Physical and chemical characteristics of surface sand in different types of dunes in Qingtu Lake, Gansu, NW China, and their environmental implications
-
摘要:
沙丘表层沉积物的理化特征在揭示风沙的来源、沉积过程、风化作用等方面具有重要作用。本研究采用野外实地采样和实验室分析方法分析了甘肃青土湖地区不同类型沙丘表层沉积物的粒度和地球化学特征。结果表明:(1)青土湖地区沙丘表层沉积物以细砂为优势粒级,平均含量达72.08%,其次为极细砂,黏粒成分很少。频率分布曲线为单峰分布,概率累积曲线表现为三段式,反映出沉积环境较为稳定。(2)研究区沙丘表层沉积物常量元素以SiO2为主,平均含量为76.40%,其次为Al2O3和CaO,平均含量分别为5.05%、3.74%。微量元素以Cr、Mn、Co、Sr、Ba、Ti、Ce和P为主,平均含量均>100 mg/L。(3)Y、Zr和Y/Zr、Rb/Zr双变量图、A-CNK-FM图解表明巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠为其沙源。风沙搬运过程中的磨蚀、风选作用是研究区富集Fe、Mg元素的主要原因。此外,下伏湖相沉积物就地起砂,石羊河冲积物也为其提供了部分沙物质。(4)A-CN-K和A-CNK-FM三角模式图表明研究区风化程度较弱,处于初期脱Na、Ca阶段。在沙丘固定过程中成土作用增强但淋溶作用减小,这是由于植被的影响导致半固定、固定沙丘Na、Ca含量较高。
Abstract:The physical and chemical imprints of surface sediments bear key information of the origination, sedimentation, and weathering of sand. Field sampling and laboratory analysis were conducted to investigate the grain size and geochemical characteristics of surface sediment with various types of sand in the Qingtu Lake, Gansu, NW China. Results show that the surface sediment is dominated by fine sand, taking an average content of 72.08%, followed by very fine sand and a minimal amount of clay. The frequency distribution curve exhibits a unimodal distribution, while the cumulative probability curve shows a three-portion pattern, indicating a relatively stable sediment environment. The predominant constant elements are mainly SiO2, occupying 76.40% in average and then Al2O3 and CaO, for 5.05% and 3.74%, respectively. The trace elements consist mainly of Cr, Mn, Co, Sr, Ba, Ti, Ce, and P, in average concentration of over 100 mg/L. The two-variable chart (Y verse Zr, Y/Zr verse Rb/Zr) and the A-CNK-FM graph demonstrate that the Badain Jaran Desert and Tengger Desert were key sand sources for the study area. The abrasion and wind erosion in sand transportation are the main factors affecting the distribution of Fe and Mg elements. In addition, lacustrine and alluvial deposits of the Shiyang River also provided a part of the sand source. The ternary diagrams A-CN-K and A-CNK-FM indicate that the study area experienced weaker wind levels during the early phases of de-Na and de-Ca processes. However, in the progress of sand fixation, pedogenesis was enhanced while eluviation was reduced due to the influence of vegetation, which caused semi-fixed and fixed sand with higher Na and Ca contents.
-
Keywords:
- sand dune /
- grain size /
- geochemical elements /
- wind deposit /
- weathering /
- Qingtu Lake
-
我国是沙漠化最为严重的国家之一,沙漠化土地占国土面积的26.81%,对人类的健康及生产生活造成严重危害[1-2]。沙丘是沙漠化土地中的一种主要地貌类型,在半干旱地区,即使在相同的气候条件和相同的地理区域内,沙丘可以呈现出流动、半固定、固定等不同状态[3-5]。沙丘的固定是沙漠化治理的主要途径。流动沙丘被草方格、沙障固定可转变为固定沙丘,地表结皮的发育会导致表层沉积物的理化性质发生显著变化[6-7]。因此,研究不同类型沙丘表层沉积物的理化性质指示的环境意义对于沙漠化防治具有重要意义[8]。
粒度特征能够反映风力对物源区物质的搬运和分选作用,以及地形、植被等对风沙流运移过程的改变,而地表沉积物中地球化学元素特征与物源区母岩的化学组成、物理化学风化、搬运、分选等相关[9-11],因此粒度和沉积物地球化学特征在揭示表层沉积物的物质来源、风化程度、沉积过程、古环境变化重建方面发挥着重要的作用[12-14]。
甘肃青土湖位于巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠的交汇处,其西南为民勤绿洲,在自然因素和人类活动的影响下荒漠和绿洲面积此消彼长,生态环境极其脆弱,人地矛盾突出[15-16]。目前学者已开展了对该区沙源及搬运途径[17]、土壤理化性质[18-19]的研究,但仍然不够全面。Ren等[17]通过地球化学元素特征差异分析了青土湖地区的沙源,但缺乏粒度方面的证据。关于沙丘粒度特征的研究多集中于灌丛沙堆[18-19],缺乏与流动沙丘的对比。此外,关于不同类型沙丘地球化学元素特征的对比研究及其反映的化学风化也较为缺乏。本文通过选取该地区具有代表性的流动沙丘(LDSQ)、半固定沙丘(BGDSQ)和固定沙丘(GDSQ),对其表沙的粒度和地球化学元素特征进行分析,揭示不同类型沙丘的形成及风化情况,可为理解沉积物性质与沙丘固定过程的关系提供必要的线索,研究结果对青土湖地区沙漠化治理和生态环境恢复具有重要意义。
1. 研究区概况与数据来源
1.1 研究区概况
青土湖位于甘肃省民勤县,是石羊河尾闾湖,也是腾格里沙漠和巴丹吉林沙漠之间的生态屏障(图1)。研究区(39°8′1′′~39°8′5′′N、103°38′12′′~103°38′27′′E)位于青土湖东侧,民勤绿洲和沙漠过渡带。该区域为温带大陆性干旱荒漠气候,年平均气温7.8°C,无霜期176 d;年平均降水量110 mm,集中在每年的6月中旬至9月中旬,约占全年降水量的80%;年平均蒸发量为2 420 mm[18]。主导风向为西北风,年平均风速2.5 m·s−1,年平均大风日数25.1 d,年平均沙尘暴日数25.6 d,年≥8级大风日数为27.8 d[20]。该地区的地貌特征是在湖相沉积基底上交错分布流动、半固定、固定沙丘和丘间低地。地带性土壤为灰棕漠土,非地带性土壤为草甸沼泽土和风沙土[21]。植被类型为荒漠植被,主要植被类型为人工梭梭林,唐古特白刺灌丛、沙蒿、盐生草、盐爪爪群落和芦苇群落等[22]。
1.2 样品采集与研究方法
1.2.1 样品采集
在研究区选择了4个典型沙丘,包括2个流动沙丘、1个半固定沙丘和1个固定沙丘。每个沙丘采集表层沉积物样品,从迎风坡到背风坡,采样间距为2 m,采样深度均在表层以下5 cm,样品在空间分布上皆具有连续性(表1)。采样点分布如图1所示。
表 1 不同类型沙丘的取样信息Table 1. Information of sampling from different types of dunes沙丘类型 位置 海拔/m 高度/m 底面直径/m 取样部位及编号 样品数/个 LDSQ1 39°8′1″N、103°38′27″E 1260 8 30 迎风坡:1-1、1-2、1-3、1-4、1-5
丘顶:1-6
背风坡:1-7、1-8、1-9、1-1010 LDSQ2 39°8′2″N、103°38′25″E 1265 6 20 迎风坡 :2-1、2-2
丘顶:2-3
背风坡:2-4、2-55 BGDSQ 39°8′5″N、103°38′14″E 1258.1 2 5 迎风坡:3-1、3-2
丘顶:3-33 GDSQ 39°8′4″N、103°38′12″E 1257.2 4.6 6 迎风坡:4-1、4-2
丘顶:4-3
背风坡:4-4、4-55 1.2.2 实验分析
表层沙粒度和地球化学元素测试实验均在西北师范大学地理与环境科学学院土壤地理学实验室及样品处理室进行。将LDSQ1、LDSQ2、BGDSQ、GDSQ样品进行粒度实验,称取3~5 g样品置入烧杯,加10 mL浓度为30%的H2O2,在电热板上煮沸至其与样品中的有机质完全反应;加10 mL浓度为10%的HCl,煮沸至无气泡产生,去除碳酸盐类杂质;待样品冷却后,加满蒸馏水,静置12 h后通过虹吸法抽掉上层清液,重复此步骤至溶液pH值达到7;加入10 ml浓度为0.05 mol/L的(NaPO3)6,振荡7~8 min,使砂粒完全分散为单粒[23]。采用英国Malvern公司的Mastersizer3000型激光粒度仪进行分析测试,仪器测量范围为0.02~3500 μm,运用GRADISTAT粒度分析软件对沙丘表层沉积物粒度测验数据计算得出平均粒径(Mz)、分选系数(σ)、偏度(SK)、峰度(Kg)4个粒度参数[24]。粒度分级依据《风沙地貌学》[25]中的原则进行划分,分为黏土(<0.004 mm)、粉砂(0.004~0.063 mm)、极细砂(0.063~0.125 mm)、细砂(0.125~0.25 mm)、中砂(0.25~0.5 mm)、粗砂(>0.5 mm)6个粒级。
将LDSQ1、BGDSQ、GDSQ样品进行地球化学元素实验,在干燥无杂的室内自然风干,研磨样品前过筛去除树叶、树根和杂质,研磨至<75 μm(过200目筛)。称取4 g研磨后的样品,采用压样机以25 t的压力压30 s将其制成加以硼酸固定的同心圆饼状标样。采用荷兰帕纳科公司生产的帕纳科Epsilon 4台式能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪进行常量元素和微量元素含量的测定[26]。常量元素包括SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO、MgO、K2O、Na2O,用%表示,微量元素包括La、V、Cr、Mn、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Sr、Pb、Ba、Ti、Y、Zr、Rb、Nb、Ga、Ce、P等,单位为mg/L。
2. 结果分析
2.1 沙丘表层沉积物粒度特征
2.1.1 粒度组成与粒度参数
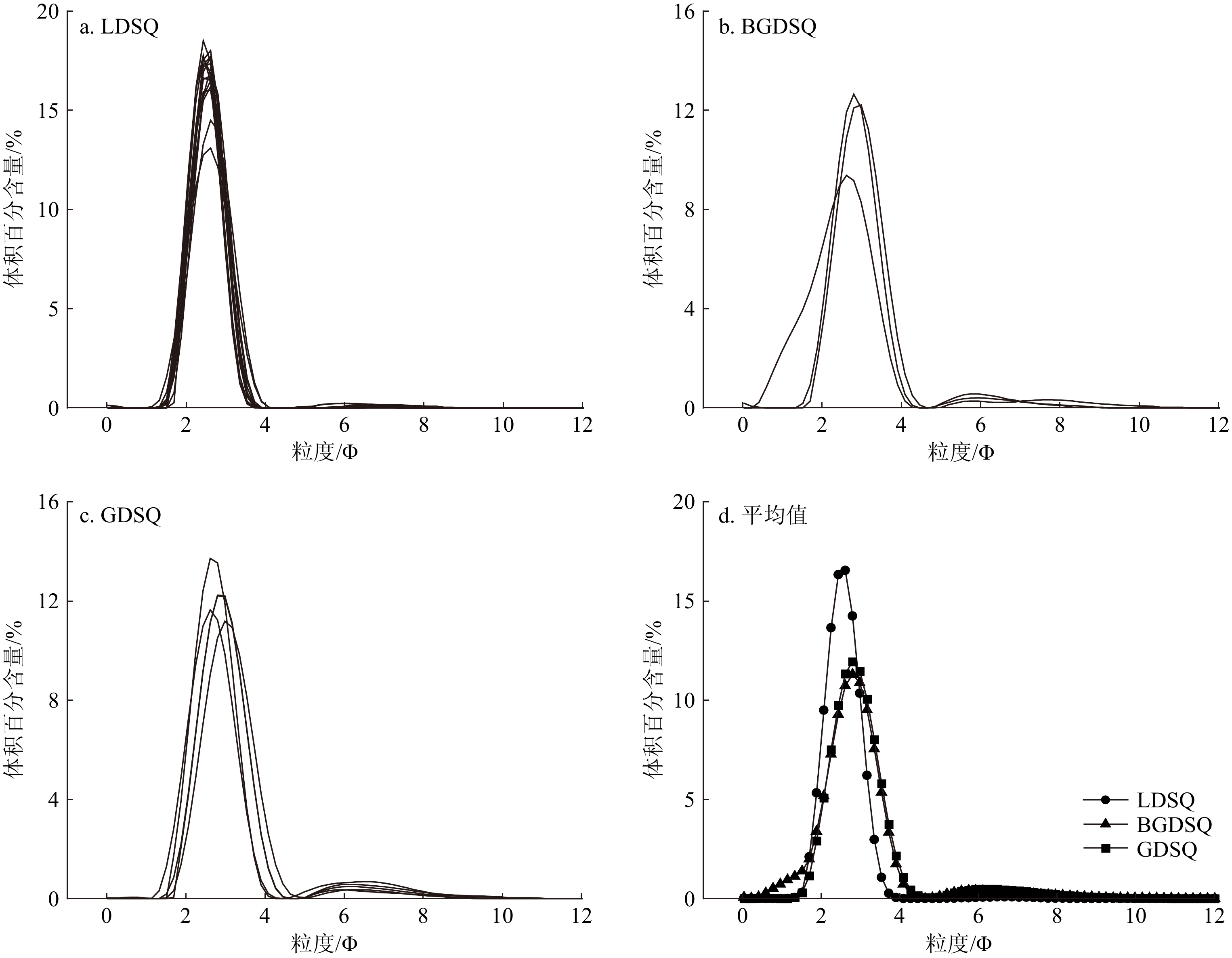
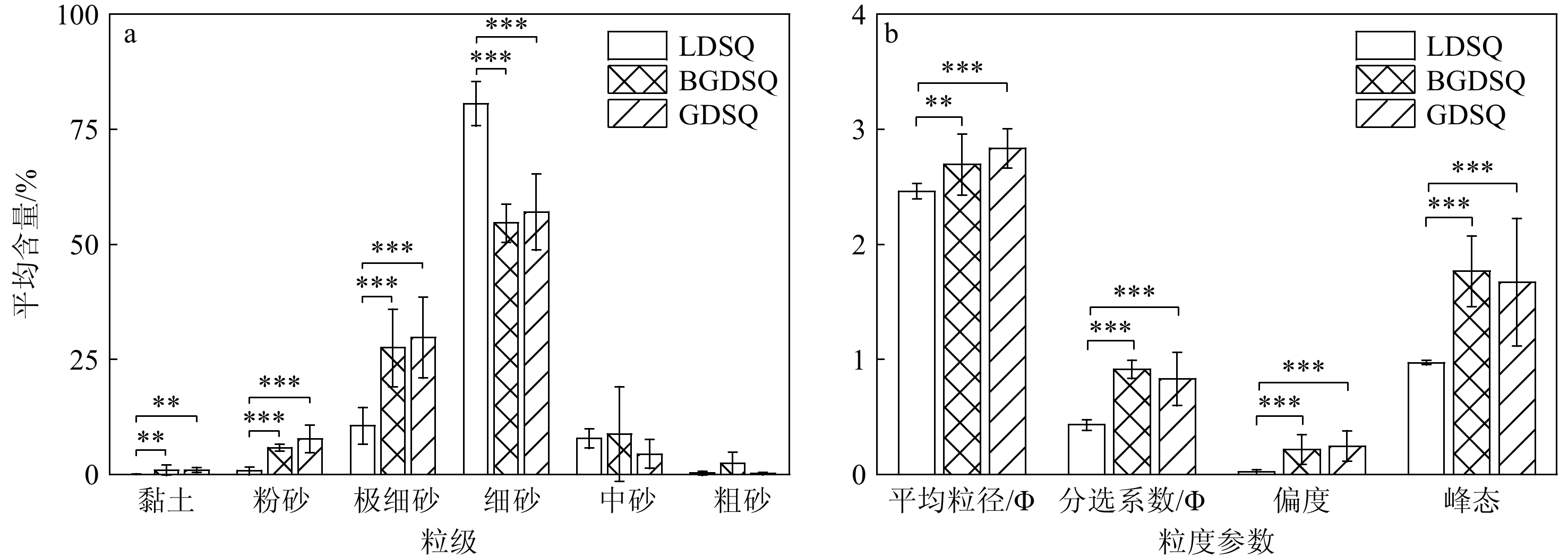
粒度组成和参数结果(表2)表明,流动沙丘以细砂为主,平均含量为80.59%,其次为极细砂和中砂,平均含量分别为10.56%和7.79%,粉砂、粗砂和黏土含量极少,平均含量之和约为1.06%;半固定沙丘以细砂和极细砂为主,两者平均含量分别为54.62%和27.47%,中砂、粉砂和粗砂含量较少,平均含量之和为16.98%,黏土含量最少,只占0.90%;固定沙丘以细砂和极细砂为主,平均含量分别为57.04%和29.75%,粉砂和中砂平均含量之和为12.12%,黏土和粗砂含量最少,平均含量之和为1.08%。从流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘,表层沉积物平均粒径逐渐变小,分选性变差,偏态由近对称逐渐变为正偏,峰态由中等峰态逐渐变为很窄峰态。
表 2 不同类型沙丘表层沉积物粒度组成及粒度参数Table 2. Composition and parameters of grain size in surface sediments from different types of dunes沙丘类型 各粒级含量/% Mz/Φ σ/Φ Sk Kg 黏土 粉砂 极细砂 细砂 中砂 粗砂 LDSQ 0.03 0.78 10.56 80.59 7.79 0.25 2.46 0.43 0.02 0.97 BGDSQ 0.90 5.83 27.47 54.62 8.79 2.36 2.69 0.91 0.21 1.77 GDSQ 0.93 7.70 29.75 57.04 4.42 0.15 2.83 0.83 0.24 1.67 平均值 0.34 2.94 16.94 72.08 7.19 0.51 2.57 0.58 0.09 1.23 2.1.2 沙丘的粒配曲线
频率分布曲线表明(图2),流动沙丘98%的砂粒均集中分布在1.69~3.53 Φ之间,样品均呈现单峰分布(图2a),表明搬运或沉积过程稳定。半固定沙丘93%的砂粒集中分布在0.59~4.27 Φ之间,样品在6Φ附近有一个微弱次峰(图2b)。固定沙丘93%的砂粒集中分布在1.51~4.45 Φ之间,6.5 Φ附近微弱次峰的存在代表了不同的搬运和沉积过程(图2c)。从流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘,频率分布曲线的峰值呈现减小趋势(对应含量分别为16.46%、11.30%和11.94%),分布范围变大,众数粒径逐渐偏向较大的Φ值(分别为2.61、2.80和2.80 Φ),表明沙丘固定过程中表层沉积物砂粒逐渐变细、分选性逐渐变差(图2d)。
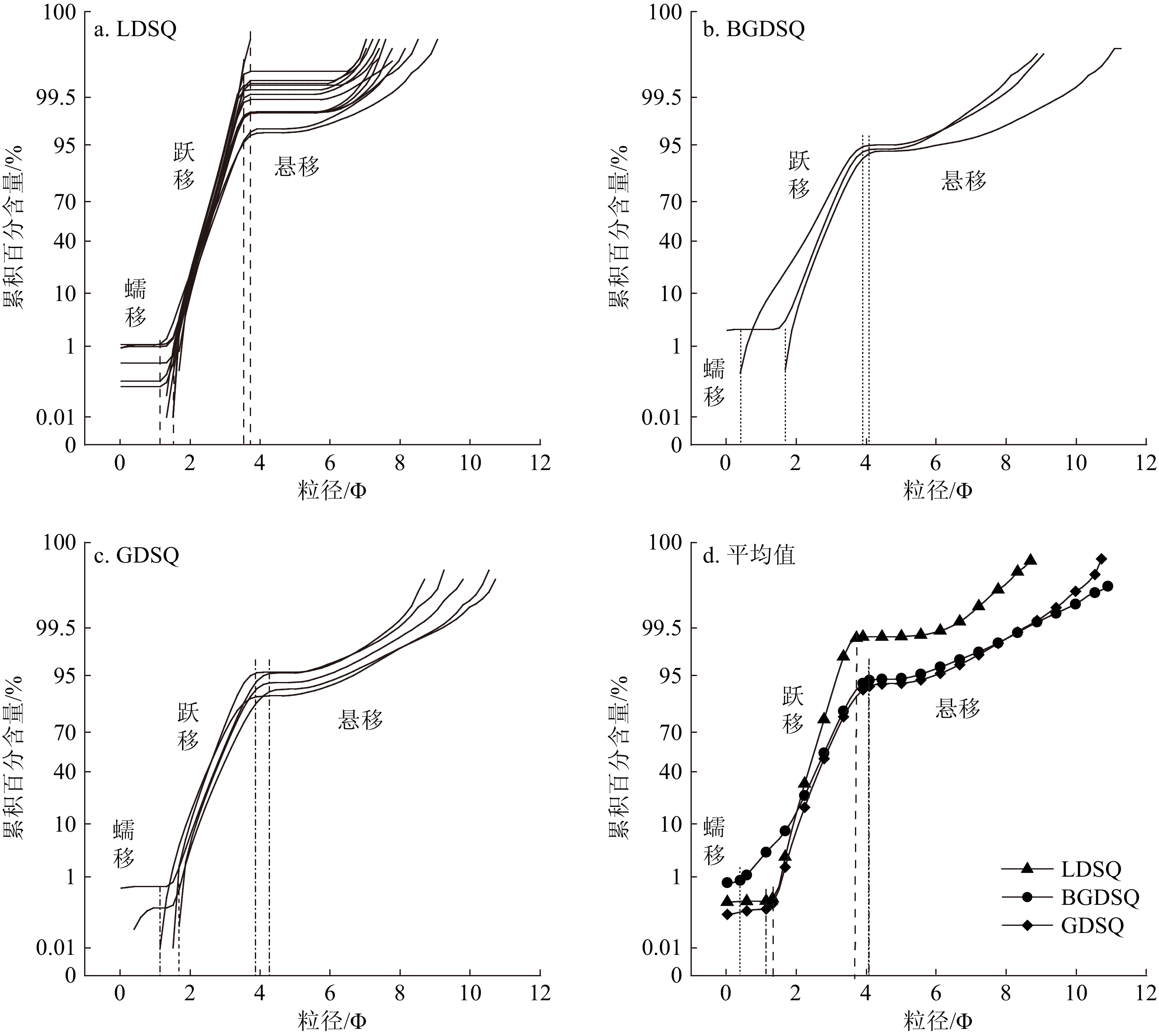
不同类型沙丘表层沉积物包括蠕移组分、跃移组分和悬移组分,概率累积曲线显示(图3),流动沙丘沉积物概率曲线分别在1.14~1.51 Φ、3.53~3.72 Φ处被截断;半固定沙丘沉积物概率曲线在0.40~1.69 Φ、3.90~4.08 Φ处发生转折;固定沙丘沉积物概率累积曲线转折点在约1.14~1.69 Φ、3.90~4.27 Φ处。总体上,沙丘固定过程中跃移组分减少,悬移组分增加;曲线斜率逐渐变小,表明分选逐渐变差。
2.2 沙丘表层沉积物地球化学元素特征
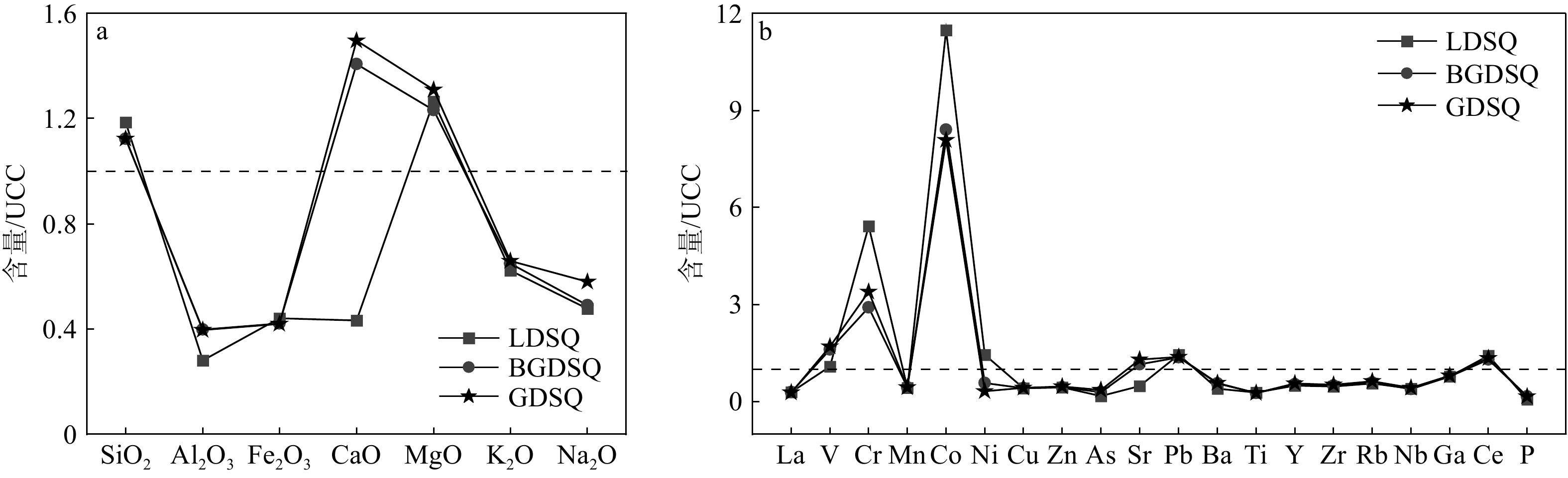
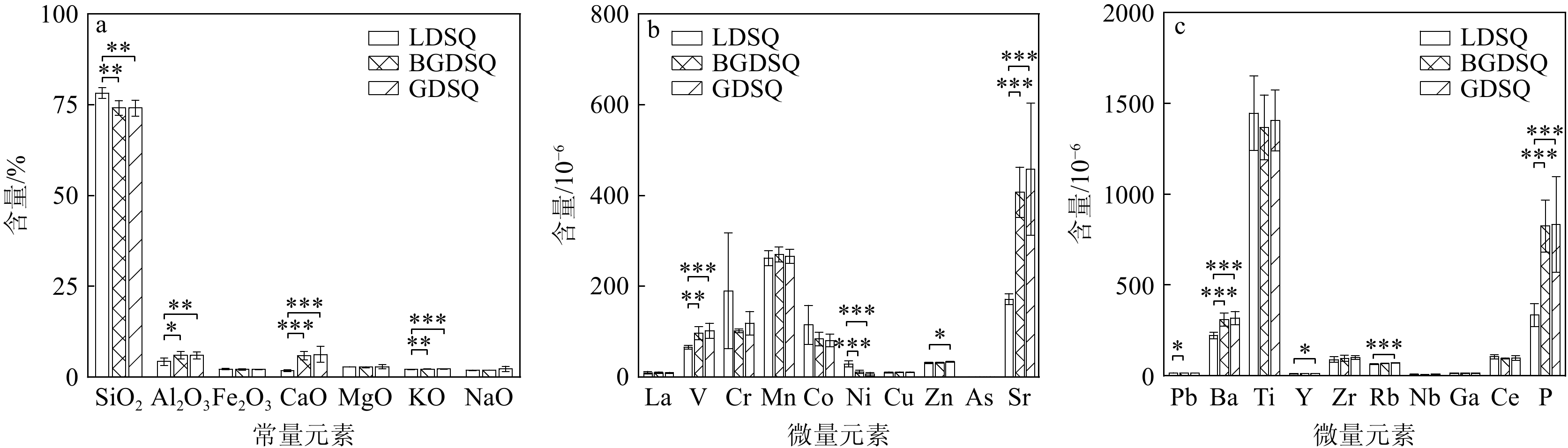
研究区沙丘表层沉积物常量元素以SiO2为主,其次为Al2O3和CaO,平均含量分别为76.40%、5.05%和3.74%,其余的MgO、K2O、Fe2O3和Na2O平均含量为1%~3%;流动沙丘以SiO2、Al2O3、MgO为主,平均含量分别为78.24%、4.27%、2.78%,与上地壳元素平均值UCC(Upper Continental Crust)[27]相比SiO2、MgO富集,其余元素亏损;半固定、固定沙丘以SiO2、Al2O3、CaO为主,与UCC相比SiO2、CaO、MgO富集,其余元素亏损。从流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘,SiO2、Fe2O3的含量逐渐减少,CaO、K2O、Na2O的含量逐渐增加,Al2O3的含量先增加后减少,MgO的含量先减少后增加。此外,不同的UCC标准化模式反映了沙丘固定过程中常量元素组成的差异性,沙丘固定过程中CaO富集(表3、图4a)。
表 3 不同类型沙丘表层沉积物常量元素组成Table 3. Major elements in surface sediments of different types of dunes% 沙丘类型 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O LDSQ 78.24 4.27 2.21 1.82 2.78 2.12 1.86 BGDSQ 74.12 6.05 2.11 5.91 2.71 2.21 1.91 GDSQ 74.08 6.02 2.10 6.28 2.88 2.24 2.26 平均值 76.40 5.05 2.16 3.74 2.80 2.17 1.98 沙丘表层沉积物的微量元素以Cr、Mn、Co、Sr、Ba、Ti、Ce和P为主,平均含量均大于100 mg/L。流动沙丘Cr、Mn、Co、Sr、Ba、Ti、Ce和P平均含量较高,与UCC相比V、Cr、Co、Ni、Pb和Ce富集,其余元素亏损。半固定沙丘的Cr、Mn、Sr、Ba、Ti和P含量较高,固定沙丘含有较高的V、Cr、Mn、Sr、Ba、Ti、Zr和P,与UCC相比,V、Cr、Co、Sr、Pb和Ce富集,其余元素亏损。从流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘,V、Cu、Zn、As、Sr、Ba、Y、Zr、Rb、P的含量逐渐增加,Co、Ni的含量逐渐减少,La、Mn的含量先增加后减少,Cr、Pb、Ti、Nb、Ga、Ce的含量先减少后增加(表4),与UCC相比,Sr富集而Ni亏损(表4、图4b)。
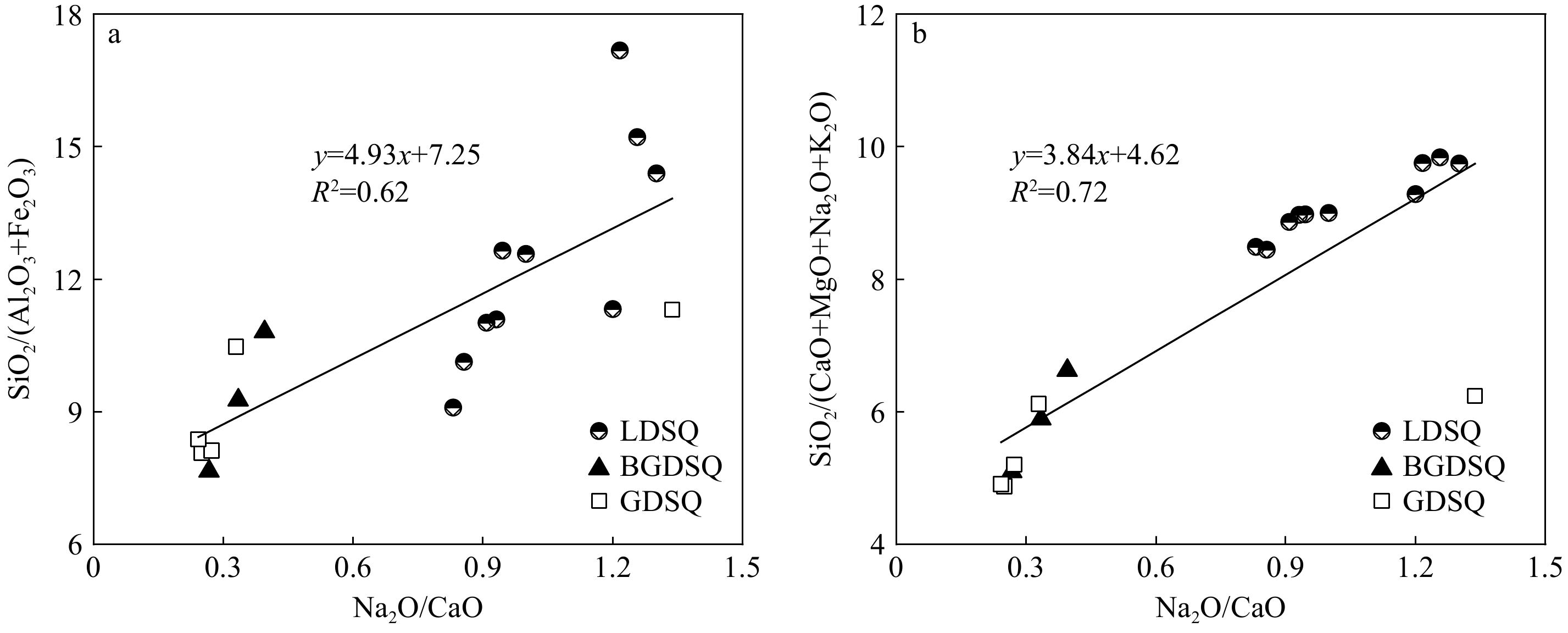
表 4 不同类型沙丘表层沉积物微量元素组成Table 4. Trace elements in surface sediments of different types of dunesmg/L 沙丘类型 La V Cr Mn Co Ni Cu Zn As Sr LDSQ 9.60 65.70 190.10 262.20 114.80 29.20 10.60 31.60 0.40 171.80 BGDSQ 9.67 96.67 102.00 270.33 84.00 11.67 10.67 32.00 0.67 407.33 GDSQ 9.40 102.20 119.00 266.80 80.80 6.60 10.80 33.40 0.80 457.80 平均值 9.56 81.00 155.67 264.83 100.22 20.00 10.67 32.17 0.53 290.50 沙丘类型 Pb Ba Ti Y Zr Rb Nb Ga Ce P LDSQ 14.90 222.20 1446.60 11.10 89.50 64.50 8.10 13.40 104.20 334.20 BGDSQ 14.00 310.00 1368.67 12.00 95.67 67.33 8.00 13.33 95.33 825.67 GDSQ 14.20 318.60 1405.40 12.40 100.80 71.40 8.60 13.80 98.00 834.40 平均值 14.56 263.61 1422.17 11.61 93.67 66.89 8.22 13.50 101.00 555.06 在地球化学元素中,Na是荒漠草原环境的标型元素,Ca是草原环境的标型元素,因此钠钙比(Na2O/CaO)是反映荒漠化程度的良好指标,其值减小代表流沙固定、荒漠化程度减弱[28]。SiO2较Al2O3、Fe2O3化学性质活泼,硅铁铝率(SiO2/(Al2O3+Fe2O3))值低代表风化成土作用增强[29]。淋溶系数SiO2/(CaO+MgO+Na2O+K2O)是衡量沉积物淋溶程度的重要指标,CaO、MgO、Na2O、K2O的化学活动性强,温湿环境下较易淋溶,导致其值增大[30]。从流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘,SiO2/(Al2O3+Fe2O3)和SiO2/(CaO+MgO+Na2O+K2O)随着Na2O/CaO减小而减小,表明沙丘固定过程中,化学风化成土作用增强但淋溶程度降低(图5)。
3. 讨论
3.1 不同类型沙丘表沙理化特征的差异
研究表明青土湖地区沙丘总体上以细砂为主,其次为极细砂、中砂和粉砂,黏土和粗砂含量较少(表2)。由ANOVA方差分析后进行最小显著性差异检验(LSD)发现流动沙丘的黏土、粉砂和极细砂含量显著低于半固定沙丘和固定沙丘(P<0.01),细砂含量则显著高于半固定沙丘和固定沙丘(P<0.001)。半固定沙丘的细砂含量最低,黏土、粉砂和极细砂含量均介于流动沙丘与固定沙丘之间。固定沙丘的黏土、粉砂和极细砂含量最高(图6)。
不同类型沙丘表沙地球化学特征存在显著的变化。与UCC相比,由流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘表层沉积物常量元素CaO富集,微量元素Ni亏损而Sr富集(图4)。由ANOVA方差分析后进行最小显著性差异检验(LSD)发现,流动沙丘、半固定沙丘、固定沙丘之间4种常量元素和9种微量元素的含量有显著差异(P<0.05)(图7),常量元素SiO2的含量逐渐减少,而CaO和K2O的含量逐渐增加,Al2O3的含量先增加后减少。微量元素V、Zn、Sr、Ba、Y、Rb和P的含量呈现增加趋势,而Ni的含量逐渐减少,Pb的含量先减少后增加。表层沉积物粒度和元素组成通常与物质来源、搬运条件、沉积过程及沉积后风化作用有关[31]。研究区植被可能是导致不同类型沙丘理化特征差异的主要因素,在沙丘固定过程中,植被覆盖度逐渐增大,由10%增至50%再到90%,从而影响了风沙沉积分选过程,同时生物风化作用增强,造成了表层沉积物理化性质的改变[32]。
3.2 青土湖地区沙丘表沙理化特征指示的环境意义
青土湖地区沙丘表层沉积物频率分布曲线总体呈单峰分布,表明搬运介质、方式较为稳定[33]。半固定、固定沙丘存在微弱次峰,可能受下伏河湖相沉积物就地起砂和石羊河下游冲洪积物的影响[34]。在干旱环境中风是运输沙物质的强大动力,物源和环流作用可以导致大区域内砂粒分选差异[9],一般认为,源区物质在风力作用下向下风向吹蚀搬运并沉积,在这一过程中,因较粗的砂粒或砾石难以吹蚀而残留原地,较细砂粒可向下风向搬运不同距离,因此砂粒平均粒径从沙源区向沉积区变小[35]。李恩菊[30]对巴丹吉林沙漠与腾格里沙漠沉积物粒度特征对比分析发现,两大沙漠均以中砂和细砂为主,而研究区以细砂为主,因此,巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠均可能为其沙源。
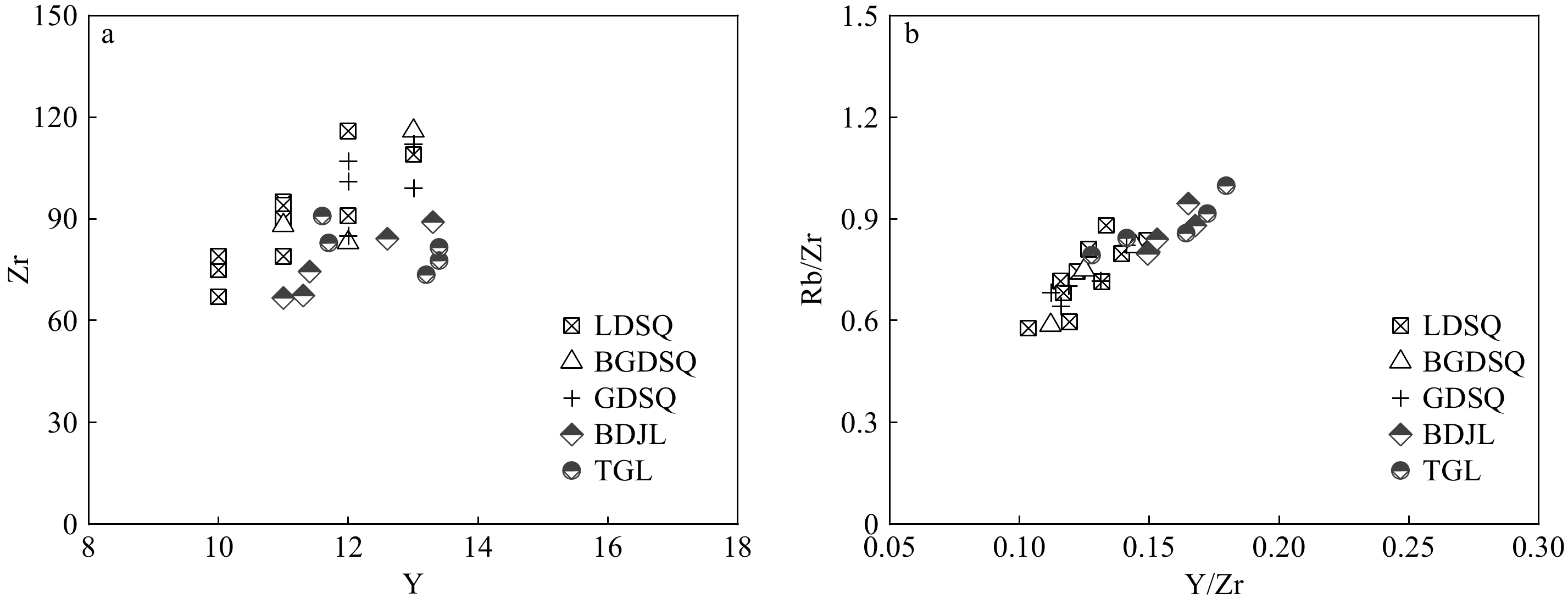
Ren等[17]结合风数据和K、Rb、Ba、Sr空间分布特征,认为巴丹吉林沙漠为其沙源。从起砂风的季节分配情况来看,腾格里沙漠一年四季均盛行西北风,但在夏季、秋季和冬季也会受到东南风影响[36],因此腾格里沙漠也可能为其提供沙物质。Y、Zr、Rb稳定性较强,基本保持原生时的丰度,常被用来作为物源示踪元素[37-38]。本文引用Ren等[17]巴丹吉林沙漠南缘和腾格里沙漠北缘样品数据进行分析(图1A),发现在Y、Zr和Y/Zr、Rb/Zr双变量图中巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠样品分布接近,表现出相似性,这与Zhang等[39]的研究结果一致。研究区样品与两大沙漠样品点距离较近,表明巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠均为其沙源(图8)。
地球化学特征能够反映化学风化程度,化学蚀变指数(CIA)是反映长石风化为黏土矿物程度的有效指标[40],CIA值越高表示硅酸盐矿物中K、Na、Ca元素风化淋溶越多,化学风化程度越高[41]。计算公式[41]及CaO*[42]的校正方法如下:
$$ \text{CIA=}{\text{Al}}_{\text{2}}{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}/\text{(}{\text{Al}}_{\text{2}}{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}\text+{\text{Na}}_{\text{2}}\text{O+Ca}{\text{O}}^{\text{*}}\text+{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}\text{O)}\text{×100} $$ 其中,CaO*为硅酸盐矿物中的CaO,运用CaO/Na2O(摩尔比)去除碳酸盐和磷酸盐中CaO的含量,当CaO*/Na2O>1时,mCaO*=mNa2O,当CaO*/Na2O≤1时,mCaO*=mCaO。
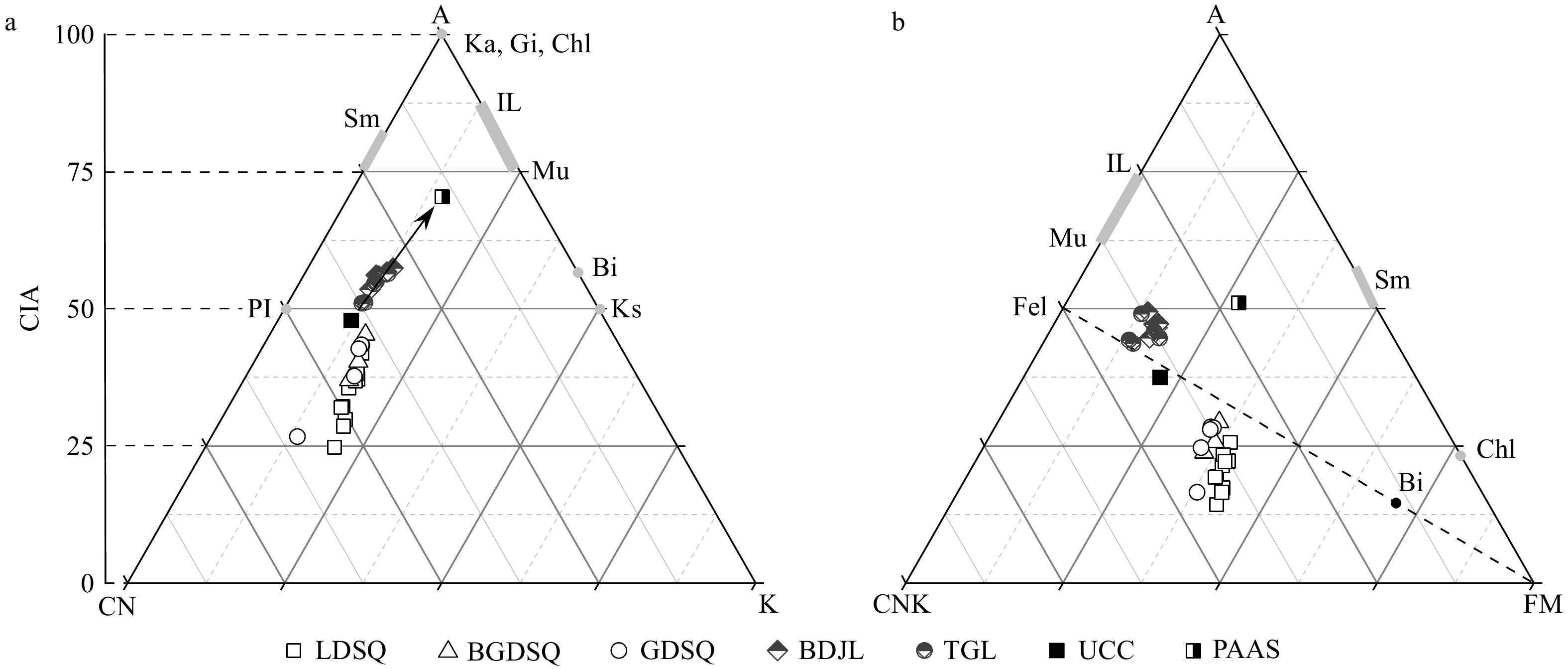
研究表明青土湖地区不同类型沙丘表层沉积物CIA为24.71~45.25,相比巴丹吉林沙漠(BDJL)和腾格里沙漠(TGL)化学风化作用弱(图9a)。从UCC至PAAS(UCC的最终风化产物)的趋势线代表典型大陆初期风化趋势[43],研究发现青土湖地区沙丘表层沉积物地球化学组分分布在风化趋势线的下方,且与其平行(图9a),反映出风化程度弱,为斜长石风化过程,表现出相对较高的Na、Ca含量未风化特征,可能是由于干旱的环境缺乏有效的风化作用所致[44]。较高的Na、Ca在半固定、固定沙丘中更为富集,导致沙丘固定过程中虽然风化成土作用增强但淋溶程度减弱(图5),这是由于植被生长过程中对Na有一定的吸附作用,植被被死亡后,会返回土层中,造成Na富集[28],植被的根系和枯落物分解,可向土壤释放Ca元素[45]。
![]() 图 9 A-CN-K和A-CNK-FM图解Ka:高岭石,Gi:水铝矿,Chl:绿泥石,IL:伊利石,PI:斜长石,Sm:蒙脱石,Ks:钾长石,Fel:长石,Mu:白云母,Bi:黑云母,BDJL:巴丹吉林沙漠南缘样品[17],TGL:腾格里沙漠北缘样品[17],UCC:平均上陆壳[27],PAAS:陆源页岩[28]。Figure 9. A-CN-K and A-CNK-FM ternary diagramsKa: kaolinite, Gi: gibbsite, Chl: chlorite, IL: illite, PI: plagioclase, Sm: smectite, Ks: K-feldspar, Fel: feldspar, Mu: white mica, Bi: biotite, BDJL: Samples from the southern edge of the Badain Jaran Desert [17], TGL: Samples from the northern edge of Tengger Desert [17], UCC: average continental crust [27], PAAS: terrigenous shale [28].
图 9 A-CN-K和A-CNK-FM图解Ka:高岭石,Gi:水铝矿,Chl:绿泥石,IL:伊利石,PI:斜长石,Sm:蒙脱石,Ks:钾长石,Fel:长石,Mu:白云母,Bi:黑云母,BDJL:巴丹吉林沙漠南缘样品[17],TGL:腾格里沙漠北缘样品[17],UCC:平均上陆壳[27],PAAS:陆源页岩[28]。Figure 9. A-CN-K and A-CNK-FM ternary diagramsKa: kaolinite, Gi: gibbsite, Chl: chlorite, IL: illite, PI: plagioclase, Sm: smectite, Ks: K-feldspar, Fel: feldspar, Mu: white mica, Bi: biotite, BDJL: Samples from the southern edge of the Badain Jaran Desert [17], TGL: Samples from the northern edge of Tengger Desert [17], UCC: average continental crust [27], PAAS: terrigenous shale [28].研究区Fe和Mg含量相似,且明显高于巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠(图9b),这是因为所含的Fe、Mg矿物物理性质较弱;从源区到沉积区,在搬运和沉积过程中矿物易受到磨蚀、风选等机械作用而风化破碎,导致Fe、Mg在细颗粒中较为富集[44]。李恩菊[30]也发现在风力分选作用下,会在其下风向形成富集Fe、Mg元素的沉积物。这也表明输沙路径为从两大沙漠向研究区,证明两大沙漠为研究区沙源。沙物质被搬运至此形成流动沙丘,且规模较大,高度较高(表1)。半固定、固定沙丘是风水交互作用下形成的,流动沙丘的沙物质及石羊河终端河湖相沉积就地起砂为沙丘的形成提供了沙源[46],研究区受干旱气候的影响主要发育耐旱型植被梭梭、白刺。在风沙流运移过程中植被改变风沙流结构,使得沙物质在灌丛周围堆积,形成灌丛沙堆[47]。半固定沙丘处于灌丛沙堆初期发育阶段,植被稀疏,拦截风沙流能力较弱,沙堆形态矮小[48],随着沙堆演化为固定沙丘,较高的植被覆盖导致水分入渗较多和蒸发较低,促进生物结皮的发育,增加土壤表面抗风蚀的能力,以及“肥岛效应”的增强,进一步改变了沙丘表沙的理化性质[49]。总之,该区不同类型沙丘的理化特征差异是沙源、气候、地形、灌丛等要素共同作用的结果。
4. 结论
(1)青土湖地区沙丘表层沉积物以细砂为主,由流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘表层沉积物平均粒径逐渐变小,分选性变差,偏态由近对称变为正偏,峰态由中等变为很窄,跃移组分所占比例减少,悬移组分增加。
(2)青土湖地区常量元素以SiO2、Al2O3、CaO为主,微量元素以Cr、Mn、Co、Sr、Ba、Ti、Ce和P为主。可能受到植被的影响由流动沙丘到半固定、固定沙丘4种常量元素(SiO2、Al2O3、CaO和K2O)和9种微量元素(V、Ni、Zn、Sr、Pb、Ba、Y、Rb、P)的含量变化显著,SiO2、Ni的含量逐渐减少,CaO、K2O、V、Zn、Sr、Ba、Y、Rb、P的含量呈增加趋势。Al2O3的含量先增加后减少,Pb的含量先减少后增加。
(3)青土湖地区表沙粒度特征显示其沉积环境以风成沉积为主,其次为河流沉积,巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠、石羊河-青土湖河湖相沉积物为其沙源。研究区总体上化学风化程度弱,含有较高的Na、Ca含量未分化,半固定、固定沙丘在植被的影响下Na、Ca含量更高,表现出淋溶作用较弱的特征。此外,研究区Fe、Mg含量较巴丹吉林沙漠和腾格里沙漠高,与风化过程中矿物磨蚀、破碎、分选作用有关。
-
图 1 研究区概况图(A)及采样点分布(B)
BDJL:巴丹吉林沙漠南缘样品[17],TGL:腾格里沙漠北缘样品[17]。a:固定沙丘,b:半固定沙丘,c:流动沙丘。
Figure 1. Overview of the research area (A) and the distribution of the sampling points (B)
BDJL: the southern edge of the Badain Jaran Desert [17]; TGL: the northern edge of Tengger Desert [17]. a: Fixed dune; b: semifixed dune; c: climbing dune.
图 8 研究区与潜在沙源微量元素双变量图
a:Y、Zr双变量图, b:Y/Zr、Rb/Zr双变量图。 BDJL:巴丹吉林沙漠南缘样品[17], TGL:腾格里沙漠北缘样品[17]。
Figure 8. Bivariate correlations of trace elements and potential sand origination
a: Y vs Zr,b:Y/Zr vs Rb/Zr. BDJL: the southern edge of the Badain Jaran Desert [17],TGL: the northern edge of Tengger Desert[17].
图 9 A-CN-K和A-CNK-FM图解
Ka:高岭石,Gi:水铝矿,Chl:绿泥石,IL:伊利石,PI:斜长石,Sm:蒙脱石,Ks:钾长石,Fel:长石,Mu:白云母,Bi:黑云母,BDJL:巴丹吉林沙漠南缘样品[17],TGL:腾格里沙漠北缘样品[17],UCC:平均上陆壳[27],PAAS:陆源页岩[28]。
Figure 9. A-CN-K and A-CNK-FM ternary diagrams
Ka: kaolinite, Gi: gibbsite, Chl: chlorite, IL: illite, PI: plagioclase, Sm: smectite, Ks: K-feldspar, Fel: feldspar, Mu: white mica, Bi: biotite, BDJL: Samples from the southern edge of the Badain Jaran Desert [17], TGL: Samples from the northern edge of Tengger Desert [17], UCC: average continental crust [27], PAAS: terrigenous shale [28].
表 1 不同类型沙丘的取样信息
Table 1 Information of sampling from different types of dunes
沙丘类型 位置 海拔/m 高度/m 底面直径/m 取样部位及编号 样品数/个 LDSQ1 39°8′1″N、103°38′27″E 1260 8 30 迎风坡:1-1、1-2、1-3、1-4、1-5
丘顶:1-6
背风坡:1-7、1-8、1-9、1-1010 LDSQ2 39°8′2″N、103°38′25″E 1265 6 20 迎风坡 :2-1、2-2
丘顶:2-3
背风坡:2-4、2-55 BGDSQ 39°8′5″N、103°38′14″E 1258.1 2 5 迎风坡:3-1、3-2
丘顶:3-33 GDSQ 39°8′4″N、103°38′12″E 1257.2 4.6 6 迎风坡:4-1、4-2
丘顶:4-3
背风坡:4-4、4-55 表 2 不同类型沙丘表层沉积物粒度组成及粒度参数
Table 2 Composition and parameters of grain size in surface sediments from different types of dunes
沙丘类型 各粒级含量/% Mz/Φ σ/Φ Sk Kg 黏土 粉砂 极细砂 细砂 中砂 粗砂 LDSQ 0.03 0.78 10.56 80.59 7.79 0.25 2.46 0.43 0.02 0.97 BGDSQ 0.90 5.83 27.47 54.62 8.79 2.36 2.69 0.91 0.21 1.77 GDSQ 0.93 7.70 29.75 57.04 4.42 0.15 2.83 0.83 0.24 1.67 平均值 0.34 2.94 16.94 72.08 7.19 0.51 2.57 0.58 0.09 1.23 表 3 不同类型沙丘表层沉积物常量元素组成
Table 3 Major elements in surface sediments of different types of dunes
% 沙丘类型 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O LDSQ 78.24 4.27 2.21 1.82 2.78 2.12 1.86 BGDSQ 74.12 6.05 2.11 5.91 2.71 2.21 1.91 GDSQ 74.08 6.02 2.10 6.28 2.88 2.24 2.26 平均值 76.40 5.05 2.16 3.74 2.80 2.17 1.98 表 4 不同类型沙丘表层沉积物微量元素组成
Table 4 Trace elements in surface sediments of different types of dunes
mg/L 沙丘类型 La V Cr Mn Co Ni Cu Zn As Sr LDSQ 9.60 65.70 190.10 262.20 114.80 29.20 10.60 31.60 0.40 171.80 BGDSQ 9.67 96.67 102.00 270.33 84.00 11.67 10.67 32.00 0.67 407.33 GDSQ 9.40 102.20 119.00 266.80 80.80 6.60 10.80 33.40 0.80 457.80 平均值 9.56 81.00 155.67 264.83 100.22 20.00 10.67 32.17 0.53 290.50 沙丘类型 Pb Ba Ti Y Zr Rb Nb Ga Ce P LDSQ 14.90 222.20 1446.60 11.10 89.50 64.50 8.10 13.40 104.20 334.20 BGDSQ 14.00 310.00 1368.67 12.00 95.67 67.33 8.00 13.33 95.33 825.67 GDSQ 14.20 318.60 1405.40 12.40 100.80 71.40 8.60 13.80 98.00 834.40 平均值 14.56 263.61 1422.17 11.61 93.67 66.89 8.22 13.50 101.00 555.06 -
[1] 周欢水, 向众, 申建军, 等. 中国荒漠化面积与分布特点[J]. 大自然探索, 1998, 17(4):61-63 ZHOU Huanshui, XIANG Zhong, SHEN Jianjun, et al. The area and distribution of the desertification affected land in China[J]. Exploration of Nature, 1998, 17(4):61-63.]
[2] 昝国盛, 王翠萍, 李锋, 等. 第六次全国荒漠化和沙化调查主要结果及分析[J]. 林业资源管理, 2023(1):1-7 ZAN Guosheng, WANG Cuiping, LI Feng, et al. Key data results and trend analysis of the sixth national survey on desertification and sandification[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2023(1):1-7.]
[3] Kocurek G, Lancaster N. Aeolian system sediment state: theory and Mojave Desert Kelso dune field example[J]. Sedimentology, 1999, 46(3):505-515. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1999.00227.x
[4] Xu Z W, Mason J A, Xu C, et al. Critical transitions in Chinese dunes during the past 12, 000 years[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(9):eaay8020. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay8020
[5] Yizhaq H, Ashkenazy Y, Tsoar H. Why do active and stabilized dunes coexist under the same climatic conditions?[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98(18):188001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.188001
[6] 凌裕泉, 屈建军, 胡玟. 沙面结皮形成与微环境变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 1993, 4(4):393-398 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1993.04.004 LING Yuquan, QU Jianjun, HU Min. Crust Formation on sand surface and microenvironmental change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1993, 4(4):393-398.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1993.04.004
[7] Danin A. Plant species diversity and plant succession in a sandy area in the northern Negev[J]. Flora, 1978, 167(5):409-422. doi: 10.1016/S0367-2530(17)31133-7
[8] Duan Z H, Xiao H L, Li X R, et al. Evolution of soil properties on stabilized sands in the Tengger Desert, China[J]. Geomorphology, 2004, 59(1-4):237-246. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2003.07.019
[9] 钱广强, 董治宝, 罗万银, 等. 巴丹吉林沙漠地表沉积物粒度特征及区域差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6):1357-1364 QIAN Guangqiang, DONG Zhibao, LUO Wanyin, et al. Grain size characteristics and spatial variation of surface sediments in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2011, 31(6):1357-1364.]
[10] 蒋凯鑫, 于坤霞, 李鹏, 等. 砒砂岩区典型淤地坝沉积泥沙特征及来源分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(1):47-53 JIANG Kaixin, YU Kunxia, LI Peng, et al. Sediment characteristics and sources analysis of typical check dam in Pisha sandstone area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(1):47-53.]
[11] 孔凡彪, 陈海涛, 徐树建, 等. 山东章丘黄土粒度指示的粉尘堆积过程及古气候意义[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(5):1163-1176 doi: 10.11821/dlxb202105009 KONG Fanbiao, CHEN Haitao, XU Shujian, et al. Dust accumulation processes and palaeoenvironmental significance of loess indicated by grain size in Zhangqiu, Shandong province[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(5):1163-1176.] doi: 10.11821/dlxb202105009
[12] 刘德政, 夏非. 江苏中部海岸晚第四纪沉积物的粒度与磁化率特征及其古环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(5):210-220 LIU Dezheng, XIA Fei. Characteristics of grain size and magnetic susceptibility of the Late Quaternary sediments from core 07SR01 in the Middle Jiangsu coast and their paleoenvironmental significances[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(5):210-220.]
[13] Chen Y G, Pan M H, Hao Z W, et al. Grain size-dependent geochemical evidence reveals provenance and implications of Aeolian sands, Dinggye region, southern Tibet[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2022, 19(7):1998-2014. doi: 10.1007/s11629-021-7225-1
[14] 丁雪, 胡邦琦, 赵京涛, 等. 九州-帕劳海脊南段及邻近海域表层沉积物元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2023, 43(1):61-70 DING Xue, HU Bangqi, ZHAO Jingtao, et al. Elemental geochemical characteristics of surface sediments from the southern Kyushu-Palau Ridge and their geological significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2023, 43(1):61-70.]
[15] 吴利禄, 高翔, 褚建民, 等. 民勤绿洲-荒漠过渡带梭梭人工林净碳交换及其影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(10):3336-3346 WU Lilu, GAO Xiang, CHU Jianmin, et al. Net carbon exchange and its driving factors of Haloxylon ammodendron plantation in the oasis-desert ecotone of Minqin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(10):3336-3346.]
[16] 贾宝全, 慈龙骏, 蔡体久, 等. 绿洲-荒漠交错带环境特征初步研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(9):1104-1108 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.09.012 JIA Baoquan, CI Longjun, CAI Tijiu, et al. Preliminary research on environmental characteristics of oasis-desert ecotone[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(9):1104-1108.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.09.012
[17] Ren X Z, Yang X P, Wang Z T, et al. Geochemical evidence of the sources of Aeolian sands and their transport pathways in the Minqin Oasis, northwestern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 334-335:165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.04.037
[18] 杨宁宁, 董治宝, 李恩菊, 等. 民勤县固定与半固定沙丘粒度特征分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2011, 31(6):11-14,20 YANG Ningning, DONG Zhibao, LI Enju, et al. Grain size characteristics of fixed and semi-fixed dunes in Minqin County[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 31(6):11-14,20.]
[19] 杜建会, 严平, 丁连刚, 等. 民勤绿洲不同演化阶段白刺灌丛沙堆表面土壤理化性质研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2009, 29(2):248-253 DU Jianhui, YAN Ping, DING Liangang, et al. Soil physical and chemical properties of Nitraria tangutorun nebkhas surface at different development stages in Minqin Oasis[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2009, 29(2):248-253.]
[20] 赵鹏, 朱淑娟, 段晓峰, 等. 民勤绿洲边缘阻沙带表层土壤粒度空间分布特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(5):1335-1345 ZHAO Peng, ZHU Shujuan, DUAN Xiaofeng, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of grain size of surface soil in the sand-resitant belt of Minqin Oasis marginal[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(5):1335-1345.]
[21] 郭树江, 杨自辉, 王强强, 等. 青土湖干涸湖底风沙流结构及输沙粒径特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(4):1166-1176 GUO Shujiang, YANG Zihui, WANG Qiangqiang, et al. The structure and grain size of wind-sand flow in the dry bottom of Qingtu Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(4):1166-1176.]
[22] 韩福贵, 满多清, 郑庆钟, 等. 青土湖典型湿地白刺灌丛沙堆群落物种多样性及土壤养分变化特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1):36-45 doi: 10.11686/cyxb2020353 HAN Fugui, MAN Duoqing, ZHENG Qingzhong, et al. Species diversity and soil nutrient changes of a Nitraria tangutorum shrub community in Qingtu Lake wetland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1):36-45.] doi: 10.11686/cyxb2020353
[23] 陈有桂. 西藏定结地区不同类型沙丘表层沉积物地球化学特征及环境意义[D]. 西北师范大学硕士学位论文, 2023 CHEN Yougui. Geochemical characteristics and environmental significance of surface sediments from different types of sand dunes in the Dinggye area, Tibet[D]. Master Dissertation of Northwest Normal University, 2023.]
[24] Blott S J, Pye K. GRADISTAT: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2001, 26(11):1237-1248. doi: 10.1002/esp.261
[25] 吴正. 风沙地貌学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987:1-316 WU Zheng. Aeolian Geomorphology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987:1-316.]
[26] Pan M H, Chen Y G, Hao Z W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of surface sediments from different types of sand dunes in the Dinggye area, southern Tibet[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(17):10628. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710628
[27] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. London: Blackwell Scientific, 1985: 277.
[28] 靳鹤龄, 苏志珠, 孙忠. 浑善达克沙地全新世中晚期地层化学元素特征及其气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2003, 23(4):366-371 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2003.04.005 JIN Heling, SU Zhizhu, SUN Zhong. Characters of chemical elements in strata of Middle and Late Holocene in hunshandake desert and the indicating climatic changes[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2003, 23(4):366-371.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2003.04.005
[29] Liu B, Jin H L, Sun L Y, et al. Geochemical evidence for Holocene millennial-scale climatic and environmental changes in the south-eastern Mu Us Desert, northern China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 104(7):1889-1900. doi: 10.1007/s00531-015-1161-7
[30] 李恩菊. 巴丹吉林沙漠与腾格里沙漠沉积物特征的对比研究[D]. 陕西师范大学博士学位论文, 2011 LI Enju. Comparative study on sediment characteristics of Badain Jaran Desert and Tengger Desert[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Shaanxi Normal University, 2011.]
[31] 庞红丽, 高红山, 李富强, 等. 黄河宁蒙段沉积物地球化学元素组成及分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5):44-53 PANG Hongli, GAO Hongshan, LI Fuqiang, et al. Geochemical element composition and spatial distribution characteristics of sediments in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia section of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5):44-53.]
[32] 刘定辉, 李勇. 植物根系提高土壤抗侵蚀性机理研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2003, 17(3):34-37,117 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2003.03.010 LIU Dinghui, LI Yong. Mechanism of plant roots improving resistance of soil to concentrated flow erosion[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2003, 17(3):34-37,117.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2003.03.010
[33] 殷志强, 秦小光, 吴金水, 等. 中国北方部分地区黄土、沙漠沙、湖泊、河流细粒沉积物粒度多组分分布特征研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(2):343-351 YIN Zhiqiang, QIN Xiaoguang, WU Jinshui, et al. The multimodal grain-size distribution characteristics of loess, desert, lake and river sediments in some areas of northern China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(2):343-351.]
[34] 董斌. 石羊河流域历史地理若干专题研究[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2016 DONG Bin. Monographic research on the historical geography of the Shiyang River Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2016.]
[35] Lancaster N. Grain-size characteristics of linear dunes in the southwestern Kalahari[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1986, 56(3):395-400.
[36] 刘英姿. 腾格里沙漠中格状沙丘形态及成因研究[D]. 陕西师范大学硕士学位论文, 2013 LIU Yingzi. Study on morphology and genesis of trellis dunes in Tengger Desert[D]. Master Dissertation of Shaanxi Normal University, 2013.]
[37] 许明, 陈建文, 袁勇, 等. 华南下扬子区早寒武世幕府山组沉积环境: 来自于全岩地球化学的启示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(6):82-90 XU Ming, CHEN Jianwen, YUAN Yong, et al. Sedimentary environment of the Lower Cambrian mufushan Formation in the Lower Yangtze region: evidence from whole-rock geochemistry[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(6):82-90.]
[38] Zhang Z C, Liang A M, Zhang C X, et al. Gobi deposits play a significant role as sand sources for dunes in the Badain Jaran Desert, Northwest China[J]. CATENA, 2021, 206:105530. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105530
[39] Zhang Z C, Pan K J, Zhang C X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and the provenance of Aeolian material in the Hexi Corridor Desert, China[J]. CATENA, 2020, 190:104483. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104483
[40] 刘璐, 谢远云, 迟云平, 等. 地球化学组成对浑善达克沙地与科尔沁沙地风化和沉积循环特征及其物源的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4):192-206 LIU Lu, XIE Yuanyun, CHI Yunping, et al. Geochemical compositions of the Onqin Daga Sand Land and Horqin Sand Land and their implications for weathering, sedimentation and provenance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4):192-206.]
[41] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885):715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[42] McLennan S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(2):295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[43] 李小妹, 严平, 吴伟, 等. 毛布拉格孔兑地表风沙沉积物粒度与地球化学元素分布特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 2016, 39(3):468-476 LI Xiaomei, YAN Ping, WU Wei, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of the grain size and geochemical elements of surface sediments of Mu Bulag River[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2016, 39(3):468-476.]
[44] Liu B, Jin H L, Sun L Y, et al. Grain size and geochemical study of the surface deposits of the sand dunes in the Mu Us desert, northern China[J]. Geological Journal, 2017, 52(6):1009-1019.
[45] 向云. 黄土丘陵区草地枯落物分解特征及其对土壤性质的影响[D]. 西北农林科技大学博士学位论文, 2018 XIANG Yun. The decomposition characteristics of grass litter and its effects on soil properties in loess hilly region[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Northwest A&F University, 2018.]
[46] 古拉依赛木·艾拜都拉, 张峰, 吴枫, 等. 腾格里沙漠沙丘沉积物粒度特征及其空间差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5):133-145 Gulayisaimu A, ZHANG Feng, WU Feng, et al. Grain size characteristics of dune sands and spatial variation in the Tengger Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5):133-145.
[47] Lang L L, Wang X M, Hasi E, et al. Nebkha (coppice dune) Formation and significance to environmental change reconstructions in arid and semiarid areas[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2013, 23(2):344-358. doi: 10.1007/s11442-013-1014-x
[48] 杜建会, 严平, 俄有浩. 甘肃民勤不同演化阶段白刺灌丛沙堆分布格局及特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2007, 26(8):1165-1170 DU Jianhui, YAN Ping, E Youhao. Distribution patterns and characteristics of Nitraria tangutorun nebkha at its different evolvement stages in the Minqin County of Gansu province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 26(8):1165-1170.]
[49] 王飞, 郭树江, 张卫星, 等. 干旱荒漠区不同演替阶段白刺灌丛沙堆土壤粒度特征[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(1):15-20,44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.01.03 WANG Fei, GUO Shujiang, ZHANG Weixing, et al. Soil grain-size characteristics of Nitraria tangutorum at different succession stages in Desert area[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2020, 35(1):15-20,44.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.01.03
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 刘文良,褚宏宪,法鸿洁,王洪松,鲍宽乐,李晓阳,刘京强. 基于机载LiDAR和剖面数据的海滩地形动态监测. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(01): 81-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴承强,董超,王建强,陈选博,周宇渤,张朋,仇建东. 瓯江口动力地貌演化的水沙环境研究. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(04): 60-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: