Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay and their sources and pollution assessment
-
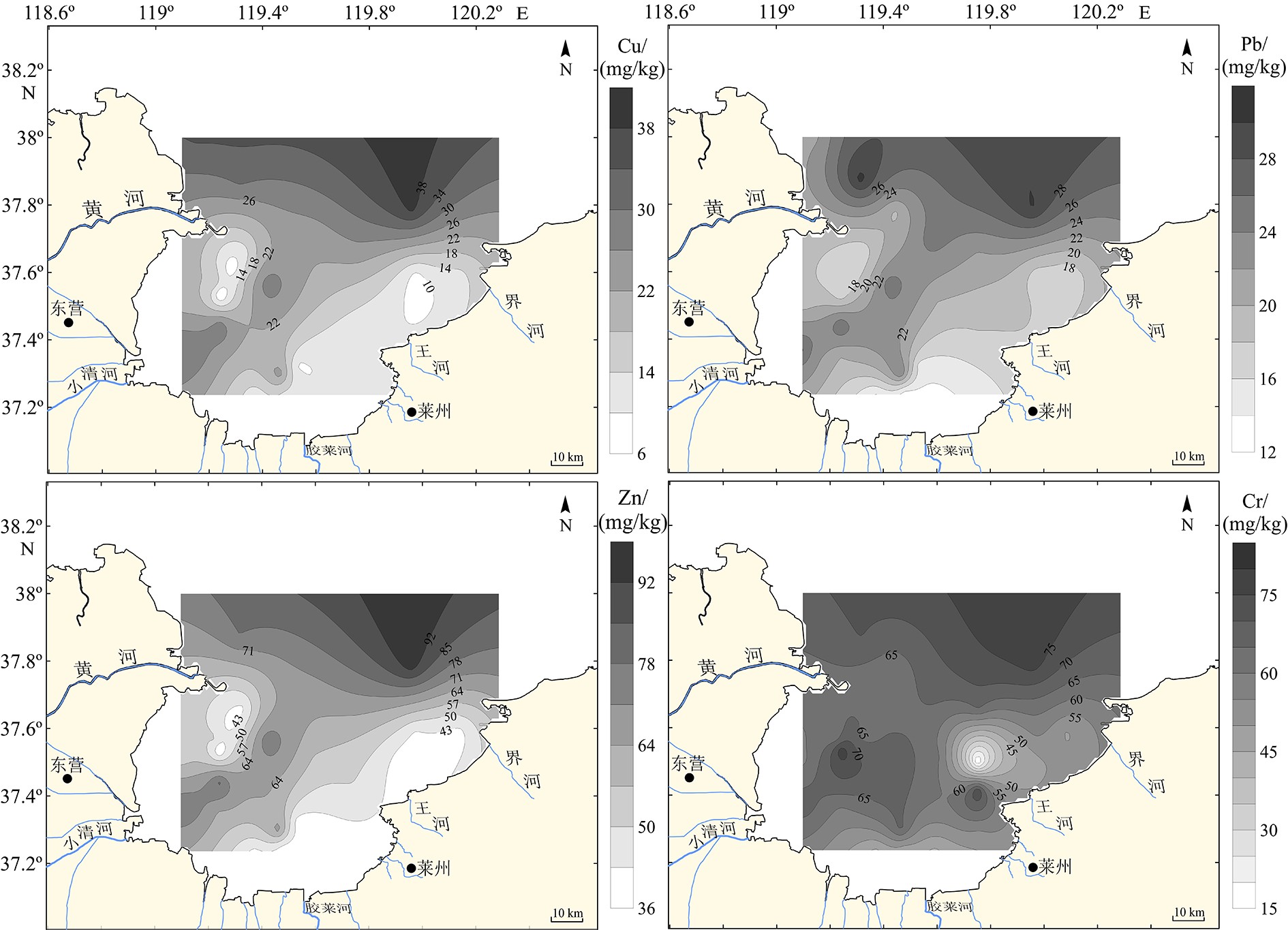
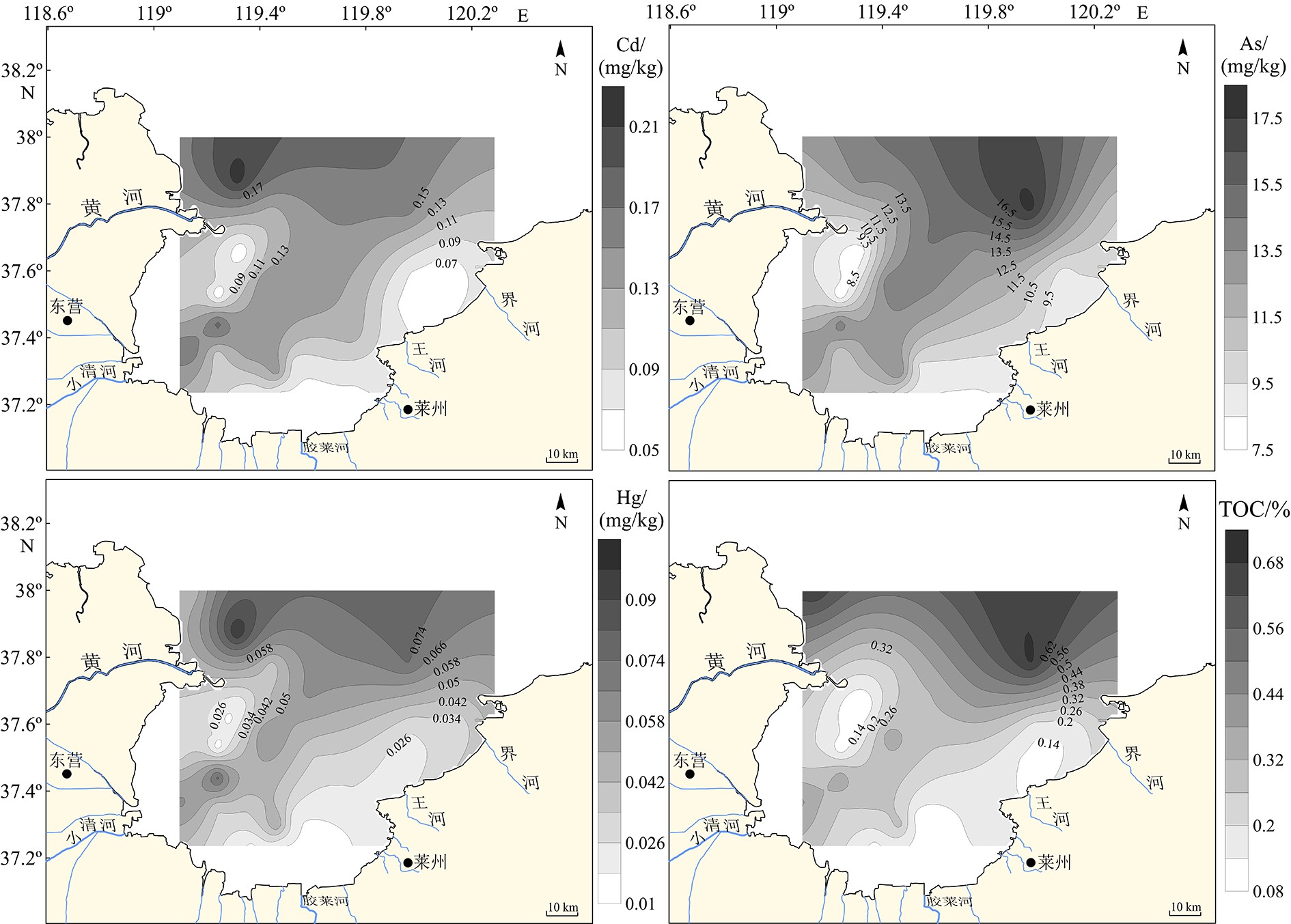
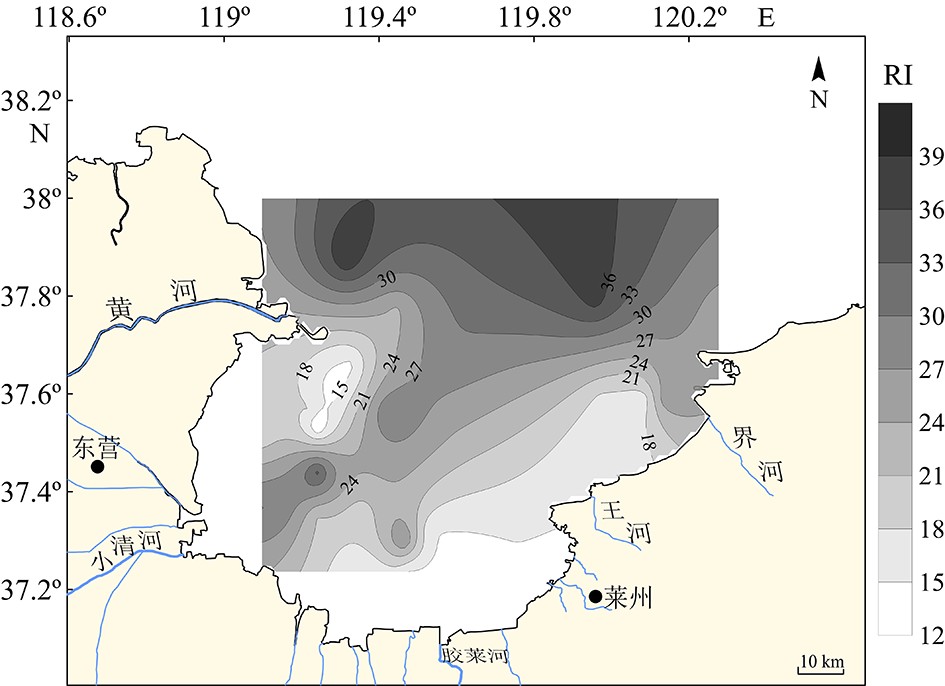
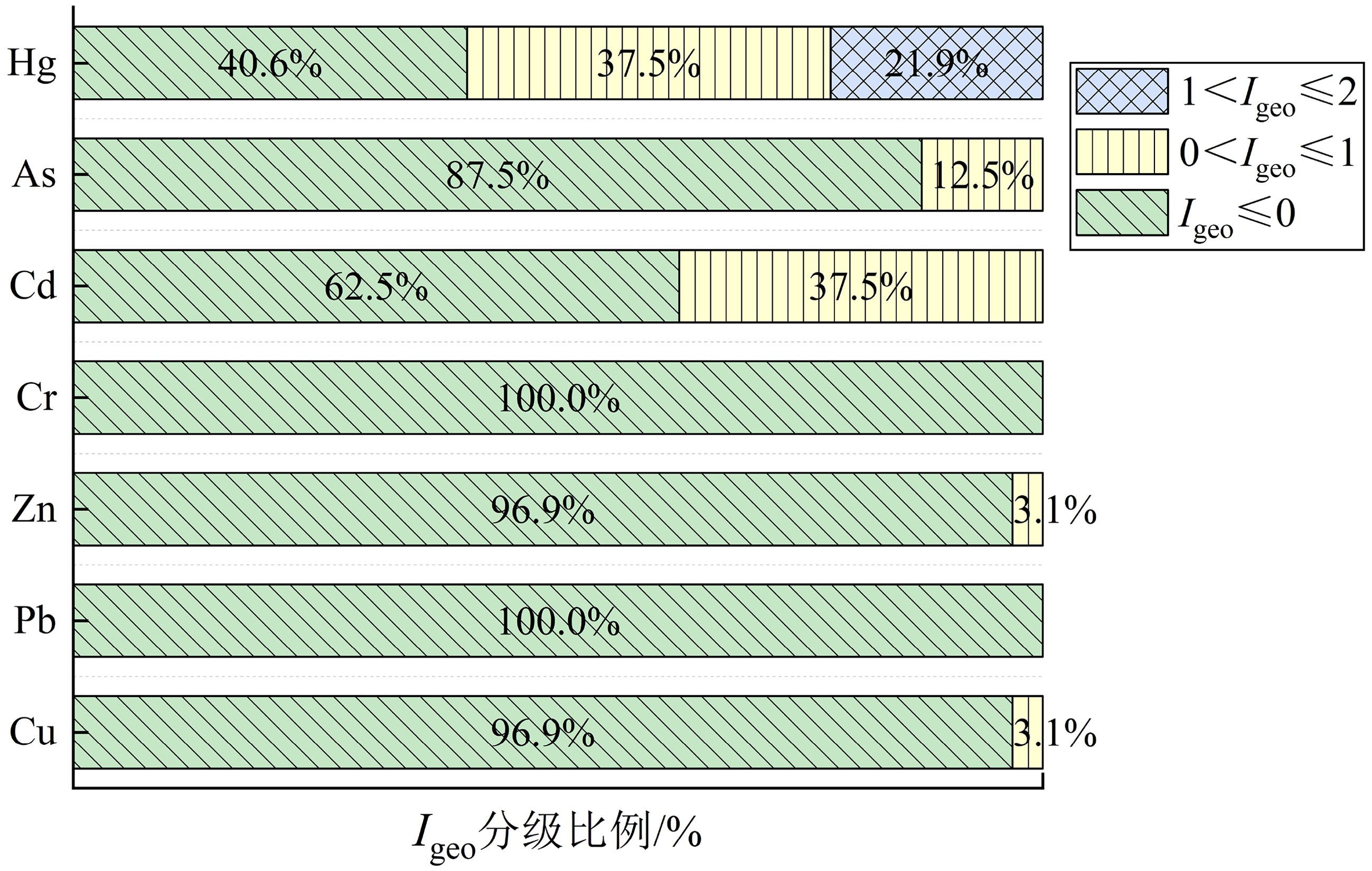
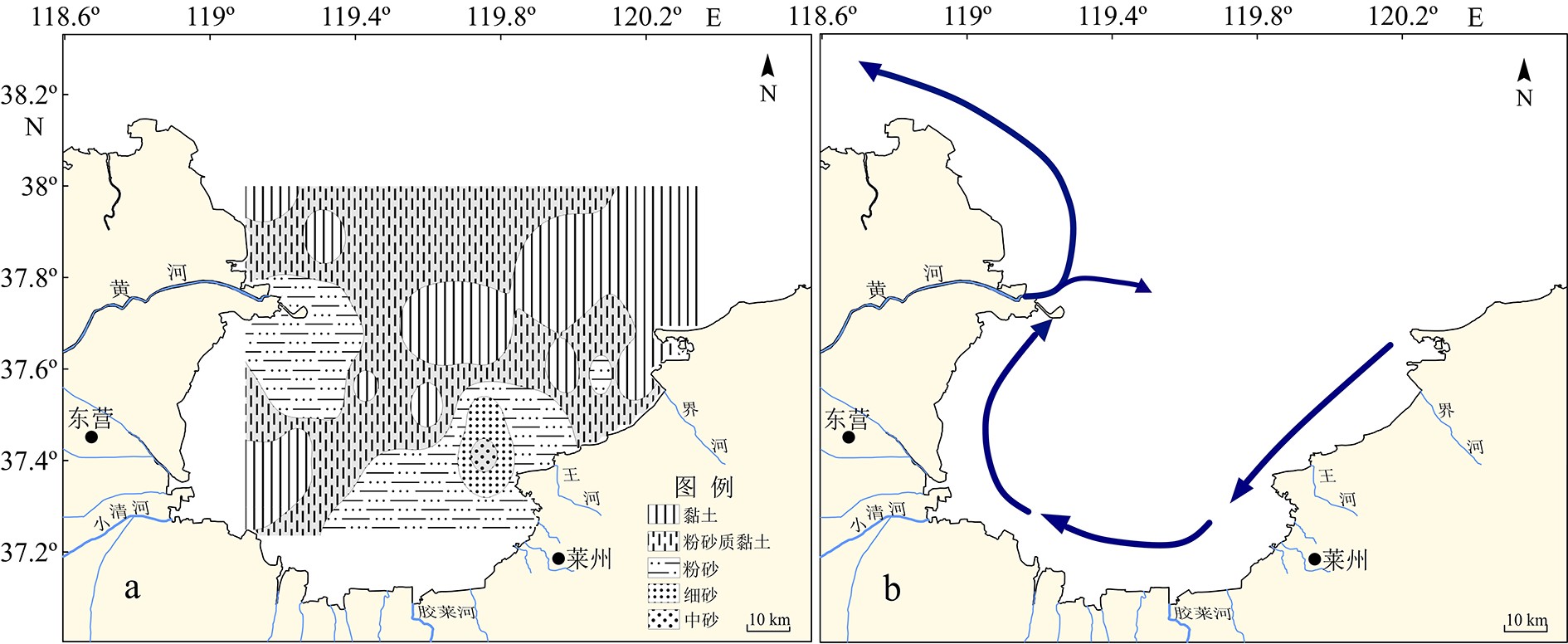
摘要: 基于2016年莱州湾32个站位表层沉积样的测试和分析并结合以往调研资料,探讨了Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Cd、As和Hg等7种重金属元素的含量、空间分布特征和相关性,并采用潜在生态风险法、地累积指数法和沉积物质量基准法对该区重金属污染状况进行了系统评价。结果表明,表层沉积物中重金属主要在黄河口以北、西南部小清河口及其东北部富集;Cr、Cd、Hg等与细颗粒沉积物相关,揭示重金属含量受沉积物粒度影响;而沉积物类型分布特征与莱州湾平均环流基本吻合,并与周围河口水动力和潮流显著相关。重金属污染评价结果表明:全部站位的重金属含量均低于PEL(可能效应水平),综合潜在生态风险为低风险;地累积指数评价结果表明:研究区约60%区域受到了Hg的污染,较多比例站位Cd(37.5%)和As(12.5%)显示为轻度污染。统计分析发现,Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、As和Hg之间存在较为显著的正相关关系,其中Cu、Pb和Zn主要受地壳自然风化过程控制,而Cu和Zn还受有机碳含量的影响;Cd和As推测与人类活动相关;Cr的含量主要来源于地壳自然风化过程,人类活动影响次之。研究结果表明黄河和小清河很有可能是莱州湾西部和西南部表层沉积物的主要来源,该结果与以往研究结果基本一致。Abstract: Surface sediment samples were collected in 2016 at 32 stations in Laizhou Bay. Studies are devoted to the concentrations, spatial distribution patterns and interrelations of seven heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As and Hg). Comparison is made with previous investigations. The pollution status is evaluated systematically with potential ecological risk index (PERI), geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and sediment quality guidelines (SQGs). Our results show that the heavy metals in the surface sediments are mainly concentrated in the north of the Yellow River estuary, Xiaoqing estuary (the southwest) and the northeast of Laizhou Bay. Cr, Cd and Hg are obviously related with fine grain sediments, indicating the control of sediment grain size over heavy metal contents. The distribution patterns of sediment types are mostly consistent with the mean circulation in Laizhou Bay, and are significantly related to the hydrodynamics of surrounding estuaries and tidal currents. Results of heavy metal pollution assessment suggest that heavy metal contents at all stations are lower than the possible effect level (PEL), and the integrated potential ecological risk is low. Geoaccumulation index suggests that about 60% of the study area are polluted by Hg, lightly polluted by Cd (37.5%) and As (12.5%). Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, As and Hg show significant positive correlations; Cu, Pb and Zn are mainly controlled by natural crust weathering process, while Cu and Zn are affected by TOC as well; Cd and As are presumed to be related to human activities; and Cr came mainly from the natural weathering process of the crust, in addition to some from human activities. Accordingly, the Yellow River and Xiaoqing River were likely to be the main sources of surface sediments in the west and southwest of Laizhou Bay, which is basically consistent with previous studies.
-
Keywords:
- heavy metals /
- surface sediments /
- spatial distribution /
- pollution assessment /
- source analysis /
- Laizhou Bay
-
中国自“十一五”以来大力发展致密砂岩气,已成为仅次于美国、加拿大的致密砂岩气生产大国[1-2]。以中西部盆地致密砂岩气勘探开发重要进展为基础,通过许多专家、学者[3-4]的努力,逐步建立起中国的致密砂岩气成藏理论。
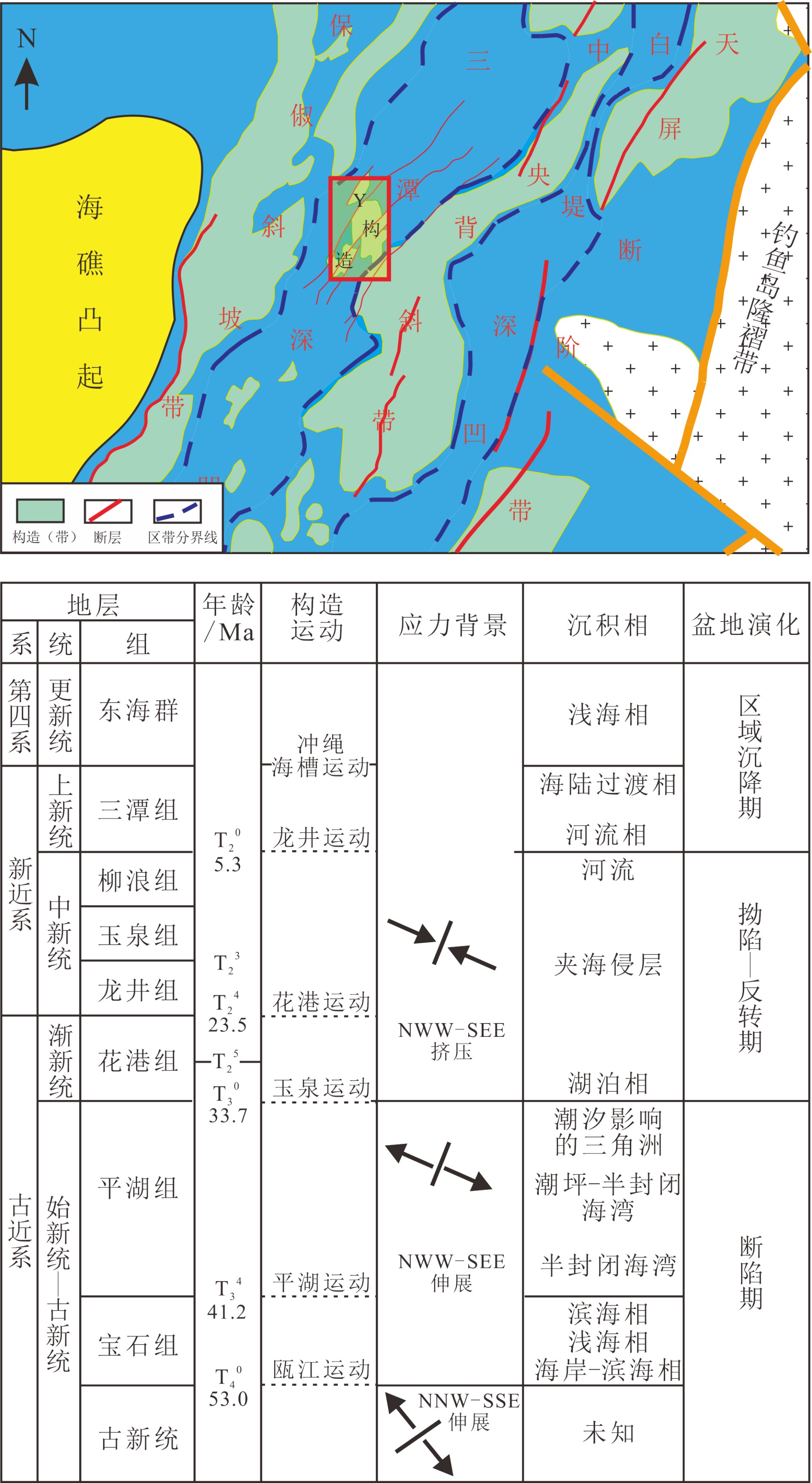
西湖凹陷是东海陆架盆地油气勘探开发的主战场,已实现常规油气的商业开发。近年来,在深层和非常规领域获得了重大突破,呈现常规、致密气并存的局面[5],非常规致密气资源正在成为西湖凹陷油气勘探开发的现实与接替领域。古近系花港组是西湖凹陷勘探的重点层位,也是近年来致密砂岩研究的热点。但研究对象主要为花港组中下部的致密层段,研究内容限于储层致密化成因[6-9]、储层致密化与油气充注时序关系[10-13]以及致密砂岩气藏形成条件[14-17]等方面,基于花港组上部常规气层和中下部致密气层的整体研究鲜有发表,关于致密气藏控制因素的研究尚未涉及。本文以西湖凹陷三潭深凹Y构造花港组为研究对象,开展上部常规砂岩和中下部致密砂岩完整序列的气藏特征及成藏主控因素研究,为东海致密砂岩气的勘探提供理论指导。
1. 地质背景
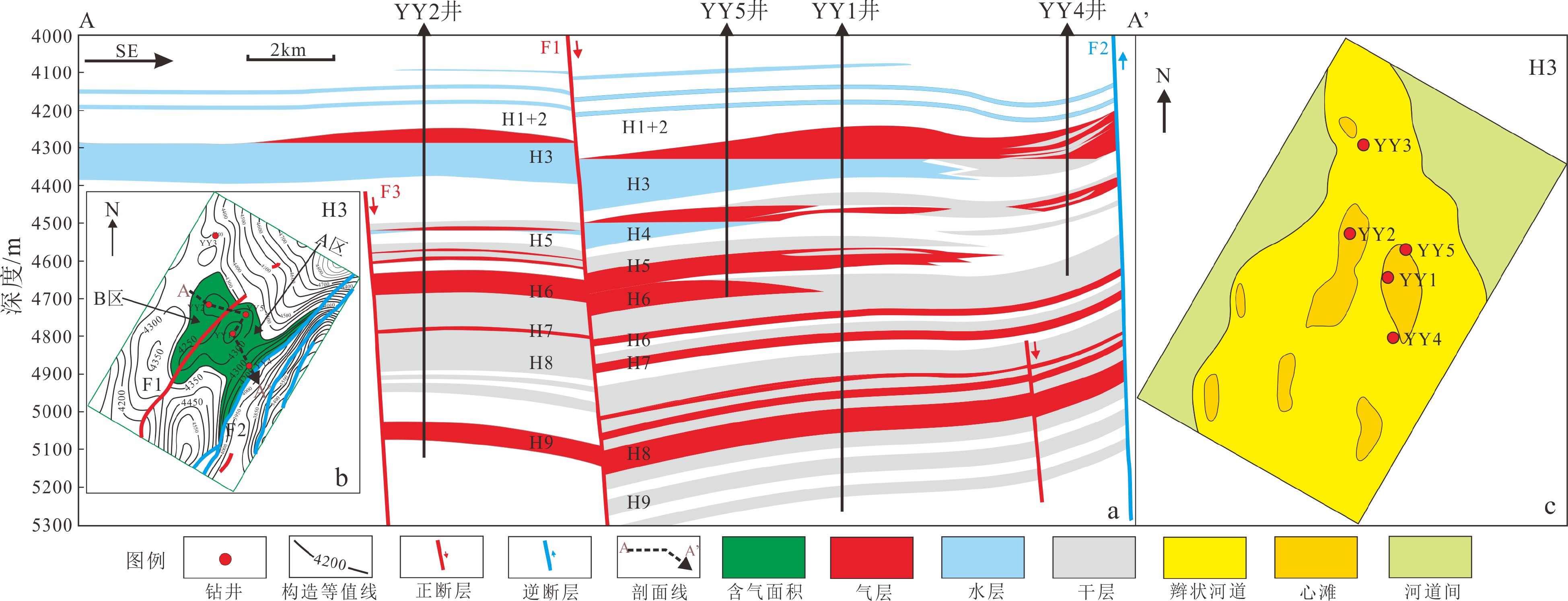
西湖凹陷东邻钓鱼岛隆褶带,西接海礁等凸起,呈NNE向展布,面积约5.9×104 km2,具有“东西分带、南北分块”的构造特征[5]。自西向东可划分为保俶斜坡带、三潭深凹、中央背斜带、白堤深凹及天屏断阶带等5个次级构造单元。西湖凹陷在演化阶段上大体经历了断陷、拗陷-反转和区域沉降3期,其中始新统宝石组、平湖组为断陷期沉积地层,渐新统花港组、中新统为拗陷-反转期沉积地层,上新统三潭组及第四系东海群为区域沉降期地层[18](图1)。现有勘探和研究成果[16-17]揭示,始新统平湖组煤系地层是西湖凹陷主力供烃层系。研究区所在的三潭深凹是平湖组烃源岩系的沉积中心和生烃中心,拥有得天独厚的烃源岩条件,也是西湖凹陷油气勘探开发的重点区域之一[5]。渐新统花港组以发育三角洲及滨浅湖沉积为主要特征,沉积厚度为1000~1800 m,纵向上发育多套储盖组合,与始新统平湖组烃源岩构成“下生上储”配置关系,是三潭深凹主力产层之一。中始新世平湖运动、始新世末玉泉运动、渐新世末花港运动和中新世末龙井运动期是西湖凹陷成盆过程转变的关键期,应力背景分别为伸展方向转变、伸展结束、挤压开始和挤压显著增强[19]。断陷期以拉张作用为主,发育NE、NNE向正断层;反转期以水平挤压作用为主,发育压性断裂。龙井运动导致了西湖中央背斜带的形成,对西湖凹陷油气藏的形成起到了决定性的作用[10-13]。研究区Y构造位于三潭深凹中北部,东侧与中央背斜带相接,目前有钻井5口,揭示花港组H1-H9地层(根据反射界面将花港组自上而下分为12个小层,其中H1-H5为花港组上段(T24-T25),H6-H12为花港组下段(T25-T30)[10])。上部的H1-H2以泥岩为主,为区域盖层发育段;H3-H9为砂岩储层发育段,储层埋深主要为4200~5200 m。
2. 气藏基本地质特征
2.1 构造特征
Y构造为继承性发育的NE-SW向低幅背斜构造,具“凹中隆”背景,面积约120~230 km2(图1,图2,表1)。构造主体受断陷期和反转期断裂影响,成为A、B两块,共有4口钻井,自西向东依次为YY2井、YY5井、YY1井、YY4井。A区为F1、F2断层夹持的断背斜构造,有北、南、东三个局部高点,东侧受反转期挤压作用影响,地层略有抬升。YY1井位于A区北高点,YY5井位于该高点翼部,YY4井位于东高点。B区下部由F1、F3断层夹持,上部仅受F1控制,包括南北两个高点,YY2井位于北高点。
表 1 研究区断裂特征Table 1. Fault features of Y structure断层 性质 期次 断距/m 断裂产状 区内延伸
长度/km断开
层位T20 T23 T24 T25 T30 走向 倾向 F1 正断层 断陷期-反转期 25~50 10~25 25~75 25~150 NE SE 20.8~49.6 T23-T34 F2 逆断层 反转期 25~150 50~175 75~150 75~125 NE SE 46.9~53.7 T23-T30 F3 正断层 断陷期 10~25 25~75 NNE SEE 7.3~41.2 T25-T34 2.2 储层特征
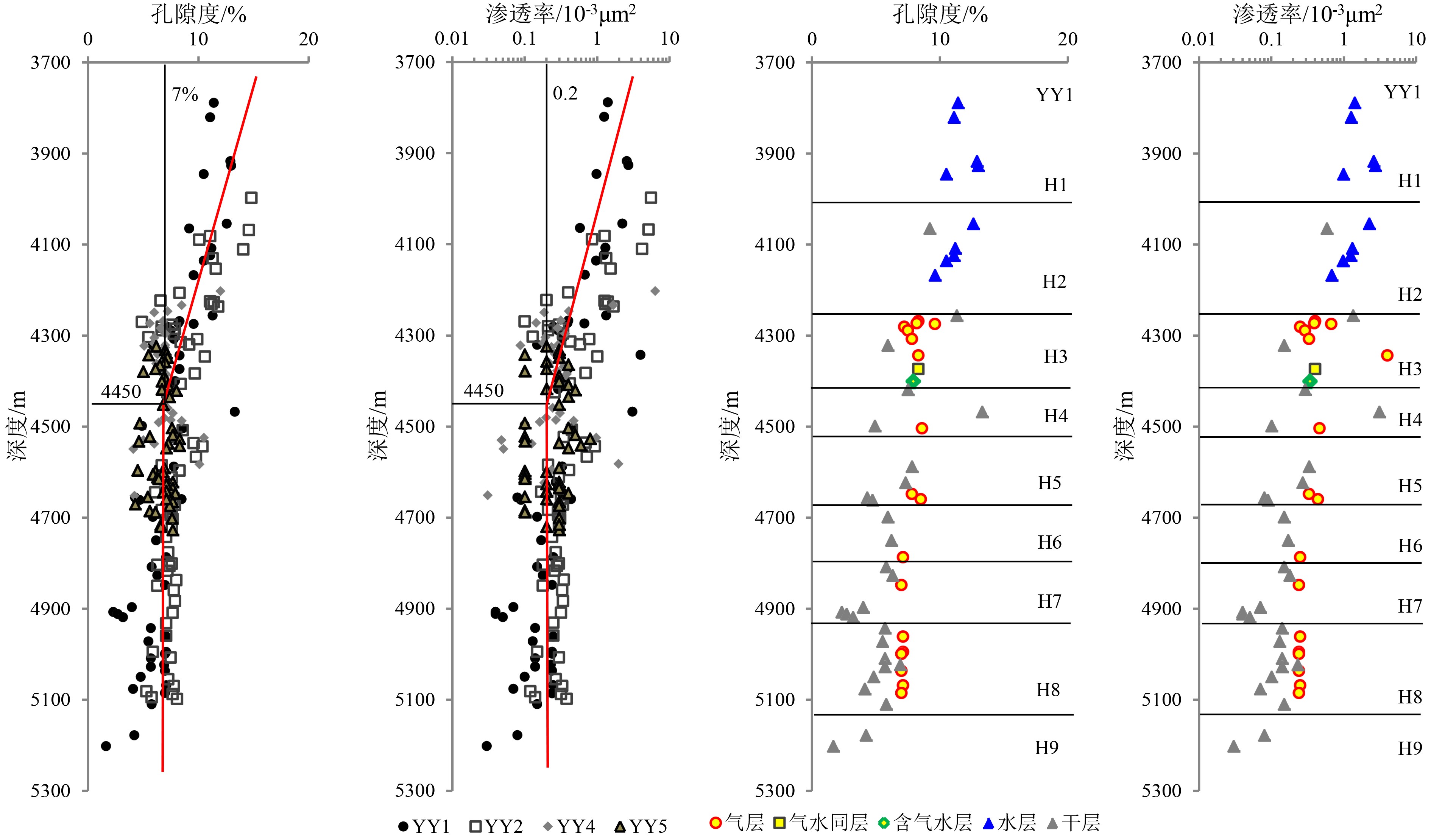
研究区花港组储集层主要分布在H3-H9砂层组,为辫状河三角洲河道沉积[6](图2)。孔隙度主要分布于1.66%~14.8%,渗透率分布范围为(0.03~6.29)×10−3 μm2,为低孔-特低孔、特低渗储层。根据储层物性纵向演化特征,以4450 m深度为界(H4顶部附近),可将花港组储层划分为上、下两段,含气性也存在明显差异,这与储层物性变化明显相关(图3)。上段以H3为主,含少量H1、H2储层,其物性随埋深增加大致呈线性减小的变化趋势,表明该段储层物性主要受压实作用控制。下段的H4-H9储层,深度对其孔渗的影响减弱,储层物性主要受差异成岩作用控制[6-7];其中,河道底部的含砾中—粗砂岩与心滩的中—细砂岩物性相对较好;该段储层非均质性较强,并呈现整体致密、甜点发育的特征。
2.2.1 压实作用段
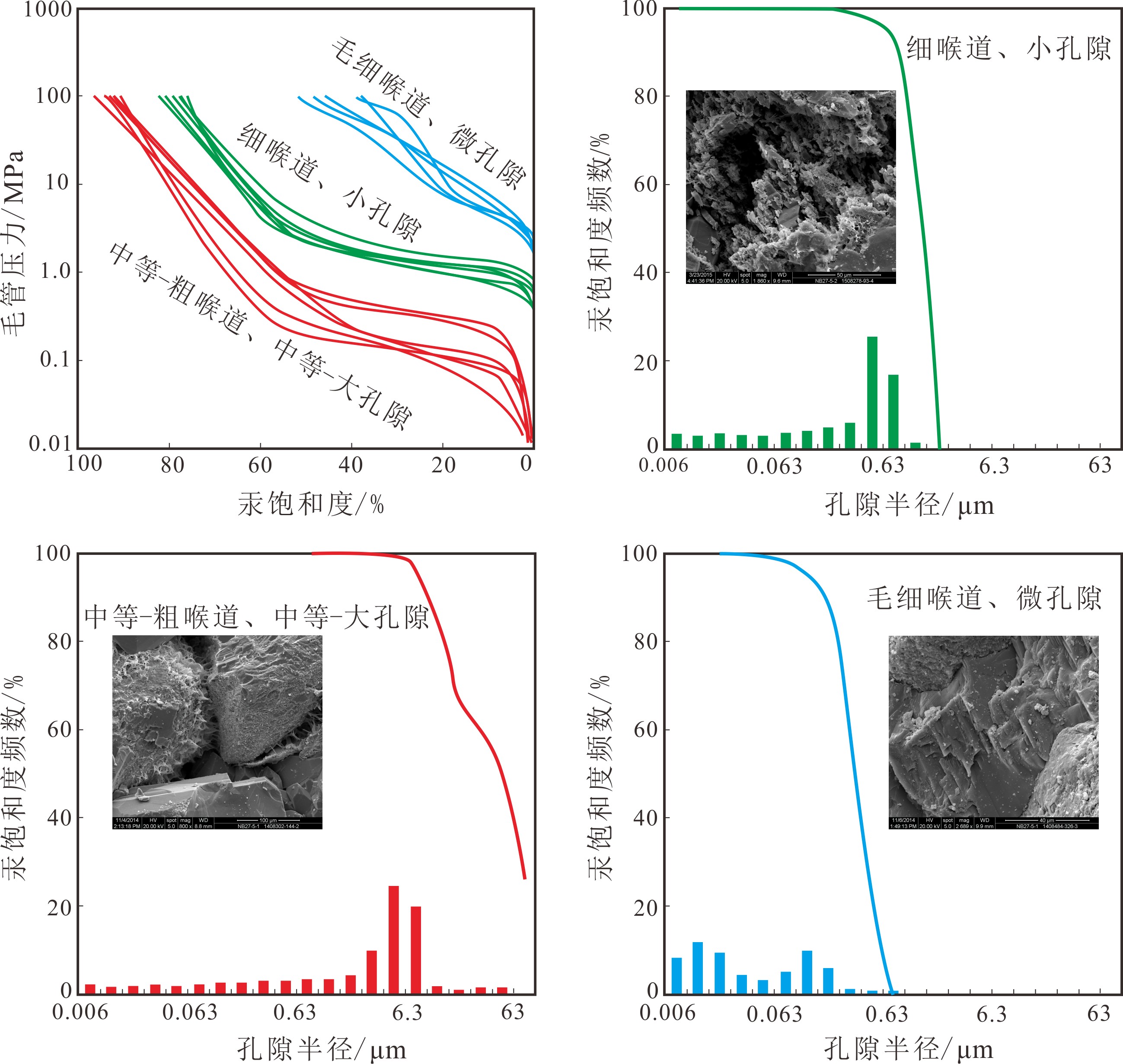
该段包括H1-H3砂层组,埋深3700~4450 m;孔隙度分布在4.9%~14.8%,其中>7%的占比61.2%;渗透率分布在(0.09~6.29)×10−3 μm2,其中>0.2×10−3 μm2的占比82.4%;底部的H3储层平均孔隙度7.16%,平均渗透率0.41×10−3 μm2。该段整体处于中成岩A成岩演化阶段[6],以中等—粗喉道、中等—大孔隙发育为特征,平均孔喉半径一般大于2 μm,大于0.1 μm孔喉体积百分数大于70%(图4),为常规储层发育段。
2.2.2 成岩作用段
研究区钻井揭示该段H4-H9砂层组,埋深4450~5200 m;孔隙度分布在1.66%~13.3%,其中>7%的占比52.5%,平均孔隙度仅6.8%;渗透率分布在(0.03~3.07)×10−3 μm2,其中>0.2×10−3 μm2的占比58.2%,平均渗透率仅0.29×10−3 μm2。该段整体进入中成岩B成岩演化阶段[6],以细喉道小孔隙和毛细喉道微孔隙为主,其中毛细喉道微孔隙砂岩的平均孔喉半径一般小于0.1 μm(图4),为致密储层发育段。
2.3 气藏源储关系
研究区渐新统花港组具“下生上储”源储配置关系,以断裂沟通始新统平湖组中下部主要烃源岩聚集成藏(图2,表1)。断陷期发育的正断层(F1、F3等)向下断穿平湖组底部(T34),是油气向上运移的主要通道;其中F1断层持续活动至反转期,为本区主要的油源断层;F2逆断层形成于反转期,下部仅断至平湖组顶部(T30),上部与储层上倾方向接触,为控圈断层。
致密砂岩气藏存在两种源储组合关系[4,20],一是临近有效烃源岩的叠覆近邻组合,二是与烃源岩垂向分隔的叠覆跨越组合。叠覆近邻组合,源岩生烃超压为近距离成藏的主要动力;研究区花港组下部致密段属于叠覆跨越组合,成藏动力主要是浮力,其次为断层等传导后的源储压力差、分子扩散力等[21]。
2.4 气藏分布特征
Y构造天然气藏中烃类含量为92.9%~99.2%,平均95.9%,另含少量CO2、N2非烃类气体;天然气干燥系数94.3%~95.7%,以干气气藏为主。
2.4.1 常规气藏
压实作用段整体呈现气层、水层伴生的流体分布关系,气水关系正常,具自然产能,为常规气藏发育段(图2,图3)。该段上部的H1、H2储层厚度小于10 m,以水层为主,不发育气层。H3为该段主力气层,其物性较好且分布稳定;上部为气层,中部为气水同层,下部为水层,正常的气水过渡特征;A区的YY1、YY5井和B区均具有统一的气水界面和气水过渡带;A区北高点的YY1井测试获得高产,瞬时最大产气超过20×104 m3/d[5];A区东侧的YY4井该层未钻遇心滩,周边发育少量干层。
2.4.2 致密气藏
成岩作用段整体呈气层、干层间互发育的特征,无明显气水界面(图2,图3);气层含气饱和度整体偏低,为40%~59.8%,测试产量低或无自然产能,为致密气藏发育段。该段顶部YY5井的H4和YY2井H5储层成岩作用强度较上覆压实作用段明显增强,具压实作用-成岩作用过渡段性质;其下部的中细砂岩分选较好,溶蚀铸膜孔发育,发育气层,亦表现为浮力驱动的常规气藏[22]气水界面和气水过渡特征。
3. 储层致密化与油气充注关系
从储层致密化与油气充注时序关系角度出发,可将致密砂岩气藏划分为先成藏后致密、先致密后成藏等几种类型;先成藏后致密型可与常规气藏相类比,而先致密后成藏型气藏的形成和分布与常规气藏明显不同[3-4]。
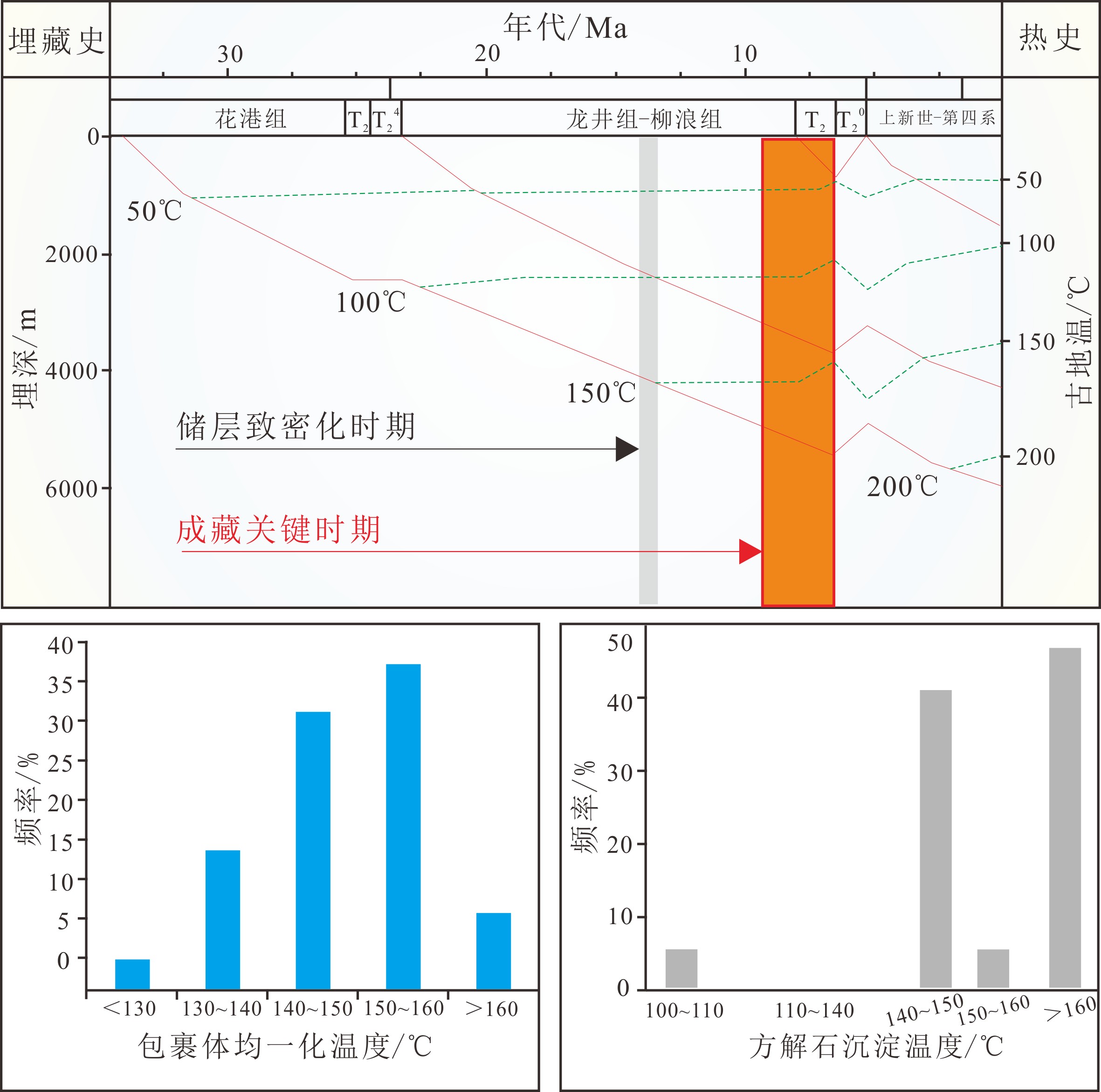
西湖凹陷花港组砂岩储层经历了复杂和强烈的成岩变化,演化程度深;主要成岩作用类型有压实压溶作用、胶结充填作用和溶解作用;主要经历同生阶段、早成岩阶段(A、B期)和中成岩阶段(A、B期)共3阶段5期次的成岩演化过程;在中成岩阶段,伴随第Ⅱ期硅质胶结物和晚期碳酸盐胶结物的沉淀以及机械压实作用持续增强,研究区花港组孔隙度下降至8%~10%以下,储层趋于致密化[6-7,10]。因此,第Ⅱ期硅质胶结物和晚期碳酸盐胶结物开始大量形成的时间即为研究区花港组储层致密化时间。
研究区花港组含烃盐水包裹体丰度普遍较低(GOI<1%),主要为油气大规模充注期之前沉淀的方解石胶结物[10];其均一化温度数据统计表明,硅质胶结物沉淀温度主要分布在140~160 ℃。利用氧同位素数据并由Narthrop[23]公式进行温度计算,确定花港组碳酸盐胶结物沉淀温度主要分布在140~150 ℃和>160 ℃之间,平均值162 ℃。将硅质和碳酸盐胶结物沉淀温度与研究区埋藏史、热史模拟结果相结合,确定研究区花港组储层致密化时间为龙井组-柳浪组沉积中晚期;而已有的成藏年代研究成果[10-17]表明,花港组储层最主要的油气充注期时间较晚,为7~0 Ma;因此,研究区花港组天然气的规模成藏阶段基本在储层致密化之后,致密砂岩气藏属于先致密后成藏类型(图5)。
4. 成藏主控因素
4.1 常规气藏
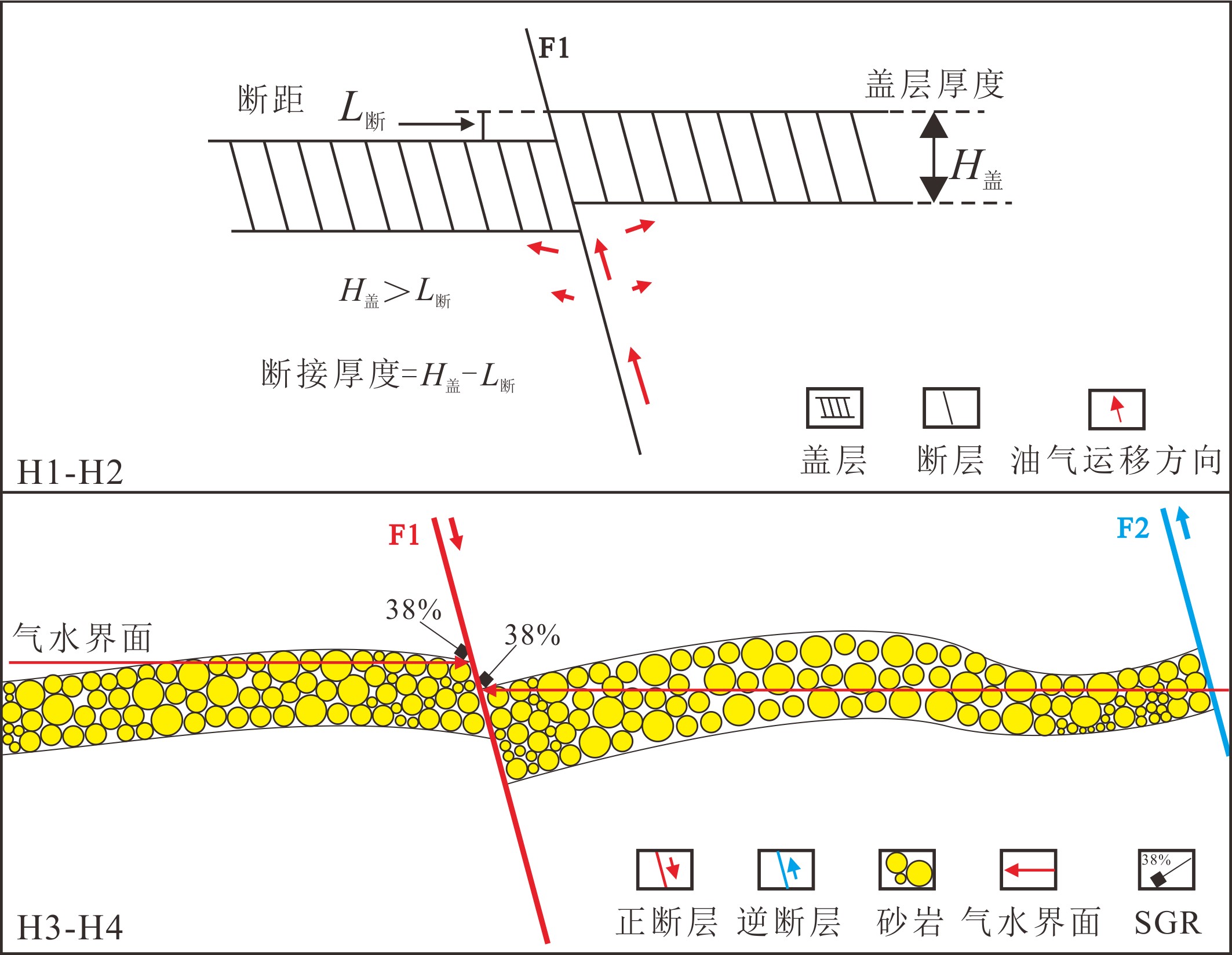
区域盖层在油气聚集和分布中起着重要作用,油气在沿着断裂向上运移过程中,其向上运移的距离和层位除受断裂本身向上延伸距离影响外,还要受到盖层被断裂破坏程度的影响;按照盖层厚度和断裂断距的相对大小,可将断盖配置对沿断裂运移油气的封闭作用分为3级模式[24]。
研究区H1-H4为常规气藏主要发育段,其中H1、H2位于区域盖层内(图2,图6)。H1、H2泥岩盖层厚度分别为101.1~147.8 m和87.9~99.5 m,油源断层F1在区域盖层段断距仅10~25 m,故H1、H2盖层的断接厚度(断接厚度=盖层厚度-断距)分别达到75~140 m和65~90 m;同时盖层段断裂密度仅1条/60 km2。盖层段断接厚度大、断裂密度小,其完整性好,垂向阻烃作用强[25]。下部油气难以穿越盖层向H1、H2内的储层充注,故H1、H2以水层为主,不发育气层,油气主要在盖层之下的地层中富集。
H3、H4(也包括YY2井H5上部)紧靠区域盖层,砂岩含量平均高达52.7%,是常规气藏聚集的优势层段(图2,图6)。A区H3、H4为F1、F2断层夹持的断背斜构造,气藏最终的规模受两条断层侧向封闭性控制。东侧边界断层F2为逆断层,同时YY4井揭示该区域砂岩分选和物性明显变差;断层的压性和砂岩致密联合作用,确保东侧边界断层具备较强的侧向封堵能力。西侧F1断层在该段地层断距<50 m,计算该段F1的断层泥比率(SGR)仅20%~40%(凹陷经验值:SGR>62%为有封堵能力),且断层两侧砂砂对接概率高,故A区H3、H4气藏仅局限分布在断背斜自圈范围内。B区H3处F1断层SGR<5%,H5处F1、F3断层的SGR仅5%和10%左右,断层侧向封堵能力差造成B区H3、H5气藏同样局限分布。
4.2 致密气藏
H5-H9是致密气藏集中发育段,属于与烃源岩垂向分隔的叠覆跨越源储组合关系;成藏过程主要为借助断层的二次运聚过程,成藏动力主要是浮力,其次为断层传导后的源储压力差;浮力大小取决于连续单体气柱高度,连续气柱高度越大,浮力越大,天然气可进入储层的孔喉半径越小,反之仅能进入相对大孔喉中;该类气藏储层总体处于气水过渡带之内,无明显的气水界面,处于不同构造位置处不同物性的储层具有不同的含气特征[20-21,26]。
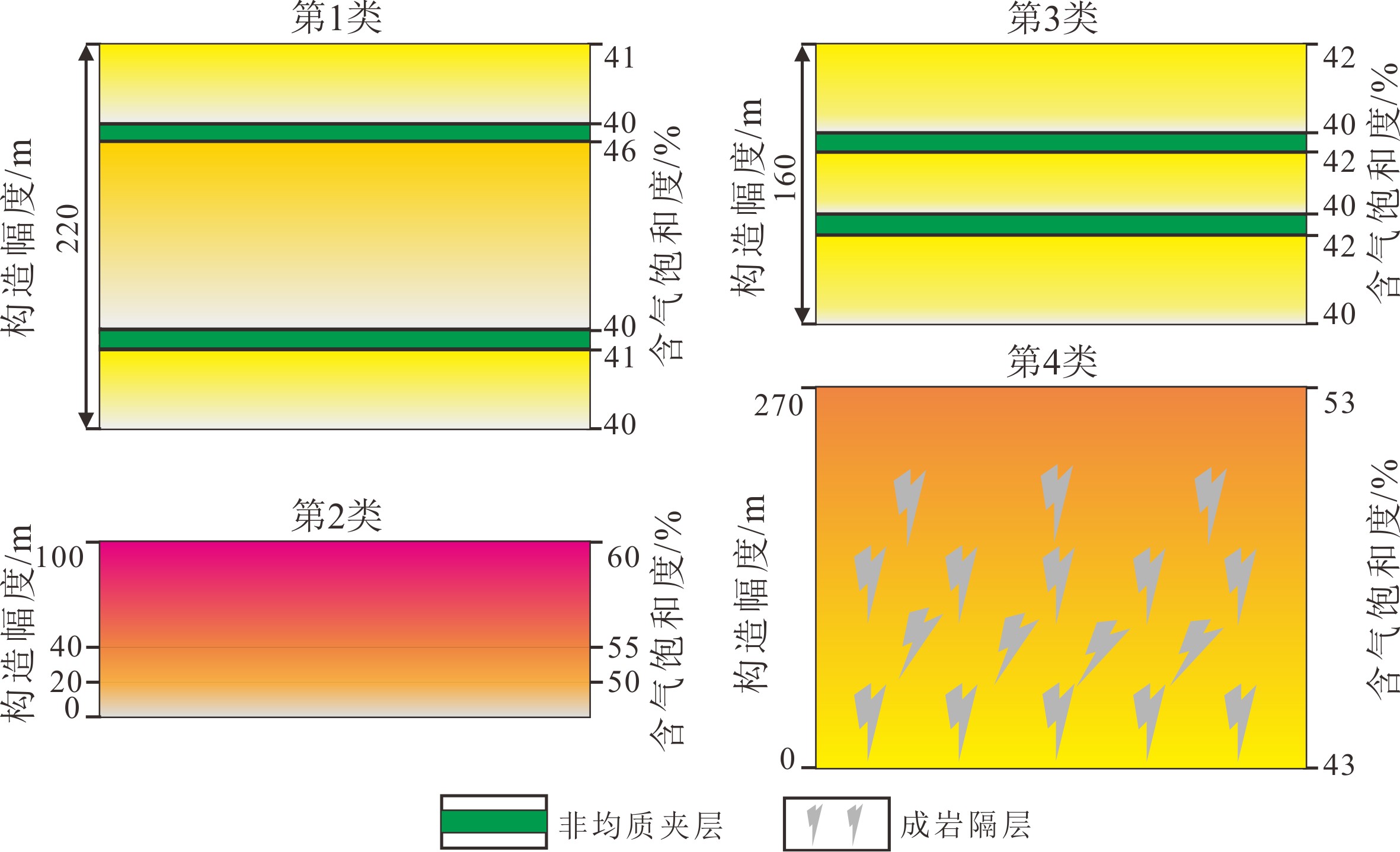
综合孔隙度、渗透率、储层非均质性及成岩特征,H5-H9气层储层大致可以划分为4种类型(表2,图2,图7)。1类:储层非均质性较强,孔隙度7.0%~7.1%,渗透率(0.24~0.25)×10−3 μm2,代表层位为YY1井的H6-H8;2类:孔隙度7.6%~8.0%,渗透率(0.30~0.35)×10−3 μm2,代表层位为YY2井的H5-H7;3类:储层孔隙度和渗透率与第2类相当,但非均质性较强,代表层位为YY1井的H5;4类:储层孔隙度和渗透率与第2类相当,但成岩作用强度明显增加,代表层位为YY2井的H9。
表 2 研究区花港组致密气藏物性、幅度和含气饱和度特征Table 2. Characteristics of physical properties, structural amplitude and gas saturation for the tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Huagang Formation of the study area构造单元 井名 层位 序号 深度/m 幅度/m 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 含气饱和度/% A区 YY1 H5 1 4648.3 160 7.8 0.33 40.5 2 4660.1 8.5 0.44 42 均值 8.2 0.39 41.3 YY1 H6 1 4787.3 150 7.1 0.25 40 YY1 H7 1 4848.8 170 7 0.24 49 YY1 H8 1 4961.7 220 7.1 0.25 40 2 4995.3 7.1 0.24 40 3 4999.4 7 0.24 40 4 5036.7 7 0.24 46 5 5068.9 7.1 0.25 41.4 6 5086 7 0.24 40 均值 7.1 0.24 41.2 B区 YY2 H5 1 4611.8 20 7.6 0.3 49.7 YY2 H6 1 4659.1 40 7.8 0.32 55 2 4672.5 7.9 0.34 50 3 4679.5 7.6 0.31 48.9 4 4703.6 7.7 0.31 50.2 均值 7.8 0.32 51 YY2 H7 1 4801.6 100 7.6 0.3 59.8 2 4806.8 7.4 0.28 49.6 3 4837.3 8 0.35 44.6 均值 7.7 0.31 51.3
YY2H9 1 5070.8 270 7.8 0.33 51.8 2 5088.6 7.7 0.32 43.9 3 5099.2 8.1 0.38 52.9 均值 7.9 0.34 49.5 根据研究区致密储层性质,应用毛细管力与水柱上升的关系[26],计算得到要突破0.1 μm孔喉半径所需气柱高度为53.35 m;核磁共振测试结果显示,研究区物性较好的第2类致密储层可动流体饱和度达到60%所需气柱高度至少为240 m。研究区H5-H9构造幅度仅20~270 m,使得致密气藏储层总体处于气水过渡带之内,含气饱和度整体偏低,仅40%~59.8%,不同部位含气性受构造幅度和储层物性共同控制(表2,图2,图7)。
A区YY1井:H5物性明显好于H8,但H5非均质程度更高且H8幅度超H5达60 m,最终两套气层含气饱和度相当,体现出物性和幅度共同作用控制致密储层含气性的特征;物性和幅度均处于中间水平的H7含气饱和度却能达到49%,这可能与H7非均质程度相对较低、更易形成较大连续气柱高度有关。
B区YY2井:各气层物性相当,但层间幅度差异明显,由H9的270 m向上降低到H5的20 m;在此背景下,构造幅度对含气饱和度的控制作用增强,H5-H7含气饱和度随幅度增加呈上升的趋势。在埋深超过5000 m的H9中,碳酸盐岩胶结,石英次生加大,黏土矿物的伊利石化和绿泥石化作用明显增强[6],加剧孔喉堵塞;但其构造幅度高达270 m,在浮力、源储压差和分子扩散力等综合作用下,高部位物性甜点含气饱和度仍可达50%以上。
从Y构造整体来看,A区相对更靠近东侧沉积中心,其储层非均质程度明显高于 B区,导致A区储层物性整体相较于B区变差,孔隙度和渗透率的差值分别达约1%和0.1×10−3 μm2;在物性明显差异的情况下,构造幅度对含气性的影响减弱,B区含气性整体好于A区。
5. 结论
(1)研究区为“凹中隆”背景下的低幅断背斜构造;主要目的层花港组上部以压实作用为主导,发育常规储层;中下部受差异成岩作用控制,呈现“整体致密、甜点发育”的致密储层特征。
(2)上部常规气藏发育段整体呈现气层、水层伴生的流体分布关系,气水关系正常;中下部致密气藏段具叠覆跨越源储组合关系,整体呈气层、干层间互发育的特征,无明显气水界面,含气饱和度低。
(3)受断盖配置对沿断裂运移油气的封闭作用影响,常规气藏主要在盖层之下的储层中分布,断层侧向封堵能力差造成油气仅局限分布于断背斜顶部;致密砂岩气藏属先致密后成藏类型,不同部位含气性受构造幅度和储层物性共同控制。
-
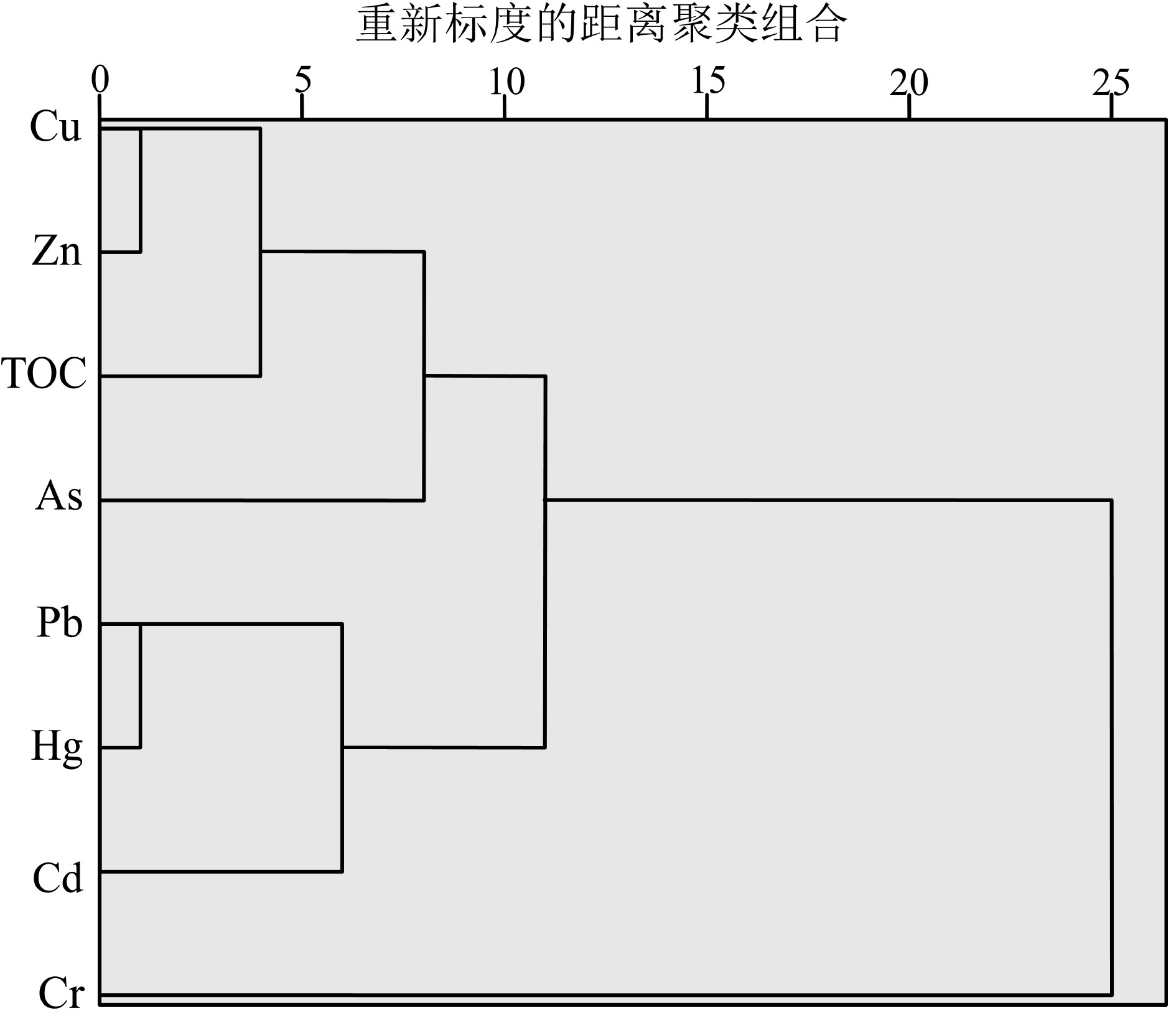
表 1 莱州湾表层沉积物中重金属的含量及相应统计参数
Table 1 Concentrations of heavy metals in surface sediments of Laizhou Bay
mg/kg 海域 Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg 参考文献 莱州湾 范围 5.8~39 12.7~30.7 16.6~95.8 14.7~78 0.051~0.22 7.4~26 0.0068~0.098 本研究 均值 19.06 20.30 55.98 60.10 0.11 11.72 0.038 标准差 8.74 4.60 16.25 9.05 0.04 2.45 0.021 变异系数 45% 23% 28% 15% 40% 22% 54% 莱州湾南部 均值 13.35 15.83 43.63 51.75 0.08 10.04 0.023 莱州湾西南部 24.81 22.76 67.87 63.54 0.14 11.98 0.051 莱州湾东北部 11.02 17.56 42.88 55.84 0.07 10.11 0.027 莱州湾西部 12.06 17.24 44.90 66.02 0.07 8.56 0.022 莱州湾湾口 27.80 24.28 72.76 67.11 0.15 13.69 0.057 辽东湾 均值 18.81 20.55 52.94 34.15 0.35 5.84 0.09 [33] 渤海湾 28.02 24.34 87.63 72.36 0.25 11.81 0.03 [16] 渤海底质沉积物 19.99 24.03 66.15 57.95 0.20 9.18 0.04 [16] 中国海域 15 20 65 60 0.065 7.7 0.025 [34] 表 2 莱州湾重金属潜在生态风险指数
Table 2 Potential ecological risk coefficients of heavy metals in Laizhou Bay
统计量 ErCu ErPb ErZn ErCr ErCd ErAs ErHg RI 最大值 3.90 2.19 0.55 1.73 6.60 11.93 15.68 38.78 最小值 0.58 0.91 0.21 0.98 1.53 4.93 2.08 12.26 均值 1.94 1.44 0.33 1.37 3.33 7.51 6.28 22.19 标准差 0.874 0.328 0.093 0.201 1.315 1.632 3.389 7.310 表 3 莱州湾表层沉积物的地累积指数
Table 3 Geoaccumulation index of surface sediments in Laizhou Bay
参数 Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg Igeo 最大值 0.115 −0.334 0.008 −0.344 0.804 0.360 1.782 最小值 −2.634 −1.608 −1.384 −1.173 −1.305 −0.915 −1.132 均值 −1.054 −0.973 −0.792 −0.703 −0.297 −0.340 0.259 表 4 莱州湾重金属基准阈值及不同浓度范围内样品的数量和百分比
Table 4 Reference threshold of heavy metals in Laizhou Bay and the number and percentage of samples in different concentration ranges
Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg TEL/(mg/kg) 18.7 30.2 124 52.3 0.68 7.24 0.13 PEL/(mg/kg) 108 112 271 160 4.21 41.6 0.7 <TEL/个 15(47%) 31(97%) 32(100%) 6(19%) 32(100%) 0(0%) 32(100%) TEL—PEL/个 17(53%) 1(3%) 0(0%) 26(81%) 0(0%) 32(100%) 0(0%) ≥PEL/个 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 表 5 7种重金属与氧化物之间的Pearson相关系数
Table 5 Pearson’s correlation coefficients among heavy metals and TOC
TOC Al2O3 TFe2O3 Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg TOC 1 Al2O3 0.86 1 TFe2O3 0.88 0.95 1 Cu 0.92 0.97 0.95 1 Pb 0.79 0.89 0.91 0.87 1 Zn 0.90 0.98 0.98 0.97 0.92 1 Cr 0.54 0.56 0.71 0.51* 0.66 0.63 1 Cd 0.77 0.90 0.91 0.87 0.87 0.89 0.61 1 As 0.80 0.84 0.87 0.83 0.82 0.85 0.46* 0.84 1 Hg 0.75 0.88 0.86 0.86 0.95 0.90 0.54 0.88 0.78 1 注:样品数N=32,置信度水平α=0.01,*表示P值>0.05,相关性不显著。 表 6 莱州湾沉积物重金属的长期变化数据
Table 6 Long-term variation of heavy metals in sediments of Laizhou Bay
mg/kg 年份 Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg 参考文献 2016(5—6) 19.061 20.297 55.976 60.1 0.111 11.716 0.038 本研究 2015(2) 9.7 11.7 40.9 46.3 0.091 9.2* 0.013* [50] 2012(夏) 22.0±6.2* 21.9±5.3* 60.4±16.3* 60.0±8.6* 0.12±0.04* 12.7±2.2* − [10] 2012(9—10) 21.96* 21.99* 60.41* 60.00* 0.12* 12.64* 0.051* [14] 2010(5/8/10/12) 17.42 20.58 51.19 49.56* 0.18* 8.99 0.07* [12] 2008(5) 14.97 11.7 50.80 − 0.11 9.20* 0.09* [15] 2007(8) 18.59 20.74 57.20 61.44 0.13* 11.47* 0.05* [16] 2007(8) 13.3 20.2 59.4 57.1* 0.081* 13.1* 0.053* [58] 注:*代表文献所采用的实验方法和仪器等与本研究相同;文献[50]样品取自莱州湾东部海域。 表 7 莱州湾周围河流和土壤重金属含量
Table 7 Concentrations of heavy metals in rivers and soils around Laizhou Bay
-
[1] Diagomanolin V, Farhang M, Ghazi-Khansari M, et al. Heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu) in the Karoon waterway river, Iran [J]. Toxicology Letters, 2004, 151(1): 63-67. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.02.018
[2] Tam N F Y, Wong Y S. Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in a simulated mangrove system treated with sewage [J]. Hydrobiologia, 1997, 352(1-3): 67-75.
[3] 吴丰昌, 万国江, 蔡玉蓉. 沉积物-水界面的生物地球化学作用[J]. 地球科学进展, 1996, 11(2):191-197 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1996.02.013 WU Fengchang, WAN Guojiang, CAI Yurong. Biogeochemical processes at the sediment-water interface [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1996, 11(2): 191-197. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1996.02.013
[4] Li X D, Wai O W H, Li Y S, et al. Heavy metal distribution in sediment profiles of the Pearl River estuary, South China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(5): 567-581. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00072-4
[5] 王勤, 彭渤, 方小红, 等. 湘江下游河床沉积物重金属污染的矿物学分析[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(3):558-575 WANG Qin, PENG Bo, FANG Xiaohong, et al. Mineralogical compositions of heavy-metal contaminated bed sediments from lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan Province of China [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39(3): 558-575.
[6] 方小红. 洞庭湖“四水”入湖沉积物重金属污染的地球化学研究[D]. 湖南师范大学博士学位论文, 2020. FANG Xiaohong. Geochemistry study on heavy-metal contamination in sediments from the Four River inlets of Dongting Lake, China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Hunan Normal University, 2020.
[7] Jain C K, Malik D S, Yadav R. Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of lake Nainital, Uttaranchal, India [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2007, 130(1-3): 129-139. doi: 10.1007/s10661-006-9383-6
[8] Singh K P, Malik A, Sinha S, et al. Estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in sediments of Gomti river (India) using principal component analysis [J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2005, 166(1-4): 321-341. doi: 10.1007/s11270-005-5268-5
[9] 张雷, 秦延文, 马迎群, 等. 大辽河感潮段及其近海河口重金属空间分布及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(9):3336-3345 ZHANG Lei, QIN Yanwen, MA Yingqun, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the tidal reach and its adjacent sea estuary of Daliaohe area, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(9): 3336-3345.
[10] Xu G, Liu J, Pei S F, et al. Sediment properties and trace metal pollution assessment in surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(15): 11634-11647. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4393-y
[11] 赵保仁, 庄国文, 曹德明, 等. 渤海的环流、潮余流及其对沉积物分布的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1995, 26(5):466-473 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003 ZHAO Baoren, ZHUANG Guowen, CAO Deming, et al. Circulation, tidal residual currents and their effects on the sedimentations in the Bohai Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1995, 26(5): 466-473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003
[12] 刘金虎, 宋骏杰, 曹亮, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物中重金属时空分布、污染来源及风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2):369-381 LIU Jinhu, SONG Junjie, CAO Liang, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 369-381.
[13] 崔毅, 马绍赛, 李云平, 等. 莱州湾污染及其对渔业资源的影响[J]. 海洋水产研究, 2003, 24(1):35-41 CUI Yi, MA Shaosai, LI Yunping, et al. Pollution situation in the Laizhou Bay and its effects on fishery resources [J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 2003, 24(1): 35-41.
[14] 郑懿珉, 高茂生, 刘森, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征及生态环境评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(3):354-360 ZHENG Yimin, GAO Maosheng, LIU Sen, et al. Distribution patterns and ecological assessment on heavy metals in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(3): 354-360.
[15] 罗先香, 张蕊, 杨建强, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(2):262-269 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.02.002 LUO Xianxiang, ZHANG Rui, YANG Jianqiang, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment in Laizhou Bay [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(2): 262-269. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.02.002
[16] 朱爱美, 张辉, 崔菁菁, 等. 渤海沉积物重金属环境质量评价及其影响因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(12):134-144 ZHU Aimei, ZHANG Hui, CUI Jingjing, et al. Environmental quality assessment and influence factor of heavy metals in the surface sediments from the Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(12): 134-144.
[17] 祝雅轩. 莱州湾与辽东湾营养盐特征及其对生态环境的影响: 对比研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2019. ZHU Yaxuan. Nutrient characteristics of Laizhou Bay and Liaodong Bay and their effects on ecological environment: a comparative study[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019.
[18] 宋晓帅, 王松涛, 吴振, 等. 莱州湾海岸带工程地质分区及其特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(1):43-52 SONG Xiaoshuai, WANG Songtao, WU Zhen, et al. Division of engineering geological zones for coastal zone of Laizhou Bay [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(1): 43-52.
[19] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检疫总局. GB/T 12763.8-2007 海洋调查规范 第8部分: 海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. General Administration of Quality Supervision and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 12763.8-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey-part 8: Marine geology and geophysics survey[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008.
[20] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 17378.3-2007 海洋监测规范 第3部分: 样品采集、贮存与运输[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB 17378.3-2007 The specification for marine monitoring-Part 3: Sample collection storage and transportation[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008.
[21] Dai J C, Song J M, Li X G, et al. Environmental changes reflected by sedimentary geochemistry in recent hundred years of Jiaozhou Bay, North China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 145(3): 656-667. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.10.005
[22] Xia N, Zhang Q, Yao D, et al. Geochemical analysis of marine sediments using fused glass disc by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008, 26(4): 475-479. doi: 10.1007/s00343-008-0475-8
[23] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[24] 徐艳东, 魏潇, 杨建敏, 等. 山东近岸海域表层沉积物7种重金属污染特征和生态风险评估研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(3):651-658 doi: 10.11693/hyhz20141200358 XU Yandong, WEI Xiao, YANG Jianmin, et al. Contaminant characteristics and ecological risk assessment on pollution by seven heavy metals in surface sediments in Shandong coastal areas [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(3): 651-658. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20141200358
[25] 刘成, 王兆印, 何耘, 等. 环渤海湾诸河口潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2002, 15(5):33-37 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2002.05.009 LIU Cheng, WANG Zhaoyin, HE Yun, et al. Evaluation on the potential ecological Risk for the River mouths around Bohai Bay [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2002, 15(5): 33-37. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2002.05.009
[26] Müller G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2(3): 109-118.
[27] 赵玉庭, 董晓晓, 王立明, 等. 海洋沉积物重金属生态风险评价方法比较及实例验证: 以莱州湾为例[J]. 海洋通报, 2019, 38(3):353-360 ZHAO Yuting, DONG Xiaoxiao, WANG Liming, et al. Selection and comparison of different methods for ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in marine sediments of Laizhou Bay [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2019, 38(3): 353-360.
[28] Birch G F, Taylor S E. Application of sediment quality guidelines in the assessment and management of contaminated surficial sediments in Port Jackson (Sydney Harbour), Australia [J]. Environmental Management, 2002, 29(6): 860-870. doi: 10.1007/s00267-001-2620-4
[29] Long E R, Macdonald D D, Smith S L, et al. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments [J]. Environmental Management, 1995, 19(1): 81-97. doi: 10.1007/BF02472006
[30] Macdonald D D, Carr R S, Calder F D, et al. Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters [J]. Ecotoxicology, 1996, 5(4): 253-278. doi: 10.1007/BF00118995
[31] Long E R, Morgan L G. The potential for biological effects of sediment-sorbed contaminants tested in the National Status and Trends Program[R]. National Oceanic & Atmospheric Admininistration (NOAA), 1990.
[32] 兰静, 朱志勋, 冯艳玲, 等. 沉积物监测方法和质量基准研究现状及进展[J]. 人民长江, 2012, 43(12):78-80, 85 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2012.12.022 LAN Jing, ZHU Zhixun, FENG Yanling, et al. Research on state quo and progress of sediment monitoring method and quality standard [J]. Yangtze River, 2012, 43(12): 78-80, 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2012.12.022
[33] 陈生涛, 苗安洋, 温婷婷, 等. 辽东湾表层沉积物重金属污染特征及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(2):256-262 doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20190214 CHEN Shengtao, MIAO Anyang, WEN Tingting, et al. Heavy metals in the surface sediment of Liaodong Bay and their potential ecological risk [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(2): 256-262. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20190214
[34] 赵一阳, 鄢明才. 中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994. ZHAO Yiyang, YAN Mingcai. Geochemistry of Sediments of the China Shelf Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994.
[35] 许艳, 王秋璐, 李潇, 等. 环渤海典型海湾沉积物重金属环境特征与污染评价[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2017, 35(3):428-438 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2017.03.012 XU Yan, WANG Qiulu, LI Xiao, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments from typical bays in the Bohai Sea [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2017, 35(3): 428-438. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2017.03.012
[36] 李宏伟, 张彦峰, 阳金希, 等. 海河流域沉积物中典型重金属的生态风险评估及验证[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(2):149-159 doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20190304001 LI Hongwei, ZHANG Yanfeng, YANG Jinxi, et al. Ecological risk assessment and verification of the typical heavy metals for sediment of Haihe River basin [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(2): 149-159. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20190304001
[37] 孙鹏, 张理博, 罗淑年. 松花江沉积物重金属赋存形态及风险特征研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2020, 45(7):142-145 SUN Peng, ZHANG Libo, LUO Shunian. Speciation and risk characteristics of heavy metals in the sediments of the Songhua River estuary [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2020, 45(7): 142-145.
[38] 计建强. 莱州湾水动力模式及沉积动力模式的构建及模拟[D]. 宁波大学硕士学位论文, 2016. JI Jianqiang. The constructions and simulation of Laizhou bay's hydrodynamic model and sedimentary dynamic model[D]. Master Dissertation of Ningbo University, 2016.
[39] 陈秀, 李爽兆, 袁德奎, 等. 渤海湾沉积物重金属的分布特征及影响因素[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2017, 35(3):382-391 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2017.03.008 CHEN Xiu, LI Shuangzhao, YUAN Dekui, et al. Distribution characteristics of sediment heavy metals in Bohai Bay and its effect factors [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2017, 35(3): 382-391. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2017.03.008
[40] 汤世凯, 张杰, 于晓静, 等. 山东丁字湾海域沉积物重金属含量、分布及与粒径之间的关系研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5):928-935 TANG Shikai, ZHANG Jie, YU Xiaojing, et al. Heavy metal contents, spatial distributions and their relationships with the grain size of surficial sediments in Dingziwan, Shandong [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(5): 928-935.
[41] 顾效源, 孔祥淮, 王伟, 等. 山东丁字湾表层沉积物重金属分布及污染评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(3):13-21 GU Xiaoyuan, KONG Xianghuai, WANG Wei, et al. Distribution and environment assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Dingzi bay, Shandong Province [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(3): 13-21.
[42] Feng H, Jiang H Y, Gao W S, et al. Metal contamination in sediments of the western Bohai Bay and adjacent estuaries, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(4): 1185-1197. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.020
[43] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985. Laboratory of Marine Geology, Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Geology of the Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[44] 刘喜惠, 刘方, 丁页, 等. 渤海环流对近岸海域无机氮分布特征的影响[J]. 中国环境监测, 2019, 35(6):78-84 LIU Xihui, LIU Fang, DING Ye, et al. Influence of circulation on the distribution characteristics of inorganic nitrogen in the Bohai Coastal Sea [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2019, 35(6): 78-84.
[45] 张爱滨, 刘明, 廖永杰, 等. 黄河沉积物向渤海湾扩散的沉积地球化学示踪[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2015, 33(2):246-256 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.02.012 ZHANG aibin, LIU Ming, LIAO Yongjie, et al. The sedimentary geochemical trace of the Yellow River sediments diffusion in the Bohai Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2015, 33(2): 246-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.02.012
[46] 赵玉玲, 冯秀丽, 宋湦, 等. 现代黄河三角洲附近海域表层沉积物地球化学分区[J]. 海洋科学, 2016, 40(9):98-106 doi: 10.11759/hykx20160422002 ZHAO Yuling, FENG Xiuli, SONG Sheng, et al. Geochemical partition of surface sediments in the seas near the modern Yellow River Delta [J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(9): 98-106. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160422002
[47] 袁萍. 渤海表层沉积物的空间分布及其与物源和沉积动力环境的关系[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2015. YUAN Ping. Distribution of surface sediment in the Bohai Sea and its relationship with sediment supply and sedimentary dynamic environment[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2015.
[48] 马绍赛, 辛福言, 崔毅, 等. 黄河和小清河主要污染物入海量的估算[J]. 海洋水产研究, 2004, 25(5):47-51 MA Shaosai, XIN Fuyan, CUI Yi, et al. Assessment of main pollution matter volume into the sea from Yellow River and Xiaoqing River [J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 2004, 25(5): 47-51.
[49] 张晓琳. 长江口、黄河口及邻近海域重金属的分布特征及影响因素研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2013. ZHANG Xiaolin. Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of heavy metals in the Yangtze River Estuary, the Yellow River Estuary and adjacent sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2013.
[50] 徐艳东, 魏潇, 夏斌, 等. 莱州湾东部海域表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险评价[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2015, 33(4):520-528 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.04.010 XU Yandong, WEI Xiao, XIA Bin, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Eastern Laizhou Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2015, 33(4): 520-528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.04.010
[51] Zhou G H, Sun B B, Zeng D M, et al. Vertical distribution of trace elements in the sediment cores from major rivers in east China and its implication on geochemical background and anthropogenic effects [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139: 53-67. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.03.007
[52] 贾磊, 刘文涛, 唐得昊, 等. 三亚湾及周边海域表层沉积物重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(12):22-31 JIA Lei, LIU Wentao, TANG Dehao, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in Sanya bay and surrounding waters [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(12): 22-31.
[53] El Bilali L, Rasmussen P E, Hall G E M, et al. Role of sediment composition in trace metal distribution in lake sediments [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17(9): 1171-1181. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00132-9
[54] Hooda P S, Alloway B J. Cadmium and lead sorption behaviour of selected English and Indian soils [J]. Geoderma, 1998, 84(1-3): 121-134. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7061(97)00124-9
[55] 张思洋, 于大涛, 张戈. 锦州湾三河入海口重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(6):20-25 ZHANG Siyang, YU Datao, ZHANG Ge. Distribtion of heavy metals at the junction of Lianshan, wuli and Cishan estuaries, Jinzhou bay and their contamination evaluation [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(6): 20-25.
[56] Li C L, Kang S C, Zhang Q G. Elemental composition of Tibetan Plateau top soils and its effect on evaluating atmospheric pollution transport [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(8-9): 2261-2265. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.03.035
[57] Çelo V, Babi D, Baraj B, et al. An assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments along the albanian coast [J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 1999, 111(1): 235-250.
[58] 胡宁静, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物中重金属分布特征和环境影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2011, 29(1):63-72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.01.008 HU Ningjing, SHI Xuefa, LIU Jihua, et al. Distributions and impacts of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay [J]. Advances in marine science, 2011, 29(1): 63-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.01.008
[59] 王钦, 丁明玉, 张志洁, 等. 太湖不同湖区沉积物重金属含量季节变化及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境, 2008, 17(4):1362-1368 WANG Qin, DING Mingyu, ZHANG Zhijie, et al. Seasonal varieties and influential factors of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008, 17(4): 1362-1368.
[60] 薛春汀, 叶思源, 高茂生, 等. 现代黄河三角洲沉积物沉积年代的确定[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(1):117-124 XUE Chunting, YE Siyuan, Gao Maosheng, et al. Determination of depositional age in the Huanghe Delta in China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(1): 117-124.
[61] 缪雄谊. 重金属污染的扩散迁移及其健康风险评价: 以三角洲和河流为例[D]. 中国科学技术大学, 2020. MIAO Xiongyi. The conversion, migration and health risk assessment of heavy metals pollution: a field study in typical delta and river[D]. University of Science and Technology of China, 2020.
[62] 王亚梦. 莱州湾南岸典型河口沉积物重金属空间分布特征及来源解析[D]. 山东师范大学硕士学位论文, 2020. WANG Yameng. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of typical estuaries on the south coast of Laizhou Bay[D]. Master Dissertation of Shandong Normal University, 2020.
[63] 沈佳裕, 罗先香, 郑浩, 等. 小清河口及邻近海域表层沉积物重金属污染及生态风险特征[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(7):1516-1524 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.07.2016112203 SHEN Jiayu, LUO Xianxiang, ZHENG Hao, et al. Pollution and ecological risk characteristics of heavy metals in surface sediments in Xiaoqing River Estuary and adjacent sea areas [J]. Environmental chemistry, 2017, 36(7): 1516-1524. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.07.2016112203
[64] Bai J H, Xiao R, Zhang K J, et al. Arsenic and heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from tidal freshwater and salt marshes before and after the flow-sediment regulation regime in the Yellow River Delta, China [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 450-451: 244-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.05.006
[65] 庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 胡雪平, 等. 山东省土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2018, 34(1):39-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2018.01.005 PANG Xugui, DAI Jierui, HU Xueping, et al. Background values of soil geochemistry in Shandong Province [J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2018, 34(1): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2018.01.005
[66] 温晓君, 白军红, 贾佳, 等. 黄河三角洲典型潮间带盐沼土壤重金属含量及来源分析[J]. 湿地科学, 2015, 13(6):722-727 WEN Xiaojun, BAI Junhong, JIA Jia, et al. Contents of heavy metals and their sources in the soils of typical intertidal salt marshes in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Wetland Science, 2015, 13(6): 722-727.
[67] 李广雪, 薛春汀. 黄河水下三角洲沉积厚度、沉积速率及砂体形态[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1993, 13(4):35-44 LI Guangxue, XUE Chunting. Sediment thickness, sedimentation rate and silt body shape of the Yellow River subaqueous delta lobe [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1993, 13(4): 35-44.
[68] Tang A K, Liu R H, Ling M, et al. Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of soluble heavy metals in the Yellow River Estuary and adjacent sea [J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2010, 2: 1193-1198. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.129
[69] 国家海洋局. 2016年中国海洋环境状况公报[EB/OL]. (2017-04-13). http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyhjzlgb/2016nzghyhjzkgb/. State Oceanic Administration. Bulletin of China's marine environment in 2016[EB/OL]. (2017-04-13). http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyhjzlgb/2016nzghyhjzkgb/.
[70] 国家海洋局. 2015年中国海洋环境状况公报[EB/OL]. (2016-04-14). http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyhjzlgb/2016nzghyhjzkgb/. State Oceanic Administration. Bulletin on the state of China's marine environment in 2015[EB/OL]. (2016-04-14). http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyhjzlgb/2016nzghyhjzkgb/.
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 陈文良,朱颖涛,尹砚军,冷星. 天津港东侧海域表层沉积物重金属污染特征研究. 中国水运. 2025(06): 62-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 项立辉,王艳芬,姜辞冬,刘强,李伟欣. 江苏中部潮间带表层沉积物重金属分布、来源及污染评价. 海洋地质前沿. 2024(08): 42-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张岚,李玲玲,孙士顺,王坤. 付疃河中下游表层沉积物污染状况评价. 环境科技. 2024(04): 51-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王海根,顾效源,王庆同,杨鹏,宇星辰,张家浩,毛方松,葛祥威. 渤海海峡南部近百年来重金属沉积记录的环境意义. 海洋地质前沿. 2024(09): 73-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 蔡传双,赵广明,苏大鹏,丁喜桂,尼鑫,张尧. 黄河三角洲北部湿地沉积物重金属污染风险评价及来源分析. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(05): 176-188 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 张绪振,褚宏宪,孔令号,曹立成,张德程,李海波,徐华源. 莱州湾表层海水重金属分布特征及生态环境评价. 海洋地质前沿. 2024(11): 25-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 雷雁翔,张斌,吴治国,王小丹,唐荣慧,胡蕾,张朋朋,王恩强,滕永波. 长岛北部海域表层沉积物重金属分布特征与风险评价及来源分析. 海洋地质前沿. 2023(03): 40-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 侯庆华,曹清,陈清香,熊梦琪,张际标. 中国海湾沉积物重金属比较分析. 海洋开发与管理. 2023(03): 83-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郭雨岸,陈秀玲,蔡炳贵,卢欣,刘杰,周玲. 闽东定海-黄岐湾表层沉积物重金属污染特征及来源解析. 环境化学. 2023(03): 769-778 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李军,李旭,李开明,焦亮,臧飞,毛潇萱,潘文惠,米璇. 黄河兰州段城市河道表层沉积物重金属空间分布特征及来源解析. 环境科学. 2023(05): 2562-2573 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 邓晓茜,毛龙江,蔡於杞,赵阳,王婷,周超凡. 基于APCS-MLR和PMF模型的海州湾沉积物重金属污染特征与来源研究. 海洋环境科学. 2023(03): 387-395 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 贾少宁,申发,颜宁,王若菲,刘苏慧,于洋,栗云召,杨继松,于君宝. 黄河三角洲不同土地利用方式下土壤重金属分析评价. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(03): 193-202 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 宇星辰,张家浩,王庆同,王海根,杨鹏,毛方松,翟如甲. 莱州湾南岸滨海湿地表层土壤重金属元素分布与生态风险评价. 中国地质调查. 2023(05): 82-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 秦华伟,陶慧敏,张娟,张潇文,宋鑫,谷伟丽,王凯,盖芸芸. 营养盐和重金属等环境因子对莱州湾浮游植物的影响. 海洋湖沼通报. 2023(05): 134-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 刘思佳,史明易,马旭,王少锋,吴星,王新,曾祥峰,贾永锋. 渤海表层沉积物中砷的含量、形态、空间分布及风险评价. 生态学杂志. 2023(12): 2844-2852 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 马占琪. 小型河流典型重金属污染分布特征及风险评价研究. 绿色科技. 2022(18): 134-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(13)



 下载:
下载: