Progress and prospect in the study of Aeolian Loess in the Yangtze River Basin
-
摘要:
中国黄土是第四纪古气候–古环境研究的重要载体,除黄土高原外,中国其他地区还零星分布有风成黄土堆积。在长江流域,从上游到下游,分布有川西、金沙江、巫山和下蜀黄土,探讨这些湿润区风成黄土的风尘来源、动力传输过程以及沉积后土壤化过程等可为研究长江流域东亚季风环流特点提供证据,对探究过去湿润区风尘风化固碳过程和效益也具有重要意义。虽然对长江流域各地区黄土已有较多的研究,但是不同地区黄土物源、物质传输过程等方面的相互联系及其在风化固碳中的作用还不清楚。本文在综述了川西、金沙江、巫山、下蜀风尘黄土的形成年代、物源等最新研究进展的基础上,提出川西、巫山、下蜀三地黄土的发育与青藏高原在青藏运动B幕、昆仑-黄河运动和共和运动3个阶段的隆升有重要对应关系;并且发现在冰期和间冰期,长江流域风成黄土的风化程度均比黄土高原黄土强,且在古土壤发育期更强;认为长江流域黄土风化过程对陆地固碳的影响及其与古气候变化的相互关系是今后湿润区黄土研究的重点。
Abstract:The loess deposition in China is an important archive of the Quaternary paleoclimate-paleoenvironmental signals. Other than the Loess Plateau, loess brough by wind deposited in the upper, middle, and lower Yangtze River basin during the Quaternary. Understanding the provenance, transportation dynamics, and post-depositional weathering processes of loess in these humid regions is important for the study of the past changes of the East Asian monsoon in the Yangtze River Basin, and is also of great significance for investigating the carbon sequestration effect during the chemical weathering process of the fine-grained loess in the humid regions. Although much studies have been conducted on loess deposition in various regions of the Yangtze River Basin, the material transport processes in different regions of the Yangtze River Basin, their interconnections, and their roles in carbon sequestration are still unclear. Here, we overviewed the latest understanding of the formation age, sources, and paleoclimatic records of the loesses in the western Sichuan, Jinsha River, Wushan, and Xiashu in the Yangtze River Basin. we found that the formation of loess in the west Sichuan, Wushan and Xiashu regions were tightly linked to the three uplift phases of the Tibetan Plateau, namely the Tibetan Movement B, the Kunlun and Yellow River Movement and the Gonghe Movement. In addition, the weathering degree of loess depositions in the Yangtze River Basin are stronger than that of loess on the Loess Plateau both during the glacial and interglacial periods. We proposed that the influence of the chemical weathering process of loess on terrestrial carbon sequestration and its correlation with paleoclimate changes are the focus of future research on loess in humid regions, e.g., the Yangtze River Basin.
-
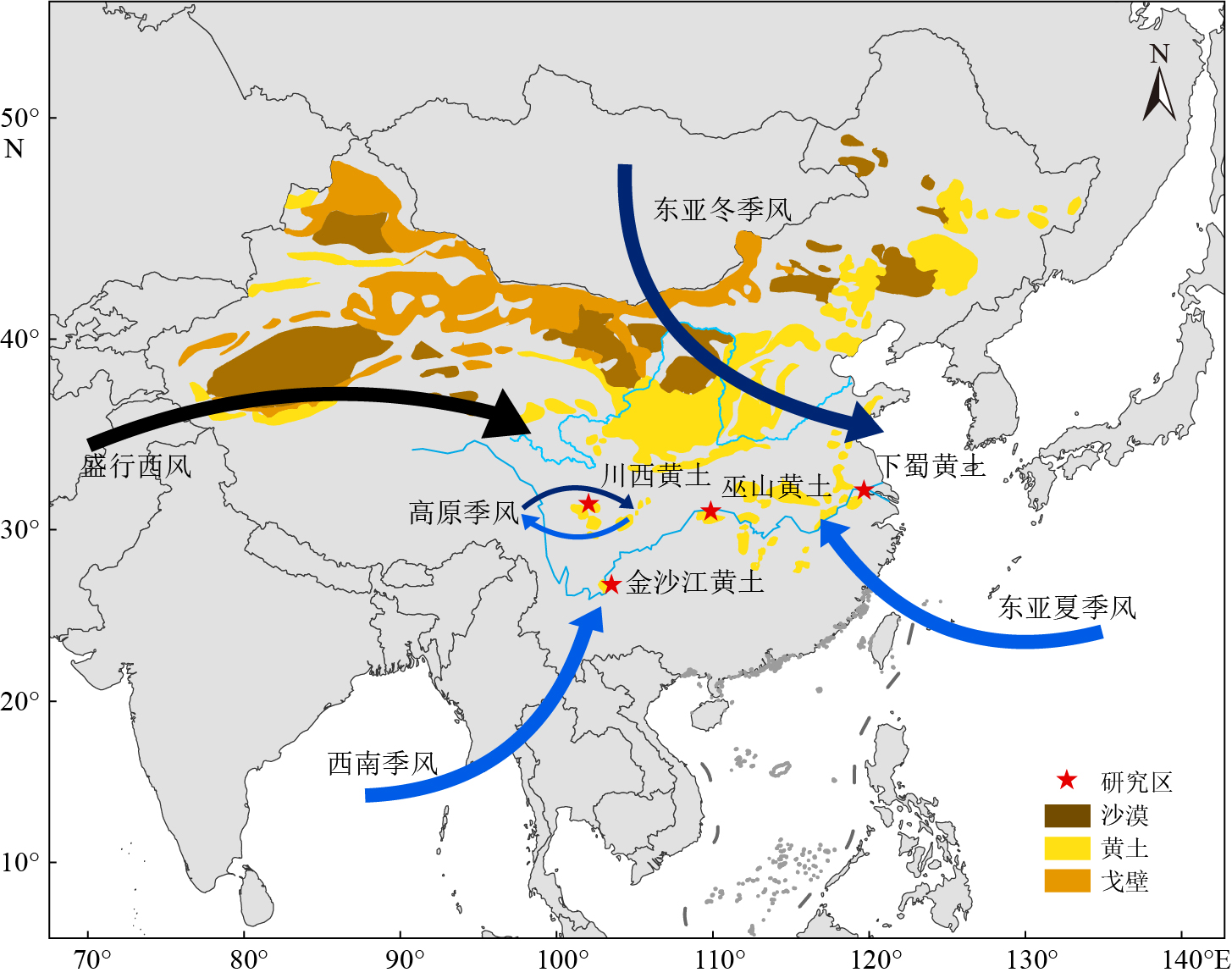
黄土、深海沉积物与极地冰芯并列被视为过去全球变化研究的三大支柱[1- 2]。中国黄土高原是全球黄土风尘堆积发育最典型的区域,目前,已有大量研究基于最典型的黄土高原黄土恢复晚新生代以来亚洲内陆的干旱化过程、东亚季风的演化历史等[3-5]。除黄土高原之外,中国南方湿润地区也发育了较多风尘堆积(图1)[6]。其中,长江流域从上游到下游,分别分布有川西黄土[7]、金沙江黄土[8]、巫山黄土[9-10]和下蜀黄土[11-14]。黄土中硅酸盐矿物在风化过程中需要消耗二氧化碳,因此,黄土的硅酸盐风化过程具有重要的固碳效益[15-16]。在长江流域沉积中新产生的、更细的、比表面积较大的风尘黄土,在降水比黄土高原更丰沛的的条件下,比黄土高原黄土更易被风化,也比长江流域表层土壤/岩石更易被风化[16],因此,长江流域湿润区风尘黄土的风化过程固碳强度比干旱区相同体积的黄土更强,对全球气候变化具有重要的贡献。另外,长江流域黄土风尘来源、传输动力过程等方面与黄土高原差异显著[17]。因此对长江流域风尘黄土的年代、物源、风化过程的详细研究一方面可为全球风尘风化固碳效应提供新的见解和视角[18],也可为探讨长江流域第四纪气候-环境变化以及大气环流模式及其与周边地区气候变化之间的关系等研究提供新的证据与思路[19-20]。
最近几年,对长江流域黄土风化固碳效应研究比较少,但已有一些研究探讨了川西黄土和下蜀黄土的成因、物源、年代以及古气候记录[21-22],而巫山地区黄土在这些方面空白较多。本文试图总结长江流域黄土的沉积年代、物质来源研究进展,并将收集到的长江流域黄土化学风化指标所反映的风化程度与黄土高原进行对比,探究湿润区黄土堆积后的风化对大气CO2变化的贡献,以明确目前中国南方黄土堆积的研究现状和未来研究的新方向。
1. 长江流域非典型黄土区域地理特征及其分布情况
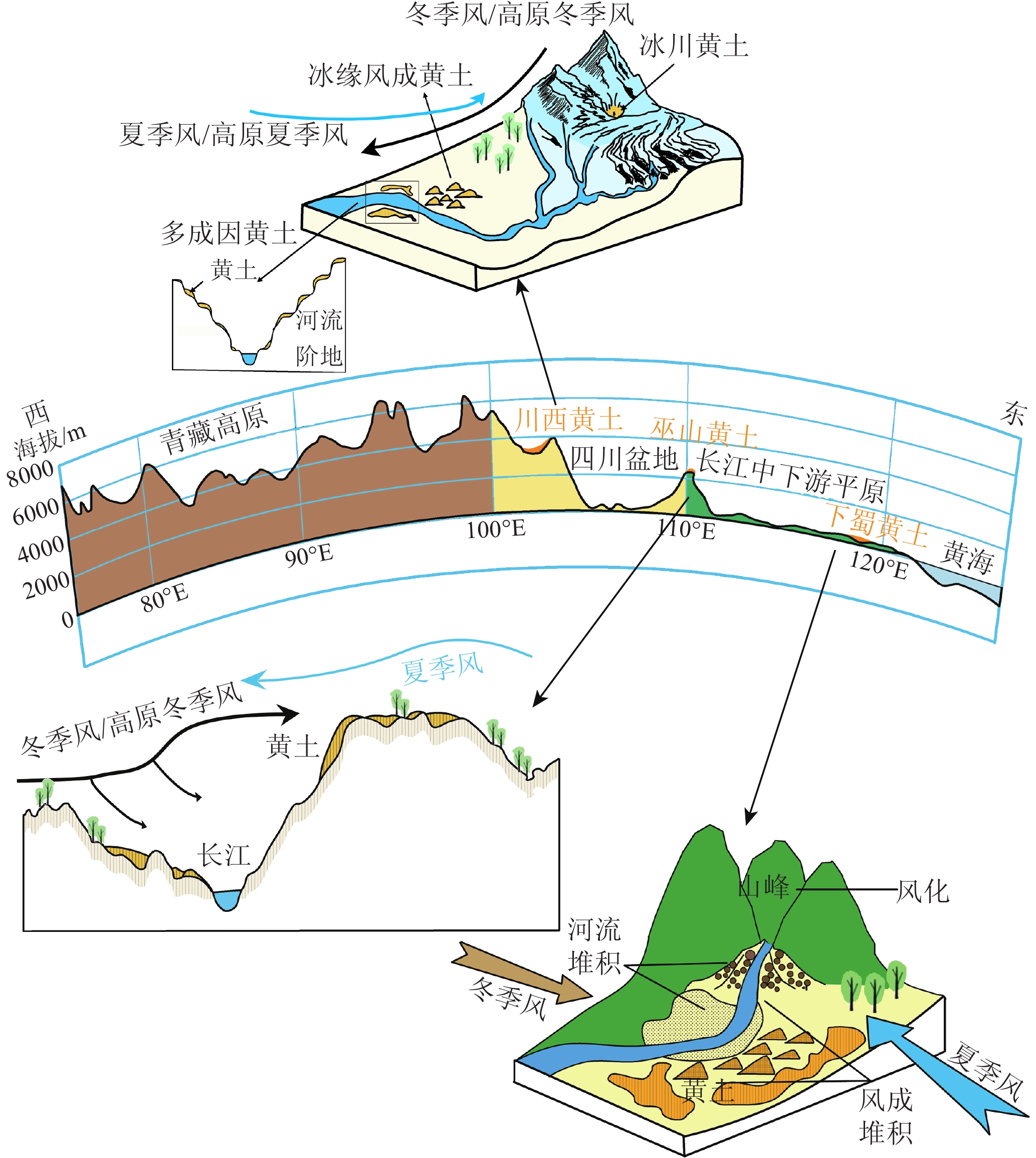
川西黄土、巫山黄土和下蜀黄土沉积位置都位于北纬30°左右,金沙江黄土则是位于北纬25°左右(图1)。川西黄土主要分布于青藏高原东缘的川西高原上(图2),该地区平均海拔约3500 m,总体地势西北高、东南低,区域内受青藏高原季风、东亚季风、盛行西风以及印度季风的影响,属于中国气候变化的敏感地带[25]。金沙江黄土大多分布于区域大型河流下切形成的深切峡谷地带,它们是高原隆升背景下河谷中岩-水-气相互作用的结果,能为研究西南季风、高原季风与青藏高原隆升的关系提供理想的地质材料[25]。巫山黄土分布于四川盆地东部边缘(图1、图3),该地除受盛行西风、东亚季风和西南季风的影响,还受青藏高原季风外延影响[26]。下蜀黄土广泛分布于长江中下游两岸(图4),是中国北方风尘堆积的南部边缘,是南方红土发育区的北界[27]该区域主要受东亚季风气候系统控制[28]。
![]() 图 2 川西黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代a:川西黄土典型剖面分布图,b:甘孜附近黄土分布。黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄,黑色数字代表海拔/沉积厚度。Figure 2. Distribution of loess profiles, origination, elevation/depositional thicknesses, and ages of formation in the western Sichuan Provincea: Information and distribution of typical loess profiles in the western Sichuan, b: distribution of loess near Ganzi. The yellow numbers represent the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the black numbers represent the elevation/depositional thickness.
图 2 川西黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代a:川西黄土典型剖面分布图,b:甘孜附近黄土分布。黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄,黑色数字代表海拔/沉积厚度。Figure 2. Distribution of loess profiles, origination, elevation/depositional thicknesses, and ages of formation in the western Sichuan Provincea: Information and distribution of typical loess profiles in the western Sichuan, b: distribution of loess near Ganzi. The yellow numbers represent the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the black numbers represent the elevation/depositional thickness.![]() 图 3 巫山黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代a:三峡库区范围图,b:巫山黄土典型剖面分布图,c:秭归地区黄土分布黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄、黑色字体代表:海拔/沉积厚度。Figure 3. Distribution, genesis, elevation/depositional thickness and age of the Wushan Loessa: The range of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, b: distribution of typical profile of Wushan Loess, c: distribution of loess at Zigui. The yellow number represents the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the black fonts represent the elevation/depositional thickness.
图 3 巫山黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代a:三峡库区范围图,b:巫山黄土典型剖面分布图,c:秭归地区黄土分布黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄、黑色字体代表:海拔/沉积厚度。Figure 3. Distribution, genesis, elevation/depositional thickness and age of the Wushan Loessa: The range of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, b: distribution of typical profile of Wushan Loess, c: distribution of loess at Zigui. The yellow number represents the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the black fonts represent the elevation/depositional thickness.![]() 图 4 下蜀黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代a:长江下游下蜀黄土典型剖面信息以及分布图, b:黄土分布密集区。黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄,绿色数字代表海拔/沉积厚度。Figure 4. Distribution, genesis, elevation/depositional thickness, and age of the Xiashu Loessa: Information and distribution of Xiashu Loess in the lower reaches of Yangtze River, b: Enlarged view of the dense distribution area of loess. The yellow numbers represent the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the green numberts represent the elevation/depositional thickness.
图 4 下蜀黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代a:长江下游下蜀黄土典型剖面信息以及分布图, b:黄土分布密集区。黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄,绿色数字代表海拔/沉积厚度。Figure 4. Distribution, genesis, elevation/depositional thickness, and age of the Xiashu Loessa: Information and distribution of Xiashu Loess in the lower reaches of Yangtze River, b: Enlarged view of the dense distribution area of loess. The yellow numbers represent the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the green numberts represent the elevation/depositional thickness.长江流域黄土呈零星点状分布。川西高原黄土分布范围较为广泛,但总体来看主要集中分布于2 000~3000 m的河流阶地、沟谷和断陷盆地等地貌单元上[29]。在高出河床100~900 m的高阶地、谷肩、山坡、断陷盆地及古冰蚀凹地和高原内部等地,黄土沉积较厚,如甘孜盆地黄土厚度达80多米[30],在河谷低阶地、古冰碛物及高原边缘则较薄[21]。金沙江黄土分布于该区域,在该区域干热河谷中,此地强烈的构造抬升促使河流从高原面上下切,形成深切峡谷,河谷地势相对高差达 2~3 km,垂直地带性显著[31]。在华弹、江边、涛源地区河谷平直宽阔,河流纵剖面平缓,利于黄土沉降,其中华弹剖面黄土状沉积物沉积比较连续,厚度较大[8]。巫山黄土分布于长江三峡地区,受峡谷地形影响及堆积之后边坡的地质改造作用,巫山黄土空间分布的连续性较差,零星分布于不同地貌单元上,目前发现的巫山黄土剖面主要位于中国第二阶梯和第三阶梯分界线上的巫山附近长江及其支流两岸、周围低山的北坡及山顶地区[17]。下蜀黄土广泛分布在长江中下游地区的河流阶地及附近低山、丘陵、岗地等区域,最具有代表性的是赣北鄱阳湖地区、皖南地区及南京宁镇地区的黄土[32-33]。
2. 研究剖面选择与数据收集和处理方法
2.1 剖面选择
目前长江流域黄土成因多样,物质来源复杂,剖面年代和古气候研究结果不完整[21, 34]。本研究依照如下的剖面和数据选择方法总结长江流域风尘黄土年代、物源以及化学风化程度特征。首先,所有参与总结的剖面都是有明确粒度[26, 35-36]、元素地球化学[7, 37]等成因指标表明是风尘沉积的剖面。其次,选取有元素地球化学、粒度[38]、环境磁学[39]两种及以上物源示踪方法交互印证的剖面进行物源总结(表1)。再者,在黄土沉积年代方面,采取满足绝对测年与相对测年相结合的原则[40- 41] ,选取有准确的测年数据(主要包括古地磁和光释光、ERS)的风尘黄土剖面进行总结分析;在进行长江流域与黄土高原黄土风化程度对比时,优先选择有年代且有对风化敏感的指标——CIA或χfd%测试结果的剖面。在进行CIA剖面选择时,优先考虑文献中有明确黄土-古土壤序列的剖面,同时也考虑到不同CIA测试方法的影响,统一选取使用X射线荧光光谱分析方法得到的数据。为避免测试频率对磁化率的影响,在选择χfd%数据时,我们对比了各文献中高低频磁化率测试频率,选择了低频测试频率为470 Hz、高频测试频率为4700 Hz的文献。
表 1 长江流域黄土成因及物源Table 1. Genesis and provenance of loess in the Yangtze River Basin剖面 海拔/沉积厚度/m 方法 成因 物源 参考文献 川西地区 甘孜剖面 3480/86 粒度分析、REE 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [71] 甘孜满地剖面 / 粒度、孢粉、冰楔构造分析 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [38] GZ-1-2 3431 微量元素和稀土元素分析 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [72] 甘孜五级阶地剖面 3455/14.5 环境磁学、地球化学元素 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [73] Garze A /28.5 微量元素、REE和Sm-Nd同位素 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [56] 甘孜寺剖面 3538/15.3(见底) 石英颗粒表面形态分析 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [74] 九寨沟荷叶黄土剖面 / 矿物成分及石英砂表面结构分析 冰川黄土 近源堆积 [75] / 粒度、REE、微量元素分析等 风成黄土 有多源性特征 [59] 可尔因剖面 / 黄土粒度分析、石英表面形态观察 风成黄土 近源堆积 [76] 叠溪剖面 2394 /(见底) 粒度分析、稀土和微量元素 风成黄土 远源堆积 [62] SC剖面A, X剖面, LBZ剖面 / 粒度、常量元素与稀土元素特征
分析等风成黄土 近源堆积 [36] 唐克索克藏寺剖面 3445/ 粒度组分、石英砂的表面结构、冰楔构造、孢粉 风成黄土 近源堆积 [77] 佳山剖面 2060/ 粒度、矿物组成\常量元素与稀土元素特征 风成黄土 近源堆积 [7] 巫山地区 巫山师范学校剖面/秭归楚王台剖面 / 粒度、重矿物、化学成分和石英电镜扫描分析 多成因 近源堆积 [78] 双堰塘 /3.7 粒度分析、常量元素组分分析 多成因 混合堆积 [58] 望天坪剖面 1350/3.1 粒度特征 风成沉积物 混合堆积 [79] 粒度参数特征 风成成因 混合堆积 [80] 粒度特征 风成成因 远源堆积 [35] 巫山博物馆剖面 258/5 分析Sa、CIA、Na/K、铁游离度等风化指标 风积成因 来源复杂 [81] 江东嘴剖面 /3.6 粒度特征 多成因 近源堆积 [35] 势大岭剖面 /8.2 粒度特征 多成因 / [67] 圣泉剖面/客运港剖面 248/15 REE分析 风积成因 混合成因 [82] 常量元素分析 风积成因 / [83] 元素地球化学特征 风积成因 远源堆积 [84] 分析Sr和Nd同位素组成 风积成因 远源堆积 [67] 稀土元素特征值 风积成因 远源堆积 [24] 分析Sr和Nd同位素组成 风积成因 近源堆积为主 [85] 粒度特征 风成沉积 近源河谷风成沉积 [35] 下蜀地区 大港剖面 26.5/59.5 粒度分析 风成堆积 混合堆积 [41, 86-87] 周家山剖面 65/51 粒度组成分析 风成堆积 混合堆积 [11,85,88-89] 老虎山剖面 50/30 粒度、矿物化学成分 混合成因 远源堆积 [90] 仙林剖面 / 环境磁学、地球化学特征 风成堆积 混合堆积 [91] 燕子矶剖面 26/23 / / 远源堆积 [92] 地球化学元素 风成堆积 远源堆积 [66] 青山剖面 36/20 粒度分析 风成堆积 / [26] 下蜀地区 Mufushan剖面 / 锆石U-Pb年龄和同位素地球
化学示踪多成因说 混合堆积 [93] 下蜀黄土
(9个采样点)/ 粒度成分、主元素和微量元素组成的分析结果 风成堆积 近源堆积 [53] 宣城剖面 / 元素地球化学 风成堆积 近源来源 [94] / 风成堆积 近源堆积 [95] 注:“/”表示在对应的文章内未提及。 2.2 风化指标数据收集与处理
在处理化学风化指数(CIA)和频率磁化率百分比(χfd%)数据时,将各个剖面获得的CIA和χfd%数据分成黄土和古土壤层分别做频率直方图,选择两参数数值频率分布相似的剖面一起代表该地区黄土/古土壤风化程度。在统计川西地区已进行过CIA与环境磁学的研究剖面时,发现进行CIA研究的甘孜寺[42]、甘孜剖面[43]以及进行 χfd%测定的甘孜XS剖面[39, 44]都位于黄土相关研究较为成熟的甘孜地区。甘孜地区选择的3个剖面黄土的物质来源于近源高原内部堆积,在该地区测黄土剖面底界年龄约为1160 ka[45]。金沙江黄土CIA指数来自华弹剖面,该剖面为风成近源河谷堆积,在深度为9 m的地方OSL测年结果为122.71 ka[31],利用古地磁测年发现剖面中未出现极性倒转,剖面底界年龄晚于780 ka[8]。巫山地区选择有CIA指数的圣泉剖面[46]和有磁学研究结果的望天坪剖面[47],两者物源兼有远源近源混合特性,前者剖面见底,剖面底部年龄为100 ka左右,后者未有年代结果。下蜀黄土的CIA指数来自于镇江圌山以及镇江下游的长山剖面[48],该剖面有明显黄土-古土壤划分层序,且是风成源堆积,环境磁学的剖面选择胡店剖面[49]、土门金[50]、石狮洼[50],这些剖面均未见底,在土门金剖面测得最老年龄为460 ka左右。黄土高原的CIA与χfd%数据选取位于黄土高原南部受风化作用相对较强的剖面,具体CIA数据选取自洛川剖面[51],χfd%数据从更靠南端的玉山剖面[52]获得。
通过上述方法选择出来的川西黄土与下蜀黄土剖面的黄土-古土壤层序可以较好地与深海氧同位素阶段的冰期-间冰期进行对比。金沙江黄土与巫山黄土缺少有效的年代序列方面的数据,但从川西与下蜀地区的对比结果推测这两地黄土均指示气候较冷的时期,古土壤发育阶段指示气候较暖时期。因此,在对比长江流域黄土与黄土高原黄土风化程度时,将所有层段的黄土层或古土壤层数据一起统计,分别代表冰期和间冰期时各区域的化学风化情况。
3. 长江流域黄土物源、年代及其与青藏高原隆升的关系研究进展
3.1 长江流域风成黄土物源研究进展
随着风尘黄土物源示踪工作的深入进行,已开发出许多新颖和可靠的示踪剂, 如稀土元素[53]、Sr-Nd-Pb 同位素[54]、碎屑锆石 U-Pb 年龄谱[55]等。但是,目前长江流域的黄土物源研究主要采用的是地球化学常量微量元素[56]、REE[57]以及粒度[58]指标,且大多研究都是基于成对元素比值在散点图中的分区定性地分析样地黄土的粉尘来源[36]。但长江流域黄土较多剖面属于混合粉尘沉积[11, 59],要明确源汇之间的物质关联性则非常困难,使得基于元素地球化学组成差异得到的示踪结果具有多解性和不确定性[60-61],因此,在之后的长江流域黄土的物质来源研究方面可以多采用Sr-Nd 同位素、碎屑锆石 U-Pb 年龄谱等新型较可靠的物源分析手段。
根据目前长江流域三地风尘黄土现有的物质来源的研究,长江流域黄土物源大致可分为近源、远源与近源远源混合源(表1)。长江流域黄土的远源一般是指来自于西北干旱沙漠地区的物质随着冬季风以及西风堆积于当地。川西地区黄土剖面为单一远源堆积的较少,在川西叠溪剖面通过粒度和元素地球化学认为叠溪黄土与北方黄土物源具有相似性[62],属于远源堆积。下蜀黄土的远源堆积则认为其是在强烈冬季风作用下“黄土南侵”的结果[63],不论是从现代气象资料记录显示下蜀地区可以接收到亚洲内陆沙尘暴传输的细颗粒粉尘[64],还是下蜀黄土样品中元素地球化学特征与黄土高原黄土相似的直接证据,都表明下蜀黄土存在远源堆积的情况,例如燕子矶剖面[65]、老虎山剖面[66]。巫山地区对圣泉黄土剖面进行的包括Sr和Nd同位素[67]、地球化学元素[68]、粒度特征[69]等在内的物源分析结果表明,巫山圣泉风成黄土与黄土高原洛川、武都黄土同源,都来源于冬季风携带而来的西北沙漠的远源风尘。另外由于巫山客运港剖面地化主量元素特征与甘孜黄土相近,因此,也有观点认为在强盛的青藏高原季风作用下,青藏高原冰缘细粒物质被高原冬季风搬运到巫山地区河谷两岸并堆积形成黄土[70]。
近源堆积观点一般认为长江流域三地的黄土物质来源是就地产生的细颗粒物质在局地天气系统的控制下所堆积而成。川西风成黄土中属于近源堆积的剖面集中分布于川西西部、北部,如甘孜A[56]、满地[38]以及甘孜寺剖面[45]的物源研究结果表明其来自于川西高原冰碛细粒物质和寒冻风化岩层产生的细粒物质。我们推测川西高原西部、北部的冰川较为发育,所产生的细碎物质更为广泛,由此集中分布于此。金沙江黄土集中于深切河谷中,两岸的植被覆盖率较低,但在金沙江巧家段河谷的华弹附近尤其是阶地等地势比较平坦草原和森林草原植被发育很好的地区,符合黄土沉降的下垫面要求,使其沉积下来形成厚达25 m的黄土状沉积物,为局地山谷风环流控制下的风成沉积,物源为相邻河谷中的古堰塞湖相或河漫滩相沉积[96-97]。处于长江流域下游的下蜀黄土其物源更为复杂,下蜀黄土最新的研究在下蜀地区横向上选择22个黄土剖面采样点,与长江流域沉积物、黄土流域泛滥平原以及淮河流域的冲积平原进行元素地球化学对比,结果表明长江泛滥平原为下游黄土沉积提供了一定的沙尘,黄河泛滥平原为淮河上游小范围的下蜀黄土沉积提供了部分沙尘。淮河流域的冲积平原是淮河与长江之间主要地区下蜀黄土的主要尘源[53],说明下蜀地区的近源堆积也存在多个局部尘源。还有通过粒度端元分析结果也得到下蜀黄土沉积物主要来源于冰期时北部淮河流域的冲积平原[98]。巫山黄土的近源物源主要是来自于长江流域河流漫滩/干涸河床沉积物,巫山师范学校剖面/秭归楚王台剖面[78]以及江东嘴剖面[35]都显示出近源堆积的特征。
很多研究结果证明长江流域黄土的物质来源不是单纯的远源或者近源堆积,而是混合源沉积,这些组分可能包括中国西北内陆远源粉尘、黄土高原黄土二次扬尘以及近源粉尘[18, 99-100]。长江流域黄土与黄土高原、长江河流沉积物进行主量、微量元素和Sr-Nd同位素地球化学对比分析[53, 56],结果表明存在多物源堆积,但不同地区的近源远源主次不同。在川西黄土九寨沟荷叶黄土剖面受到高原冬季风、冬季风以及盛行西风的动力作用,物源结果呈现近源远源混合而成的现象[59],而在巫山望天坪剖面[80]、博物馆剖面[81]的物源结果都显示存在由近地面风以及盛行西风、冬季风携带而来的近源远源物质,尤其是位于长江流域下游地区的下蜀黄土,在大港剖面[41]、周家山剖面[11]、仙林剖面[91]同时发现了近源河流冲积物以及西北干旱物质,都表现出近源远源混合的性质。长江流域目前除金沙江黄土以外的其他三地黄土堆积都存在近源远源混合堆积的证据,只是不同剖面的近源远源混合比率不同,不同剖面占主导的成分不同。如何在长江流域风成黄土复杂的物源中剥离出来,是今后的工作需要解决的问题。
总体来讲,因长江流域上中下游在不同时间段都受到不同的气候系统的主导,风尘所受到的沉积动力也不同,动力控制着地区的黄土物质来源进而导致长江流域风成黄土物质来源主要存在近源堆积、远源堆积、混合源堆积三种方式[101](图5),在今后利用长江流域黄土进行古气候研究时,需要注意各地区黄土来源特征。
3.2 长江流域风成黄土形成年代与青藏高原隆升的耦合关系
年代学结果表明川西黄土和下蜀黄土在不同地区、不同地貌部位上的黄土剖面沉积的起始年代不同(表2)。川西黄土的沉积年龄分布存在一定的规律,大体来讲西部、中部年龄较老,东部年龄较年轻。西部以甘孜地区的黄土为例,多为早更新世以来的黄土堆积,黄土年龄可达1.16~0.76 Ma[45, 115]、中部大多数剖面(金川马厂、可尔因剖面)都为中晚更新世以来的堆积,东部的黄土剖面除去九寨沟荷叶剖面、漳腊剖面为中更新世堆积形成,其余黄土堆积开始于晚更新世,黄土年龄在128~9.3 ka 之间(如唐克索克藏寺剖面[77]、叠溪[62]、布瓦[36]、佳山[36]、喇嘛寺剖面[36])。目前川西地区发现的底界年龄最老的黄土剖面发育于川西高原中部金川县内大渡河第12级阶地的角木牛剖面,其底界年龄为2.84 Ma[107]。下蜀黄土是在中、晚更新世期间开始堆积的(表2),新生抒剖面[113]的底界年龄为500 ka,最近有学者将下蜀地区大港[41]和青山剖面[28]中黄土 -古土壤磁化率旋回与北方黄土地层以及深海氧同位素阶段(MIS)对比,将下蜀黄土堆积的起始年龄往前推到了早更新世末期(约为0.9 Ma),成为下蜀地区黄土堆积的最老年龄[28, 40],这一年代结果也在周家山剖面通过古地磁年代法得到证实[11]。目前关于巫山黄土有确定测年的典型剖面较少,主要集中于巫山县城的圣泉剖面。该剖面光释光测年结果显示,在10 m左右年龄为约44.4 ka,在底部15 m年龄为100 ka 左右[10, 84],因此巫山黄土应属于末次冰期沉积。总体来看川西黄土底界年龄多处于早更新世到晚更新世之间,下蜀黄土获得的年代主要介于中、晚更新世期间,巫山黄土目前的年龄都在末次冰期期间。金沙江区域黄土的年代还有待研究,目前在华弹剖面深度为9 m的地方OSL测年结果显示为122.71 ka[31],利用古地磁测年发现剖面中未出现极性倒转,剖面底界年龄晚于780 ka[8]。
表 2 长江流域黄土沉积年龄Table 2. Sedimentary age of loess in the Yangtze River Basin地区 剖面 海拔/沉积厚度/m 测年方法 年龄/ka 可靠性证据 参考文献 川西
地区甘孜寺剖面 3538/15.3(见底) OSL&古地磁 1160
1150热退磁(−620°C)、有退磁结果的剩磁矢量正交投影图;存在B/M倒转以及贾拉米洛正极性亚时的2个界限点年龄、2个OSL样品(样品A:12 ka;样品B:
79 ka)(一共存在5个绝对年龄值)[45, 102] 新市区剖面, 满地剖面 3390/23.7
3470/26
(两剖面综合得到的深度为30.2 m)古地磁&TL 120 热退磁、热释光两剖面各存在2个(新市:4.2 m、11 m;满地:3.2 m、13.1 m) [103] 甘孜六级阶地剖面 3480/32(见底) 1130
1150交变退磁为主与不稳定样的热退磁
(0~690°C)为辅、L1底部热释光年龄为
(74±5) ka[104-105] 叠溪剖面 2394 /(见底) 14C&OSL 62 14C一个、OSL两个(3个控制点都集中于380~450 cm) [62] 九寨沟荷叶黄土剖面 / 14C&ESR 321 14C两个控制点、ESR存在4个控制点 [75] 甘孜A剖面 3483/32.5(见底) 古地磁 1160 热退磁(100~675°C)、存在B/M倒转、有退磁结果的剩磁矢量正交投影图 [56,106] 金川角木牛剖面 3538/46.2 2840 热退磁(存在B/M和M/G两个倒转界限) [107-108] 甘孜剖面 3480/86(见底) 800
766热退磁、存在B/M界限 [30, 71] 金川马厂剖面 2480/19.4 200 热退磁、未出现B/M界限 [109] 茂县三级阶地黄土 ERS 62 3个阶地的样品、1个黄土样品 [110] 可尔因剖面 / 206~145 6个控制点 [76] 唐克索克藏寺剖面 3445/ 128 2个样品控制点 [77] 布瓦剖面 1990/ OSL 23.1±1.8 2个样品控制点 [7] 佳山剖面 2060/ 43.3±1.9 2个样品控制点 喇嘛寺剖面 1995/ 9.3±0.9 2个样品控制点 汪布顶剖面 /8 128 / [29] 巫山
地区漳腊剖面 3030/9.5 磁化率年龄模型 157.6±1.18 / [110] 圣泉剖面/客运港剖面 /15(见底) 14C 12.1 / [111] OSL 100 / [82] /10 44.4 4个样品控制点 [10] 下蜀
地区大港剖面
青山剖面26.5/59.5
36.3/17.3
(见底)OSL&古地磁 900 3个OSL测年样品(青山2个,大港1个);热退磁(−620°C)、有退磁结果的剩磁矢量正交投影图、大港存在B/M倒转 [26, 41] 周家山剖面 /50.7(见底) 880 1.4 m的OSL年龄(>50 ka)和B/M边界年龄(0.78 Ma),基于该堆积速率推得底部年龄约为880 ka [11, 85] 青山剖面 36/20(见底) 900 6个OSL测年样品(25.4~270.9 ka); 热退磁(680°C)存在B/M倒转 [40] 大港剖面 26.6/59.5 古地磁测年 700~800 2个OSL测年样品(根据剖面磁化率旋回 ,与北方黄土地层以及深海氧同位素阶段 ( M IS)对比 ,推算大港剖面的下限年代约为700~ 800 ka) [40] 燕子矶剖面 /23 220 交变退磁;从 0到22.5 m T逐步退磁 [112] 新生抒剖面 /33(见底) 红外释光 500 6个红外释光样品 [113] 仙林剖面 45/7.1 OSL 139.7±14.8 2处OSL年龄 [91] 周家山剖面 /6.1 ESR测年 350 / [88] 燕子矶剖面 /26.5 563.6 / [92] 宣城剖面 /11 700
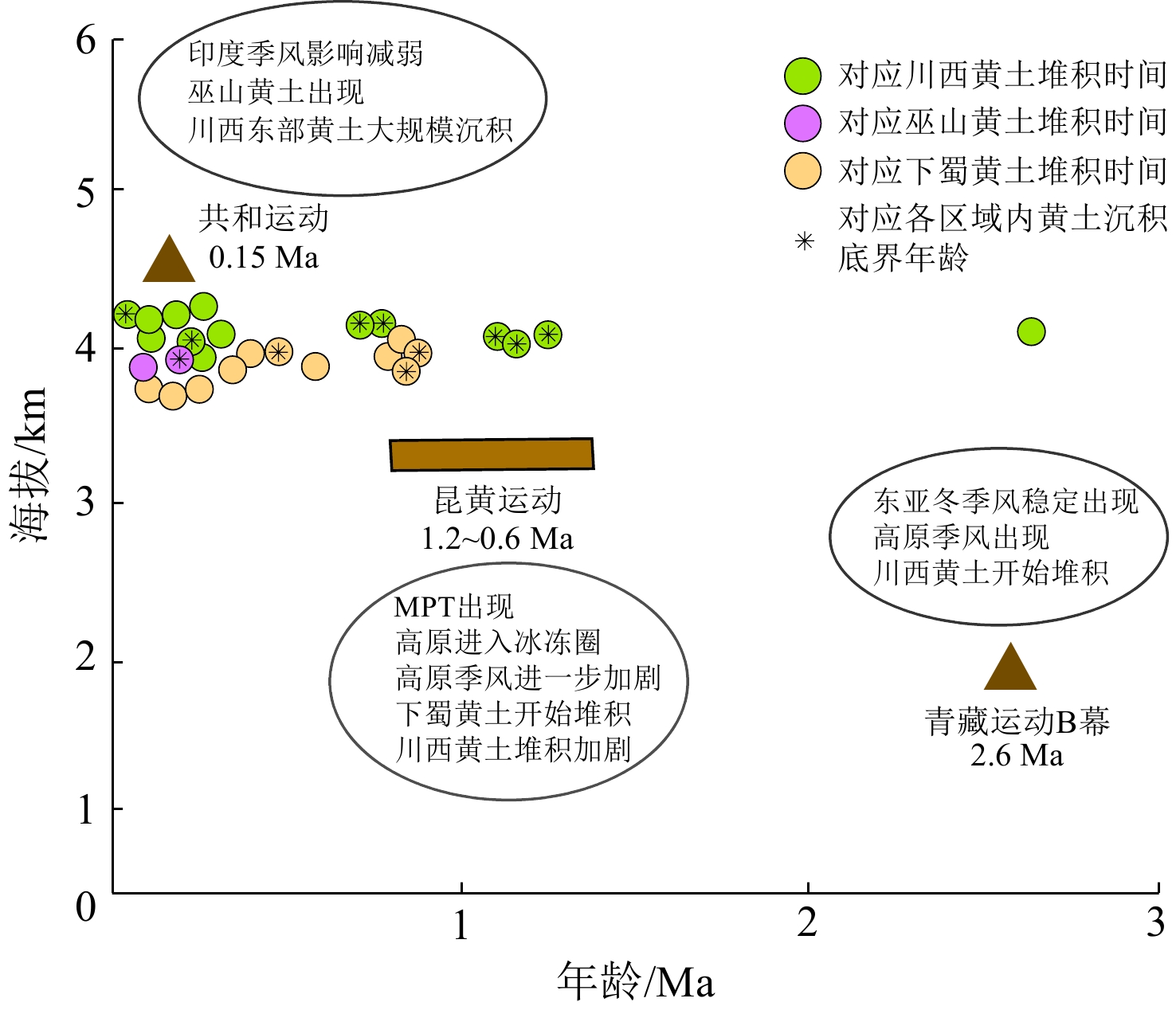
850/ [27, 114] 青藏高原隆升是影响中国大气环流的重要因素之一,对青藏高原季风、东亚季风的形成与演化具有重要的动力与热力作用[116]。在第四纪青藏高原发生了青藏运动、昆仑-黄河运动(简称昆黄运动)以及共和运动三次隆升过程,三次运动发生的时间与长江流域川西、下蜀、巫山地区的黄土堆积的底部年代存在一定耦合性(图6)[116-117]。
约2.6 Ma,青藏高原发生青藏运动B幕,并抬升至约2 000 m, 这时高原面与周围地区开始出现热力性质差异,冬季,青藏高原冷高压加强,形成反气旋,高原季风开始显现[89]。这一过程发生的时间与川西高原目前最老的角木牛黄土剖面沉积年龄(2.84 Ma)存在一致性(图6),推测此时在反气旋式的高原冬季风作用下,青藏高原冰川作用形成的细粒物质、河湖堆积物、基岩风化产物被携带到位于高原外围的川西高原,并在低洼的河流阶地/谷地、断陷盆地等区域沉积,由此拉开川西黄土堆积的序幕。
在1.2~0.6 Ma期间青藏高原发生昆黄运动,青藏高原进一步隆升达到3000~3500 m,高原进入冰冻圈[118 ]。高原上的冰碛物和寒冻风化岩层产生了丰富的细粒物质为黄土堆积提供大量物源,同时高原季风增强,使得川西高原黄土在早更新世之后进一步堆积[21]。在中更新世气候转型(Mid-Pleistocene Transition, MPT)之后全球进一步变冷[119],与此同时,青藏高原冷源增强,对东亚冬季风的影响也增强,西风带受青藏高原的阻挡而发生分流,北支分流绕过青藏高原和东亚冬季风结合而形成的强化西北风[120](但目前在黄土的沉积过程中很难区分两者的动力过程),东亚冬季风随之急剧增加,致使大量的粉尘物质被搬运到中国中东部地区堆积,与长江中下游下蜀黄土目前测得的最老的剖面底部年龄(0.9 Ma)相吻合。
约150 ka时,青藏高原发生共和运动,并抬升到4000 m以上,对西南季风的阻挡作用进一步加强,青藏高原与西北地区干旱加剧,粉尘物质变多,同时青藏高原冷源作用加强,高原季风进一步增强,致使川西高原东部开始出现大规模的黄土沉积(图2,图6),且在青藏高原作用下,冬季风进一步增强[121],下蜀黄土也继续接受沉积。巫山地区见底的风成黄土剖面的年代结果也表明巫山地区黄土开始沉积的年代大约在100 ka,巫山黄土的物源与甘孜地区存在相似性[70],不排除此时高原季风的影响范围可能扩张到了四川盆地东部边缘[118],高原冬季风以及加强的东亚冬季风,共同导致巫山黄土的形成。
4. 长江流域风成黄土风化固碳分析
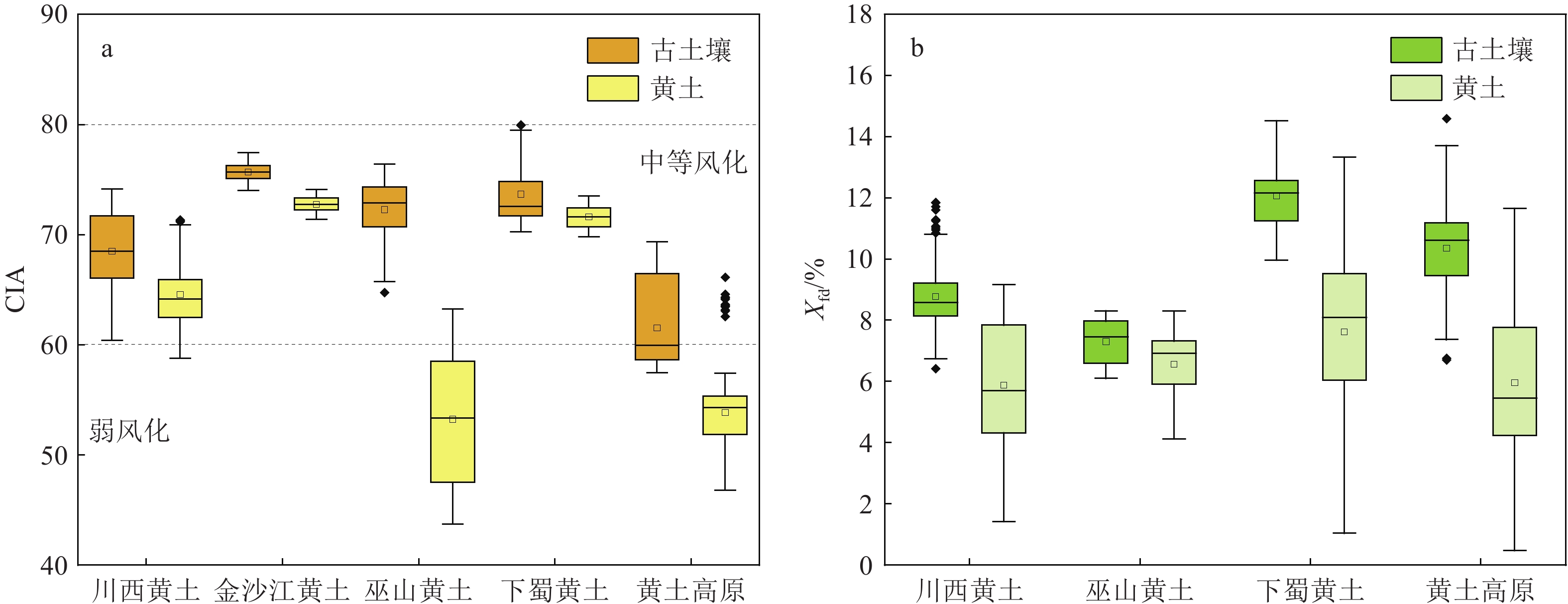
化学蚀变指数(CIA)是元素含量的比值,可以衡量长石类矿物风化成黏土矿物的程度[122],是指示化学风化程度的常用指标[48]。CIA 值在不同的区间范围代表不同的风化程度,CIA 值高,指示化学风化程度较强,而 CIA 的低值表示区域内风化程度较弱[123]。长江流域三地黄土与黄土高原古土壤层段CIA平均值(图7)对比发现金沙江黄土(75.9)>下蜀黄土(74.6)>巫山黄土(72.2)>川西黄土(68.6)>黄土高原(61.5),表明长江流域黄土-古土壤层为中等的化学风化程度,黄土高原古土壤层风化程度相对更弱;对于黄土层,CIA平均值整体呈现金沙江黄土(72.7)>下蜀黄土(71.6)>川西黄土(64.5)>黄土高原(54.9)>巫山黄土(53.8)的趋势,整体上,CIA数据显示除巫山黄土外,其他长江流域的黄土层风化层度也比黄土高原高。频率磁化率百分比(χfd%)是成壤作用形成的超顺磁性颗粒(<0.03 μm)对磁化率的贡献量度,可以很好地指示风化成壤作用的强度[3, 124-125]。古土壤层段的χfd%(图7)平均值总体表现为下蜀黄土(12.1%)>黄土高原(10.3%)>川西黄土(8.8%)>巫山黄土(7.3%),黄土层段表现为下蜀黄土(7.6%)>巫山黄土(6.6%)>黄土高原(5.9%)>川西黄土(5.9%),χfd%对比结果表明总体下蜀黄土不论黄土层还是古土壤层段的风化指数大于黄土高原,而在黄土层段巫山黄土χfd%比黄土高原更高,川西黄土与黄土高原相当。
CIA的结果(图7a)表明,总体上,长江流域不论是在冰期还是间冰期的风化强度都比黄土高原更为强烈,且长江流域黄土与古土壤层的风化指标差值相对于黄土高原差距更小(巫山黄土CIA值除外)。长江流域内部黄土剖面的风化情况也存在差异,金沙江黄土位于纬度更低位置,且受干热河谷影响,此地黄土风化作用最强;下蜀地区黄土剖面地处季风强度较高的长江下游地区,不论是古土壤层还是黄土层的风化情况都比其余两地更为剧烈。另外,川西地区气温较冷,蒸发较弱,夏季冰川融水补给,土层保水高,因此黄土整体风化也比黄土高原强[126]。另外,发现川西与巫山(巫山黄土层段除外)黄土与古土壤层的CIA值都大于黄土高原,但χfd%(图7b)表现为黄土高原大于川西和巫山黄土(巫山黄土层段除外),这主要与黄土高原更靠南端其土壤化作用较强以及两种指标受控的因素还存在一些差异有关,在后续的研究中需要进一步分析χfd%在风化程度研究中的作用。
已有研究表明,与工业革命前相比,末期冰盛期传输到年降水量大于400 mm地区的粉尘硅酸盐风化每年至少净增加(0.431±0.030) Tmol的大气CO2消耗[127],说明在一定范围内降水与风尘风化固碳成正比[128]。根据各个风化指标,总体可以看出长江流域风成黄土剖面无论是在冰期还是在间冰期都比黄土高原的风化程度更高,因此,在冰期长江流域风尘风化过程可能抵消了冰期温度降低对陆地风化速率的抑制作用,进而促进了大气CO2的降低,而在间冰期,长江流域可能与黄土高原黄土一起通过风化固碳,进而可能抑制/减缓了大气CO2的升高。因此,中国湿润区风尘可能在维持陆地表面的碳源碳汇平衡方面发挥了关键作用[128]。
5. 结论与展望
(1)长江流域黄土沉积动力的不同直接导致这些地区黄土的物源也存在近源、远源、混合源堆积三种情况,而不同物源的剖面所反映的古环境也会存在不同。因此在后续长江流域风尘风化及相关研究中,剖面的选择至关重要。在年代学方面,长江流域黄土沉积年代差距较大,推测与第四纪青藏高原的隆升运动存在一定关系。将目前已知的三地黄土最老底界川西(2.84 Ma)、下蜀(0.9 Ma)和巫山(100 ka)与青藏运动B幕、昆黄运动、共和运动阶段性隆升进行对比发现它们在时间上存在耦合性。接下来还需要更多对长江流域黄土研究的底界年龄的结果,特别是还需要补充巫山地区黄土沉积的底界年代。
(2)地处湿润区的长江流域风尘黄土,在冰期与间冰期的风化程度相比受限于干旱气候的黄土高原更高,同等体积的长江流域黄土相比干旱区黄土中的硅酸盐消耗的大气CO2的能力更强、风化固碳作用更为显著[129]。因此,研究湿润区风尘黄土对大气CO2的调控具有重要意义。但是目前还需要更细致地分析长江流域三地黄土风化程度的时空异质性以及造成这种情况的内部机制,这需要后期对长江流域更多风尘黄土剖面进行系统的年代和风化过程研究。
-
图 1 中国黄土分布及研究区分布图
参考自文献[23- 24]。底图来自自然资源部标准底图服务系统;世界底图审图号:GS(2016)665号;中国底图审图号:GS(2023)2765号。
Figure 1. The distribution of loess in China and the locations of the study areas (starred)
References from [23- 24]. The base map is taken from the standard base map service system of the Ministry of Natural Resources. World regional Base map No. GS (2016) No. 665; China regional base map review No. GS(2023)2765.
图 2 川西黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代
a:川西黄土典型剖面分布图,b:甘孜附近黄土分布。黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄,黑色数字代表海拔/沉积厚度。
Figure 2. Distribution of loess profiles, origination, elevation/depositional thicknesses, and ages of formation in the western Sichuan Province
a: Information and distribution of typical loess profiles in the western Sichuan, b: distribution of loess near Ganzi. The yellow numbers represent the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the black numbers represent the elevation/depositional thickness.
图 3 巫山黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代
a:三峡库区范围图,b:巫山黄土典型剖面分布图,c:秭归地区黄土分布黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄、黑色字体代表:海拔/沉积厚度。
Figure 3. Distribution, genesis, elevation/depositional thickness and age of the Wushan Loess
a: The range of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, b: distribution of typical profile of Wushan Loess, c: distribution of loess at Zigui. The yellow number represents the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the black fonts represent the elevation/depositional thickness.
图 4 下蜀黄土剖面分布、成因、海拔/沉积厚度及其形成年代
a:长江下游下蜀黄土典型剖面信息以及分布图, b:黄土分布密集区。黄色数字代表该剖面黄土的沉积年龄,绿色数字代表海拔/沉积厚度。
Figure 4. Distribution, genesis, elevation/depositional thickness, and age of the Xiashu Loess
a: Information and distribution of Xiashu Loess in the lower reaches of Yangtze River, b: Enlarged view of the dense distribution area of loess. The yellow numbers represent the depositional age of loess in the profile, and the green numberts represent the elevation/depositional thickness.
表 1 长江流域黄土成因及物源
Table 1 Genesis and provenance of loess in the Yangtze River Basin
剖面 海拔/沉积厚度/m 方法 成因 物源 参考文献 川西地区 甘孜剖面 3480/86 粒度分析、REE 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [71] 甘孜满地剖面 / 粒度、孢粉、冰楔构造分析 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [38] GZ-1-2 3431 微量元素和稀土元素分析 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [72] 甘孜五级阶地剖面 3455/14.5 环境磁学、地球化学元素 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [73] Garze A /28.5 微量元素、REE和Sm-Nd同位素 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [56] 甘孜寺剖面 3538/15.3(见底) 石英颗粒表面形态分析 风成黄土 近源高原内部堆积 [74] 九寨沟荷叶黄土剖面 / 矿物成分及石英砂表面结构分析 冰川黄土 近源堆积 [75] / 粒度、REE、微量元素分析等 风成黄土 有多源性特征 [59] 可尔因剖面 / 黄土粒度分析、石英表面形态观察 风成黄土 近源堆积 [76] 叠溪剖面 2394 /(见底) 粒度分析、稀土和微量元素 风成黄土 远源堆积 [62] SC剖面A, X剖面, LBZ剖面 / 粒度、常量元素与稀土元素特征
分析等风成黄土 近源堆积 [36] 唐克索克藏寺剖面 3445/ 粒度组分、石英砂的表面结构、冰楔构造、孢粉 风成黄土 近源堆积 [77] 佳山剖面 2060/ 粒度、矿物组成\常量元素与稀土元素特征 风成黄土 近源堆积 [7] 巫山地区 巫山师范学校剖面/秭归楚王台剖面 / 粒度、重矿物、化学成分和石英电镜扫描分析 多成因 近源堆积 [78] 双堰塘 /3.7 粒度分析、常量元素组分分析 多成因 混合堆积 [58] 望天坪剖面 1350/3.1 粒度特征 风成沉积物 混合堆积 [79] 粒度参数特征 风成成因 混合堆积 [80] 粒度特征 风成成因 远源堆积 [35] 巫山博物馆剖面 258/5 分析Sa、CIA、Na/K、铁游离度等风化指标 风积成因 来源复杂 [81] 江东嘴剖面 /3.6 粒度特征 多成因 近源堆积 [35] 势大岭剖面 /8.2 粒度特征 多成因 / [67] 圣泉剖面/客运港剖面 248/15 REE分析 风积成因 混合成因 [82] 常量元素分析 风积成因 / [83] 元素地球化学特征 风积成因 远源堆积 [84] 分析Sr和Nd同位素组成 风积成因 远源堆积 [67] 稀土元素特征值 风积成因 远源堆积 [24] 分析Sr和Nd同位素组成 风积成因 近源堆积为主 [85] 粒度特征 风成沉积 近源河谷风成沉积 [35] 下蜀地区 大港剖面 26.5/59.5 粒度分析 风成堆积 混合堆积 [41, 86-87] 周家山剖面 65/51 粒度组成分析 风成堆积 混合堆积 [11,85,88-89] 老虎山剖面 50/30 粒度、矿物化学成分 混合成因 远源堆积 [90] 仙林剖面 / 环境磁学、地球化学特征 风成堆积 混合堆积 [91] 燕子矶剖面 26/23 / / 远源堆积 [92] 地球化学元素 风成堆积 远源堆积 [66] 青山剖面 36/20 粒度分析 风成堆积 / [26] 下蜀地区 Mufushan剖面 / 锆石U-Pb年龄和同位素地球
化学示踪多成因说 混合堆积 [93] 下蜀黄土
(9个采样点)/ 粒度成分、主元素和微量元素组成的分析结果 风成堆积 近源堆积 [53] 宣城剖面 / 元素地球化学 风成堆积 近源来源 [94] / 风成堆积 近源堆积 [95] 注:“/”表示在对应的文章内未提及。 表 2 长江流域黄土沉积年龄
Table 2 Sedimentary age of loess in the Yangtze River Basin
地区 剖面 海拔/沉积厚度/m 测年方法 年龄/ka 可靠性证据 参考文献 川西
地区甘孜寺剖面 3538/15.3(见底) OSL&古地磁 1160
1150热退磁(−620°C)、有退磁结果的剩磁矢量正交投影图;存在B/M倒转以及贾拉米洛正极性亚时的2个界限点年龄、2个OSL样品(样品A:12 ka;样品B:
79 ka)(一共存在5个绝对年龄值)[45, 102] 新市区剖面, 满地剖面 3390/23.7
3470/26
(两剖面综合得到的深度为30.2 m)古地磁&TL 120 热退磁、热释光两剖面各存在2个(新市:4.2 m、11 m;满地:3.2 m、13.1 m) [103] 甘孜六级阶地剖面 3480/32(见底) 1130
1150交变退磁为主与不稳定样的热退磁
(0~690°C)为辅、L1底部热释光年龄为
(74±5) ka[104-105] 叠溪剖面 2394 /(见底) 14C&OSL 62 14C一个、OSL两个(3个控制点都集中于380~450 cm) [62] 九寨沟荷叶黄土剖面 / 14C&ESR 321 14C两个控制点、ESR存在4个控制点 [75] 甘孜A剖面 3483/32.5(见底) 古地磁 1160 热退磁(100~675°C)、存在B/M倒转、有退磁结果的剩磁矢量正交投影图 [56,106] 金川角木牛剖面 3538/46.2 2840 热退磁(存在B/M和M/G两个倒转界限) [107-108] 甘孜剖面 3480/86(见底) 800
766热退磁、存在B/M界限 [30, 71] 金川马厂剖面 2480/19.4 200 热退磁、未出现B/M界限 [109] 茂县三级阶地黄土 ERS 62 3个阶地的样品、1个黄土样品 [110] 可尔因剖面 / 206~145 6个控制点 [76] 唐克索克藏寺剖面 3445/ 128 2个样品控制点 [77] 布瓦剖面 1990/ OSL 23.1±1.8 2个样品控制点 [7] 佳山剖面 2060/ 43.3±1.9 2个样品控制点 喇嘛寺剖面 1995/ 9.3±0.9 2个样品控制点 汪布顶剖面 /8 128 / [29] 巫山
地区漳腊剖面 3030/9.5 磁化率年龄模型 157.6±1.18 / [110] 圣泉剖面/客运港剖面 /15(见底) 14C 12.1 / [111] OSL 100 / [82] /10 44.4 4个样品控制点 [10] 下蜀
地区大港剖面
青山剖面26.5/59.5
36.3/17.3
(见底)OSL&古地磁 900 3个OSL测年样品(青山2个,大港1个);热退磁(−620°C)、有退磁结果的剩磁矢量正交投影图、大港存在B/M倒转 [26, 41] 周家山剖面 /50.7(见底) 880 1.4 m的OSL年龄(>50 ka)和B/M边界年龄(0.78 Ma),基于该堆积速率推得底部年龄约为880 ka [11, 85] 青山剖面 36/20(见底) 900 6个OSL测年样品(25.4~270.9 ka); 热退磁(680°C)存在B/M倒转 [40] 大港剖面 26.6/59.5 古地磁测年 700~800 2个OSL测年样品(根据剖面磁化率旋回 ,与北方黄土地层以及深海氧同位素阶段 ( M IS)对比 ,推算大港剖面的下限年代约为700~ 800 ka) [40] 燕子矶剖面 /23 220 交变退磁;从 0到22.5 m T逐步退磁 [112] 新生抒剖面 /33(见底) 红外释光 500 6个红外释光样品 [113] 仙林剖面 45/7.1 OSL 139.7±14.8 2处OSL年龄 [91] 周家山剖面 /6.1 ESR测年 350 / [88] 燕子矶剖面 /26.5 563.6 / [92] 宣城剖面 /11 700
850/ [27, 114] -
[1] 刘东生, 安芷生, 文启忠, 等. 中国黄土的地质环境[J]. 科学通报, 1978, 23(1):1-9,26 doi: 10.1360/csb1978-23-1-1 LIU Dongsheng, AN Zhisheng, WEN Qizhong, et al. The geological environment of Chinese loess[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1978, 23(1):1-9,26.] doi: 10.1360/csb1978-23-1-1
[2] Sun Y B, An Z S, Clemens S C, et al. Seven million years of wind and precipitation variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 297(3-4):525-535. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.07.004
[3] 李秉成, 雷祥义, 李正泽, 等. 西安白鹿塬全新世黄土剖面磁化率的古气候特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(1):115-121 LI Bingcheng, LEI Xiangyi, LI Zhengze, et al. Palaeoclimate character of susceptibility of Holocene loess section in Xi'an Bai Luyuan[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(1):115-121.]
[4] 王攀, 张培新, 杨振京, 等. 靖边黄土剖面记录的末次冰期以来的气候变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3):162-170 WANG Pan, ZHANG Peixin, YANG Zhenjing, et al. Climate change since the last glacial stage recorded in Jingbian loess section[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(3):162-170.]
[5] 周家兴, 于娟, 杨丽君, 等. 铜川地区早中全新世黄土沉积特征及其古气候意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(1):160-166 ZHOU Jiaxing, YU Juan, YANG Lijun, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the Early and Middle Holocene loess in Tongchuan area and their implications for paleoclimate[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(1):160-166.]
[6] 陈明扬. 中国风尘堆积与全球干旱化[J]. 第四纪研究, 1991, 11(4):361-372 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1991.04.008 CHEN Mingyang. The evolution of Chinese aeolian deposits and global aridification[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1991, 11(4):361-372.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1991.04.008
[7] 臧楠. 川西杂谷脑河流域黄土特征及成因分析[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2021 ZANG Nan. Characteristics and genetic analysis of loess in Zagnao river basin, western Sichuan[D]. Master Dissertation of Chengdu University of Technology, 2021.]
[8] 管东升. 金沙江河谷黄土状沉积物的成因及其古气候意义[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2012 GUAN Dongsheng. The origin and palaeoclimatic implications of the Loess-like sediment in the valley of Jinshajiang River[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2012.]
[9] 陶莉. 长江三峡地区第四纪沉积物质来源及其沉积环境意义的探讨[D]. 西南师范大学硕士学位论文, 2005 TAO Li. The origin of quaternary deposit and its environmental significance in Three Gorges of the Yangtze River[D]. Master Dissertation of Southwest Normal University, 2005.]
[10] 吴可, 彭红霞, 时冉. 长江三峡地区黄土粒度特征及其成因分析[J]. 华中师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 48(2):284-289 WU Ke, PENG Hongxia, SHI Ran. Analysis on the characteristics and their origin of the grain-size of Wushan loess in the Three Gorges area, China[J]. Journal of Huazhong Normal University:Natural Sciences, 2014, 48(2):284-289.]
[11] Wang X Y, Lu H Y, Zhang H Z, et al. Distribution, provenance, and onset of the Xiashu Loess in Southeast China with paleoclimatic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 155:180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.11.022
[12] Yi S W, Li X S, Han Z Y, et al. High resolution luminescence chronology for Xiashu Loess deposits of Southeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 155:188-197. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.11.027
[13] Fan Q B, Liao J, Yan L, et al. Quartz grain surface microtextural evidence for provenance of the Quaternary aggradation red earth deposit, southern China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2021, 18(8):2048-2060. doi: 10.1007/s11629-020-6523-3
[14] Guan H C, Dai S Q, Ma C M, et al. Paleoclimatic changes during the penultimate interglacial period archived by multiple proxies of Xiashu Loess in the Chaohu Lake Basin, East China[J]. Quaternary International, 2022, 607:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2021.08.003
[15] Bufe A, Hovius N, Emberson R, et al. Co-variation of silicate, carbonate and sulfide weathering drives CO2 release with erosion[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2021, 14(4):211-216. doi: 10.1038/s41561-021-00714-3
[16] Zan J B, Maher B A, Yamazaki T, et al. Mid-Pleistocene links between Asian dust, Tibetan glaciers, and Pacific iron fertilization[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(24):e2304773120.
[17] 张小曳. 亚洲粉尘的源区分布、释放、输送、沉降与黄土堆积[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001, 21(1):29-40 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.01.004 ZHANG Xiaoye. Source distributions, emission, transport, deposition of Asian dust and loess accumulation[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, 21(1):29-40.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.01.004
[18] Caves Rugenstein J K, Ibarra D E, von Blanckenburg F. Neogene cooling driven by land surface reactivity rather than increased weathering fluxes[J]. Nature, 2019, 571(7763):99-102. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1332-y
[19] Kang S G, Wang X L, Roberts H M, et al. Late Holocene anti-phase change in the East Asian summer and winter monsoons[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 188:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.03.028
[20] Zhang Z, Jia Y L. Different provenance of separate loess sites in Yangtze River Basin and its paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2019, 16(7):1616-1628. doi: 10.1007/s11629-018-5278-6
[21] 欧先交, 曾兰华, 周尚哲, 等. 四川西部黄土沉积与环境演变研究综述[J]. 地球环境学报, 2012, 3(1):692-704 OU Xianjiao, ZENG Lanhua, ZHOU Shangzhe, et al. A review on research of loess and environmental change in west Sichuan Plateau of the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2012, 3(1):692-704.]
[22] 孟宝航, 郑坤, 银雪琴. 我国南方下蜀黄土的一些研究进展[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(S1):33-35 MENG Baohang, ZHENG Kun, YIN Xueqin. Some research progress of the loess of Lower Shu in southern China[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(S1):33-35.]
[23] Chen J, Li G J, Yang J D, et al. Nd and Sr isotopic characteristics of Chinese deserts: Implications for the provenances of Asian dust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(15):3904-3914. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.033
[24] 郭正堂. 黄土高原见证季风和荒漠的由来[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47(4):421-437 GUO Zhengtang. Loess Plateau attests to the onsets of monsoon and deserts[J]. Scientia SinicaTerrae, 2017, 47(4):421-437.]
[25] 王治祥. 中新世以来轨道尺度的古气候变化在青藏高原东北缘湖盆记录中的沉积响应[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2019 WANG Zhixiang. Sedimentary response of orbital-scale paleoclimate changes in the lake basin record on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau since the Miocene[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2019.]
[26] 张玉芬, 李长安, 熊德强, 等. 长江三峡巫山黄土稀土元素特征及古环境[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(3):901-911 ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang'an, XIONG Deqiang, et al. Features of rare earth elements and paleoenvironment of Wushan Loess in the Three Gorges, Yangtze River[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(3):901-911.]
[27] 杨达源. 中国东部的第四纪风尘堆积与季风变迁[J]. 第四纪研究, 1991, 11(4):354-360 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1991.04.007 YANG Dayuan. The quaternary dust-fall accumulation and the monsoon variability in eastern China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1991, 11(4):354-360.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1991.04.007
[28] 李徐生, 韩志勇, 鹿化煜, 等. 下蜀黄土底界的年代及其对区域气候变干的指示[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(2): 210-223 LI Xusheng, HAN Zhiyong, LU Huayu, et al. Onset of Xiashu loess deposition in southern China by 0.9 Ma and its implications for regional aridification[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 48(2): 210-223.]
[29] 王建民, 潘保田. 青藏高原东部黄土沉积的基本特征及其环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 1997, 17(4):395-402 WANG Jianmin, PAN Baotian. Loess deposit in eastern part of Qinghai Xizang plateau: its characteristics and environment[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1997, 17(4):395-402.]
[30] 陈富斌, 高生淮, 陈继良, 等. 甘孜黄土剖面磁性地层初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1990, 35(20):1600 doi: 10.1360/csb1990-35-20-1600 CHEN Fubin, GAO Shenghuai, CHEN Jiliang, et al. Preliminary study on the magnetic strata of the Loess profile of Ganzi[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1990, 35(20):1600.] doi: 10.1360/csb1990-35-20-1600
[31] 刘芬良, 高红山, 潘保田, 等. 金沙江干热河谷华弹段黄土状土的成因、年龄及其古气候指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4):60-70 LIU Fenliang, GAO Hongshan, PAN Baotian, et al. The genesis, age and its paleoclimatic significance of loess-like sediments in the Huatan section of the dry-hot valley of the Jinsha River[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4):60-70.]
[32] 许程, 戴国亮. 镇江地区下蜀黄土物理力学性质指标的相关性研究[J]. 城市勘测, 2020(2):200-203,208 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2020.02.050 XU Cheng, DAI Guoliang. Correlations of physical and mechanical properties of Xiashu Loess in Zhenjiang[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2020(2):200-203,208.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2020.02.050
[33] Li X S, Zhou Y W, Han Z Y, et al. Loess deposits in the low latitudes of East Asia reveal the ~20-kyr precipitation cycle[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1):1023. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45379-9
[34] 郑力. 中国东部主要黄土分布区的Sr-Nd同位素物源示踪研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2018, 24(2):246-250 ZHENG Li. Provenances of the major loess deposits in eastern China based on Sr and Nd isotopic characteristics[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2018, 24(2):246-250.]
[35] 朱晓雨, 刘连文, 孟先强. 巫山地区三类黄土沉积物的粒度特征及物源启示[J]. 地球环境学报, 2019, 10(6):579-589 ZHU Xiaoyu, LIU Lianwen, MENG Xianqiang. Grain size characteristics and source enlightenment of the Wushan loess in the Yangtze Three Gorges area[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2019, 10(6):579-589.]
[36] 杨文博. 汶川-茂县地区黄土沉积物特征及物源研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2020 YANG Wenbo. Research on the characteristics of loess sediments and the provenance in Mao County-Wenchuan County[D]. Master Dissertation of Chengdu University of Technology, 2020.]
[37] Hao Q Z, Oldfield F, Bloemendal J, et al. The record of changing hematite and goethite accumulation over the past 22 Myr on the Chinese Loess Plateau from magnetic measurements and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2009, 114(B12):B12101.
[38] 王运生, 李永昭, 向芳. 川西高原甘孜黄土的成因[J]. 地质力学学报, 2003, 9(1): 91-96 WANG Yunsheng, LI Yongzhao, XIANG Fang. The Ganzi loess origin in the West Sichuan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2003, 9(1): 91-96.]
[39] 陈梓炫. 青藏高原东部黄土的铁磁性矿物特征及其古环境意义[D]. 兰州大学博士学位论文, 2023 CHEN Zixuan. Characteristics of iron mineralogy in the loess of the eastern Tibetan Plateau and their paleoenvironmental significance[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2023.]
[40] 李洋. 江苏仪征青山剖面下蜀黄土年代地层学研究[D]. 南京大学硕士学位论文, 2016 LI Yang. The chronostratigraphy study of Xiashu Loess in Qingshan town of Yizheng City, Jiangsu Province[D]. Master Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2016.]
[41] Li X S, Han Z Y, Lu H Y, et al. Onset of Xiashu loess deposition in southern China by 0.9 Ma and its implications for regional aridification[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(3):256-269. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9134-2
[42] 乔彦松, 赵志中, 王燕, 等. 川西甘孜黄土-古土壤序列的地球化学演化特征及其古气候意义[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(3): 255-260 QIAO Yansong, ZHAO Zhizhong, WANG Yan, et al. Variations of geochemical compositions and the paleoclimatic significance of a loess-soil sequence from Garzê County of western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(24): 4697-4703.]
[43] 陈梓炫. 川西高原黄土环境磁学研究[D]. 福建师范大学硕士学位论文, 2019 CHEN Zixuan. Environmental Magnetism of Loess on the Western Sichuan Plateau[D]. Master Dissertation of Fujian Normal University, 2019.]
[44] 陈慧. 末次冰期以来甘孜黄土环境磁学特征及其环境意义[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2019 CHEN Hui. Environmental magnetic characteristics of Ganzi loess and its environmental significance since the last glacial[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2019.]
[45] 乔彦松, 赵志中, 王燕, 等. 川西甘孜黄土磁性地层学研究及其古气候意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(2):250-256 QIAO Yansong, ZHAO Zhizhong, WANG Yan, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and its paleoclimatic significance of a loess-soil sequence from Ganzi area, west Sichuan plateau[J]. Quaternary Research, 2006, 26(2):250-256.]
[46] 张玉芬, 李长安, 熊德强, 等. “巫山黄土”氧化物地球化学特征与古气候记录[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(1):352-360 ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang'an, XIONG Deqiang, et al. Oxide geochemical characteristics and paleoclimate records of "Wushan loess"[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(1):352-360.]
[47] 侯跃伟. 三峡库区巫山望天坪沉积物环境磁学特征研究[D]. 西南大学硕士学位论文, 2010 HOU Yuewei. Primary research on magnetic characteristics of Wangtianping sediment in Wushan County of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[D]. Master Dissertation of Southwest University, 2010.]
[48] 吴超. 长江和黄河下游风尘黄土沉积源汇过程与第四纪晚期东亚干旱化[D]. 华东师范大学博士学位论文, 2021 WU Chao. Source-sink processes of wind-dusted loess deposition in the lower reaches of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers and late Quaternary aridification in East Asia[D]. Doctor Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2021.]
[49] 韩艳. 大别山北麓黄土磁性变化机理研究[D]. 福建师范大学, 2022 HAN Yan. Study on the mechanism of magnetic variations of loess in the northern piedmont of the Dabie Mountains[D]. Fujian Normal University, 2022.]
[50] 宋祎晴. 扬州地区下蜀黄土中的炭屑特征及古环境意义[D]. 华东师范大学, 2023 SONG Yiqing. Characterization and paleoenvironmental significance of charcoal debris in the Lower Shu loess of YangZhou area[D]. East China Normal University, 2023.]
[51] 陈骏, 安芷生, 刘连文, 等. 最近2.5Ma以来黄土高原风尘化学组成的变化与亚洲内陆的化学风化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(2): 136-145 CHEN Jun, AN Zhisheng, LIU Lianwen, et al. Variations in chemical compositions of the eolian dust in Chinese Loess Plateau over the past 2.5 Ma and chemical weathering in the Asian inland[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2001, 44(2): 403-413.]
[52] 吴翼, 朱照宇, 饶志国, 等. 蓝田玉山第四纪中后期黄土-古土壤序列环境磁学研究[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(22):2214-2225 doi: 10.1360/csb2010-55-22-2214 WU Yi, ZHU Zhaoyu, RAO Zhiguo, et al. Mid-Late Quaternary loess-paleosol sequence in Lantian’s Yushan, China: An environmental magnetism approach and its paleoclimatic significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(22):2214-2225.] doi: 10.1360/csb2010-55-22-2214
[53] Han L, Hao Q Z, Qiao Y S, et al. Geochemical evidence for provenance diversity of loess in southern China and its implications for glacial aridification of the northern subtropical region[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 212:149-163. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.04.002
[54] Bird A, Millar I, Rodenburg T, et al. A constant Chinese Loess Plateau dust source since the late Miocene[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 227:106042. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.106042
[55] Stevens T, Carter A, Watson T P, et al. Genetic linkage between the Yellow River, the Mu Us desert and the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 78:355-368. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.11.032
[56] Qi L, Qiao Y S. Geochemical characteristics of Eolian deposits on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and implications for provenance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica - English Edition, 2014, 88(3):963-973. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12249
[57] 文星跃, 黄成敏, 王成善. 重要环境与气候变化事件: 深时古土壤的记录与响应[J]. 土壤通报, 2015, 46(5):1272-1280 WEN Xingyue, HUANG Chengmin, WANG Chengshan. Critical events in paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic change revealed by deep-time paleosols[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2015, 46(5):1272-1280.]
[58] 张芸, 朱诚, 张强, 等. 长江三峡大宁河流域3000年来的沉积环境和风尘堆积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(4):83-88 ZHANG Yun, ZHU Cheng, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Sedimentary environment and eolian deposits in past 3000 a in Daning valley of the three gorges of the Yangtze river[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(4):83-88.]
[59] 文星跃, 唐亚, 黄成敏, 等. 青藏高原东缘风成黄土的多源性: 以九寨沟黄土为例[J]. 山地学报, 2014, 32(5):603-614 WEN Xingyue, TANG Ya, HUANG Chengmin, et al. Multi-material source of loess deposits from the Jiuzhaigou national nature reserve on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Mountain Research, 2014, 32(5):603-614.]
[60] 陈骏, 李高军. 亚洲风尘系统地球化学示踪研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(9): 1211-1232 CHEN Jun, LI Gaojun. Geochemical studies on the source region of Asian dust[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(9): 1211-1232]
[61] 曹向明, 钟威, 张智, 等. 赣北风沙-粉尘堆积体系元素地球化学变化特征及其对黄土物源示踪意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(1):203-213 CAO Xiangming, ZHONG Wei, ZHANG Zhi, et al. The systematic variation of geochemistry in Furong-Zhouxi aeolian sand-dust deposital cell in middle and lower reaches of Yangtze river and its implications for provenance of loess[J]. Quaternary Research, 2020, 40(1):203-213.]
[62] 文星跃, 吴勇, 黄成敏, 等. 岷江上游晚更新世黄土粒度与元素组成特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 山地学报, 2019, 37(4):488-498 WEN Xingyue, WU Yong, HUANG Chengmin, et al. Grain size & elements composition characteristics and their implications for provenance of the late pleistocene loess in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River, China[J]. Mountain Research, 2019, 37(4):488-498.]
[63] 杨达源. 晚更新世冰期最盛时长江中下游地区的古环境[J]. 地理学报, 1986(4):302-310 YANG Dayuan. The paleoenvironment of the mid-lower regions of Changjiang in the full-glacial period of late Pleistocene[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1986(4):302-310.]
[64] 钱鹏, 郑祥民, 周立旻. 沙尘暴期间上海市大气颗粒物元素地球化学特征及其物源示踪意义[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(5):2010-2017 QIAN Peng, ZHENG Xiangmin, ZHOU Limin. Geochemical characteristics and sources of atmospheric particulates in Shanghai during dust storm event[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(5):2010-2017.]
[65] 黎兴国, 何娟华, 李立文. 南京燕子矶下蜀黄土中铁含量与古气候变化[J]. 铁道师院学报:自然科学版, 1993, 10(1):48-56 LI Xingguo, HE Juanhua, LI Liwen. Ferrum in loess strata and palaeoclimatic changes of the Xiashu Loess in Yanziji of Nanjing[J]. Journal of Suzhou Railway Teachers College, 1993, 10(1):48-56.]
[66] 王爱萍, 杨守业, 李从先. 南京地区下蜀土元素地球化学特征及物源判别[J]. 同济大学学报, 2001, 29(6):657-661 WANG Aiping, YANG Shouye, LI Congxian. Elemental geochemistry of the Nanjing Xiashu loess and the provenance study[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2001, 29(6):657-661.]
[67] 张玉芬, 李长安, 李启文, 等. 三峡巫山黄土Sr-Nd同位素组成与物源示踪[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(3):960-967 ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang'an, LI Qiwen, et al. Sr-Nd isotopic composition and provenance tracing of Wushan Loess, Three Gorges, Yangtze River[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(3):960-967.]
[68] 何永峰, 王建力, 王勇. 长江三峡巫山地区第四纪沉积物元素地球化学特征[J]. 太原师范学院学报:自然科学版, 2009, 8(4):94-100,110 HE Yongfeng, WANG Jianli, WANG Yong. Geochemistry characteristics of quaternary sediments from Wushan District in Three Gorges[J]. Journal of Taiyuan Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2009, 8(4):94-100,110.]
[69] 刘冬雁, 李巍然, 彭莎莎, 等. 粒度分析在中国第四纪黄土古气候研究中的应用现状[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2010, 40(2):79-84 LIU Dongyan, LI Weiran, PENG Shasha, et al. Current application of grain size analysis in Chinese loess paleoclimatic study[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2010, 40(2):79-84.]
[70] 赵小明, 李长安, 王孔伟, 等. 三峡库区宜昌-重庆段基础地质与地质灾害[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社有限责任公司, 2012 ZHAO Xiaoming, LI Chang'an, WANG Kongwei, et al. Basic Geological and Geological Disasters in the Yichang-Chongqing Section of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2012.]
[71] 方小敏, 陈富斌, 施雅风, 等. 甘孜黄土与青藏高原冰冻圈演化[J]. 科学通报, 1996, 41(20):1865-1867 doi: 10.1360/csb1996-41-20-1865 FANG Xiaomin, CHEN Fubin, SHI Yafeng, et al. Evolution of Ganzi Loess and the ice circle of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1996, 41(20):1865-1867.] doi: 10.1360/csb1996-41-20-1865
[72] Feng J L, Hu Z G, Ju J T, et al. Variations in trace element (including rare earth element) concentrations with grain sizes in loess and their implications for tracing the provenance of eolian deposits[J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 236(1-2):116-126. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.04.024
[73] Hu P X, Liu Q S, Heslop D, et al. Soil moisture balance and magnetic enhancement in loess–paleosol sequences from the Tibetan Plateau and Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 409:120-132. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.10.035
[74] 乔彦松, 刘冬雁, 李朝柱, 等. 川西甘孜地区黄土的磁性地层学研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2007, 13(4):289-296 QIAO Yansong, LIU Dongyan, LI Chaozhu, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of a loess-soil sequence in the Garze area, western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2007, 13(4):289-296.]
[75] 彭东, 曹俊, 杨俊义, 等. 四川九寨沟地区黄土的初步研究[J]. 中国区域地质, 2001, 20(4):359-365 PENG Dong, CAO Jun, YANG Junyi et al. Study of loess in the Jiuzhaigou area, Sichuan[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2001, 20(4):359-365.]
[76] 刘维亮, 李国新, 谷曼. 川西高原可尔因地区黄土成因研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2007, 16(4):300-302 LIU Weiliang, LI Guoxin, GU Man. Study on the origin of the loess in Keryin area, West Sichuan Plateau[J]. Geology and Resources, 2007, 16(4):300-302.]
[77] 盛海洋. 青藏高原东北缘若尔盖盆地黄土的成因[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(1):62-74 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.007 SHENG Haiyang. Zoigê basin loess origin in the northeast Tibet Plateau[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2010, 35(1):62-74.] doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.007
[78] 谢明. 长江三峡地区的黄土状堆积物[J]. 地球化学, 1991(3):292-300 XIE Ming. Loessal deposits in the Three-Gorge area of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River[J]. Geochimica, 1991(3):292-300.]
[79] 王建明, 王勇, 王建力. 巫山第四纪沉积物粒度特征研究[J]. 人民长江, 2009, 40(13):13-15 WANG Jianming, WANG Yong, WANG Jianli. Research on granular characteristics of Quaternary deposit in Wushan County[J]. Yangtze River, 2009, 40(13):13-15.]
[80] 黄臻, 王建力, 王勇. 长江三峡巫山第四纪沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 热带地理, 2010, 30(1):30-33,39 HUANG Zhen, WANG Jianli, WANG Yong. Grain-size features of quaternary sediments in Changjiang Three Gorge Reservoir of the Wushan area[J]. Tropical Geography, 2010, 30(1):30-33,39.]
[81] 刘俊延, 陈林, 慈恩, 等. 巫山黄土成因及其发育土壤特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2022, 53(2):262-269 LIU Junyan, CHEN Lin, CI En, et al. The origin of Wushan loess and the characteristics of soil derived from it[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 53(2):262-269.]
[82] 张玉芬, 李长安, 邵磊, 等. “巫山黄土”的稀土元素特征与成因[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(1):181-187 ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang'an, SHAO Lei, et al. REE compositions of the “Wushan Loess” and its origin[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2013, 38(1):181-187.]
[83] 李长安, 张玉芬, 熊德强, 等. “巫山黄土”常量元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2013, 38(5):916-922 LI Chang'an, ZHANG Yufen, XIONG Deqiang, et al. Major element compositions of the “Wushan Loess”[J]. Journal of Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2013, 38(5):916-922.]
[84] 张玉芬, 邵磊, 熊德强. “巫山黄土”元素地球化学特征及成因和物源意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1):78-84 ZHANG Yufen, SHAO Lei, XIONG Deqiang. Elemental compositions of the "Wushan Loess": Implications for origin and sediment source[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1):78-84.]
[85] Zhu X Y, Liu L W, Wang X Y, et al. The Sr-Nd isotope geochemical tracing of Xiashu Loess and its implications for the material transport mechanism of the Yangtze River[J]. Catena, 2021, 203:105335. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105335
[86] 李徐生, 杨达源, 鹿化煜. 镇江下蜀黄土粒度特征及其成因初探[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(1):25-32 LI Xusheng, YANG Dayuan, LU Huayu. Grain-size features and genesis of the Xiashu loess in Zhenjiang[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(1):25-32.]
[87] 刘梦慧, 李徐生, 韩志勇, 等. 下蜀黄土参数化粒度端元分析及其物源示踪[J]. 地球环境学报, 2021, 12(5):510-525 LIU Menghui, LI Xusheng, HAN Zhiyong, et al. Parametric end-member analysis of the grain size distribution of the Xiashu loess and its provenance tracing[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2021, 12(5):510-525.]
[88] 刘峰, 王昊, 秦艺帆, 等. 南京周家山下蜀黄土色度特征及其意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):143-151 LIU Feng, WANG Hao, QIN Yifan, et al. Chroma characteristics of the Zhoujiashan Xiashu loess profile in Nanjing and its significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5):143-151.]
[89] 陈璞皎, 郑祥民, 周立旻, 等. 宁镇地区下蜀黄土粒度特征及其古环境意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5):7-13 CHEN Pujiao, ZHENG Xiangmin, ZHOU Limin, et al. Grain size distribution and its significance of the Xiashu Loess in Nanjing-Zhenjiang area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(5):7-13.]
[90] 邵家骥. 长江下游第四纪下蜀黄土的成因探讨[J]. 中国区域地质, 1988(4):312-319 SHAO Jiaji. The origin of the Xiashu loess in the lower reaches of the Yangzi River[J]. Regional Geology of China, 1988(4):312-319.]
[91] 陈玉美, 舒强, 张茂恒, 等. 南京下蜀黄土记录的250~100ka期间的环境演化信息[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(6):55-59,77 CHEN Yumei, SHU Qiang, ZHANG Maoheng, et al. Environmental evolution information recorded in the Xiashu Loess (250-100 ka) in Nanjing, China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(6):55-59,77.]
[92] 黎兴国, 何娟华, 李德生, 等. ESR在下蜀黄土测年中的尝试[J]. 南京师大学报:自然科学版, 1993, 16(3):86-91 LI Xingguo, HE Juanhua, LI Desheng, et al. The attempt of ESR in the measurement of the loess of Xiashu[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University:Natural Science, 1993, 16(3):86-91.]
[93] Liu F, Li G J, Chen J. U-Pb ages of zircon grains reveal a proximal dust source of the Xiashu loess, Lower Yangtze River region, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(20):2391-2395. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0318-2
[94] Qiao Y S, Hao Q Z, Peng S S, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the eolian deposits in southern China, and their implications for provenance and weathering intensity[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 308(3-4):513-523. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.06.003
[95] Hao Q Z, Guo Z T, Qiao Y S, et al. Geochemical evidence for the provenance of middle Pleistocene loess deposits in southern China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(23-24):3317-3326. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.08.004
[96] 王泽丽. 金沙江河谷黄土状物质的成因及其环境指示意义研究[D]. 云南师范大学硕士学位论文, 2016 WANG Zeli. Study on the genesis of loess-like materials in the Jinshajiang River Valley and their environmental indications[D]. Master Dissertation of Yunnan Normal University, 2016.]
[97] 叶玉林, 苏怀, 董铭, 等. 元素和矿物组成揭示的金沙江干热河谷黄土状物质的物源[J]. 地球环境学报, 2018, 9(3):238-244 YE Yulin, SU Huai, DONG Ming, et al. Elements and mineral composition indicating the provenance of loess-like sediments in Dry-Hot Valleys of Jinsha River[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2018, 9(3):238-244.]
[98] Jiang Q D, Hao Q Z, Peng S Z, et al. Grain-size evidence for the transport pathway of the Xiashu loess in northern subtropical China and its linkage with fluvial systems[J]. Aeolian Research, 2020, 46:100613. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2020.100613
[99] Shang Y, Prins M A, Beets C J, et al. Aeolian dust supply from the Yellow River floodplain to the Pleistocene loess deposits of the Mangshan Plateau, central China: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age spectra[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 182:131-143. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.01.001
[100] Xiang F, Huang H X, Ogg J G, et al. Quaternary sediment characteristics and paleoclimate implications of deposits in the Three Gorges and Yichang areas of the Yangtze River[J]. Geomorphology, 2020, 351:106981. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.106981
[101] 王博, 王牛牛, 王志远, 等. MIS13时期黄土高原东西部地区夏季风不对称演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):185-192 WANG Bo, WANG Niuniu, WANG Zhiyuan, et al. Unparallel MIS13 climate evolution between western and eastern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3):185-192.]
[102] 李名则. 川西甘孜黄土地层与古气候变化[D]. 中国地质科学院硕士学位论文, 2008 Li Mingze. Garze loess strata and its implication to paleoclimatic change in the western Sichuan[D]. Master Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2008.]
[103] 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 肖华国, 等. 川西高原甘孜黄土地层学[J]. 地球学报, 1997, 18(4):413-420 JIANG Fuchu, WU Xihao, XIAO Huaguo, et al. The Ganzi Loess stratigraphy in the West Sichuan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1997, 18(4):413-420.]
[104] 颜茂都, 方小敏, 陈诗越, 等. 青藏高原更新世黄土磁化率和磁性地层与高原重大气候变化事件[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(S1):182-186 YAN Maodu, FANG Xiaomin, CHEN Shiyue, et al. Pleistocene magnetic susceptibility and paleomagnetism of the Tibetan loess and its implications on large climatic change events[J]. Science China (Series D:Earth Sciences), 2001, 31(S1):182-186.]
[105] 陈诗越, 方小敏, 王苏民. 川西高原甘孜黄土与印度季风演化关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(3):41-46 CHEN Shiyue, FANG Xiaomin, WANG Sumin. Relation between the loess stratigraphy on the eastern Tibetan Plateau and Indian monsoon[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(3):41-46.]
[106] 刘冬雁, 彭莎莎, 乔彦松, 等. 青藏高原东南缘甘孜黄土磁化率揭示的西南季风演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5):115-121 LIU Dongyan, PENG Shasha, QIAO Yansong, et al. Evolution of the southwest monsoon on orbital time-scale revealed by a loess-paleosol sequence on the southeastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau for the last 1.16 Ma[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5):115-121.]
[107] Qiao Y S, Wang Y, Yao H T, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of a loess-paleosol sequence from higher terrace of the Daduhe River in the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2015, 89(1):316-317. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12421
[108] 白文彬. 川西金川黄土地层时代与15万年以来环境演化[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2020 BAI Wenbin. The stratigraphic age of the loess and the environmental evolution since 150, 000 years in Jinchuan County, Western Sichuan Plateau[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020.]
[109] 王书兵. 川西中部晚更新世地层与环境[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2005 WANG Shubing. Late Pleistocene stratigraphy and environment in central western Sichuan[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2005.]
[110] 杨文光, 朱利东, 罗虹, 等. 川西漳腊黄土地层与气候变化[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2011, 27(3):231-237 YANG Wenguang, ZHU Lidong, LUO Hong, et al. Stratigraphy of Zhangla loess in western Sichuan plateau and its paleoclimatic change record[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2011, 27(3):231-237.]
[111] 柯于义, 尹华刚, 郭峰, 等. 三峡库区“巫山黄土”成因研究[J]. 人民长江, 2007, 38(9):72-73,76 KE Yuyi, YIN Huagang, GUO Feng, et al. Research on the causes of "Wushan Loess" in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Yangtze River, 2007, 38(9):72-73,76.]
[112] 武春林, 朱诚, 鹿化煜, 等. 南京地区下蜀黄土磁性地层年代与古环境变化[J]. 地层学杂志, 2006, 30(2):116-123 WU Chunlin, ZHU Cheng, LU Huayu, et al. Magnetostratigraphical dating of the Xiashu Lower Shu loess in Nanjing area and its paleoenvironmental interpretation[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2006, 30(2):116-123.]
[113] 赖忠平, 周杰, 夏应菲, 等. 南京下蜀黄土红外释光地层年代学[J]. 中国沙漠, 2001, 21(2):116-121 LAI Zhongping, ZHOU Jie, XIA Yingfei, et al. Luminescence geochronology of Xiashu Loess near Nanjing[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2001, 21(2):116-121.]
[114] Qiao Y S, Guo Z T, Hao Q Z, et al. Loess-soil sequences in southern Anhui Province: Magnetostratigraphy and paleoclimatic significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(19):2088-2093. doi: 10.1360/03wd0183
[115] 成婷. 川西高原黄土石英光释光测年研究[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2018 CHENG Ting. Quartz OSL dating of loess sequences from the Western Sichuan Plateau[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2018.]
[116] Lai Z P, Zhang W G, Chen X, et al. OSL chronology of loess deposits in East China and its implications for East Asian monsoon history[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2010, 5(2-3):154-158. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2009.02.006
[117] Fang X M, Li J J, Van der Voo R. Rock magnetic and grain size evidence for intensified Asian atmospheric circulation since 800, 000 years B. P. related to Tibetan uplift[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 165(1):129-144. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00259-3
[118] 李吉均. 青藏高原的地貌演化与亚洲季风[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(1):1-12 LI Jijun. Studies on the geomorphological evolution of the Qinghai Xizang (Tibetan) plateau and Asian monsoon[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(1):1-12.]
[119] Peng S Z, Hao Q Z, Wang L, et al. Geochemical and grain-size evidence for the provenance of loess deposits in the Central Shandong Mountains region, northern China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2016, 85(2):290-298. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2016.01.005
[120] Gong H J, Zhang R, Yue L P, et al. Magnetic fabric from red clay sediments in the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1):9706. doi: 10.1038/srep09706
[121] 刘维明, 杨胜利, 方小敏. 川西高原黄土记录的末次冰期气候变化[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2013, 43(3):974-982 LIU Weiming, YANG Shengli, FANG Xiaomin. Loess recorded climatic change during the last glaciation on the eastern Tibetan Plateau, Western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2013, 43(3):974-982.]
[122] 石天宇, 张样洋, 翟秋敏, 等. 临汾盆地晚冰期至中全新世黄土-古土壤序列的风化特征及指示的气候意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2023, 43(2):181-191 SHI Tianyu, ZHANG Yangyang, ZHAI Qiumin, et al. Characteristics of weathering of the loess-paleosol sequences in the Late Glacial Period to Middle Holocene in Linfen Basin and implication for climatic significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2023, 43(2):181-191.]
[123] 徐小涛, 邵龙义. 利用泥质岩化学蚀变指数分析物源区风化程度时的限制因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(3):515-522 XU Xiaotao, SHAO Longyi. Limiting factors in utilization of chemical index of alteration of mudstones to quantify the degree of weathering in provenance[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2018, 20(3):515-522.]
[124] Wang S M, Xue B. Environmental evolution of Zoigê Basin since 900 kaB. P. and comparison study with Loess Plateau[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 1997, 40(3):329-336. doi: 10.1007/BF02877543
[125] 强小科, 安芷生, 常宏. 佳县红粘土堆积序列频率磁化率的古气候意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3):91-96 QIANG Xiaoke, AN Zhisheng, CHANG Hong. Implication of frequency-dependent magnetic susceptibility of red clay sequences in the Jiaxian profile of northern China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3):91-96.]
[126] 沈小晓. 川西地区风成沉积物上土壤发生学特征及环境意义[D]. 西华师范大学硕士学位论文, 2019 SHEN Xiaoxiao. Soil pedogenesis and environmental significance based on Aeolian parent materials in western Sichuan[D]. Master Dissertation of China West Normal University, 2019.]
[127] Rao W B, Han G L, Tan H B, et al. Chemical and Sr isotopic characteristics of rainwater on the Alxa Desert Plateau, North China: Implication for air quality and ion sources[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 193:163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.04.007
[128] Yang Y, Galy A, Zhang J, et al. Dust transport enhanced land surface weatherability in a cooling world[J]. Geochemical Perspectives Letters, 2023, 26:36-39. doi: 10.7185/geochemlet.2322
[129] Hilley G E, Porder S. A framework for predicting global silicate weathering and CO2 drawdown rates over geologic time-scales[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(44):16855-16859.



 下载:
下载: