Controlling factors and distribution of geochemical characteristics of the surface sediments in the Yellow River Delta
-
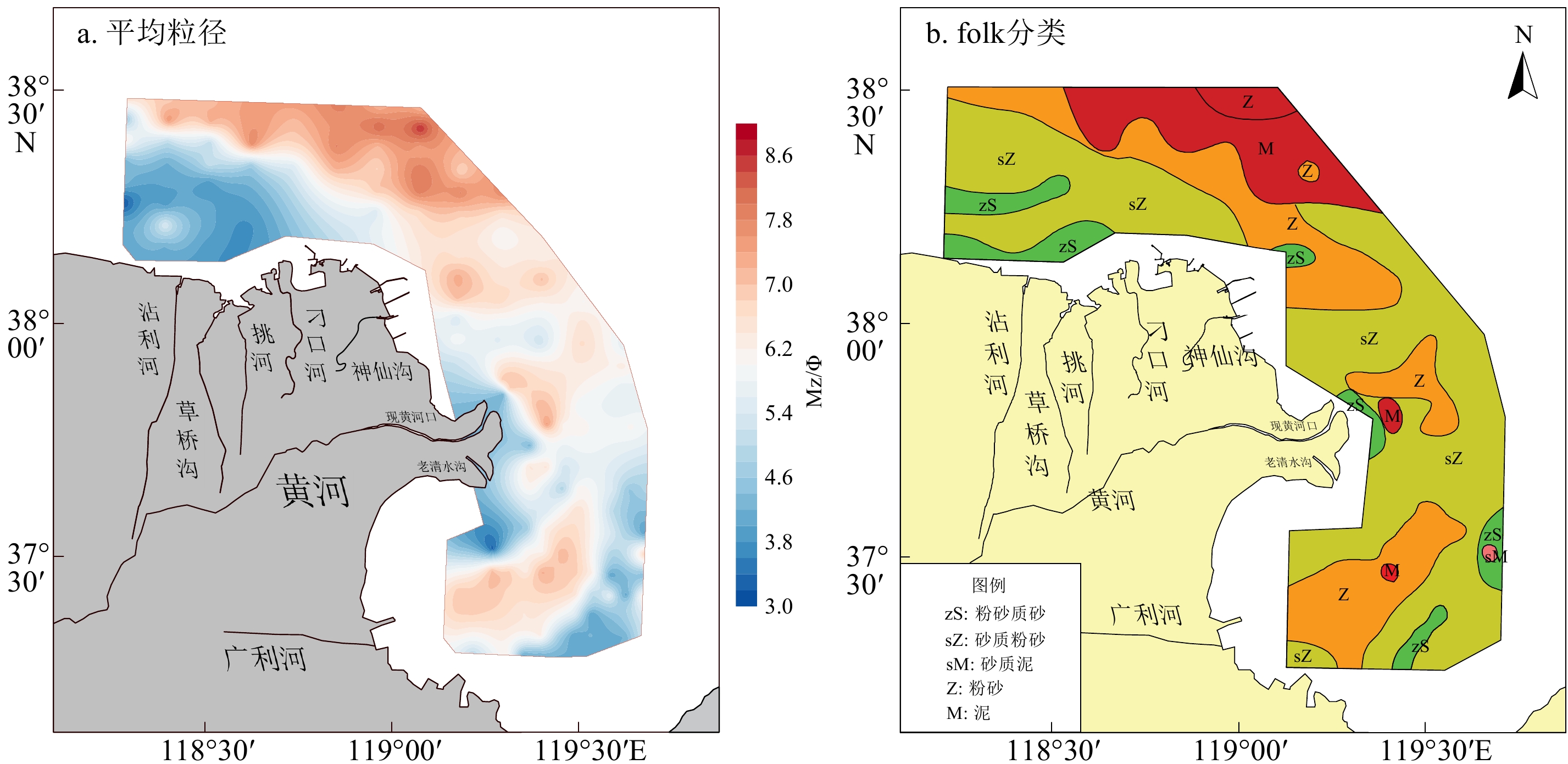
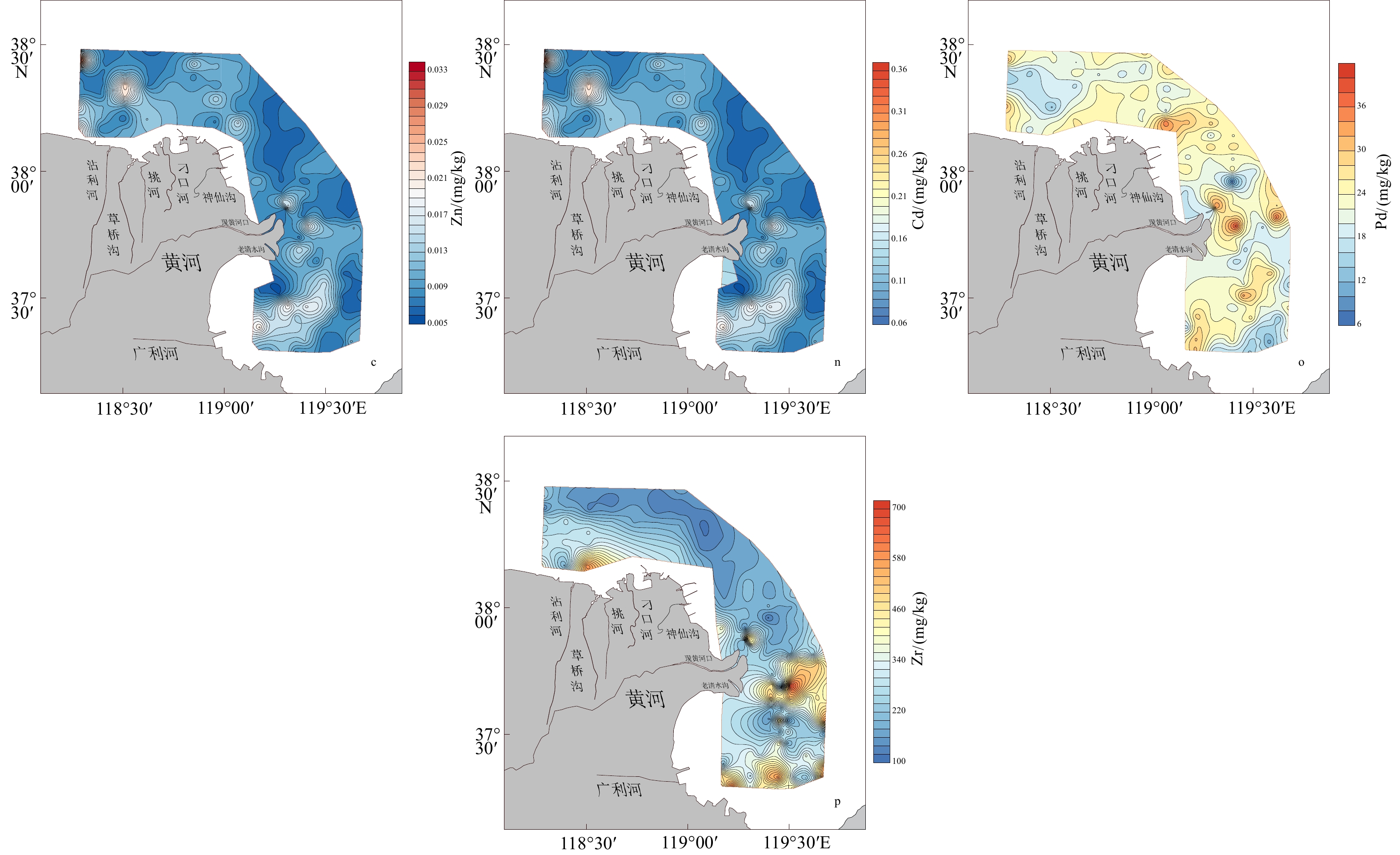
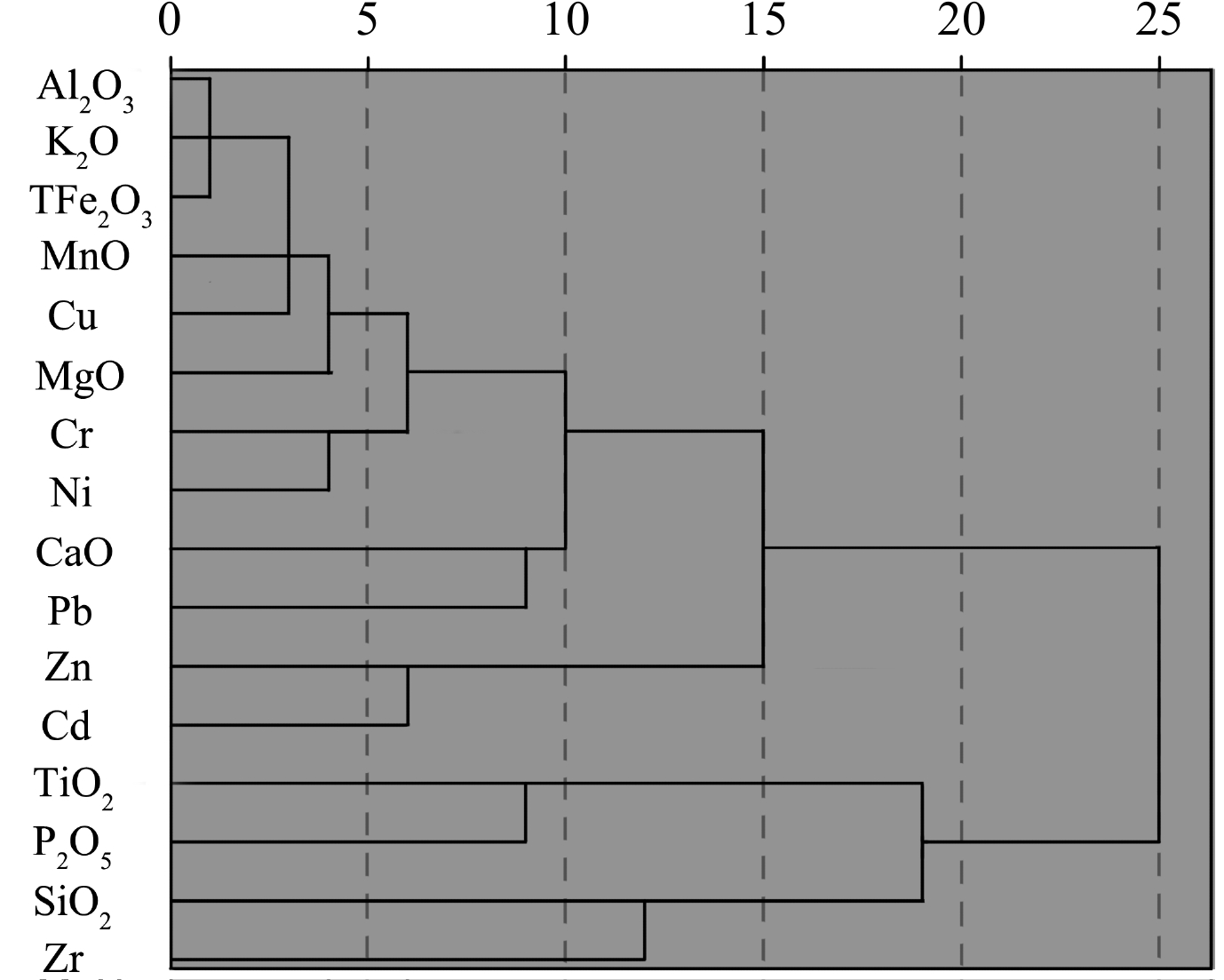
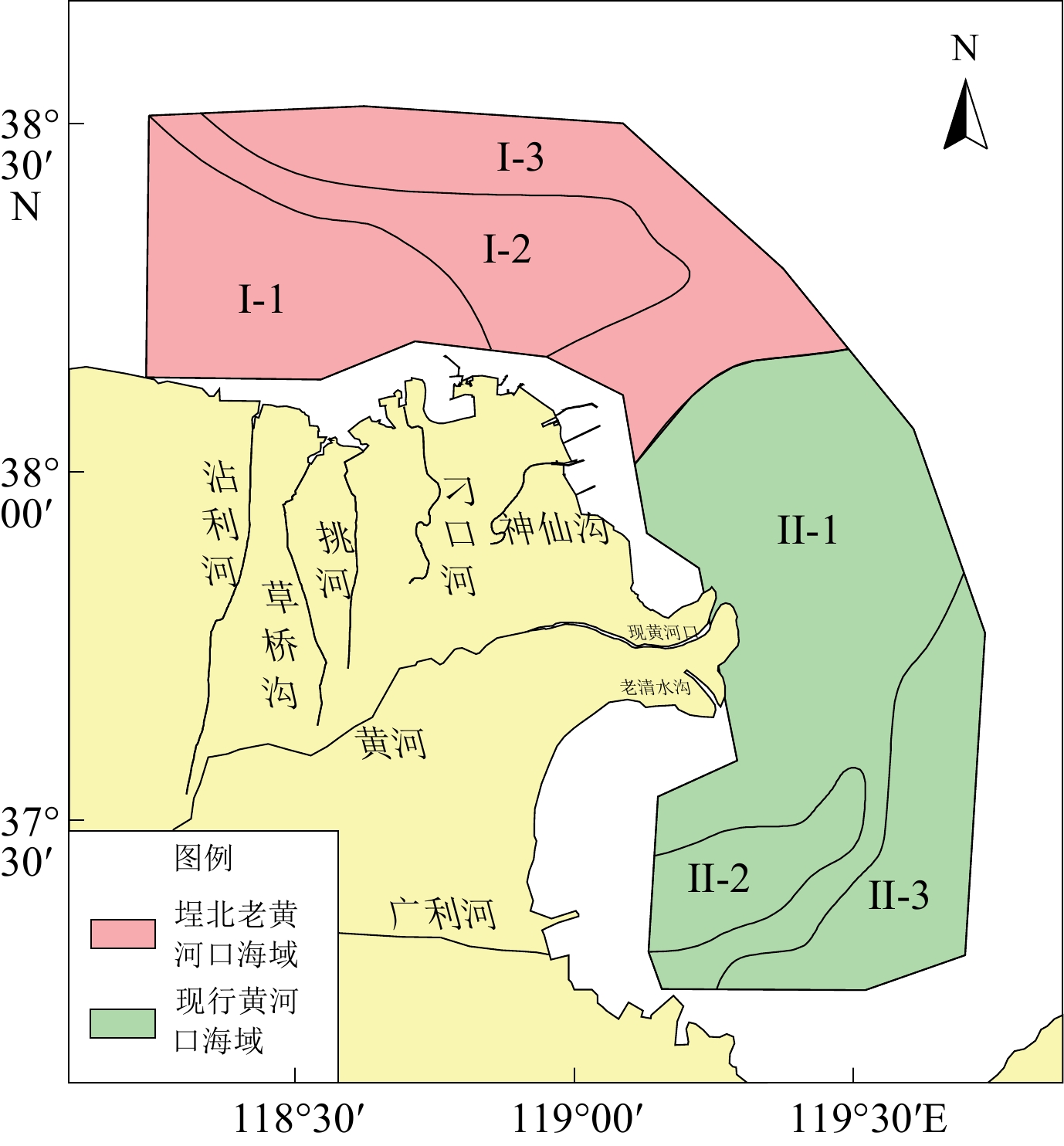
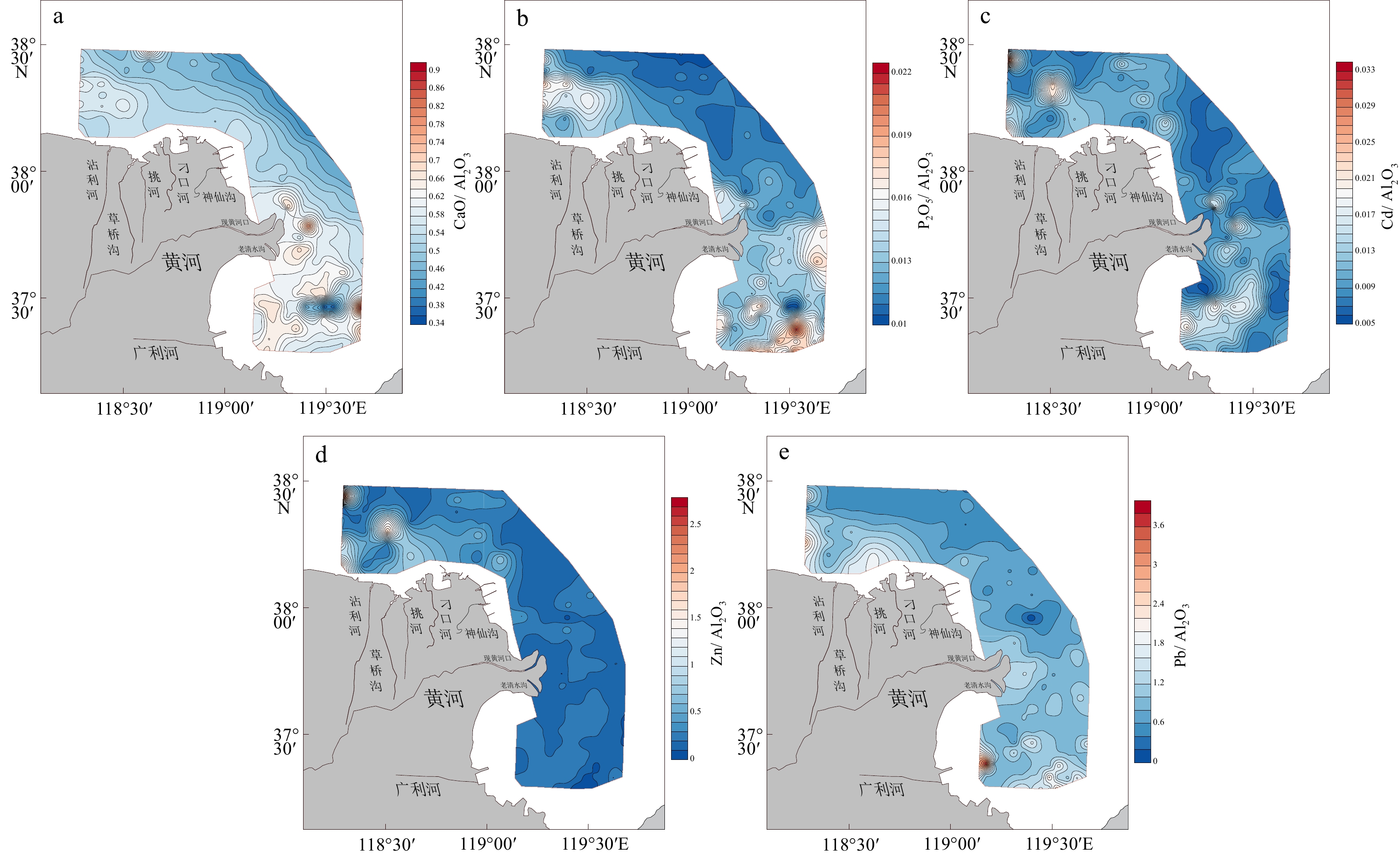
摘要: 基于黄河三角洲周边海域180个站位的表层沉积物资料,分析了16种地球化学元素的分布特征,利用多元统计分析、数值模拟、元素比值等方法,探讨了沉积物粒度、水动力环境以及物质来源等因素对于表层沉积物地球化学特征的影响。在地球化学元素分布的基础上,运用聚类分析将研究区划分为6个地球化学区域。I-2区、I-3区、II-1区和II-2区东部的大部分元素(TFe2O3、Al2O3、MgO、MnO、K2O、Cr、Ni、Cu)含量较高,沉积物粒度较细;I-1区、II-3区的SiO2含量较高,沉积物粒度较粗。潮流控制着沉积物的起动及运移,潮余流影响着细粒沉积物以及多数元素的富集,水动力作用通过改变沉积物粒度空间格局进而控制这些元素的分布。研究区黄河物质输入以及人类活动影响的区域性差异明显,黄河物质输入主要作用于现行黄河口海域,人类活动对埕北老黄河口的Cd、Zn、Pb、P2O5影响最为显著。自然因素是控制研究区表层沉积物地球化学特征分布的主要原因,人类活动则进一步改变了部分元素的空间分布规律。Abstract: The distribution characteristics of 16 elements in the surface sediments from 180 sites in the Yellow River Delta were analyzed. The effects of sediment grain size, hydrodynamic environment, and material sources on geochemical characteristics of the surface sediments were analyzed using multivariate statistical analysis, numerical modelling, and element ratio; and the main controlling factors of geochemical characteristics of surface sediments in the study area were discussed. Based on the distribution of geochemical elements, the study area was divided into six geochemical regions by cluster analysis. Most of the elements (TFe2O3, Al2O3, MgO, MnO, K2O, Cr, Ni, Cu) in Regions I-2, I-3, II-2, and the eastern part of II-1 are characterzied by elevated concentrations, and the sediment grain size in these areas is fine. The contents of SiO2 are higher in Regions I-1 and II-3, and the sediment grain size is coarser. Results show that tidal current controled the initiation and transport of sediment in the study area, and tidal residual currents affected the enrichment of fine-grained sediment and most elements. Local hydrodynamic environment controlled the spatial pattern of grain size in surface sediments. Obvious regional differences in material input from the Yellow River and human activities were revealed. The modern Yellow River estuary was strongly controlled by material input from the Yellow River. Human activities had a stronger impact on Chengbei Old Yellow River estuary, especially Cd, Zn, Pb and P2O5. Natural factors were the main factors on the geochemical distribution of surface sediments, while human activities further alytered the spatial distribution of some elements.
-
水体中悬浮体是入海河流向海洋输送污染物和营养物质的主要载体之一,其不仅反映了海洋沉积动力特征,同时也记录了源区、输运路径的地球化学元素和矿物等信息。悬浮体在水体中的浓度大小、分布特征及输运规律对海洋生态环境和资源的分布有重要影响。中国入海河流悬浮体向渤黄东海输运会影响中国海洋物质通量,对全球海洋物质循环的研究具有重要意义[1-3]。由于陆源物质供给和海洋水动力的季节变化,陆架浅海悬浮体浓度和分布也呈季节性变化[4-6]。受东亚季风影响,渤、黄海水动力整体呈现冬强、夏弱的特征,陆源河流携带的大量物质在夏季沉积后,在冬季又发生再悬浮继续输运[7]。悬浮体浓度分布能较好地反映物源供给、水动力及季风的周期性变化特征。山东半岛近岸泥质区呈“Ω”型或反C型的独特分布特征,其物质主要来源于沿岸流携带的黄河入海沉积物,平均沉积速率约3.7 mm/ka[8-13],泥沙沉积后受潮流、波浪以及水团的多重影响发生再悬浮和搬运过程。前人通过海洋观测、遥感反演和数值模拟等方法,对山东半岛附近海域的悬浮体输运和沉积过程开展了研究,并取得了一系列成果。Wang 等[14]通过高分辨率海洋-大气-波浪-沉积耦合COAWST模式系统的数值模拟,认为锋面和跃层对山东半岛近岸海域的悬浮体输运和沉积产生了明显影响,并且控制了泥质体沉积中心的发育。王勇智等[15]通过对山东半岛东部冬季潮流和悬浮体浓度观测,认为每年冬季约有(8.09~22.91)×104 t的悬浮体经山东半岛东部近岸海域向南输运。学者普遍认为山东半岛附近海域悬浮体主要来自于沉积物的再悬浮,但是对波浪和潮流在沉积物再悬浮过程中的作用存在争议。赵一阳等[16]认为冬季风浪是底层沉积物再悬浮的主要动力,而边昌伟[17]及Zeng等[18]则认为强风浪能显著增强海底沉积物的再悬浮,但波高<1 m的风浪,对底质沉积物的再悬浮作用较小,主要影响水体的垂向混合,潮流是沉积物再悬浮的主控因素。
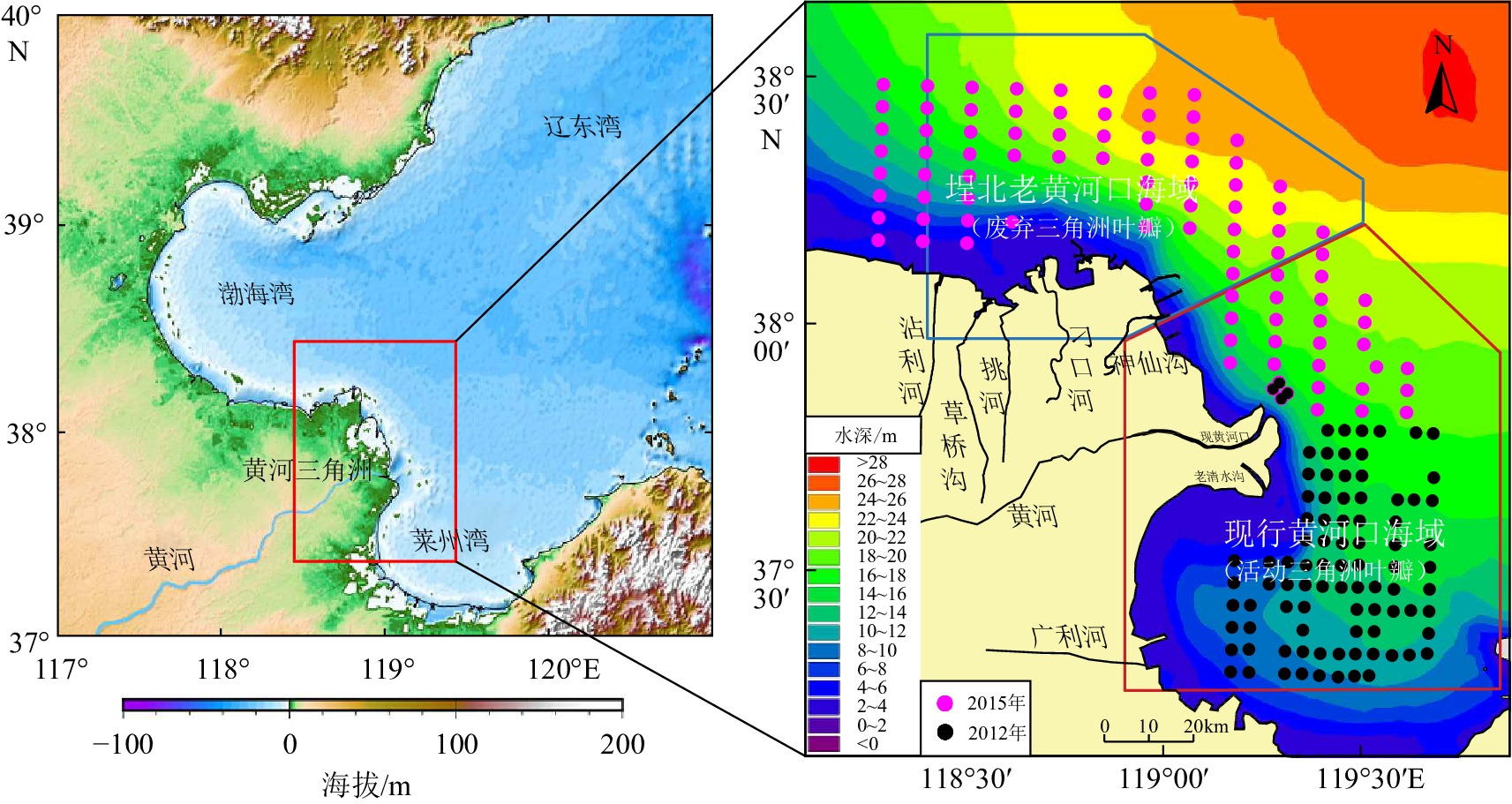
前人对山东半岛附近海域的悬浮体输运取得了丰硕的研究成果,但是研究多集中于大海域范围,缺少近岸大比例尺、高精度的实测资料。本文选择山东半岛近岸泥质区分布的典型区域——东北部近岸海域作为研究区(如图1、图2所示),其位于北黄海与南黄海的交界区域,不仅是内外海之间重要的物质输运通道,而且是多源物质的汇聚区 [19-22]。通过开展大比例尺、高精度的不同季节水文泥沙调查,分析山东半岛近岸海域悬浮体的水平和垂向季节分布特征,探讨悬浮体浓度分布和季节变化的控制因素,研究成果对于完善山东半岛泥质区沉积物输运机制具有重要意义。
![]() 图 1 黄海冬季环流及夏季冷水团分布图[23]B.S.: 渤海海峡,SLCC:辽南沿岸流,SBCC:渤南沿岸流,NSCC:鲁北沿岸流,SSCC山东半岛南部沿岸流,KCC:朝鲜半岛沿岸流,NJCC:苏北沿岸流,YSWC:黄海暖流,CDW:长江冲淡水,KC:黑潮,YSCW:黄海冷水团(10 ℃等温线包围的水体)。Figure 1. Winter circulation and cold water mass in summer in Yellow Sea[23]B.S.: Bohai Strait, SLCC: South Liaoning coastal current, SBCC: South Bohai coastal current, NSCC: North Shandong Peninsula coastal current, SSCC: South Shandong Peninsula coastal current, KCC: Korean Peninsula coastal current, NJCC: North Jiangsu coastal current, YSWC: Yellow Sea warm current, CDW: Changjiang River diluted water, KC: Kuroshio Current, YSCW: Yellow Sea Cold Water (Water surrounded by isotherms at 10 ℃).
图 1 黄海冬季环流及夏季冷水团分布图[23]B.S.: 渤海海峡,SLCC:辽南沿岸流,SBCC:渤南沿岸流,NSCC:鲁北沿岸流,SSCC山东半岛南部沿岸流,KCC:朝鲜半岛沿岸流,NJCC:苏北沿岸流,YSWC:黄海暖流,CDW:长江冲淡水,KC:黑潮,YSCW:黄海冷水团(10 ℃等温线包围的水体)。Figure 1. Winter circulation and cold water mass in summer in Yellow Sea[23]B.S.: Bohai Strait, SLCC: South Liaoning coastal current, SBCC: South Bohai coastal current, NSCC: North Shandong Peninsula coastal current, SSCC: South Shandong Peninsula coastal current, KCC: Korean Peninsula coastal current, NJCC: North Jiangsu coastal current, YSWC: Yellow Sea warm current, CDW: Changjiang River diluted water, KC: Kuroshio Current, YSCW: Yellow Sea Cold Water (Water surrounded by isotherms at 10 ℃).1. 区域概况
研究区位于山东半岛东北部近岸海域、北黄海南部。该区属于温带季风性气候,冬季以强度大的北风和西北风最为盛行,平均风速较高,约为6~7 m/s,夏季以南风和东南风为优势风向,风速较小,平均约为5~6 m/s。研究区最大水深42 m,平均水深约25 m,以正规半日潮占主导,M2分潮为黄海潮波的主要分潮[23]。潮流流速约为20~60 cm/s,自成山头向西北方向M2分潮流速逐渐减小[24]。研究区受季节性环流影响明显,冬季鲁北沿岸流和黄海暖流作用较大[25-26];夏季北黄海冷水团主要影响水深50 m以上海域[27-28],与研究区距离也较近(如图1所示)。受到季风和地形影响,波浪表现出显著的季节性变化,冬季波高较大,平均波高为0.9~1.9 m;夏季波高较小,平均波高为0.5~1.0 m[23]。研究区沉积物类型以砂质粉砂和粉砂为主[10]。
2. 资料与方法
2.1 资料来源
中国海洋大学于2018年夏季(8月1—5日)和冬季(12月22—25日)在山东半岛东北部海域开展了7条断面、87个站位大面站水文泥沙现场调查,取样站位如图2所示。调查内容包括水体温度、盐度、悬浮体浓度和浊度。
2.2 调查与处理方法
水体温度(℃)、盐度(PSU)、水深(m)采用美国TRDI公司CTD-NV型温盐深仪进行测量,采样频率5 Hz,温度和盐度测量精度为±0.005 ℃和±0.005PSU;水体浊度(FTU)采用英国Aquatec公司生产的Aqualogger 310TY型浊度仪进行现场测量,采样频率1 Hz,量程0~200FTU,测量精度为±0.01FTU。仪器从水面下海底匀速释放,释放速度约0.5 m/s。同时,各站位采集表层(距海面约1 m)、中层(0.5H,H为水深)和底层(距海底约1 m)水样,体积约1000 mL,用于悬浮体质量浓度的测定。水体悬浮体浓度通过室内抽滤实验测定[29]。温度、盐度和浊度平面和垂向分布图采用surfer11.0软件绘制,运用克里金差值方法,平面分布图差值步长约330 m,垂向分布图差值步长约370 m。
2.3 悬浮体浓度与浊度的关系
研究区每个站位只进行了表、中、底3层水体取样,无法详细呈现悬浮体浓度的垂向变化特征。由于浊度采用仪器测量,采样精度高,为更清晰地呈现悬浮体浓度垂向分布特征,本文采用水体浊度(单位:FTU)替代悬浮体浓度(单位:mg/L)进行分析[30-32]。通过冬季各站位表、中、底3层水体悬浮体浓度实验结果和相应的浊度测量结果相关性分析表明,研究区水体悬浮体浓度与浊度的相关性非常好(R2=0.92)(图3),说明水体浊度是悬浮体浓度(SSC)的良好替代性指标。
3. 结果
3.1 研究区水温和盐度分布特征
3.1.1 夏季水温和盐度分布特征
(1)水温和盐度分布特征
夏季,研究区各层水温平面分布显示,表层水温普遍较高,温度为20.4~28.8 ℃,呈近岸低、远岸高的特征;中层(0.5H)水温为15.0~21.7 ℃;底层水温为14.2~21.0 ℃,呈近岸高、远岸低的特征(图4)。在近岸浅水区域不同层位水温变化较小,远岸深水区域分布不同层位水温差异较明显;随着水深增大,中、底层水温差异减小。水温垂向分布显示(图5),夏季水体层化现象显著,但近岸浅水区域水体层化呈上下波动的特征。底层冷水向岸呈楔形分布,且其楔入程度受水深地形影响,近岸海域水深越大,受冷水影响越大(图5 Trend 01,Trend 02),水深相近海域冷水楔进程度相近(图5 Trend 05, Trend 06)。
夏季,研究区各层水体盐度平面分布显示,表、中、底三层水体盐度分别为31.71~32.28PSU、31.70~32.25PSU、31.85~32.31PSU(表1)。各层盐度平面分布总体趋势一致,均呈东南高、西北低的特征(图4)。水体盐度垂向上变化较小,从底到表有先增大后减小的变化特征(图5)。
表 1 夏季温度、盐度Table 1. Water temperature and salinity in summer层位 表层 中层 底层 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 最大值 28.8 32.28 21.7 32.25 21.0 32.31 最小值 20.4 31.71 15.0 31.70 14.2 31.85 平均值 25.4 32.00 18.6 31.98 17.4 31.99 (2)温跃层特征
根据垂直梯度法,浅水海域(水深<200 m),温跃层的温度梯度最低标准值为0.2 ℃/m[33]。本文将垂直梯度值大于或等于上述最低指标值的水层划定为温度跃层,其上下端点所在深度作为跃层上界深度和下界深度。分析结果表明,研究区夏季水体存在明显的温跃层。温跃层的上界在0~1 m水深范围,下界深度在2.4~22.2 m水深范围,下界深度明显受水深地形影响,在研究区北部深水区,温跃层下界可达20 m水深处;在近岸浅水区域,温跃层仅在5 m以浅范围内。在水深相近的研究区中部海域,温跃层的下界深度也存在明显差异,研究区东部的温跃层下界深度(8~10 m)要明显浅于西部区域(约14 m)(图6)。
3.1.2 冬季水温和盐度分布特征
冬季,研究区水温和盐度平面分布显示,各层水温均为6.3~9.9 ℃,盐度均为31.1~32PSU(表2),水温和盐度均呈近岸低、远岸高的特征(图7)。
表 2 冬季水温和盐度特征值Table 2. Water temperature and salinity in winter层位 表层 中层 底层 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 最大值 9.9 31.97 9.9 31.99 9.9 31.99 最小值 6.4 31.13 6.3 31.19 6.3 31.15 平均值 7.4 31.36 7.4 31.39 7.4 31.38 从冬季典型断面水温和盐度剖面显示,水体垂向混合剧烈,近岸和远岸水体之间存在明显的温、盐切变锋面(图8),在Trend 01断面上锋面在WH06和WH07之间,Trend 02断面上锋面在WH16和WH17之间。在锋面两侧的水体温度和盐度比较均匀。其他断面由于离岸较近,未观测到明显的水温和盐度锋面。
3.2 研究区水体浊度分布特征
3.2.1 夏季浊度分布特征
夏季,研究区水体浊度平面分布特征显示,表层浊度普遍较低(0.2~2.3FTU)(表3),威海湾及刘公岛近岸区域水体浊度相对较高;中层(0.5H)浊度(0.2~8.9FTU)略高于表层,呈近岸高、远岸低,东南高、西北低的分布特征;底层浊度(2.9~37.8FTU)最高,呈东南高、西北低的分布特征(图9)。
表 3 冬季和夏季水体浊度特征值Table 3. Water turbidity in winter and summerFTU 夏季 冬季 表层 中层 底层 表层 中层 底层 最大值 2.3 8.9 37.8 22.4 44.0 100.1 最小值 0.2 0.2 2.9 1.5 2.3 3.9 平均值 0.6 2.5 9.3 9.2 13.0 23.4 研究区典型断面水体浊度垂向分布显示,悬浮体浊度明显呈底层高、表层低的梯度变化(图10)。在20 m以深区域,水体上部存在厚10 ~20 m且浊度较小(<1FTU)的均匀层,其厚度与水深大小大致呈正相关关系,水深大则均匀层厚,水深小则均匀层薄。
3.2.2 冬季浊度分布特征
冬季,研究区水体浊度从表至底逐渐增大,表层水体浊度为1.5~22.4FTU,中层(0.5H)水体浊度为2.3~44.0FTU,底层水体浊度为3.9~100.1FTU。各层水体浊度平面分布特征基本一致,研究区中部存在高浊度区,自东向西呈舌状分布,自中部向海湾和外海两侧浊度逐渐降低(图11)。
研究区水体浊度垂向分布特征显示,底层浊度略高于表层,沿剖面方向底部浊度越高、表层浊度相应也较高(如图12所示)。受水体垂向混合作用,浊度分层现象不明显,例如Trend 02断面的WH16、WH17和WH18站位的水体浊度基本不随水深变化。
4. 讨论
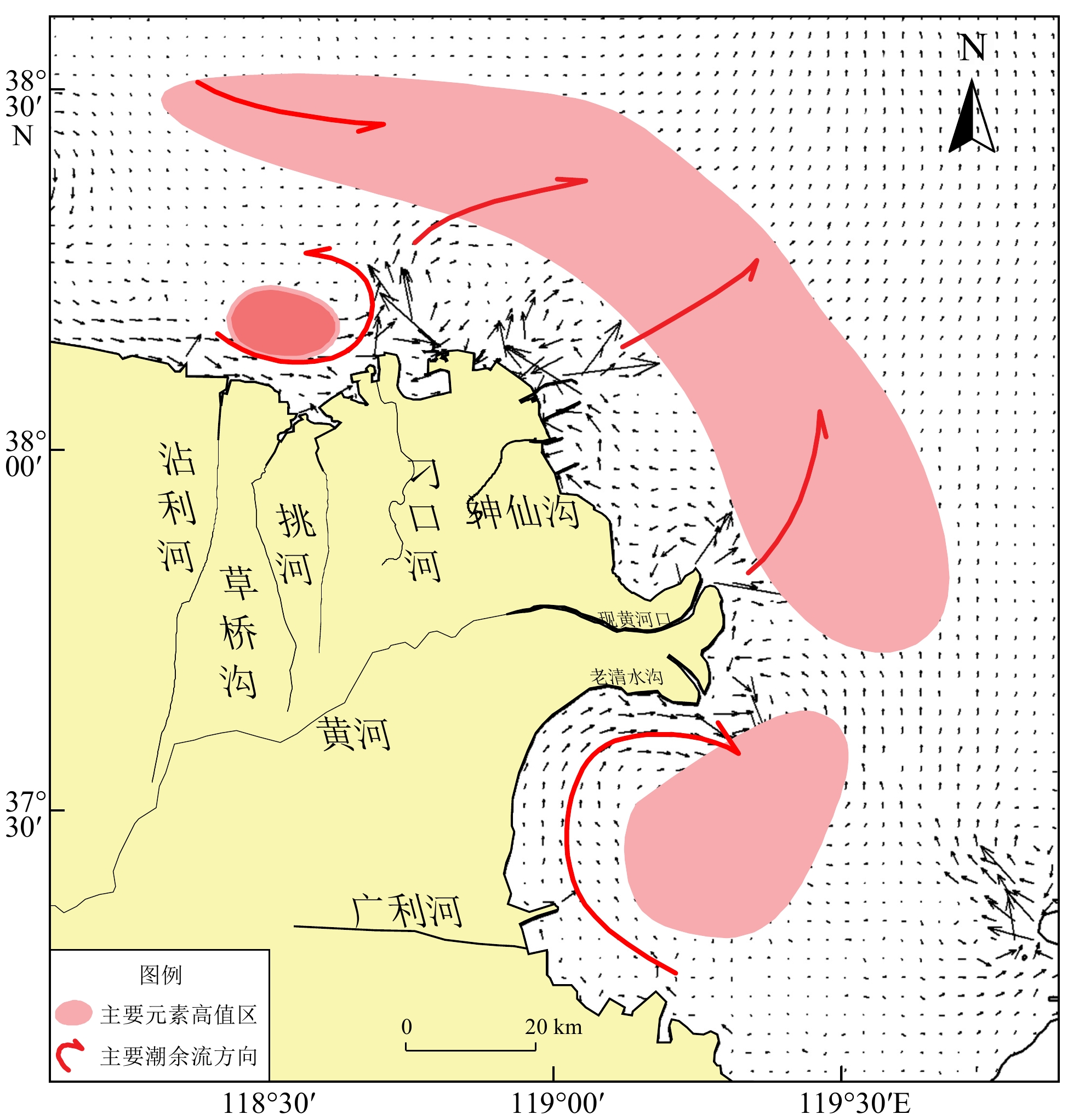
前人研究表明,山东半岛泥质区的沉积物主要来源于冬季发育的由西向东的鲁北沿岸流携带的黄河物质[8-13]。但是,从研究区浊度平面分布来看,冬、夏两季均呈现出东高西低的特征,这一特征与沿岸流的运动方向相反,说明悬浮体的来源有待商榷。同时,浊度垂向分布特征显示,底层的悬浮体浓度明显高于表层,尤其夏季浊度自底层往上阶梯式减小,说明底质沉积物再悬浮才是悬浮体的主要来源,与前人研究结论一致[14-15]。沉积物再悬浮之后,在潮流、波浪以及水体结构等综合因素的控制下发生输运和再次沉积。
4.1 潮流对悬浮体输运的影响
M2分潮是研究区的主要分潮[17],如图13可见,研究区以东为成山头强潮区海域,M2分潮流速可达50~70 cm/s;以西为威海北部弱潮区海域,M2分潮流速低至30 cm/s[34]。潮流平面不均匀性对泥沙输运的作用不容忽视。
夏季,整个黄海受东南季风的影响,波浪作用很小,水体垂向混合弱,潮流对悬浮体的分布、输运及沉积过程起到了主导作用[35-36]。由于海底底摩擦作用,潮流出现水体层间流速不等现象,平均运动的动能将转化成湍流而消耗,湍流应力将克服海水浮力而做功。水深越小,湍流越强[37]。远岸深水区域,地势平缓,水体湍动能较小,无法打破水体层化,使得上层海水悬浮体浓度非常低并且均匀分布;而在近岸浅水区,潮混合作用的效果体现的异常明显,上层水体的悬浮体浓度较深水区明显增大,说明在潮混合和波浪的共同作用下,近岸水体的层化被打破,水体垂向混合加强,底层的悬浮体被带到上层水体中。同时,潮混合作用使上层水体温度相对降低,下层水体温度相对升高。这一个过程使得深水和浅水区域之间温度梯度增大,阻碍了悬浮体在深水和浅水区域的交换,一定程度上影响了悬浮体的水平输运。
冬季由于强风浪的影响,潮流作用在垂向上的体现相对变弱,主要是体现在悬浮体平面分布特征上。东部强潮区底层水体悬浮体浓度明显比西部弱潮区水体悬浮体浓度高,冬季潮流主要影响研究区悬浮体的平面分布。
4.2 波浪对悬浮体输运的影响
波浪也是黄海沉积物再悬浮的主要动力之一。研究区夏季盛行偏南风,风速弱;冬季盛行偏北风,风速强。受季风影响,研究区波浪也存在季节性变化。冬季研究区平均波高为0.9~1.9 m,夏季平均波高约为0.5~1 m[35-36]。Wei Zhong等[38]根据风况资料计算,夏季浪基面可达30 m以上(大于研究区平均水深25 m),冬季浪基面更深,波浪对悬浮体的影响不容忽视。
研究区浊度分布特征显示,冬季底层水体浊度最大值达到100.1FTU,明显大于夏季(37.8FTU);冬季表层水体的浊度最大值为22.4FTU,明显高于夏季(2.3FTU)。温盐的垂向分布显示,冬季水体垂向上的温盐值基本一致,而夏季水体的温度随水深增大逐渐降低。综合温盐和浊度特征表明,波浪不仅促进了沉积物的再悬浮,而且加强了水体的垂向混合及悬浮体的垂向运动。
4.3 温跃层对悬浮体输运的影响
温跃层附近常发育湍流边界层,水体变得极为稳定,抑制了底层悬浮体向上扩散,使得沉积物主要集中在温跃层以下输运[39-40]。从WH06、WH15和WH75三个典型站位水温和浊度的垂向分布可见,温度和浊度在垂向上的变化相反,温跃层以下水体浊度显著高于上部水体浊度(图14)。底部再悬浮的泥沙在湍流作用下随机向上运动,但是受到温跃层的阻隔,再悬浮的泥沙无法向上部运动,使得上部水体中的悬浮体浓度很低,浊度相应地减小,小于1FTU。因此,温跃层阻碍了悬浮体的垂向运动。
4.4 温盐锋面对悬浮体输运的影响
锋面是指物理性质不同的两种水团或水系的交界面,其常常表现为梯度变化的极大值。最明显的锋面发生在两种不同密度的水体之间。锋面不仅会影响水体的混合及营养元素、污染物等的富集[41-42],同时其稳定的水体结构和弱水动力条件,对沉积物输运及沉降过程起到了重要作用[43-44]。
冬季水体垂向混合均匀,其温盐锋面与夏季的形成机理完全不同,起因于环流作用。在强冬季风的影响下,低温、低盐的鲁北沿岸流和高温、高盐的黄海暖流发育明显,黄海暖流进入北黄海之后在123°E、37.7°N左右自东向西经过研究区北部[45]。由研究区表层水体T-S图可见,研究区可分为三种不同性质的水体,分别为高温高盐水、低温低盐水和过渡带水(图15左),这一特征恰好响应了研究区的环流特征。近岸低温低盐水体(温度:6.2~7.8 ℃,盐度:31.1~31.5PSU),影响研究区约离岸30 km以内的整个近岸海域;远岸高温高盐水体(温度:9.8~10 ℃,盐度:31.9~32.1PSU),影响研究区的北部海域。在两个性质迥异的水团之间,水温和盐度均呈现阶梯式变化,形成近东西向的水温和盐度的切变锋。在温盐锋面的影响下,东部高浓度悬浮体难以向北扩散,主要向西扩散,使得研究区北部的悬浮体浓度急剧下降,浊度在5FTU以内,研究区中部形成了条带状的高浊度带。从典型断面Trend03的浊度分布与温盐锋面图可知(图15右),锋面两侧的浊度相差巨大,说明温盐锋面阻碍了悬沙的水平输运。输运模式概念图详见图16。
5. 结论
(1)研究区悬浮体浓度存在明显的季节变化,夏季浊度为0.2~37.8FTU,冬季浊度为1.5~100.1FTU,均表现为底高表低、东高西低的特征。
(2)夏季水温分层明显,表现为表高底低的特征,盐度整体变化较小;冬季温盐垂向上混合均匀,平面上表现为近岸低温低盐水体向远岸高温高盐水体的过渡。
(3)研究区悬浮体浓度分布特征受控于潮流、波浪、温跃层和温盐锋面。夏季,悬浮体垂向上受到温跃层影响,底层悬浮体难以向表层输运;平面上近岸潮混合和波浪作用阻碍了悬浮体的水平输运。冬季,强风浪促使悬浮体垂向混合剧烈,表层悬浮体浓度明显较夏季变高;平面上鲁北沿岸流和黄海暖流形成的温、盐锋面阻碍了水团间悬浮体的输运。
-
表 1 潮流潮位验证点概况
Table 1 Information of tidal current and tidal level verified on site
潮流验证点 北纬 东经 潮位验证点 北纬 东经 1 38°11′51.84″ 118°17′58.62″ 大口河(1#) 38°15′ 117°50′ 2 38°14′04.20″ 118°23′39.60″ 塘沽(2#) 38°59′ 117°45′ 3 38°16′45.12″ 118°39′06.54″ 曹妃甸(3#) 38°57′ 118°31′ 4 38°13′30.48″ 119°00′43.20″ 八角(4#) 37°39′ 121°08′ 5 37°54′30.60″ 119°18′12.60″ 北隍城(5#) 38°22′ 120°51′ 6 37°43′17.76″ 119°25′00.00″ 大连港(6#) 38°56′ 121°40′ 表 2 研究区表层沉积物常量元素含量
Table 2 Contents of major elements of surface sediments in the study area
% 常量组分 SiO2 TFe2O3 Al2O3 TiO2 CaO MgO K2O MnO P2O5 平均值 59.38 4.46 12.30 0.66 6.77 2.37 2.52 2.71 0.09 最大值 68.94 6.11 14.57 0.76 10.55 3.19 2.93 3.88 0.13 最小值 45.73 2.84 8.89 0.45 4.16 1.43 2.06 1.83 0.05 表 3 研究区表层沉积物微量元素含量
Table 3 Contents of trace elements of surface sediments in the study area
mg/kg 微量组分 Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb Zr 平均值 67.45 27.58 23.73 79.60 0.13 22.60 273.10 最大值 83.20 40.50 66.33 332.96 0.36 39.20 685.00 最小值 36.80 14.80 4.18 34.70 0.07 6.56 113.79 表 4 埕北老黄河口海域表层沉积物元素相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation coefficients between values of elements and average particle size in Chengbei Old Yellow River estuary
SiO2 TFe2O3 Al2O3 TiO2 CaO MgO K2O MnO P2O5 Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb Zr Mz SiO2 1 TFe2O3 −0.99 1 Al2O3 −0.96 0.98 1 TiO2 −0.57 0.58 0.50 1 CaO −0.57 0.44 0.41 0.33 1 MgO −0.81 0.81 0.72 0.58 0.38 1 K2O −0.96 0.99 0.99 0.49 0.36 0.75 1 MnO −0.94 0.94 0.93 0.55 0.47 0.75 0.91 1 P2O5 0.17 −0.19 −0.27 0.26 −0.07 0.16 −0.26 −0.15 1 Cr −0.84 0.84 0.78 0.70 0.45 0.84 0.80 0.88 −0.01 1 Ni −0.91 0.92 0.92 0.52 0.44 0.69 0.91 0.76 −0.24 0.75 1 Cu −0.78 0.78 0.77 0.40 0.39 0.57 0.76 −0.11 −0.24 0.60 0.74 1 Zn 0.11 −0.10 −0.11 0.00 −0.01 −0.11 −0.13 −0.16 −0.07 0.16 −0.06 0.03 1 Cd 0.12 −0.15 −0.17 −0.02 −0.07 −0.09 −0.17 0.36 0.13 0.18 −0.16 −0.01 0.98 1 Pb −0.22 0.23 0.21 0.26 0.12 0.11 0.21 0.27 0.10 0.17 0.38 0.25 0.48 0.37 1 Zr 0.78 −0.77 −0.79 −0.08 −0.38 −0.64 −0.78 −0.73 −0.14 0.52 −0.68 −0.61 0.11 0.11 0.03 1 Mz −0.94 0.94 0.94 0.47 0.43 0.75 0.94 0.85 −0.20 0.75 0.86 0.77 0.10 0.14 0.13 −0.78 1 注:n=62。 表 5 现行黄河口海域表层沉积物元素相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation coefficients between values of elements and average particle size in modern Yellow River estuary
SiO2 TFe2O3 Al2O3 TiO2 CaO MgO K2O MnO P2O5 Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb Zr Mz SiO2 1 TFe2O3 −0.91 1 Al2O3 −0.78 0.84 1 TiO2 −0.10 0.31 0.16 1 CaO −0.80 0.74 0.54 0.08 1 MgO −0.88 0.92 0.77 0.30 0.80 1 K2O −0.75 0.77 0.84 0.14 0.57 0.69 1 MnO −0.78 0.87 0.76 0.25 0.59 0.75 0.70 1 P2O5 0.11 −0.02 −0.27 0.71 0.06 0.06 0.34 −0.06 1 Cr −0.64 0.62 0.58 0.37 0.22 0.53 0.38 0.58 0.01 1 Ni −0.81 0.66 0.56 0.06 0.39 0.57 0.46 0.56 −0.2 0.78 1 Cu −0.87 0.90 0.79 0.20 0.70 0.80 0.76 0.81 −0.12 0.57 0.67 1 Zn −0.76 0.84 0.85 0.21 0.54 0.75 0.71 0.75 −0.19 0.59 0.61 0.82 1 Cd −0.68 0.50 0.21 0.01 0.41 0.49 0.26 0.36 0.02 0.54 0.80 0.46 0.39 1 Pb −0.81 0.78 0.70 0.10 0.66 0.74 0.71 0.72 −0.10 0.52 0.63 0.86 0.69 0.49 1 Zr 0.19 −0.14 −0.34 0.08 0.02 −0.07 0.23 −0.13 0.38 0.29 −0.28 0.15 0.24 0.01 0.07 1 Mz −0.74 0.58 0.54 0.05 0.34 0.50 0.45 0.48 −0.20 0.69 0.90 0.58 0.54 0.71 0.52 −0.25 1 注:n=118。 表 6 因子分析结果
Table 6 Results of factor analysis
元素
组分埕北老黄河口海域 现行黄河口海域 F1 F2 F3 F1 F2 F3 F4 SiO2 −0.988 0.007 −0.067 −0.829 −0.517 0.018 −0.079 TFe2O3 0.989 0.004 0.054 0.910 0.300 0.165 0.110 Al2O3 0.978 −0.013 −0.068 0.882 0.012 −0.020 0.385 TiO2 0.544 0.094 0.674 0.163 −0.045 0.955 0.104 CaO 0.503 0.028 0.123 0.792 0.212 −0.011 −0.333 MgO 0.789 −0.049 0.407 0.875 0.274 0.181 −0.030 K2O 0.973 −0.024 −0.048 0.855 0.068 −0.295 0.142 MnO 0.951 −0.001 0.066 0.836 0.188 0.135 0.161 P2O5 −0.237 0.011 0.835 −0.115 0.028 0.846 −0.393 Cr 0.833 −0.069 0.366 0.400 0.537 0.319 0.555 Ni 0.936 0.071 −0.026 0.446 0.776 −0.021 0.352 Cu 0.812 0.139 −0.103 0.882 0.292 0.040 0.114 Zn −0.114 0.966 0.011 0.825 0.159 0.054 0.312 Cd −0.168 0.924 0.050 0.243 0.933 0.007 −0.043 Pb 0.257 0.678 −0.002 0.808 0.334 −0.026 0.008 Zr −0.784 0.089 0.195 −0.093 0.021 0.189 −0.806 方差贡献 57.68% 13.53% 9.04% 45.48% 19.86% 11.40% 9.96% 累积方差贡献 57.68% 71.21% 80.25% 45.48% 65.34% 76.74% 86.70% -
[1] 韩宗珠, 张军强, 邹昊, 等. 渤海湾北部底质沉积物中黏土矿物组成与物源研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2011, 41(11):95-102 HAN Zongzhu, ZHANG Junqiang, ZOU Hao, et al. Characteristics and provenance of clay mineral assemblage of sediments from the northern part of the Bohai Bay [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2011, 41(11): 95-102.
[2] Li B W, Jia Y G, Liu J P, et al. The controlling factors of high suspended sediment concentration in the intertidal flat off the Huanghe River Estuary [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2020, 39(10): 96-106. doi: 10.1007/s13131-020-1679-9
[3] Bi N S, Yang Z S, Wang H J, et al. Sediment dispersion pattern off the present Huanghe (Yellow River) subdelta and its dynamic mechanism during normal river discharge period [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 86(3): 352-362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.06.005
[4] 吕成功, 陈真. 渤海表层沉积物地球化学分析[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1993, 23(3):91-98 LV Chenggong, CHEN Zhen. Geochemical analysis of the surface sediments of the Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1993, 23(3): 91-98.
[5] 赵一阳, 鄢明才. 中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994 ZHAO Yiyang, YAN Mingcai. Geochemistry of Sediments of the China Shelf Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994.
[6] 蓝先洪, 李日辉, 王中波, 等. 渤海西部表层沉积物的地球化学记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):75-85 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.03.008 LAN Xianhong, LI Rihui, WANG Zhongbo, et al. Geochmical records of surface sediments in the western Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3): 75-85. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.03.008
[7] 赵玉玲, 冯秀丽, 宋湦, 等. 现代黄河三角洲附近海域表层沉积物地球化学分区[J]. 海洋科学, 2016, 40(9):98-106 doi: 10.11759/hykx20160422002 ZHAO Yuling, FENG Xiuli, SONG Sheng, et al. Geochemical partition of surface sediments in the seas near the modern Yellow River Delta [J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(9): 98-106. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160422002
[8] Qiao S Q, Shi X F, Gao J J, et al. The distribution and variation of elements in sediments off the Huanghe (Yellow) River mouth [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013, 31(4): 876-885. doi: 10.1007/s00343-013-2126-y
[9] Chu Z X, Sun X G, Zhai S K, et al. Changing pattern of accretion/erosion of the modern Yellow River (Huanghe) subaerial delta, China: Based on remote sensing images [J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 227(1-2): 13-30. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.11.013
[10] Li G S, Wang H L, Liao H P. Numerical simulation on seasonal transport variations and mechanisms of suspended sediment discharged from the Yellow River to the Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2010, 20(6): 923-937. doi: 10.1007/s11442-010-0821-6
[11] 张连杰, 朱龙海, 张盼, 等. 渤海湾表层沉积物元素地球化学分布特征与影响因素[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(6):78-87 doi: 10.11759/hykx20190122004 ZHANG Lianjie, ZHU Longhai, ZHANG Pan, et al. Geochemical distribution and its controlling factors of the surface sediments in the Bohai Bay [J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(6): 78-87. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190122004
[12] 徐艳东, 高会旺, 魏潇, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物中重金属污染特征和生态风险评估[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2021, 51(11):74-85 XU Yandong, GAO Huiwang, WEI Xiao, et al. Heavy metals and their ecological risk in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(11): 74-85.
[13] Wang Z H, Guo X, Zhang K, et al. Environmental changes in Jiaozhou Bay of northern China during the past 90 years using metals and biogenic elements in sediments [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 53: 301-312. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.06.002
[14] Zhang P, Hu R J, Zhu L H, et al. Distributions and contamination assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of western Laizhou Bay: Implications for the sources and influencing factors [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 119(1): 429-438. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.03.046
[15] Wei W H, Zhang J, Zeng H Z. Particulate element inventory of the Huanghe (Yellow River): A large, high-turbidity river [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(10): 3669-3680. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90160-K
[16] Liu Q Q, Wang F F, Meng F P, et al. Assessment of metal contamination in estuarine surface sediments from Dongying City, China: Use of a modified ecological risk index [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 126: 293-303. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.017
[17] 刘志杰, 李培英, 张晓龙, 等. 黄河三角洲滨海湿地表层沉积物重金属区域分布及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(4):1182-1188 doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.04.035 LIU Zhijie, LI Peiying, ZHANG Xiaolong, et al. Regional distribution and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in surface sediments from coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(4): 1182-1188. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.04.035
[18] Hu N J, Liu J H, Huang P, et al. Sources, geochemical speciation, and risk assessment of metals in coastal sediments: a case study in the Bohai Sea, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(8): 309. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-6599-4
[19] Liu L, Wang H J, Yang Z S, et al. Coarsening of sediments from the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta-coast and its environmental implications [J]. Geomorphology, 2022, 401: 108105. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.108105
[20] Udden J A. Mechanical Composition of clastic sediments [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1914, 25(1): 655-744. doi: 10.1130/GSAB-25-655
[21] Wentworth C K. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1922, 30(5): 377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910
[22] Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River Bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1): 3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[23] 郑世雯, 范德江, 刘明, 等. 渤海中部现代黄河沉积物影响范围的稀土元素证据[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(6):95-103 ZHENG Shiwen, FAN Dejiang, LIU Ming, et al. Rare earth element evidence for the Modern Yellow River Origin sediments in the middle Bohai Sea [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(6): 95-103.
[24] Fu Y T, Chen S L, Ji H Y, et al. The modern Yellow River Delta in transition: Causes and implications [J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 436: 106476. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106476
[25] 林炳煌. 泉州湾沉积物粒度和元素组成特征及其沉积环境意义[D]. 厦门大学硕士学位论文, 2009 LIN Binghuang. Characteristics of sediment granularity, element geochemistry and their significance for identifying sedimentary dynamic environment in the Quanzhou estuary[D]. Master Dissertation of Xiamen University, 2009.
[26] 王悦, 林霄沛. 地形变化下渤海湾M2分潮潮致余流的相应变化及其对污染物输运的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(1):1-6 WANG Yue, LIN Xiaopei. The variation of M2 constituent corresponding to the change of topography in Bohai Bay and its effects on the transport of pollutants [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(1): 1-6.
[27] 赵保仁, 庄国文, 曹德明, 等. 渤海的环流、潮余流及其对沉积物分布的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1995, 26(5):466-473 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003 ZHAO Baoren, ZHUANG Guowen, CAO Deming, et al. Circulation, tidal residual currents and their effects on the sedimentations in the Bohai Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1995, 26(5): 466-473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003
[28] 李春雨. 黄河三角洲北部海域的冲淤演化与成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(11):17-21 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2014.11.004 LI Chunyu. Erosional and depositional pattern to the northern offshore area of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2014, 30(11): 17-21. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2014.11.004
[29] 刘鑫仓, 刘艳玲, 迟万清, 等. 胶州湾潮余流和物质输送之间的关系[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2019, 40(2):10-17 doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2019.02.002 LIU Xincang, LIU Yanling, CHI Wanqing, et al. Relationship between tidal residual current and mass transport in Jiaozhou bay [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019, 40(2): 10-17. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2019.02.002
[30] Howarth M J, Huthnance J M. Tidal and residual currents around a Norfolk Sandbank [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1984, 19(1): 105-117. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(84)90055-6
[31] 乔淑卿, 石学法, 王国庆, 等. 渤海底质沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(4):139-147 QIAO Shuqing, SHI Xuefa, WANG Guoqing, et al. Discussion on grain-size characteristics of seafloor sediment and transport pattern in the Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(4): 139-147.
[32] 袁萍, 毕乃双, 吴晓, 等. 现代黄河三角洲表层沉积物的空间分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2):49-57 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2016.02.006 YUAN Ping, BI Naishuang, WU Xiao, et al. Surface sediments at the subaqueous Yellow River Delta: classification and distribution [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 49-57. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2016.02.006
[33] 任韧希子, 陈沈良. 黄河三角洲的沉积动力分区[J]. 上海国土资源, 2012, 33(2):62-68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.02.016 REN Renxizi, CHEN Shenliang. Sediment dynamics in the littoral zone of the Yellow River delta [J]. Shanghai Land & Resource, 2012, 33(2): 62-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.02.016
[34] 窦衍光. 长江口邻近海域沉积物粒度和元素地球化学特征及其对沉积环境的指示[D]. 国家海洋局部第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2007 DOU Yanguang. Characteristics of sediment granularity, element geochemistry and their significance for identifying sedimentary environment in the contiguous sea areas of Changjiang River Estuary[D]. Master Dissertation of First Institute of Oceanography, MNR, 2007.
[35] 刘素美, 张经. 沉积物中重金属的归一化问题: 以Al为例[J]. 东海海洋, 1998, 16(3):48-55 LIU Sumei, ZHANG Jing. Normalization of heavy metals to aluminum in marine sediments [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1998, 16(3): 48-55.
[36] 岳维忠, 黄小平, 孙翠慈. 珠江口表层沉积物中氮、磷的形态分布特征及污染评价[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(2):111-117 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2007.02.003 YUE Weizhong, HUANG Xiaoping, SUN Cuici. Distribution and pollution of nitrogen and Phosphorus in surface sediments from the Pearl River estuary [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38(2): 111-117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2007.02.003
[37] Yang Z S, Ji Y J, Bi N S, et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 93(3): 173-181.
[38] 吴明清, 文启忠, 潘景瑜, 等. 中国黄土的平均化学成分: 上部大陆地壳的一种典型代表[J]. 岩相古地理, 1995, 15(2):127-136 WU Mingqing, WEN Qizhong, PAN Jingyu, et al. Average chemical composition of loess in China: as a good pepresentative of the upper continental crust [J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeograpgy, 1995, 15(2): 127-136.
[39] 乔淑卿, 方习生, 石学法, 等. 黄河口及邻近渤海海域表层沉积物中CaO和蒙皂石分布及其对黄河入海物质运移的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(1):17-23 QIAO Shuqing, FANG Xisheng, SHI Xuefa, et al. Distribution of CaO and smectite in surface sediments off the Yellow River mouth and in the nearby Bohai Sea and the implications for dispersion of the river sediments to the sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(1): 17-23.
[40] Xing G P, Wang H J, Yang Z S, et al. Spatial and temporal variation in erosion and accumulation of the subaqueous Yellow River Delta (1976-2004) [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2016, 74(sp1): 32-47.
[41] 柳后起. 黄河三角洲微量元素环境地球化学研究[D]. 中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2016 LIU Houqi. Environmental geochemistry research of trace elements in the Yellow River Delta[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of University of Science and Technology of China, 2016.
[42] Bi N S, Wang H J, Wu X, et al. Phase change in evolution of the modern Huanghe (Yellow River) Delta: process, pattern, and mechanisms [J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 437: 106516. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106516
[43] 赵志梅, 秦延文. 渤海湾表层沉积物磷形态分析[J]. 海洋技术, 2006, 25(4):51-53,87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2006.04.014 ZHAO Zhimei, QIN Yanwen. The analysis of the phosphorus forms in the sediment of Bohai Bay [J]. Ocean Technology, 2006, 25(4): 51-53,87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2006.04.014
[44] 江辉煌. 渤海沉积物中生源要素的研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2012 JIANG Huihuang. Study on biogenic elements in sediments of the Bohai Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2012.
[45] 李梦露. 磷观渤海: 由陆向海磷的输送和收支及其生态环境指示意义[D]. 自然资源部第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2021 LI Menglu. Insighting into the Bohai Sea from the phosphorus dimension: A study of gluxes and budget of phosphorus from land to sea with implication for the environment change[D]. Master Dissertation of First Institute of Oceanography, MNR, 2021.
[46] 林建斌, 王剑锋. 水产养殖与生态营养[J]. 科学养鱼, 2009, 28(5):65-66 LIN Jianbin, WANG Jianfeng. Aquaculture and ecological nutrition [J]. Scientific Fish Farming, 2009, 28(5): 65-66.
[47] 张汉珍, 王菲菲, 姜磊, 等. 东营市挑河和神仙沟的河水重金属污染评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(4):1536-1542 doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2017.04.063 ZHANG Hanzhen, WANG Feifei, JIANG Lei, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the surface water of Tiaohe river and Shenxiangou Brook, Dongying City, Shangdong [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(4): 1536-1542. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2017.04.063
[48] 刘群群, 孟范平, 王菲菲, 等. 东营市北部海域沉积物中重金属的分布、来源及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(9):3635-3644 doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201701048 LIU Qunqun, MENG Fanping, WANG Feifei, et al. Spatial distribution, source and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the coastal sediments of northern Dongying City [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(9): 3635-3644. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201701048
[49] 张亮, 叶芳, 王尽文, 等. 黄河口埕岛油田周边海域的生态环境特征及变化趋势[J]. 海洋学研究, 2015, 33(3):75-83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2015.03.011 ZHANG Liang, YE Fang, WANG Jinwen, et al. The eco-environmental characteristics and variation trends around Chengdao Oilfield Sea areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2015, 33(3): 75-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2015.03.011
[50] 卢芳. 胜利埕岛油田海洋石油勘探开发生态环境影响研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2010 LU Fang. Eco-environmental impact of Shengli Chengdao offshore oil exploration and development[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2010.
[51] 刘金虎, 宋骏杰, 曹亮, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物中重金属时空分布、污染来源及风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2):369-381 doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20140630002 LIU Jinhu, SONG Junjie, CAO Liang, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 369-381. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20140630002
[52] Huang W W, Zhang J. Effect of particle size on transition metal concentrations in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) and The Huanghe (Yellow) River, China [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 1990, 94(3): 187-207. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(90)90170-Y
[53] 石学法, 刘升发, 乔淑卿, 等. 中国东部近海沉积物地球化学: 分布特征、控制因素与古气候记录[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(5):883-894 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.05.001 SHI Xuefa, LIU Shengfa, QIAO Shuqing, et al. Geochemical Characteristics, controlling factor and record of paleoclimate in sediments from Eastern China Seas [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(5): 883-894. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.05.001
[54] Kang X M, Song J M, Yuan H M, et al. Speciation of heavy metals in different grain sizes of Jiaozhou Bay sediments: Bioavailability, ecological risk assessment and source analysis on a centennial timescale [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 143: 296-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.036
[55] Gao X L, Song J M, Li X G, et al. Sediment quality of the Bohai Sea and the northern Yellow Sea indicated by the results of acid-volatile sulfide and simultaneously extracted metals determinations [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 155: 111147. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111147
[56] Kumar A, Singhal R K, Rout S, et al. Spatial geochemical variation of major and trace elements in the marine sediments of Mumbai Harbor Bay [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 70(7): 3057-3066. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2366-3
[57] Hossen M A, Chowdhury A I H, Mullick M R A, et al. Heavy metal pollution status and health risk assessment vicinity to Barapukuria coal mine area of Bangladesh [J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2021, 16: 100469.
[58] 尹秀珍, 刘万洙, 蓝先洪, 等. 南黄海表层沉积物的碎屑矿物、地球化学特征及物源分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2007, 37(3):491-499 YIN Xiuzhen, LIU Wanzhu, LAN Xianhong, et al. Detrital minerals and geochemistry of the surface soft sediments and their provenance south Yellow Sea, China [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2007, 37(3): 491-499.
[59] 张文博. P、Ti的地球化学性质及其在深成岩中的含量与变化[J]. 世界有色金属, 2016(19):81-82 ZHANG Wenbo. The geochemical properties of phosphorus、titanium and its content in the plutonic rock and changes [J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2016(19): 81-82.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 马江波,冯纪慧,李刚,韩彦斌,张寰萌,郭岭. 安塞油田黑山梁区长6油层组单砂体构型分析及平面展布特征. 地质科学. 2024(04): 1018-1033 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王青,王佳,董杰,邹亮,王汝杰,解永健,徐美君,解小东,周晓雪. 胶州湾表层沉积物地球化学特征及控制因素. 海洋地质前沿. 2023(08): 8-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: