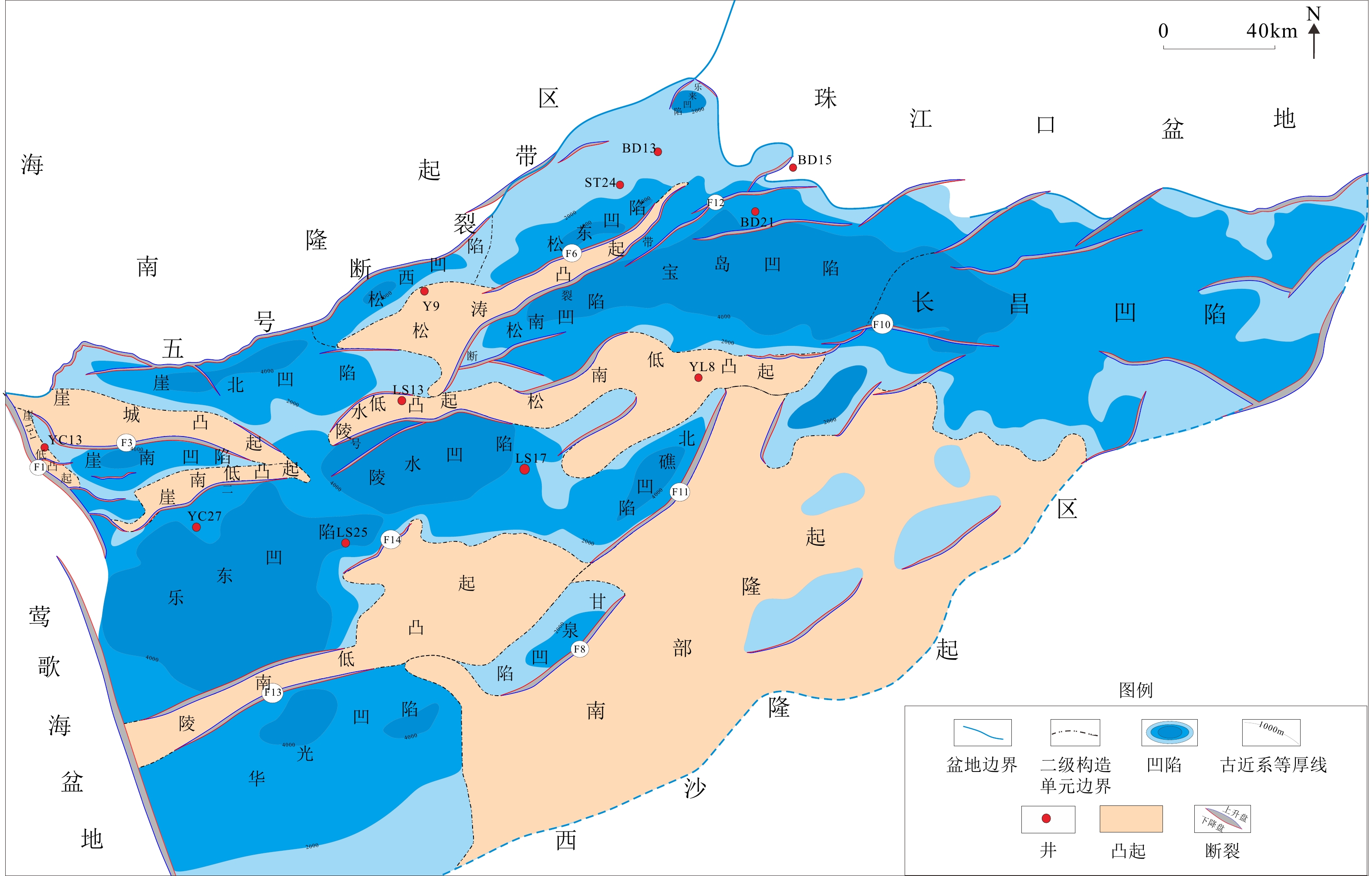
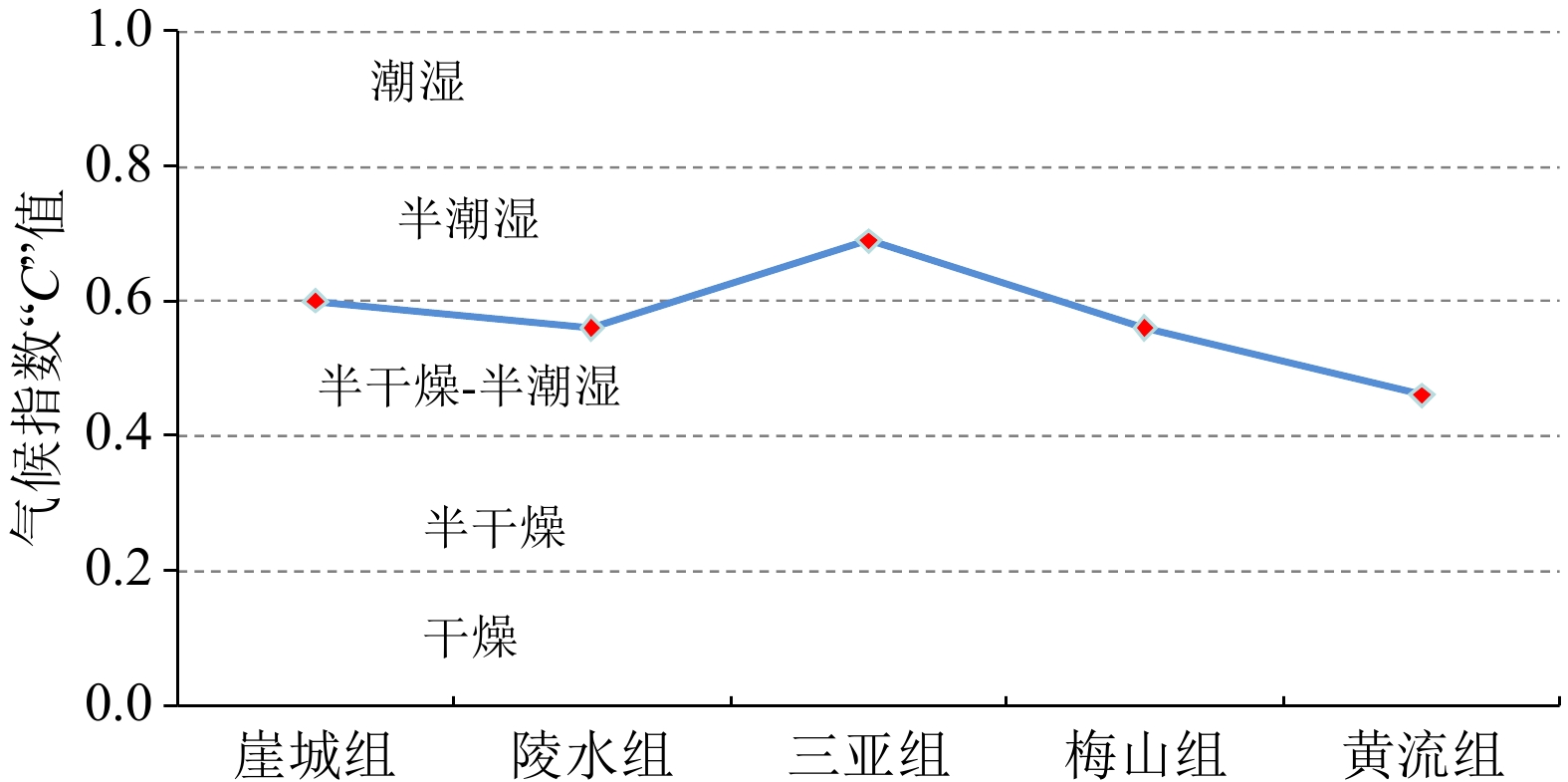
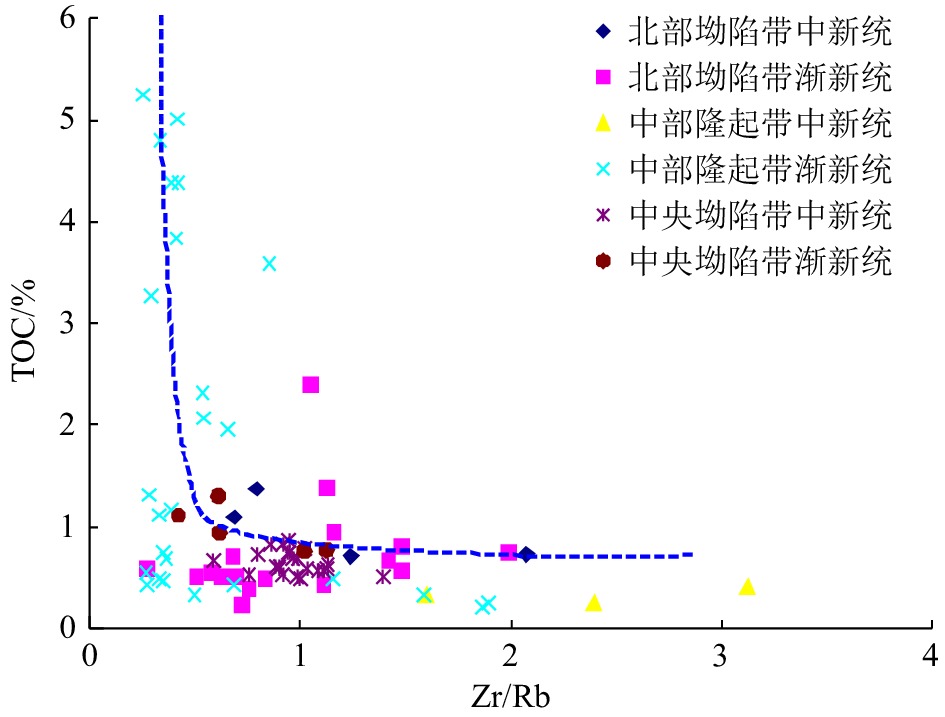
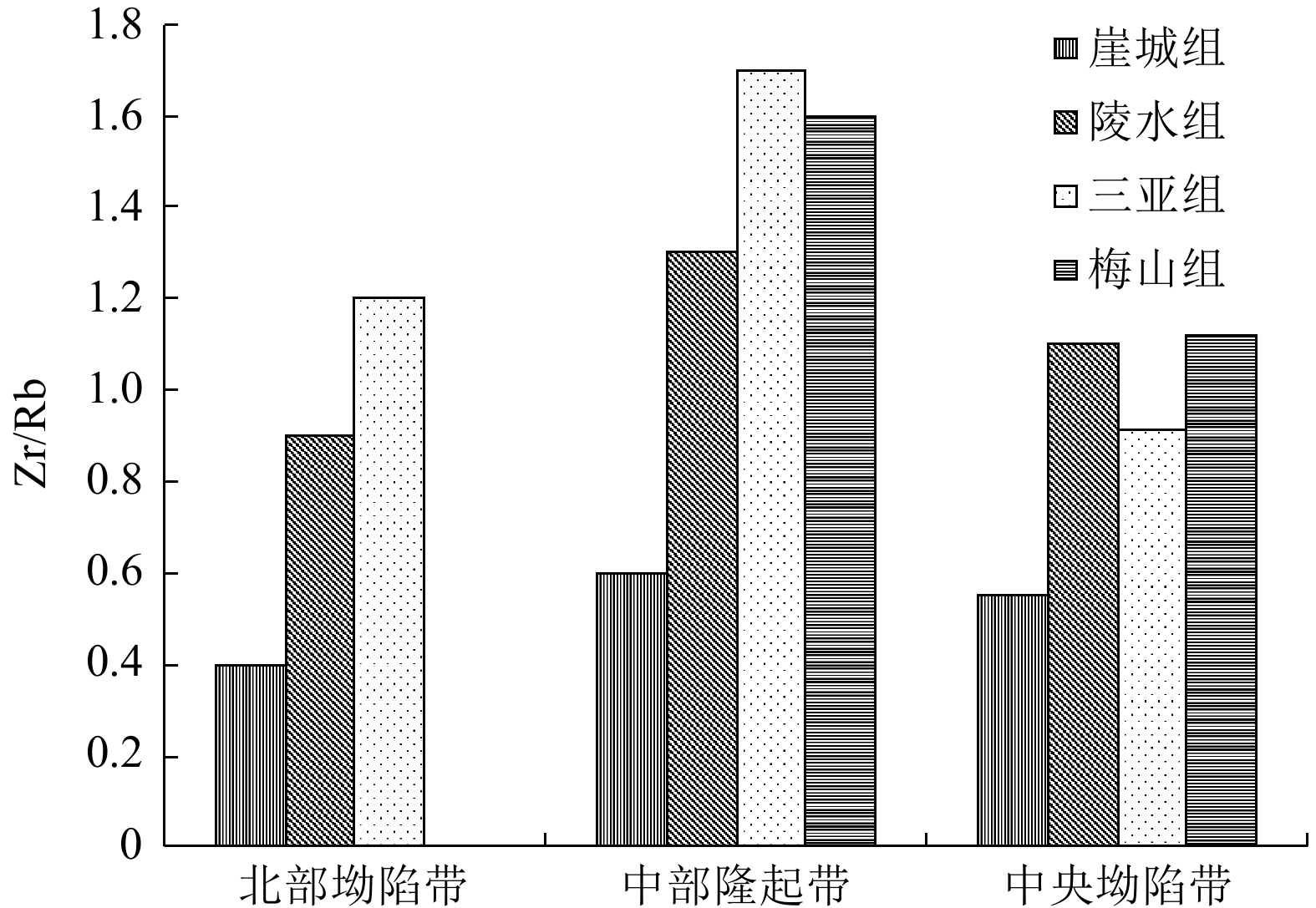
Developmental characteristics of source rock and gas source analysis in Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea
-
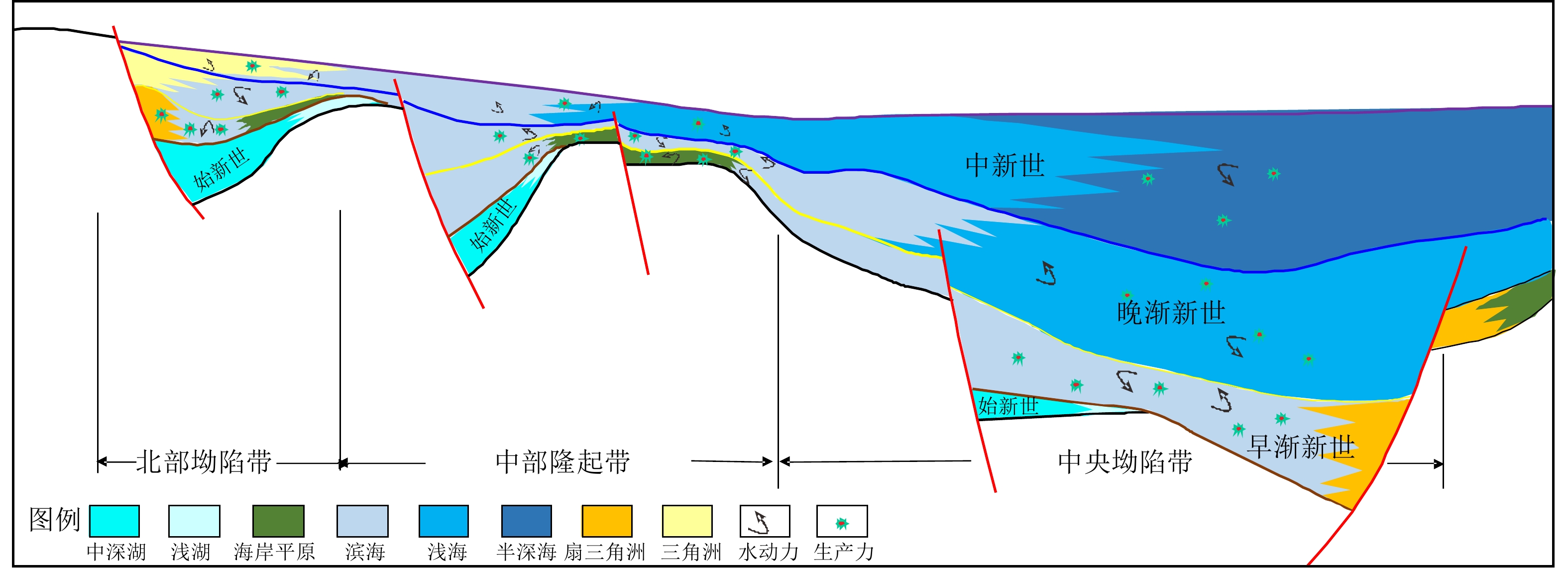
摘要: 琼东南盆地是一个具有巨厚古近系和新近系沉积的新生代沉积盆地,烃源岩主要发育于始新世、渐新世、中新世3个时期。渐新统煤系烃源岩具有广覆式分布的特点,有机质丰度最高,是盆地主力烃源岩;中新统浅海—半深海相烃源岩在深水区中央坳陷厚度大且分布稳定,生烃转化率较高,但有机质丰度较渐新统偏低,是盆地潜在烃源岩;始新统湖相地层虽然探井尚未钻遇,但地震相特征及烃源对比表明,盆地大部分地区均存在始新统中深湖相烃源岩。应用元素地球化学方法分别对盆地不同区带不同时期生物发育的古生产力、古气候及水动力特征等进行了分析研究,初步证实中央坳陷古生产力最高,其次为中部隆起区,北部坳陷则相对较低。基于以上研究,提出了琼东南盆地烃源岩主要发育于3个时期,有4种类型:始新统中深湖相烃源岩、早渐新统崖城组海陆过渡相煤系烃源岩、中—晚渐新统崖城-陵水组半封闭浅海相陆源烃源岩及中新统浅海-半深海相陆源潜在烃源岩。在此基础上,根据大量油气勘探成果及油气地球化学特征,综合判识认为盆地中央坳陷带是渐新统烃源岩最有利发育区且生烃潜力大,其次为北部坳陷带和中部隆起区。气源综合判识表明,中央坳陷带目前勘探发现的深水气田群气源供给主要来自渐新统崖城组煤系烃源岩及半封闭浅海相陆源烃源岩,而北部坳陷带广大区域油气来源则可能主要来自始新统湖相烃源岩。Abstract: The Cenozoic Qingdongnan Basin hosts a very thick Tertiary strata including three sets of source rocks from bottom to top: the Eocene, the Oligocene (containing Lingshui-Yacheng Formation), and the Miocene. The Oligocene is the key source rock with high abundance of organic matter widespread in basin and coal-bearing strata developed locally. The Miocene is thick neritic-bathyal facies that distributed stably in the central depression zone with high hydrocarbon conversion rate and is potential type of source rock. The Eocene is a set of important hydrocarbon source rocks and has not been drilled through at present. However, seismology study shows that the northern depression belt developed source rocks of semi-deep lacustrine deposits. Study of elemental geochemistry shows that the central depression zone has the highest paleoproductivity; the central uplift belt is in the second place; and the northern depression belt has the lowest paleoproductivity. The paleoclimate of the early Oligocene and early Miocene were warm and favorable to the development of source rocks. Based on the above information, three developmental modes was put forward, i.e., the transitional facies, the semi-enclosed marine facies, and the marine facies. On the basis of modes above, the most advantageous zones that contain high quality source rock is the central depression belt. The northern depression belt and the central uplift belt are in the second place. In addition, geochemistry data, the composition and carbon isotope characteristics of gas indicate that the gas-bearing structure in the northern depression belt is characterized by oil type gas, which may be contributed by the Eocene. The gas fields in the central depression mainly come from the Oligocene Yacheng Formation, featured coal type gas.
-
红河三角洲位于越南北部(图1),面积约为17 000 km2[1],受波浪、潮流、河流共同控制[2]。红河一共有8条支流,年均径流量达120 km3[3],其中大型的河口主要有白藤(Bach Dang)河口、太平(Thai Binh)河口、巴拉特(Balat)河口、宁科(Ninh Co)河口、天(Day)河口,其中巴拉特河口的径流量约占总量的65%[4]。红河年均入海泥沙量约8.2×107 m3[5],其中90%在雨季输送[6],主要沉积在北部湾西南近海区域[7]。
![]() 图 1 1987—2015年红河三角洲海岸线背景为2005年遥感影像图;a. 红河三角洲地理位置,b. 红河三角洲岸线,c. 巴拉特河口岸线。Figure 1. Red River Delta coastline changes from 1987 to 2015The background map is from the remote sensing image of 2005; a. Geographical location of the Red River Delta, b. Red River Delta coastline, c. Balat estuary coastline.
图 1 1987—2015年红河三角洲海岸线背景为2005年遥感影像图;a. 红河三角洲地理位置,b. 红河三角洲岸线,c. 巴拉特河口岸线。Figure 1. Red River Delta coastline changes from 1987 to 2015The background map is from the remote sensing image of 2005; a. Geographical location of the Red River Delta, b. Red River Delta coastline, c. Balat estuary coastline.红河三角洲所位于的北部湾海域以全日潮为主,平均潮差2.5~3.5 m;波浪在旱季为东—东北方向,在雨季为东—东南方向,平均和最大波高分别为0.7~1.3 m和3.5~4.5 m[8]。根据前人研究,北部湾1990—2010年海岸线的总长度在持续减小,20年间减小了118.50 km,其中后10年减小幅度明显大于前10年[9],且岸线趋向于平直化[10]。北部湾岸线的变迁主要和人类活动有关[11-12],海岸线被大量开发为港口、码头、养殖区等[13]。砂质、淤泥和基岩岸线的占比逐渐减小[14],到1998年人工堤坝已占北部湾岸线总长度的39.46%[15]。除人类活动影响外,河口岸线变化也较大[16-17]。
关于红河三角洲岸线,前人主要分析了岸线变化特征以及河口沙坝、上游大坝等对其的影响:红河三角洲岸线在1999年之后的10年总体上向陆迁移[5],岸线变化频繁剧烈,受多种因素共同影响。关于河口沙坝的影响,Do Minh Duc等发现,河流输送的泥沙主要聚集在河口,使海岸线快速淤积(可达100 m/a),而其他岸段因缺少泥沙供应,导致侵蚀[4, 18-19]。关于上游大坝的影响,Tran Duc Thanh等发现,和平大坝建立之后,大坝下游河水中泥沙含量减少,宁科(Ninh Co)河口附近岸线的年平均后退速率从1965—1990年的0.41 m/a提高到了1990—1998年的14.5 m/a[20],但对主要河口巴拉特的岸线变化速率在大坝建立前后的变化缺少研究。另外,入海泥沙量变化导致的河口演变[18]、波浪斜向入射[21]、潮流和波浪流[22]都会对海岸侵蚀产生重要影响。近年来岸线趋于平直,各种人工建筑物也会影响波浪和潮汐的动力作用,从而影响岸线侵蚀[13, 23]。虽然红树林能很好地应对海岸侵蚀[24],但由于人类的砍伐,红树林也受到了很大程度的破坏。加剧的岸线侵蚀将导致建筑物不稳定等各种灾害发生,三角洲生态服务功能也会逐渐减弱[25-27]。
前人对红河三角洲岸线演变进行了定性描述,但缺少定量化分析,而且研究年份仅截止于2001年,对人类活动频繁的近20年的海岸变化相关报道较少。近年来,由于全球变暖,海平面上升,台风发生频率增加[28],海洋动力发生了重要变化,对岸线变化产生了重要影响。在岸线变化机制上,前人的研究分析了海洋动力和河流入海泥沙对岸线变化的影响,但是对于北部湾海域每年夏季高频次的台风作用分析较少。前人已在山东威海海滩观测发现,台风梅花(1109号)过境后,天鹅湖沙滩后退了3.6 m[29],热带气旋对岸线变化产生了剧烈影响。因此,本文基于1987—2015年Landsat遥感数据,收集1935—1985年历史数据、红河多年径流量与输沙量,以及该海域多年热带气旋数量等数据,对红河三角洲变化最频繁剧烈的巴拉特河口的岸线演变开展研究,从而为岸线防护以及海岸带经济发展提供科学支撑。
1. 数据与方法
本文采用的基础数据来自Landsat系列卫星的影像数据,从美国地质勘探局官网(网址:https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/)下载,影像分辨率为30 m。为保证影像精度及多年研究中的可对比性,选取云量小于10%、高潮时的遥感影像进行对比分析。基于ENVI软件,进行辐射校正、拼接、大气校正、研究区裁剪、几何精校正等预处理[30]。预处理之后,根据“我国近海海洋综合调查与评价项目(908专项)”海岸带遥感调查和前人岸线解译经验[31-32],在MapInfo软件中提取大潮高潮线作为岸线,共提取了1987、1990、1995、2000、2005、2010、2015近30年共7张红河三角洲的岸线,结果如图1所示。
2. 多年岸线变化特征
2.1 1930—1985年巴拉特地区岸线变化
根据收集的资料[8],前人已对1930—1985年巴拉特地区岸线变化进行了研究(图2),可以看出在巴拉特河口地区前进与后退剧烈,在靠近河口部位发生明显前进,而远离河口部位发生明显后退。
2.2 1987—1990年红河三角洲岸线变化
1987—1990年,红河三角洲南部岸线有多处明显前进,而北部出现多处后退,中部变化不大(图1),主要是巴拉特地区变化明显。通过计算得到如图3所示的巴拉特地区主岸线沿岸平均年变化率,可以看出巴拉特地区沿岸大部分岸线以后退为主。河口位置发生明显后退,从遥感图像上对比发现,该岸线后退可能与入海泥沙量减少和沙坝侵蚀有关。定量对比发现,1987—1990年巴拉特地区年平均前进速率为39.19 m/a,年平均后退速率为30.68 m/a。
2.3 1990—1995年红河三角洲岸线变化
1990—1995年,红河三角洲除河口岸线以前进为主外,河口的南部和北部岸线均出现了多处明显后退(图1)。巴拉特地区变化明显,通过计算得到如图4所示的巴拉特地区主岸线沿岸平均年变化率,可以看出巴拉特地区沿岸大部分岸线以前进为主,而河口位置发生明显后退,从遥感图像上对比发现,在这一时期,由于波浪等导致沙坝侵蚀或者由于海平面上升,主岸线与沙坝之间的人工养殖池长时间被水淹没,主岸线发生明显后退。1990—1995年巴拉特地区年平均前进速率为28.26 m/a,年平均后退速率为87.25 m/a。
2.4 1995—2000年红河三角洲岸线变化
1995—2000年,红河三角洲岸线变化不大,南部出现了几处明显前进,北部也出现几处明显前进,中部变化不大(图1)。对于巴拉特地区,岸线的后退与前进交替出现,在河口位置发生了一处明显前进(图5),从遥感图像上对比发现,该岸线前进与人工养殖池有关。1995—2000年巴拉特地区年平均前进速率为23.63 m/a,年平均后退速率为11.57 m/a。
2.5 2000—2005年红河三角洲岸线变化
2000—2005年,红河三角洲南部岸线发生一处明显前进,而北部出现几处后退,中部变化不大(图1)。巴拉特地区岸线的后退与前进交替出现,变化不剧烈(图6)。2000—2005年巴拉特地区年平均前进速率为5.93 m/a,年平均后退速率为5.06 m/a。
2.6 2005—2010年红河三角洲岸线变化
2005—2010年,红河三角洲南部岸线有多处明显前进,而北部出现多处明显后退,中部出现多处前进(图1)。巴拉特地区沿岸岸线以后退为主(图7),从遥感图像上(图8)对比发现,该岸线后退可能与2009年宣光(Tuyen Quang)大坝和2010年桑拉(Sonla)大坝建成导致入海泥沙量减少有关,因此沙坝侵蚀,人工养殖池被水淹没,主岸线发生明显后退。2005—2010年巴拉特地区年平均前进速率为20.87 m/a,年平均后退速率为56.19 m/a。
2.7 2010—2015年红河三角洲岸线变化
2010—2015年,红河三角洲南部岸线以明显前进为主,北部也以明显前进为主,但出现几处后退,中部以前进为主(图1)。巴拉特地区沿岸岸线以前进为主,后退仅限于河口东北部(图9),从遥感图像上对比发现,该岸线后退可能与入海泥沙量减少,沙坝侵蚀有关。2010—2015年巴拉特地区年平均前进速率为22.13 m/a,年平均后退速率为89.72 m/a。
2.8 1987—2015年红河三角洲岸线总体变化
观察多年岸线变化图(图1),可以看出沿岸地区变化不一致,部分岸段前进与后退交替变化特征明显,在巴拉特河口地区淤进与蚀退频繁,变化剧烈,河口北部岸线后退明显,主要受沙坝侵蚀影响。计算得到1987—2015年巴拉特地区主岸线年平均前进速率为3.94 m/a,年平均后退速率为29.43 m/a。前人计算得到长江口河口岸线1974年到2015年的平均变化速率为34 m/a[20],与其对比,发现巴拉特地区主岸线年平均变化速率大小与其类似(图10)。
3. 岸线多年变化原因分析
通过调查资料,发现红河三角洲海岸线演变受热带气旋以及河流上游水坝等多种因素共同影响。
3.1 河口沙坝的影响
海岸线的向海推进与沙坝的形成和扩大密切相关。大量入海沉积物在河口前形成沙坝,沙坝的快速增长降低了波浪的破坏作用,为海岸线和沙坝之间的河道中沉积物沉降提供了良好的环境[9]。河口沙坝在红河三角洲的巴拉特地区作用非常明显。当沙坝被侵蚀时,沙坝与主岸线之间的人工养殖池也被水淹没,因此,主岸线明显后退,如1990—1995年和2005—2010年。
3.2 河流上游建坝的影响
红河入海径流量和输沙量受堤坝建设影响明显(图11),进而会对岸线前进与后退速率产生影响[20]。前人在1972年第一个大坝塔婆建立之后,在山西站(Son Tay,图11e)观测到的年输沙量下降[33]。根据前人对1965—1990年宁科(Ninh Co)地区岸线变化的研究结果,可以发现在和平大坝建立之后,宁科河口岸线的年平均后退速率从1965—1990年的0.41 m/a提高到了1990—1998年的14.5 m/a[21]。而前人对1930—1985年巴拉特地区岸线变化的研究结果表明,在塔婆大坝建立之后巴拉特河口前进速率相应发生了降低[3]。本文对比发现,在2009年宣光(Tuyen Quang)大坝和2010年桑拉(Sonla)大坝建成之后,沉积物供应减少,2005—2015年巴拉特河口岸线后退速率有所提高。
3.3 气候变化影响
厄尔尼诺现象可造成世界气候的变化,使局部地区降雨量过多,极大地影响岸线的变化速率。调查资料发现,红河上游的大东勇站、中游的元江站、下游的蛮耗站的年径流序列在1993年均由枯水期突变为丰水期[34],这可能与1991—1994年发生的厄尔尼诺带来的强降雨有关[4],沙坝与主岸线之间的人工养殖池被水淹没,1990—1995年巴拉特河口岸线的后退速率明显增长。同时,2006—2007年、2009—2010年均发生了厄尔尼诺现象,对应的2005—2010年巴拉特河口岸线的后退速率也有明显增长。
海平面上升对海岸侵蚀速率的影响也很大。根据前人研究结果,1965—1995年期间,海平面上升对红河三角洲海岸侵蚀速率增加的作用约占34%,而1995—2005年为12%。
3.4 热带气旋的影响
热带气旋是越南北部地区典型的天气事件,台风数量与岸线年平均后退速率有很好相关性(图12),台风数量越多,平均后退速率越大。1990—1995年经过红河三角洲台风数量增多,年平均后退速率有明显提高;1995—2005年经过红河三角洲台风数量减少,年平均后退速率对应有明显降低;2005—2015年经过红河三角洲台风数量增多,年平均后退速率对应有明显提高。海后(Hai Hau)潮汐站曾测得当波高为4.25 m,持续时间2.4 h的情况下,岸线后退了7.1 m[8]。
3.5 海洋动力的影响
海流和波浪是影响海岸侵蚀的重要因素[5]。前者在红河三角洲海域呈现出明显的季节性变化:冬季流向南、夏季流向北[7],并可能通过诱发增水等影响岸线变化。后者在近岸破碎并诱生沿岸流,进而引起沿岸输沙作用,造成海岸侵蚀[8]。
无论旱季或者雨季,巴拉特河口南部海域平均波高始终高于河口北部(图13a,图13b),河口南部的海洋动力始终强于北部。从沉积物输运方向(图14)也可以看出:在巴拉特、拉赫(Lach)和天河口,5~10 m等深线海域,沉积物主要向东南输运,5 m等深线以浅的区域,沉积物沿岸向西南输运;在特雷(Tra Ly)河口,沉积物向东北输运;在太平河口,沉积物向东输运[35]。因此,巴拉特河口北部和南部岸线呈现不一样的变化特征;北部岸线后退与前进交替出现,总体以前进为主,可能与复杂的岸线和动力条件及河流入海物质变化有关;南部岸线持续后退,与波浪导致的沿岸南向输沙密切相关。
4. 结论
(1)在时间变化上,红河三角洲岸线表现为前进与后退交替变化特征。南部岸线变化趋势较为稳定,除1990—1995年、2010—2015年以前进为主外,1935—2015年其他年份均以后退为主,与波浪导致的沿岸南向输沙密切相关。红河三角洲北部岸线由于岸线复杂且为河流入海物质控制区,表现为后退与前进交替出现,总体以前进为主。
(2)红河主要支流之一巴拉特河口地区淤进与蚀退变化剧烈,1987—2015年巴拉特河口主岸线年平均前进速率为3.94 m/a,年平均后退速率为29.43 m/a。该河口岸线的频繁变化主要与上游建坝造成入海沙量变化、台风造成的侵蚀有关。
-
表 1 琼东南盆地第三系烃源岩岩性特征及有机质丰度综合评价
Table 1 Comprehensive evaluation of lithologic characteristics and organic matter abundance of the Tertiary source rocks in Qiongdongnan Basin
层位 岩性 TOC/% 级别 S1+S2/(mg/g) 级别 HC/10-6 级别 总评 黄流组 暗色泥岩 0.22~2.76 中等烃源岩 0.01~2.14 较差烃源岩 40.1~295.4 较差烃源岩 较差—中等烃源岩 0.62(82) 0.53(72) 132.2(60) 梅山组 暗色泥岩 0.22~2.1 中等烃源岩 0.03~3.35 较差烃源岩 55.2~335.6 较差烃源岩 较差—中等烃源岩 0.60(37) 0.63(32) 170.2(30) 三亚组 暗色泥岩 0.21~0.90 较差烃源岩 0.04~5.21 较差烃源岩 78.4~378.2 较差烃源岩 较差烃源岩 0.58(41) 0.62(43) 187.6(24) 陵水组 暗色泥岩 0.22~5.45 中等烃源岩 0.03~11.6 较差烃源岩 60.7~356.6 中等烃源岩 中等—较差烃源岩 0.72(41) 0.84(33) 212(30) 崖城组 暗色泥岩 0.22~4.17 中等烃源岩 0.06~6.78 较差烃源岩 99.5~500.2 中等烃源岩 0.88(60) 0.80(56) 260.2(46) 碳质泥岩 6.69~9.90 好的烃源岩 7.7~23.42 好的烃源岩 好的烃源岩 8.44(7) 16.37(7) 煤 32.27~81.7 好的烃源岩 12.4~154.4 好的烃源岩 52.03(10) 93.31(10) 注:表中数据格式:最小值~最大值/平均值(样品数)。 表 2 琼东南盆地主要气田及含油气构造天然气组成与碳同位素特征
Table 2 Natural gas composition and carbon isotope characteristics of major gas fields and hydrocarbon-bearing structures in Qiongdongnan Basin
区带 井号 地层 取样
方式井深/m 烃类气/% 非烃气
/%干燥
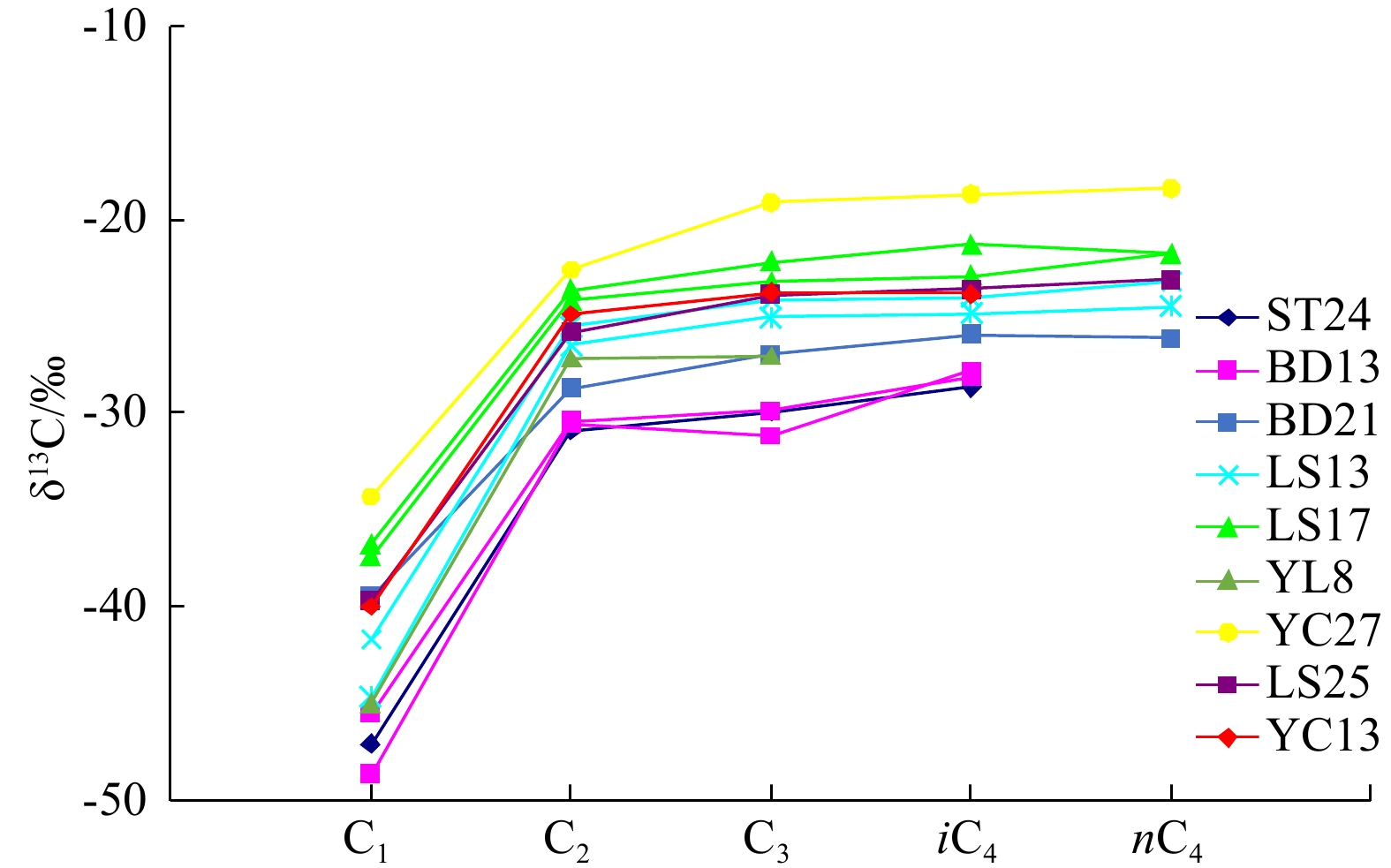
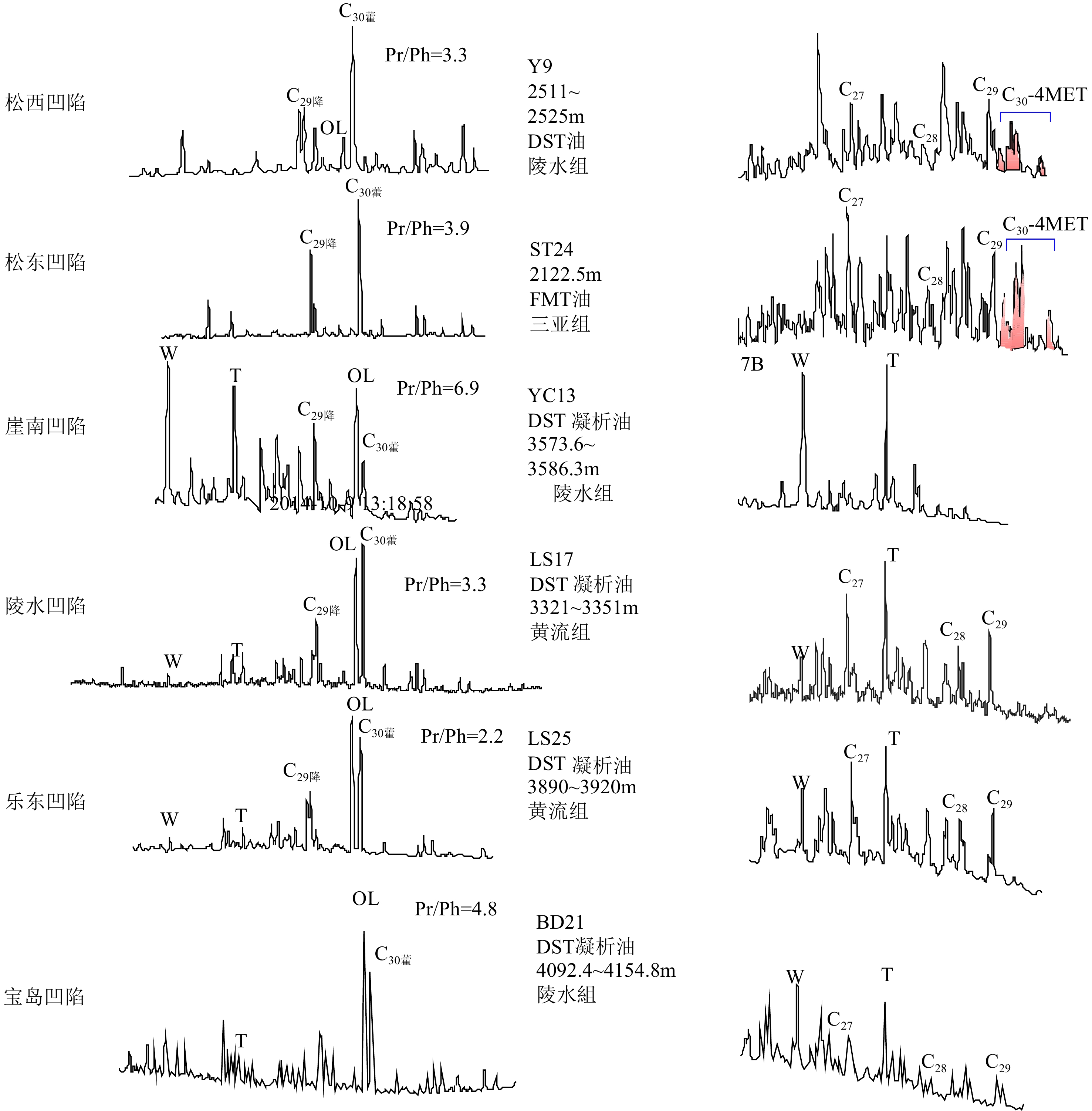
系数碳同位素δ13C/‰ C1 C2—5 N2 CO2 C1/C1—5 C1 C2 C3 iC4 nC4 CO2 松东凹陷 ST24 SY MDT 2 122.2 74.30 9.80 6.77 7.81 0.88 −47.06 −30.92 −29.96 −7.61 宝岛凹陷北坡 BD13A MS DST 1 573~1 580 86.14 10.24 2.46 0.72 0.89 −48.65 −30.53 −31.15 −25.54 BD13B MS MDT 1967.5 82.48 8.09 6.67 1.18 0.91 −45.53 −30.39 −29.84 −29.33 宝岛凹陷北部断阶 BD21A LS DST 4 092.4~4 154 67.14 5.74 0.27 26.55 0.92 −39.46 −28.69 −26.96 −25.89 −26.10 −5.03 BD21B LS MDT 4 268.50 60.38 9.06 2.57 27.71 0.86 −39.83 −29.43 −27.37 −26.24 −26.35 −4.76 陵水低凸起 LS13A MS MDT 3 607.8 69.19 24.24 0.63 4.10 0.74 −41.66 −25.41 −24.17 −24.00 −23.20 −12.61 LS13B MS DST 3 776.9~3 786 79.52 15.76 0.53 3.86 0.83 −44.67 −26.49 −25.02 −24.82 −24.46 −7.88 陵水凹陷 LS17A HL MDT 3 324.0 93.25 5.79 0.62 0.21 0.94 −36.78 −23.62 −22.17 −21.26 −21.75 −17.76 LS17B HL MDT 3 331.3 91.51 6.01 2.15 0.07 0.94 −37.40 −24.16 −23.21 −22.89 −21.75 −18.08 松南低凸起 YL8A YC MDT 2 880.5 95.65 2.81 0.79 0.65 0.97 −44.97 −27.17 −27.04 −12.43 YL8B Pre-Tertiary DST 2 828.8~2 936 95.67 3.30 0.19 0.83 0.97 −43.39 −26.92 −26.76 −2.98 乐东凹陷 YC27 HL MDT 4 390.0 90.6 2.77 1.30 5.24 0.97 −34.31 −22.55 −19.08 −18.66 −18.35 −9.23 LS25 HL MDT 3 760.8 87.89 7.82 1.48 2.20 0.92 −39.69 −25.78 −23.86 −23.56 −23.07 −12.48 崖南凹陷 YC13A LS DST 3 658.8~3 701.9 84.18 3.36 1.04 10.79 0.96 −35.50 YC13B LS DST 3 888.6~3 907.5 86.63 1.81 0.10 11.60 0.98 −35.12 YC13C LS DST 3 898.3~3 921.3 84.58 4.65 1.76 8.73 0.95 −37.09 −26.29 −27.71 −24.78 YC13D LS DST 3 901.4~3 938.0 82.96 7.86 0.26 8.33 0.91 −39.99 −24.88 −23.72 −23.84 -
[1] 何家雄, 张伟, 卢振权, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘主要盆地含油气系统及油气有利勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(6):943-959 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.06.0943 HE Jiaxiong, ZHANG Wei, LU Zhenquan, et al. Petroleum system and favorable exploration directions of the main marginal basins in the northern South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(6): 943-959. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.06.0943
[2] 何家雄, 陈胜红, 刘海龄, 等. 南海北部边缘莺-琼盆地油气资源前景及有利勘探方向分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(4):492-498 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.04.492 HE Jiaxiong, CHEN Shenghong, LIU Hailing, et al. Petroleum resource potential and advantageous exploration targets in Ying-Qiong Basin, northern margin of South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(4): 492-498. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.04.492
[3] 何家雄, 李福元, 王后金, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘深水盆地成因机制与油气资源效应[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(3):1-11 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2019.213 HE Jiaxiong, LI Fuyuan, WANG Houjin, et al. Genetic mechanism of deepwater basins and their effects on oil and gas resources on the continental margin of the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(3): 1-11. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2019.213
[4] 李绪深, 王振峰, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区烃源岩地球化学特征与天然气潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(4):1-7 HUANG Baojia, LI Xushen, WANG Zhenfeng, et al. Source rock geochemistry and gas potential in the deep water area, Qiongdongnan basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(4): 1-7.
[5] 梁刚, 甘军, 李兴, 等. 琼东南盆地浅水区与深水区烃源岩热演化差异性影响因素研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(1):69-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.01.012 LIANG Gang, GAN Jun, LI Xing, et al. Influential factors of thermal evolution difference of source rocks in shallow and deep water areas of southeastern Hainan Basin [J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(1): 69-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.01.012
[6] 杨计海, 黄保家, 杨金海. 琼东南盆地深水区松南低凸起天然气成藏条件与勘探潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2019, 31(2):1-10 YANG Jihai, HUANG Baojia, YANG Jinhai. Gas accumulation conditions and exploration potentials of natural gases in Songnan low uplift, deep water area of Qiongdongnan basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019, 31(2): 1-10.
[7] 龚再升, 李思田, 谢泰俊, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 1-510 GONG Zaisheng, LI Sitian, XIE Taijun, et al. Continental Margin Basin Analysis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the Northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 1-510.
[8] 李绪宣, 钟志洪, 董伟良, 等. 琼东南盆地古近纪裂陷构造特征及其动力学机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(6):713-721 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.06.014 LI Xuxuan, ZHONG Zhihong, DONG Weiliang, et al. Paleogene rift structure and its dynamics of Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(6): 713-721. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.06.014
[9] 张功成, 杨少坤, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地天然气地质[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2007: 8-52 ZHU Weilin, ZHANG Gongcheng, YANG Shaokun, et al. Natural Gas Geology of Continental Margin Basins of the Northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2007: 8-52.
[10] 黄保家, 王振峰, 梁刚. 琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷天然气来源及运聚模式[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(5):8-14 HUANG Baojia, WANG Zhenfeng, LIANG Gang. Natural gas source and migration-accumulation pattern in the central canyon, the deep water area, Qiongdongnan basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(5): 8-14.
[11] 梁刚, 甘军, 李兴. 琼东南盆地陵水凹陷天然气成因类型及来源[J]. 中国海上油气, 2015, 27(4):47-53 LIANG Gang, GAN Jun, LI Xing. Genetic types and origin of natural gas in Lingshui sag, Qiongdongnan basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(4): 47-53.
[12] 王振峰, 何家雄. 琼东南盆地中新统油气运聚成藏条件及成藏组合分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(2):107-115 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.02.107 WANG Zhenfeng, HE Jiaxiong. Miocene hydrocarbon’s transferring and collecting condition and reservoir combination analysis in Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(2): 107-115. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.02.107
[13] 王元, 李贤庆, 王刚, 等. 莺琼盆地中新统海相烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃潜力评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3):500-510 doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.03.08 WANG Yuan, LI Xianqing, WANG Gang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon generation potential of Miocene marine source rocks in the Ying-Qiong Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 500-510. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.03.08
[14] 李春荣, 陈开远. 潜江凹陷潜江组元素演化特征及其古气候意义[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2007, 21(6):18-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2007.06.005 LI Chunrong, CHEN Kaiyuan. Evolutional characteristics and their paleoclimate significance of elements in the Qianjiang formation, Qianjiang depression [J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2007, 21(6): 18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2007.06.005
[15] Francois R, Honjo S, Manganini S J, et al. Biogenic barium fluxes to the deep sea: implications for paleoproductivity reconstruction [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 1995, 9(2): 289-303. doi: 10.1029/95GB00021
[16] Dymond J, Suess E, Lyle M. Barium in deep-sea sediment: A geochemical proxy for paleoproductivity [J]. Paleoceanography, 1992, 7(2): 163-181. doi: 10.1029/92PA00181
[17] Murray R W, Leinen M. Scavenged excess aluminum and its relationship to bulk titanium in biogenic sediment from the central equatorial Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20): 3869-3878. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00236-0
[18] 韦刚健, 刘颖, 李献华, 等. 南海沉积物中过剩铝问题的探讨[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2003, 22(1):23-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2003.01.005 WEI Gangjian, LIU Ying, LI Xianhua, et al. Excess Al in the sediments from South China Sea [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2003, 22(1): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2003.01.005
[19] 陈亮, 刘春莲, 庄畅, 等. 三水盆地古近系下部湖相沉积的稀土元素地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(6):1155-1162 doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2009.06.014 CHEN Liang, LIU Chunlian, ZHUANG Chang, et al. Rare earth element records of the lower paleogene sediments in the Sanshui Basin and their paleoclimate implications [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(6): 1155-1162. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2009.06.014
[20] 苗建宇. 新疆北部主要盆地二叠系烃源岩沉积环境与生烃特征[D]. 西北大学博士学位论文, 2001: 65-98 MIAO Jianyu. The depositional environment of Permian system hydrocarbon source rocks and its potential hydrocarbon generating characteristics in major basins in North Xinjiang[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Northwest University, 2001: 65-98.
[21] 刘昭蜀, 赵焕庭, 范时清, 等. 南海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 315-400 LIU Zhaoshu, ZHAO Huanting, FAN Shiqing, et al. Geology of the South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 315-400.
[22] 赵一阳, 鄢明才. 中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 15-22 ZHAO Yiyang, YAN Mingcai. Chemistry of Sediments of the China Shelf Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 15-22.
[23] 王争鸣. 缺氧沉积环境的地球化学标志[J]. 甘肃地质学报, 2003, 12(2):55-58 WANG Zhengming. Geochemical indicators for diagnosing anoxic sedimentary environment [J]. Acta Geologica Gansu, 2003, 12(2): 55-58.
[24] 秦建中, 腾格尔, 付小东. 海相优质烃源层评价与形成条件研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(4):366-372,378 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.04.010 QIN Jianzhong, TENGER, FU Xiaodong. Study of forming condition on marine excellent source rocks and its evaluation [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(4): 366-372,378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.04.010
[25] Ashan S A, Karlsen D A, Mitchell A W, et al. Inter and intrafield hydrocarbon compositional variations in the Ula and the Gyda fields (Central Graben-North Sea)-Implication for understanding the controls on hydrocarbon distribution within and between these fields [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 29(1-3): 429-448. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(98)00053-9
[26] 张迎朝, 甘军, 徐新德, 等. 琼东南盆地深水东区Y8-1含气构造天然气来源及侧向运聚模式[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(8):2609-2618 ZHANG Yingzhao, GAN Jun, XU Xinde, et al. The source and natural gas lateral migration accumulation model of Y8-1 gas bearing structure, east deep water in the Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(8): 2609-2618.
[27] 戴金星, 邹才能, 李伟, 等. 中国大气田及其气源[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2014: 50-62 DAI Jinxing, ZOU Caineng, LI Wei, et al. Giant Coal-Derived Gasfields and Their Gas Sources in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 416-420.
[28] 梁刚, 甘军, 游君君, 等. 琼东南盆地低熟煤型气地球化学特征及勘探前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(7):895-903 LIANG Gang, GAN Jun, YOU Junjun, et al. Geochemical characteristics and exploration prospect of low mature coal-derived gas in Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(7): 895-903.
[29] 何家雄, 马文宏, 祝有海, 等. 南海北部边缘盆地天然气成因类型及成藏时间综合判识与确定[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(1):145-160 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.01.016 HE Jiaxiong, MA Wenhong, ZHU Youhai, et al. Integrated identification and determination of genetic types and accumulation time in the marginal basin of northern South China Sea [J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(1): 145-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.01.016
[30] 何家雄, 姚永坚, 刘海龄, 等. 南海北部边缘盆地天然气成因类型及气源构成特点[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(5):1007-1016 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.05.020 HE Jiaxiong, YAO Yongjian, LIU Hailing, et al. Genetic types of natural gas and characteristic of the gas source composition in marginal basins of the northern South China Sea [J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(5): 1007-1016. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.05.020
[31] 何家雄, 马文宏, 祝有海, 等. 南海北部边缘盆地天然气成因类型及运聚规律与勘探新领域[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(4):1-10 HE Jiaxiong, MA Wenhong, ZHU Youhai, et al. Genetic types, migration and accumulation of gas in the north marginal basins of South China Sea and new exploration targets [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2011, 27(4): 1-10.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 胡广,黄建宇,杨胜雄,李沅衡,田冬梅,曹荆亚,周军明,邓雨恬. 琼东南海域冷泉微地震响应特征初探——以“海马”冷泉为例. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(06): 12-24 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 田兆阳,贾永刚,朱超祁,卢龙玉,郭煦,冯学志,王慧,王宏威,何满潮,彭建兵. 海床流体迁移致灾机理与风险防控研究现状及展望. 中国工程科学. 2023(03): 131-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: