Characteristics, distribution and implication of hydrothermal minerals in Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field, Carlsberg Ridge, northwest Indian Ocean
-
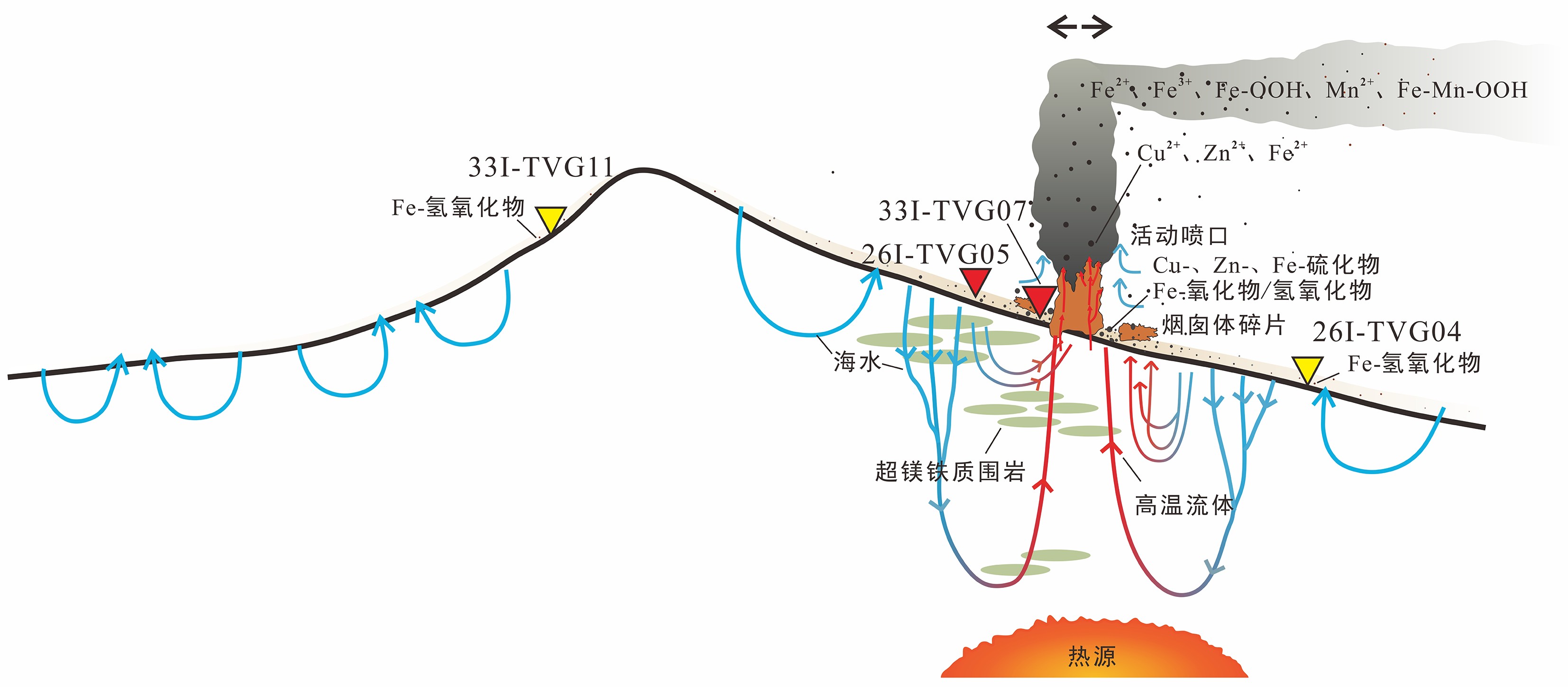
摘要: 海底沉积物中的热液成因矿物主要来自热液区热液产物堆积体的失稳垮塌搬运迁移和热液羽流自生矿物颗粒的沉降。热液成因矿物的类型和空间分布特征对于了解热液活动区的位置与范围具有重要的指示作用。天休热液区(3°41′N、63°50′E)位于卡尔斯伯格脊超镁铁岩系中,本文对采自该热液区及其周边的共4站表层沉积物样品进行研究,分析热液成因矿物的组成、丰度和粒度的空间变化情况。研究表明,在热液喷口近端(0 ~0.22 km)同时分布有垮塌迁移及热液羽流沉降来源的热液成因矿物,其中垮塌来源的矿物呈砾—粗砂级,以古巴矿等金属硫化物矿物及铁氧化物为主;羽流沉降来源的矿物呈砂—泥级,以Cu-Zn-Fe硫化物矿物(等轴古巴矿、古巴矿、闪锌矿和磁黄铁矿等)为主。在远喷口端(1.84 ~ 6.05 km)主要分布有羽流沉降来源的热液成因矿物,以砂—泥级的金属氧化物和氢氧化物为主。热液成因矿物的类型、粒度、丰度在空间上呈现出的规律性分布特征可以示踪未知的活动和非活动热液区的位置,并作为多金属硫化物资源的找矿标志。Abstract: Hydrothermal minerals could originate from mass wasting of hydrothermal deposits or from the hydrothermal plume falling-out. The types and their spatial distribution of hydrothermal minerals are important indicators for constraining the location of hydrothermal field. The Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field (3°41′N,63°50′E) is an ultramafic-hosted field located on the Carlsberg Ridge, northwest Indian Ocean. In this paper, surface sediments collected from 4 stations near the active venting site of Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field and its surrounding regions were studied on hydrothermal minerals to understand their spatial variations on morphology, composition, abundance and particle size. Near the venting site (0 ~ 0.22 km) the hydrothermal minerals are dominated by Cu-Zn-Fe containing sulfide aggregates, in the size from gravel to sand, originated from the mass wasting of the sulfide deposits and precipitation from the hydrothermal fluid. For samples collected outside of the hydrothermal field (1.84 ~ 6.05 km away), the hydrothermal minerals are dominated by fine grain hydrothermal oxides and hydroxides derived from plume fallout. Our results suggest that the types and grain size of hydrothermal minerals and their spatial distribution can be served as a good indicator for tracking unknown active and inactive hydrothermal field and prospecting of the associated hydrothermal sulfide resources.
-
雅浦岛弧位于菲律宾海板块东南边界,是太平洋板块和加罗林板块向菲律宾海板块之下俯冲的结果。前人研究将雅浦岛弧和帕劳岛弧归结为伊豆-小笠原-马里亚纳岛弧体系的组成部分[1],并认为马里亚纳、雅浦和帕劳岛弧分别代表岛弧演化过程中的最初阶段、过渡阶段和成熟阶段[2]。与其他岛弧相比,雅浦岛弧具有十分独特的地质特征,主要包括以下几个方面:(1)雅浦岛弧主要由变质岩组成,自西向东由绿片岩相转变为角闪岩相,变质程度逐渐加深,而雅浦岛弧火山岩分布较少[3-4];(2)雅浦岛弧地震以浅源地震为主,震源深度多小于40 km[5];(3)雅浦岛弧沟弧距离为50 km左右[6],明显短于西太平洋区域其他成熟岛弧的沟弧距离(100~200 km)[7-8];(4)雅浦岛弧缺少典型的弧前增生楔[9]。
McCabe和Uyeda[10]认为加罗林海岭在早中新世与雅浦海沟碰撞,后人对于雅浦区域的研究则集中在加罗林海岭碰撞的影响,认为该碰撞导致了雅浦岛弧火山活动的终止[4]或减弱[5-6],而雅浦岛弧缺失的增生楔可能与加罗林海岭俯冲碰撞导致的俯冲侵蚀有关[4, 6]。然而,现今地形资料显示加罗林海岭与雅浦海沟并非直接接触,二者中间存在一个明显的低地形区域,前人认为该区域可能是俯冲板片前缘正断层控制的半地堑结构[6, 11-12]。同时雅浦岛的变质基底以及雅浦岛以南的岛弧变质岩为高温—中温、低压—中压变质作用的产物[3, 13],缺少与碰撞相关的高压变质岩。因此,加罗林海岭是否与雅浦岛弧发生碰撞仍需要进一步研究,而前人所提出的雅浦岛弧构造演化模型[4, 6, 10, 12]多数以加罗林海岭与雅浦岛弧的碰撞为前提,这些模型也需要重新考虑。由此,本文通过总结雅浦区域的地球化学、地震、重力异常等多方面证据,对雅浦沟-弧体系的构造演化过程提出了一个全新的解释。
1. 区域地质背景
雅浦海沟和雅浦岛弧是太平洋板块、加罗林板块和菲律宾海板块汇聚所形成的沟-弧构造体系,大地构造背景十分复杂(图1a)。雅浦海沟北侧与帕里西维拉海盆扩张中心相接,南侧与帕劳海沟相连,东侧为加罗林热点作用下形成的加罗林海岭,索罗尔海槽将加罗林海岭分为东加罗林海岭和西加罗林海岭两个部分(图1b)。
![]() 图 1 四国海盆、帕里西维拉海盆以及加罗林板块区域构造简图(a)与雅浦岛弧及周边的区域地质概况(b)水深数据来源于GEBCO 2019;地震数据来源于USGS和CMTFigure 1. a: Regional tectonic map of the Shikoku basin, the Parece-Vela basin and the Caroline plate; b: Geological map of the Yap arc and its vicinitybathymetry data from GEBCO 2019; Earthquake data from USGS and CMT
图 1 四国海盆、帕里西维拉海盆以及加罗林板块区域构造简图(a)与雅浦岛弧及周边的区域地质概况(b)水深数据来源于GEBCO 2019;地震数据来源于USGS和CMTFigure 1. a: Regional tectonic map of the Shikoku basin, the Parece-Vela basin and the Caroline plate; b: Geological map of the Yap arc and its vicinitybathymetry data from GEBCO 2019; Earthquake data from USGS and CMT帕里西维拉海盆是渐新世沿着九州-帕劳海岭打开的弧后盆地,海盆内部S型转换断层分割的洋中脊段呈雁列状排布(图1a)[14]。前人通过对地形和磁条带研究,提出帕里西维拉海盆经历了两个阶段的盆地扩张过程,其初始扩张方向为E-W向,在20~19 Ma扩张方向转变为NE-SW[14-15]。帕里西维拉海盆的洋壳扩张过程最终在约15 Ma终止[16],然而沿着帕里西维拉海盆的扩张中心还存在一期13~8.7 Ma的岩浆事件,分别为四国海盆的Kinan海山链[17]、帕里西维拉海盆中部的Gadzilla Megamullion拆离断层[18]以及海盆最南部的岛弧岩浆事件[19](图1a)。
加罗林海岭为古近纪加罗林热点作用所形成的隆起,其包括东加罗林海岭和西加罗林海岭两个部分,分别属于太平洋板块和加罗林板块,二者之间以索罗尔海槽为界(图1b)。然而,太平洋板块和加罗林板块沿着马里亚纳-雅浦海沟俯冲速率差异较大,北部的太平洋板块的俯冲速率为20 mm/a,而加罗林板块的俯冲速率仅为5 mm/a[20]。地震以及重力资料研究显示索罗尔海槽具有扩张中心的属性,并且有洋壳的存在[21],然而现今索罗尔海槽内部的地震多为走滑型地震(图1),这与太平洋板块和加罗林板块之间相对运动相对应。Hawkins和Batiza[4]认为加罗林海岭与雅浦岛弧在早中新世时发生碰撞,致使雅浦岛弧的火山活动停止以及弧前侵蚀[10]。虽然,岩石地球化学研究证实雅浦岛弧以变质岩为主,岩浆活动较少,但是雅浦岛弧变质岩多为中—低压变质作用导致[3, 13],缺少与碰撞相关的高压—超高压变质岩的报道。同时,雅浦海沟和加罗林海岭之间存在一个三角形的地形平坦区域(图1),该区域内没有与加罗林热点相关的地形隆起。
雅浦岛弧西侧为帕里西维拉海盆的洋壳,主体构造线走向为N-S向(图1b)。Okino等[22]通过地球物理资料的研究发现在该区域内存在一条近E-W向延伸的扩张中心。该扩张中心形成的洋壳构造线走向为NE-SW向,其东侧为帕里西维拉海盆的洋壳的N-S向构造线区域,二者之间以假断层为界(图1)。Okino等[22]认为这段扩张中心可能为帕里西维拉海盆早期扩张中心的一部分。
2. 雅浦岛弧的地壳性质
前人对于雅浦岛弧岩石地球化学研究多集中在雅浦岛。Tayama[23]最早将雅浦岛地层划分为4个组,分别为雅浦组、Map组、Tomil集块岩和第四纪沉积地层(图2)。雅浦组是雅浦岛的基底,主要由基性火山岩变质而成的绿片岩和角闪岩组成,同时可见超基性—酸性侵入体和岩脉。覆盖在雅浦组之上的Map组主要为构造角砾岩、砂岩以及粉砂岩组成的沉积岩系,底部发现有角闪岩和绿片岩碎块,Map组有孔虫化石指示其沉积发生在晚渐新世—中新世[24]。Tomil集块岩由安山岩熔岩、角砾岩和凝灰岩组成,不整合于雅浦组和Map组之上。岩石地球化学研究表明Tomil集块岩中的安山岩属于钙碱性或岛弧拉斑玄武岩系列,与马里亚纳岛弧和帕劳岛弧类似[3]。由此可见,雅浦岛的构造演化可大体分为3个阶段:晚渐新世以前雅浦组的基性火山岩喷发以及绿片岩相和角闪岩相的变质作用、晚渐新世—中新世雅浦组变质岩风化沉积作用形成的Map组、中新世以后岛弧岩浆作用形成的Tomil集块岩。
岛弧火山岩组合多数以钙碱性系列的安山岩-英安岩-流纹岩组合为主,且K2O含量较低。雅浦组由绿片岩相-角闪岩相的变质岩组成,根据Pearce[25]提出的F1-F2判别图解(图3a),雅浦组变质岩原岩属于洋底玄武岩,明显区分于岛弧玄武岩。在板片俯冲过程中,由于Ti存于金红石和钛铁矿等残留体中进入地幔,加上其他不相容元素由于俯冲流体萃取作用,最终导致岛弧火山岩的TiO2含量较低,因此Ti含量在岛弧和弧后盆地区域样品中差别较为明显。雅浦组的变质岩Ti含量较高,与帕里西维拉海盆玄武岩相近,在Cr-Ti图解上多落于洋中脊玄武岩区域(图3b),与帕里西维拉海盆洋壳玄武岩类似。雅浦岛弧在同位素方面的研究十分匮乏,仅有Matsuda等[2]报道了一个雅浦岛绿片岩的87Sr/86Sr比值,为0.702 9。马里亚纳岛弧岩浆岩的87Sr/86Sr比值远高于0.703(图3c),雅浦岛绿片岩的87Sr/86Sr比值更接近于四国海盆洋壳的Sr同位素比值。因此,雅浦组在地球化学特征上更接近于帕里西维拉海盆洋壳,并非与岛弧岩浆作用相关。根据雅浦岛弧及周边区域构造解析,在雅浦岛弧西侧可以识别出NE-SW向的转换断层以及与之相关的NW-SE向海底构造线(图1),表明雅浦组的岩浆作用发生在帕里西维拉海盆NE-SW向扩张时期,也就是20~15 Ma期间[16]。
![]() 图 3 雅浦岛变质岩和岛弧岩浆岩F1-F2图解(a)与雅浦组变质岩Cr-Ti图解(b)及帕里西维拉海盆洋壳以及马里亚纳火山弧的Pb-Sr同位素图解(c)WPB:板内玄武岩;SHO:钾玄岩;CAB:钙碱性玄武岩;LKT:低钾拉斑玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩;OFB:洋底玄武岩. 雅浦组变质岩数据来自于参考文献[3, 4, 26],雅浦岛弧岩浆岩数据来自于参考文献[19],帕里西维拉海盆数据来自于参考文献[27-29],马里亚纳火山弧数据来自于参考文献[30-34],全球岛弧数据来自于GEOROCFigure 3. a: F1-F2 diagram of the metamorphic rocks and island arc igneous rocks from the Yap island(WPB: Within Plate Basalts; SHO: Shoshonites; CAB: Calc-Alkali Basalts; LKT: Low-potassium Tholeiites and Island Arc Basalts; OFB: Ocean Floor Basalts); b: Cr-Ti diagram of the metamorphic rocks from the Yap Formation; c: Isotope Pb-Sr diagram of the Parece-Vela basin and the Mariana volcanic arc
图 3 雅浦岛变质岩和岛弧岩浆岩F1-F2图解(a)与雅浦组变质岩Cr-Ti图解(b)及帕里西维拉海盆洋壳以及马里亚纳火山弧的Pb-Sr同位素图解(c)WPB:板内玄武岩;SHO:钾玄岩;CAB:钙碱性玄武岩;LKT:低钾拉斑玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩;OFB:洋底玄武岩. 雅浦组变质岩数据来自于参考文献[3, 4, 26],雅浦岛弧岩浆岩数据来自于参考文献[19],帕里西维拉海盆数据来自于参考文献[27-29],马里亚纳火山弧数据来自于参考文献[30-34],全球岛弧数据来自于GEOROCFigure 3. a: F1-F2 diagram of the metamorphic rocks and island arc igneous rocks from the Yap island(WPB: Within Plate Basalts; SHO: Shoshonites; CAB: Calc-Alkali Basalts; LKT: Low-potassium Tholeiites and Island Arc Basalts; OFB: Ocean Floor Basalts); b: Cr-Ti diagram of the metamorphic rocks from the Yap Formation; c: Isotope Pb-Sr diagram of the Parece-Vela basin and the Mariana volcanic arc3. 加罗林海岭对雅浦沟-弧系统的影响
加罗林海岭与雅浦岛弧的碰撞一直是雅浦岛弧研究的重点。McCabe和Uyeda1[10]认为加罗林海岭在早中新世与雅浦岛弧发生碰撞,并导致雅浦岛弧活动停止。Fujiwara等[6]认为碰撞发生在晚渐新世,碰撞导致雅浦岛弧的弧前部分缺失、异常近的沟-弧距离、雅浦弧前下地壳物质的暴露以及雅浦岛弧的变质作用。然而,现今地形数据显示,加罗林海岭并未与雅浦岛弧相接,二者之间存在一个三角形的平坦地形区域(图1),该区域水深较深。在俯冲前缘区域的俯冲板片弯曲通常情况下会导致平行于海沟的正断层,Fujiwara等[6]认为这些正断层所控制的半地堑结构形成了这个三角形区域,Dong等[12]认为加罗林海岭和雅浦岛弧在早中新世发生碰撞,晚中新世时期开始的索罗尔海槽的扩张导致了半地堑结构的形成。
加罗林海岭是热点所导致的地形隆起,热点的岩浆作用通常会形成沿着热点轨迹的地球物理特征异常,包括凸起的地形、加厚的洋壳、高的自由空间重力异常以及较低的布格重力异常。与加罗林海岭相比,雅浦海沟东侧的三角形区域水深较深,在重力上表现为较低的自由空间重力异常。根据Fujiwara等[6]的半地堑模型,该区域东部边界为切穿岩石圈的正断层,然而该三角形区域内地震较少,在其东部边界并没有观测到与正断层相关的地震发生(图1b)。在半地堑模型中的正断层不会改变地壳厚度,然而该三角形区域内的地壳厚度明显比加罗林海岭薄(图4c)。对于Dong等[12]提出的索罗尔海槽扩张形成半地堑的模型,该三角区域内应该存在索尔罗海槽向西的延伸,然而该区域内并没有观测到与索尔罗海槽现今地震类似的走滑性质的地震(图1b),说明索罗尔海槽的中央裂谷并未延伸到该区域内部。同时该区域内构造线多为N-S走向,与索罗尔海槽N-S向扩张形成的E-W向构造线相悖。因此,该三角形区域内的洋壳并未受到加罗林热点的影响,同时也表明加罗林海岭并未与雅浦岛弧发生碰撞。另一方面,雅浦岛弧基底是中温—高温变质作用导致的绿片岩相-角闪岩相变质作用[3, 13],并非碰撞相关的高压—超高压变质作用,这也印证了雅浦岛弧与加罗林海岭之间并未发生碰撞。
![]() 图 4 雅浦岛弧及周边区域自由空间重力异常(a)与布格重力异常(b)、莫霍面起伏(c)及地磁场强度(d)a、b的数据来源于BGI,d的数据来源于NGDCFigure 4. a: The free air gravity anomalies of the Yap arc and its vicinity; b: the bouguer gravity anomalies; c: The undulation of Moho; d: The geomagnetic field intensitya, b. data from BGI, d. geomagnetism data from NGDC
图 4 雅浦岛弧及周边区域自由空间重力异常(a)与布格重力异常(b)、莫霍面起伏(c)及地磁场强度(d)a、b的数据来源于BGI,d的数据来源于NGDCFigure 4. a: The free air gravity anomalies of the Yap arc and its vicinity; b: the bouguer gravity anomalies; c: The undulation of Moho; d: The geomagnetic field intensitya, b. data from BGI, d. geomagnetism data from NGDC4. 雅浦沟-弧系统俯冲启动时间
雅浦岛弧的岛弧岩浆作用最典型代表为雅浦岛上的Tomil集块岩,根据Map组晚渐新世—中新世的沉积历史[24]推断,Tomil集块岩所代表的岛弧岩浆作用不会早于中新世。九州-帕劳海岭上的始新世岛弧记录表明太平洋板块的俯冲在始新世已经开始[35]。作为太平洋板块向菲律宾海板块之下俯冲导致的弧后盆地,帕里西维拉海盆在约29 Ma开始扩张[16],雅浦岛的变质岩基底则为帕里西维拉海盆NE-SW向扩张(20~15 Ma)形成的洋壳,除此之外在雅浦岛弧上并没有存在其他更老的地质记录。因此,雅浦岛弧的岛弧岩浆事件与其东侧的太平洋板块俯冲时间相悖。
板片俯冲启动时间可以根据俯冲板片形态和俯冲速率进行大致推测。前人根据雅浦岛弧地震数据,推测雅浦岛弧之下的俯冲板片深度为40 km左右[5, 36]。因此,根据最新的雅浦岛弧地震数据以及微地震数据[5],我们沿着剖面a推测了俯冲板片的大致形态(图5)。同时,根据Ulithi岛礁的GPS观测数据[36-37]可知,雅浦海沟的俯冲速率为5 mm/a左右,因此沿着雅浦海沟的板片俯冲启动时间为约12.5 Ma。但这同样与太平洋板块始新世的俯冲以及帕里西维拉海盆渐新世的扩张相悖。在渐新世时期雅浦岛弧为帕里西维拉弧后盆地洋壳的一部分,在这一时期雅浦岛弧东侧还应该存在一个俯冲带对应于太平洋板块的俯冲以及帕里西维拉海盆作为弧后盆地的扩张,直到中新世时期雅浦海沟才形成与俯冲相关的沟-弧体系。由于初始俯冲位置并非雅浦海沟,所以雅浦海沟约12.5 Ma的俯冲起始时间不可信。
地球物理资料显示(图4),雅浦岛弧与加罗林海岭并未直接发生碰撞,二者之间存在一个三角形区域,该区域具有较深的水深、较低的自由空间重力异常以及较薄的地壳厚度。热点导致的地形隆起与周边原始地形区域之间通常为渐变过渡,例如加罗林海岭南部和北部边界的渐变地形变化。然而加罗林海岭与三角形区域之间的弧形边界十分陡峭,地震记录(图1)否定了东部边界切穿岩石圈正断层的存在。导致这种陡峭地形的另外一种可能是俯冲作用,在俯冲过程中俯冲板片上的海山等隆起地形会被上覆板块切割并且拼贴在增生楔区域[38],而上覆板块的巨大压力会导致俯冲板片被压缩而变薄。现今,在雅浦海沟东侧的三角形区域之上不存在上覆板块,然而该三角形区域减薄的地壳以及陡峭的东部边界(图4)均与俯冲板片特征相符合。将三角形区域东部边界假设为起始俯冲带的位置,根据板片形态(图5)以及俯冲速率[11, 26]计算雅浦海沟东侧的太平洋板块俯冲起始时间为29~28 Ma,这与帕里西维拉海盆的弧后扩张开始时间相符合。
5. 讨论
雅浦岛弧的构造解析(图1)以及地球化学(图2)等方面证据表明雅浦沟-弧系统的构造演化经历了3个阶段,分别为晚渐新世以前帕里西维拉海盆弧后扩张以及中温—高温变质作用形成变质基底、晚渐新世—中新世变质基底风化形成Map组沉积层以及中新世发生岛弧岩浆作用。这说明雅浦海沟在中新世才出现,而在此之前雅浦岛弧东部必然存在另外一条俯冲带对应始新世以来太平洋板块的俯冲[35]和渐新世—中新世帕里西维拉海盆的扩张[16]。俯冲起始年龄的计算(图5)则表明这条中新世以前的俯冲带很可能位于加罗林海岭西边界,上覆板块则位于雅浦岛弧和加罗林海岭之间的三角形区域之上,为帕里西维拉海盆的一部分。因此,中新世时期在雅浦岛弧及邻区发生的构造事件最终导致了雅浦海沟的出现以及雅浦海沟东侧上覆板块的消失。
前人根据地形、地球物理以及磁条带等方面的研究证实帕里西维拉海盆在约20 Ma扩张方向由E-W转变为NE-SW[16]。帕里西维拉海盆在20~15 Ma的NE-SW向扩张最直接的表现为S型转换断层、雁列式排布的洋中脊段、NW-SE向的海底构造线[14]。同时洋壳NE-SW向扩张会将两侧洋壳沿着NE-SW方向推离,从而导致帕里西维拉海盆洋中脊东侧和西侧的洋壳发生类似于左旋走滑的相对运动(图1a,图6)。帕里西维拉海盆西侧的洋壳与西菲律宾海盆相连,根据古地磁研究发现西菲律宾海盆在20~15 Ma期间基本不发生向北移,同时其顺时针旋转也基本停止[39-40]。因此,20~15 Ma帕里西维拉海盆洋中脊东侧和西侧洋壳的相对运动更多地表现为海盆东部洋壳向NE方向推离。而海盆东部洋壳向NE方向移动会导致在帕里西维拉海盆南部原本已经俯冲的部分洋壳重新暴露,对应于加罗林海岭和雅浦岛弧之间的三角形区域,而该三角形区域东侧的弧形边界也与西马里亚纳海岭南部的弧形岛弧形态相符合(图1)。帕里西维拉海盆东部洋壳向NE方向移动另外一方面结果则是帕里西维拉海盆南部的一部分扩张中心暴露出来。太平洋板块和加罗林板块向NW方向连续的俯冲则导致帕里西维拉海盆南部暴露的部分洋中脊转变成了雅浦海沟。
雅浦沟-弧系统与西太平洋其他的沟-弧-盆体系存在很大的不同,主要表现在很少的岛弧岩浆作用、极短的沟-弧距离以及弧前增生楔的缺失[3-8]。板块构造理论中,增生楔是由板块俯冲过程中上覆板块切削下来的沉积物以及岩石等在弧前区域堆积形成。俯冲到一定深度的板块在温度和压力作用下脱水形成流体,而流体会导致地幔岩石熔点降低形成向上的岛弧岩浆。俯冲板片在俯冲初期角度较小,随着俯冲深度的加深,俯冲角度逐渐变陡,这也是典型沟-弧-盆体系中具有一定的沟-弧距离的原因。雅浦海沟是由洋中脊暴露而产生的,其东侧的三角形区域为原本已经俯冲的板块,因而在雅浦海沟区域的俯冲板块缺少了俯冲初期的较小的俯冲角度(图5),导致在距离岛弧较近的位置就达到俯冲板片脱水的深度,形成了雅浦沟-弧系统很短的沟-弧距离。雅浦岛弧的弧前增生楔缺失则与东侧部分已俯冲的洋壳重新暴露有关,由于重新暴露的洋壳之上没有沉积物,加上雅浦海沟较低的俯冲速率[11, 37],在雅浦岛弧的弧前区域很难形成增生楔。同时,较低的俯冲速率[11, 37]也是导致岛弧岩浆作用较少的原因。
雅浦沟-弧系统为帕里西维拉海盆的一部分,帕里西维拉海盆的扩张过程直接控制了雅浦沟-弧系统的产生以及构造演化。雅浦沟-弧系统西侧具有N-S向构造线的洋壳为帕里西维拉海盆在29~20 Ma期间E-W向扩张的产物。在这一时期,马里亚纳俯冲带、西马里亚纳海岭以及雅浦岛弧西侧N-S向构造线的洋壳组成了帕里西维拉海盆南部正常的沟-弧-盆体系,马里亚纳俯冲带位于现今雅浦海沟东侧三角形区域的东部边界位置。此时,加罗林海岭与帕里西维拉海盆之间的碰撞发生在西马里亚纳海岭南部(图6a)。在20~15 Ma期间,帕里西维拉海盆的扩张方向变为NE-SW向。扩张方向的改变将帕里西维拉海盆东侧的洋壳向NE方向推离,帕里西维拉海盆南部的部分洋中脊暴露形成了雅浦俯冲带(图6b)。俯冲伴随的岛弧岩浆作用则导致了雅浦岛弧的隆升以及雅浦岛上Tomil集块岩为代表的岛弧岩浆作用,而雅浦组的角山岩相-绿片岩相变质岩则可能为岛弧隆升过程中暴露的深部地壳。在这一时期,帕里西维拉海盆南侧已经俯冲的板片也由于帕里西维拉海盆东侧洋壳的NE方向移动而重新暴露,形成了现今雅浦海沟东侧的三角形区域(图6b)。
6. 结论
雅浦岛弧原本为帕里西维拉海盆NE-SW向扩张形成的洋壳。帕里西维拉海盆在20~15 Ma的NE-SW向扩张使海盆东西两侧洋壳发生相对移动,这导致了帕里西维拉海盆南部的部分洋中脊段暴露而转变为雅浦海沟。同时雅浦海沟东侧部分已经俯冲的板片重新暴露形成了一个地球物理特征十分特殊的三角形区域。
-
图 3 表层沉积物热液成因矿物中粗颗粒(>1 mm)和细颗粒(<1 mm)的占比及细颗粒热液成因矿物的丰度与喷口距离变化的关系图
Figure 3. The weight percentage of coarse size(>1 mm)and fine size(<1 mm)hydrothermal minerals in the surface sediments and the variation of abundances of fine size hydrothermal minerals ( <1 mm ) with distance from active venting site
The bar graph represents the weight percentage of minerals for two grain sizes in metalliferous sediments
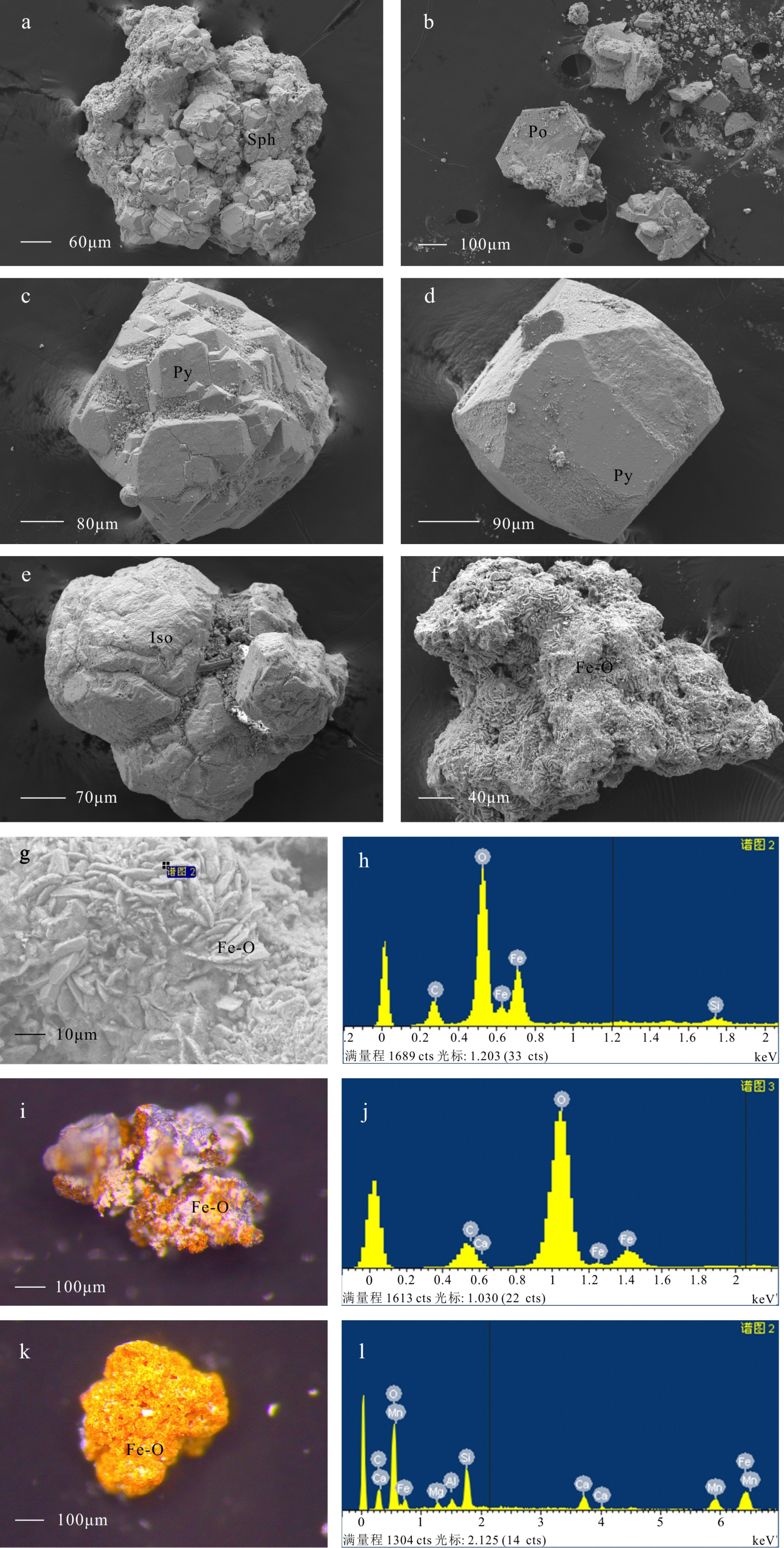
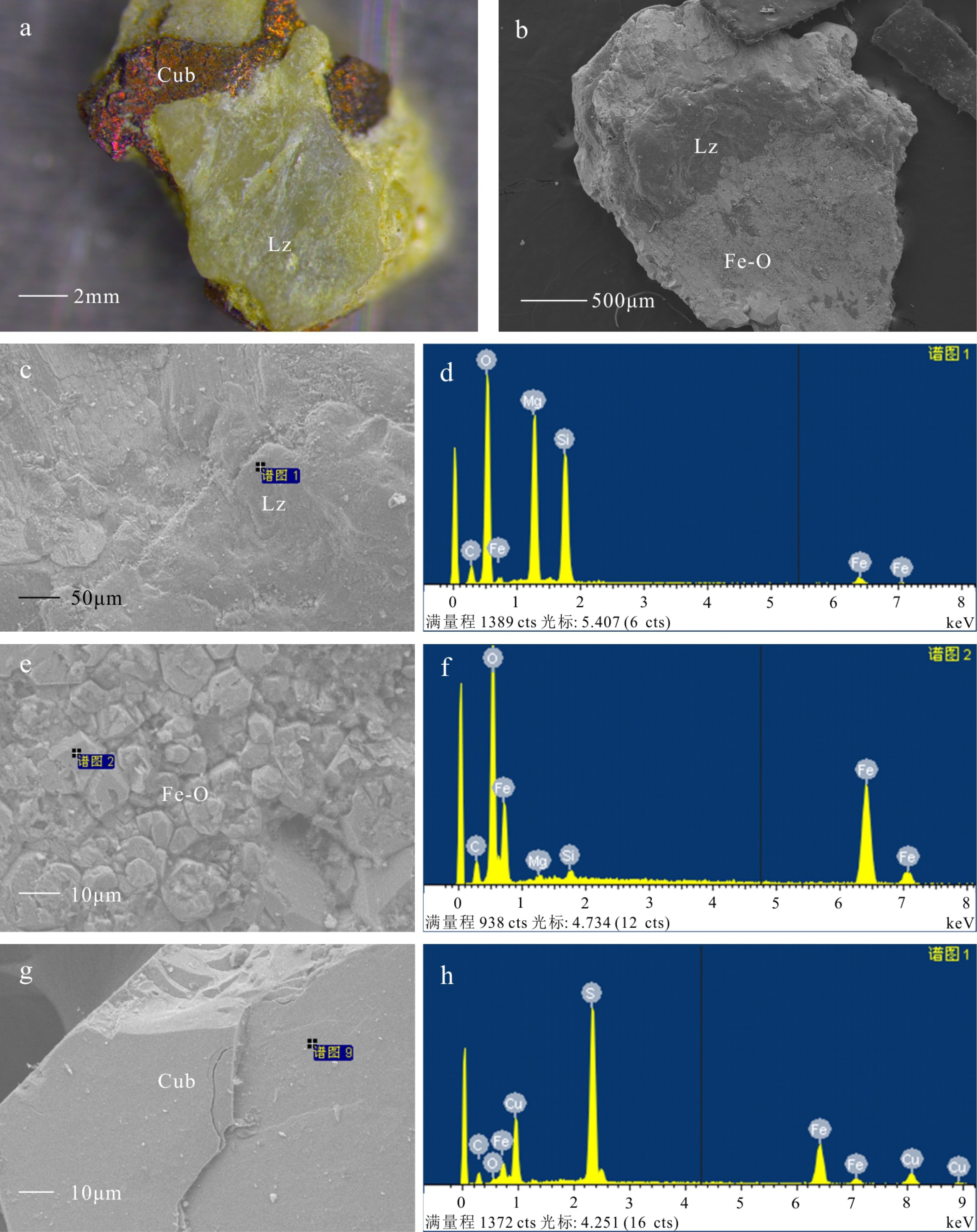
图 6 沉积物中粒径<1mm的热液成因矿物典型扫描电镜形貌和能谱图
a-f. 33I-TVG07和26I-TVG05站位粒径<1 mm的硫化物矿物和氧化物矿物,g和h. 分别为f的局部放大图像及其对应能谱图,i-l. 分别为26I-TVG04和33I-TVG11站位铁的氢氧化物和能谱图,a-f和g. 扫描电子显微镜拍摄的二次电子图像,i和k. 双目体视显微镜镜下图像。Sph-闪锌矿,Po-磁黄铁矿,Py-黄铁矿,Iso-等轴古巴矿,Fe-O-铁的(氢)氧化物。
Figure 6. SEM Photos and EDS data of typical hydrothermal minerals in sediments with grain size <1 mm
a-f. sulfide and oxide minerals at station 33I-TVG07 and 26I-TVG05,g. enlargement of image f and h is corresponding EDS figure,i-l. oxide minerals at station 26I-TVG04 and 33I-TVG11, a-f and g. SEM images, i and k. images taken by optical microscope.
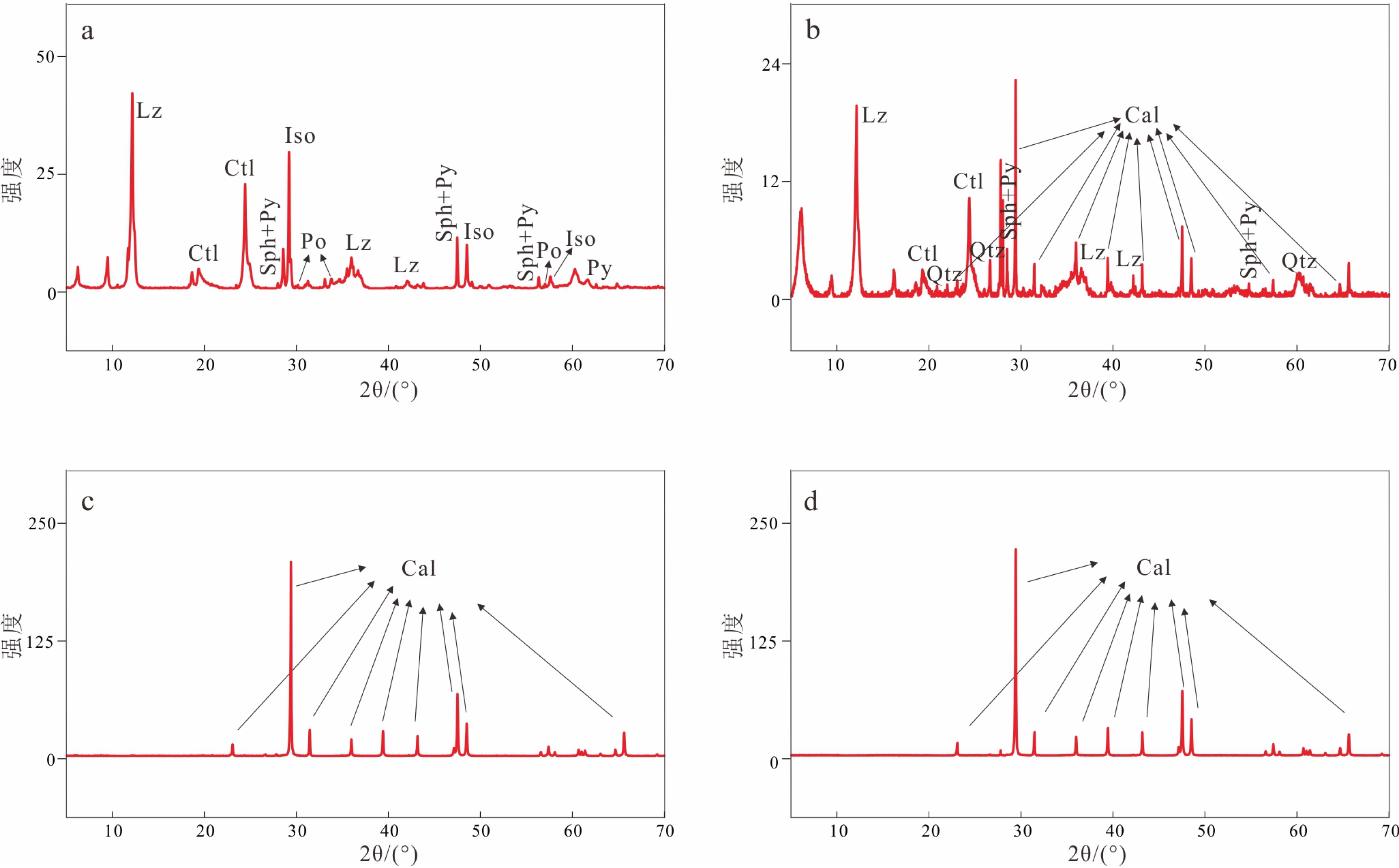
图 4 各站位沉积物样品中粒径<1 mm矿物的X射线衍射分析图谱
a. 33I-TVG07站位,b. 26I-TVG05站位,c. 26I-TVG04站位,d. 33I-TVG11站位。Iso-等轴古巴矿;Sph-闪锌矿,Py-黄铁矿,Po-磁黄铁矿,Lz-利蛇纹石,Ctl-纤蛇纹石,Cal-方解石,Qtz-石英。
Figure 4. XRD patterns of sediments ( grain size <1 mm) from different sampling station
a. station 33I-TVG07,b. station 26I-TVG05, c. station 26I-TVG04,d. station 33I-TVG11.
图 5 沉积物中粒径>1 mm的碎屑矿物的典型显微照片和能谱图
a和b. 33I-TVG07站位粒径>1 mm的矿物集合体,c-h. a和b的局部放大图像及对应能谱图,a. 双目体视显微镜镜下图像,b、c、e和g. 扫描电子显微镜拍摄的二次电子图像;Cub-古巴矿,Lz-利蛇纹石,Fe-O-铁的(氢)氧化物。
Figure 5. Microphotos of typical minerals and their EDS data in sediments with grain size >1 mm
a, b. mineral aggregates from station 33I-TVG07 (grain size >1 mm),c-h. enlargement of image a or b and corresponding EDS figures,a. images taken by optical microscope,b, c, e and g. SEM images.
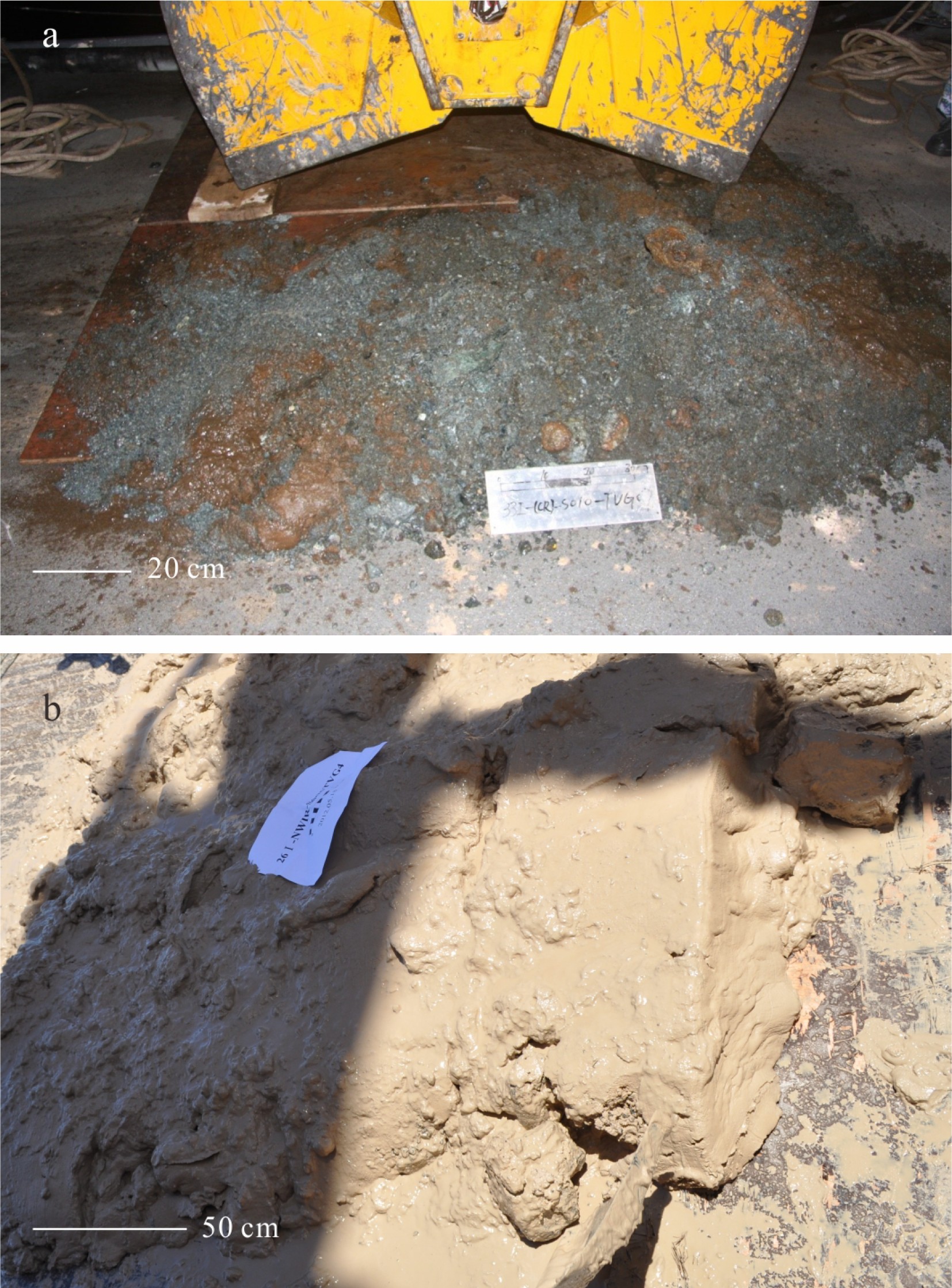
表 1 采样位置信息
Table 1 The coordinates of sampling stations
站位号 纬度(N) 经度(E) 水深/m 采样位置 33I-TVG07 3.68 63.83° 3 504 活动热液喷口处 26I-TVG05 3.69° 63.83° 3 477 活动热液喷口西南侧0.22 km 26I-TVG04 3.70° 63.82° 3 611 活动热液喷口西北侧1.84 km 33I-TVG11 3.66° 63.79° 2 789 活动热液喷口西南侧6.05 km 表 2 粒径<1 mm沉积物中主要矿物半定量统计分析
Table 2 Abundance of major minerals in sediments with grain size <1 mm
矿物名称 理想化学式 近端 远端 33I-TVG07 26I-TVG05 26I-TVG04 33I-TVG11 金属硫化物 磁黄铁矿 Fe1-XS ++ + 黄铁矿 FeS2 ++ ++ 闪锌矿 (Zn,Fe)S ++ + 古巴矿/等轴古巴矿 CuFe2S3 ++ + 金属氧化物 铁的氧化物/氢氧化物 Fe2O3/Fe3O4/Fe-(Mn)-OOH ++ ++ + + 围岩碎屑 +++ +++ 钙质生物碎屑 + + +++ +++ 注:+++ 代表数量百分比>70%,++ 代表数量百分比1%~10%,+ 代表数量百分比<1%。 -
[1] Pirajno F. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2009.
[2] Fouquet Y, Cambon P, Etoubleau J, et al. Geodiversity of hydrothermal processes along the mid-atlantic ridge and ultramafic-hosted mineralization: A new type of oceanic Cu-Zn-Co-Au volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit[M]//Rona P A, Devey C W, Dyment J, et al. Diversity of Hydrothermal Systems on Slow Spreading Ocean Ridges. Washington, D.C.: AGU, 2010: 321-367.
[3] Wang Y J, Han X Q, Petersen S, et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of hydrothermal precipitates from kairei hydrothermal field, Central Indian Ridge [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 354: 69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.05.003
[4] Firstova A, Stepanova T, Cherkashov G, et al. Composition and formation of gabbro-peridotite hosted seafloor massive sulfide deposits from the ashadze-1 hydrothermal field, Mid-Atlantic Ridge [J]. Minerals, 2016, 6(1): 19. doi: 10.3390/min6010019
[5] Mills R, Elderfield H, Thomson J. A dual origin for the hydrothermal component in a metalliferous sediment core from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1993, 98(B6): 9671-9681. doi: 10.1029/92JB01414
[6] Mills R A, Elderfield H. Rare earth element geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from the Active TAG Mound, 26°N Mid-Atlantic Ridge [J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3511-3524. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00224-N
[7] German C R, Barreiro B A, Higgs N C, et al. Seawater-metasomatism in hydrothermal sediments (Escanaba Trough, Northeast Pacific) [J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 119(1-4): 175-190. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00052-A
[8] German C R, Seyfried W E Jr. Hydrothermal processes[M]//Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. New York: Elsevier, 2014, 8: 191-233.
[9] Gurvich E G. Metalliferous Sediments of the World Ocean[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2006.
[10] Andreani M, Escartin J, Delacour A, et al. Tectonic structure, lithology, and hydrothermal signature of the Rainbow massif (Mid-Atlantic Ridge 36°14′N) [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(9): 3543-3571. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005269
[11] Dias Á S, Barriga F J A S. Mineralogy and geochemistry of hydrothermal sediments from the serpentinite-hosted saldanha hydrothermal field (36°34′N; 33°26′W) at MAR [J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 225(1-4): 157-175. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.07.013
[12] Gràcia E, Charlou J L, Radford-Knoery J, et al. Non-transform offsets along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge south of the Azores (38°N-34°N): Ultramafic exposures and hosting of hydrothermal vents [J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 177(1-2): 89-103.
[13] 李家彪. 现代海底热液硫化物成矿地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017. LI Jiabiao. Modern Seafloor Hydrothermal Mineralization[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017.
[14] Barrett T J, Taylor P N, Lugoqski J. Metalliferous sediments from DSDP Leg 92: The East Pacific Rise transect [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(9): 2241-2253. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90278-X
[15] Hepburn L E. Hydrothermal sediment geochemistry south of the Antarctic Polar Front[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Southampton, 2015.
[16] Mills R A, Elderfield H. Hydrothermal activity and the geochemistry of metalliferous sediment[M]//Humphris S E, Zierenberg R A, Mullineaux L S, et al. Seafloor Hydrothermal Systems: Physical, Chemical, Biological, and Geological Interactions. Washington, D.C., USA: American Geophysical Union, 1995.
[17] Han X, Wang Y, Li X. First ultramafic-hosted hydrothermal sulfide deposit discovered on the Carlsberg Ridge, Northwest Indian Ocean[C]//Proceedings of the the Third InterRidge Theoretical Insitute. Hangzhou, 2015.
[18] 邱中炎, 韩喜球, 王叶剑, 等. 西北印度洋卡尔斯伯格脊沉积物特征及其找矿启示[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(S1):776. [QIU Zhongyan, HAN Xiqiu, WANG Yejian, et al. The characteristics of sediments in Carlsberg Ridge, Northwest Indian Ocean and the implications for prospection [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(S1): 776. [19] Kamesh Raju K A, Chaubey A K, Amarnath D, et al. Morphotectonics of the Carlsberg Ridge between 62°20′ and 66°20′E, Northwest Indian Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 252(3-4): 120-8. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.03.016
[20] 韩喜球, 吴招才, 裘碧波. 西北印度洋Carlsberg脊的分段性及其构造地貌特征——中国大洋24航次调查成果介绍[C]//第二届深海研究与地球系统科学学术研讨会论文集. 上海: 同济大学, 2012: 259-259. HAN Xiqiu, WU Zhaocai, QIU Bibo. Segmentation of the Carlsberg Ridge in the Northwest Indian Ocean — Report for Chinese DY24th Cruise[C]. 2012.
[21] Ray D, Misra S, Banerjee R. Geochemical variability of MORBs along slow to intermediate spreading Carlsberg-Central Indian Ridge, Indian Ocean [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 70.
[22] 余星, 韩喜球, 邱中炎, 等. 西北印度洋脊的厘定及其地质构造特征[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(2):626-639. [YU Xing, HAN Xiqiu, QIU Zhongyan, et al. Definition of Northwest Indian Ridge and its geologic and tectonic signatures [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(2): 626-639. [23] 韩喜球, 王叶剑, 李洪林, 等. 国际海底区域资源研究开发“十二五”课题课题研究报告[R].中国大洋协会办公室, 2015. HAN Xiqiu, WANG Yejian, LI Honglin, et al. Report of the 12th five-year plan on the research and development of resources in the international seafloor[R]. 2015.
[24] Folk R L. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks[M]. Austin, Texas: Hemphill Publishing Company, 1980.
[25] Tucker M E. Sedimentary Rocks in the Field[M]. 3rd ed. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd., 2003.
[26] Popoola S O, Han X Q, Wang Y J, et al. Geochemical investigations of Fe-Si-Mn oxyhydroxides deposits in wocan hydrothermal field on the slow-spreading Carlsberg Ridge, Indian Ocean: Constraints on their types and origin [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(1): 19.
[27] Humphris S E, Herzig P M, Miller D J, et al. The internal structure of an active sea-floor massive sulphide deposit [J]. Nature, 1995, 377(6551): 713-716. doi: 10.1038/377713a0
[28] Tivey M K, Humphris S E, Thompson G, et al. Deducing patterns of fluid flow and mixing within the TAG active hydrothermal mound using mineralogical and geochemical data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1995, 100(B7): 12527-12555. doi: 10.1029/95JB00610
[29] Feely R A, Geiselman T L, Baker E T, et al. Distribution and composition of hydrothermal plume particles from the ASHES Vent Field at Axial Volcano, Juan de Fuca Ridge [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1990, 95(B8): 12855-12873. doi: 10.1029/JB095iB08p12855
[30] German C R, Campbell A C, Edmond J M. Hydrothermal scavenging at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Modification of trace element dissolved fluxes [J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 107(1): 101-114.
[31] Rudnicki M D, Elderfield H. A chemical model of the buoyant and neutrally buoyant plume above the TAG Vent Field, 26 degrees N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(13): 2939-2957. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90285-5
[32] Feely R A, Massoth G J, Trefry J H, et al. Composition and sedimentation of hydrothermal plume particles from North Cleft Segment, Juan de Fuca Ridge [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1994, 99(B3): 4985-5006. doi: 10.1029/93JB02509
[33] René C, Cervelle B, Cesbron F, et al. Isocubanite, a new definition of the cubic polymorph of cubanite CuFe2S3 [J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1988, 52(367): 509-514. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1988.052.367.10
[34] Jamieson J W, Hannington M D, Petersen S, et al. Volcanogenic massive sulfides[M]//Harff J, Meschede M, Petersen S, et al. Encyclopedia of Marine Geosciences. Dordrecht: Springer, 2014: 1-9.
[35] Vaughan D J, Craig J R. Mineral Chemistry of Metal Sulfides[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1978.




 下载:
下载: