution of submarine channel-lobe in Baiyun Deepwater area, Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(4): 71-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200904009
[28] 刘昌岭, 孟庆国, 李承峰, 等.南海北部陆坡天然气水合物及其赋存沉积物特征[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 41-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201704005 LIU Changliang, MENG Qingguo, LI Chengfeng, et al. Characterization of natural gas hydrate and its deposits recovered from the Northern Slope of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 41-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201704005
[29] Collett T, Johnson A, Knapp C, et al. Natural Gas Hydrates Energy Resource Potential and Associated Geologic Hazards[M]. Tulsa: AAPG, 2009: 89.
[30] Hui G G, Li S Z, Guo L L, et al. Source and accumulation of gas hydrate in the northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 69: 127-145. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.10.009
[31] Su Z, Cao Y, Wu N. Modeling dynamic accumulation of gas hydrates in Shenhu area, northern South China Sea[C]//American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2013. Washington: AGU, 2013. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013agufmos21b1625s
[32] 何静, 刘学伟, 余振, 等.含天然气水合物地层的孔隙度影响因素分析[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(3): 368-378. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201303005 HE Jing, LIU Xuewei, YU Zhen, et al. Factors influencing the porosity of gas hydrate bearing sediments[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(4): 557-567. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201303005
[33] 陈芳, 苏新, 周洋.南海神狐海域水合物钻探区钙质超微化石生物地层与沉积速率[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(1): 1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201301001 CHEN Fang, SU Xin, ZHOU Yang. Late Miocene-Pleistocene calcareous nannofossil biostratigraphy of Shenhu Gas hydrate drilling Area in the South China Sea and variations in sedimentation rates[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(1): 1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201301001
[34] Fraser D R A, Gorman A R, Pecher I A, et al. Gas hydrate accumulations related to focused fluid flow in the Pegasus Basin, southern Hikurangi Margin, New Zealand[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.06.025
[35] 王力峰, 陆敬安, 梁金强, 等.南海东北部陆坡水合物钻探区BSR推导流体运移速率研究[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 78-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201704009 WANG Lifeng, LU Jing'an, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Research on fluid migration rates derived from BSR at the hydrate drilling area off the northeastern slope of South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 78-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201704009
[36] Vadakkepuliyambatta S, Hornbach M J, Bünz S, et al. Controls on gas hydrate system evolution in a region of active fluid flow in the SW Barents Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 66: 861-872. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.07.023
[37] Zerpa L E, Sloan E D, Sum A K, et al. Overview of CSMHyK: A transient hydrate formation model[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2012, 98-99: 122-129. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9262888
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 孙鲁一,张广旭,王秀娟,靳佳澎,何敏,朱振宇. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物饱和度的数值模拟分析. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2021(02): 210-221 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 康玉柱. 中国南海地块天然气水合物成藏条件探讨. 油气藏评价与开发. 2021(05): 659-668 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 于兴河,付超,华柑霖,孙乐. 未来接替能源——天然气水合物面临的挑战与前景. 古地理学报. 2019(01): 107-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 付超,樊雪,于兴河,赵晨帆,何玉林,梁金强,苏丕波. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域水合物储层分层建模方法与有利区带预测. 中国海上油气. 2019(02): 83-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 付康伟,张学强,彭炎. BP神经网络算法在陆域天然气水合物成藏预测中的应用. 物探与化探. 2019(03): 486-493 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: