Distribution, transport and controlling factors of suspended sediment near Rizhao in the west of South Yellow Sea
-
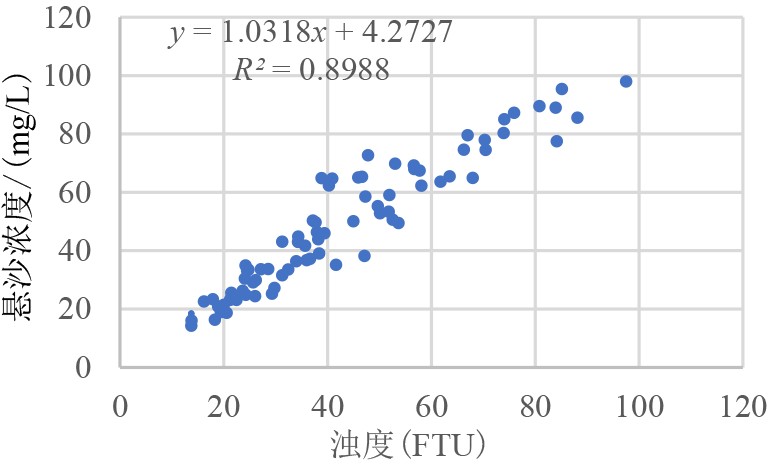
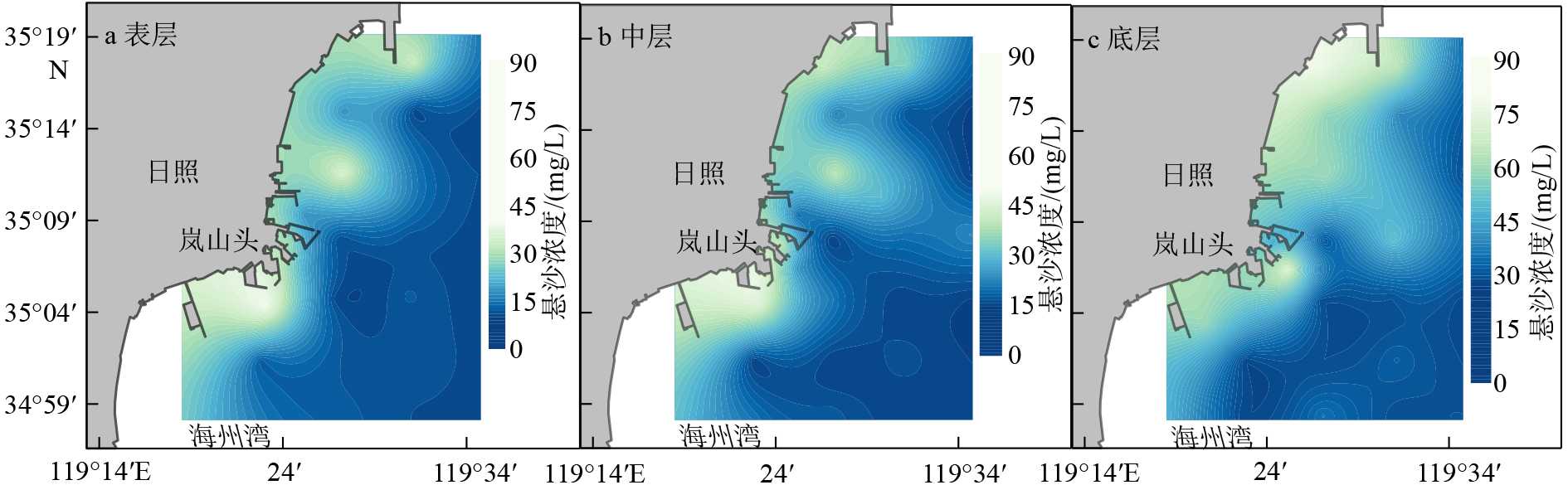
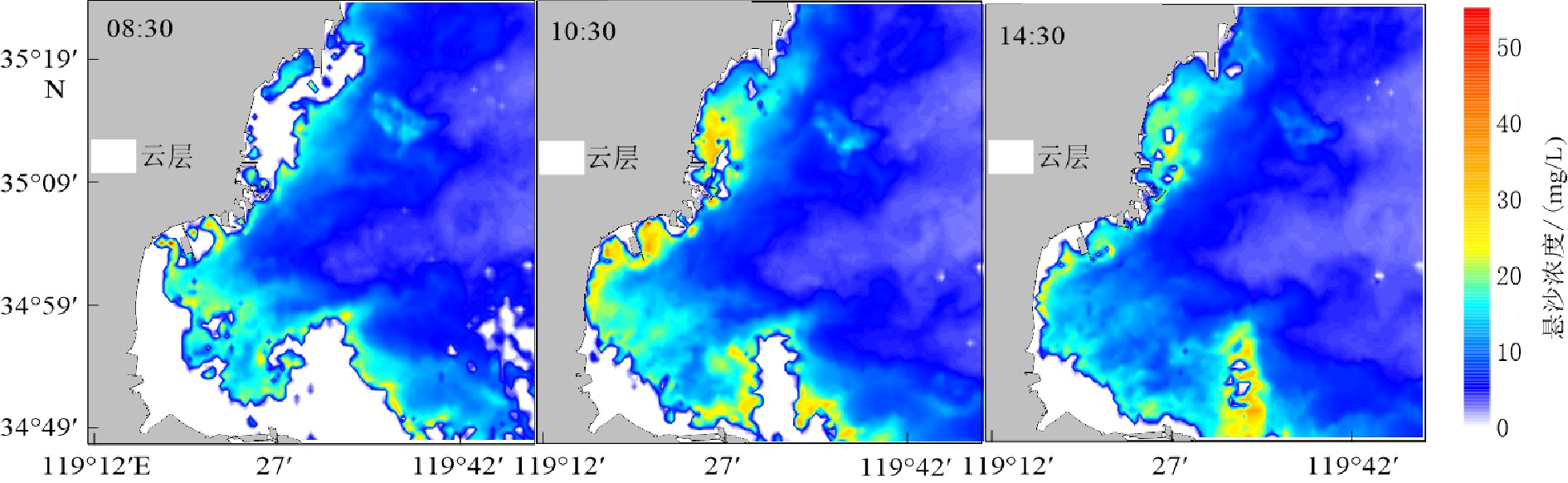
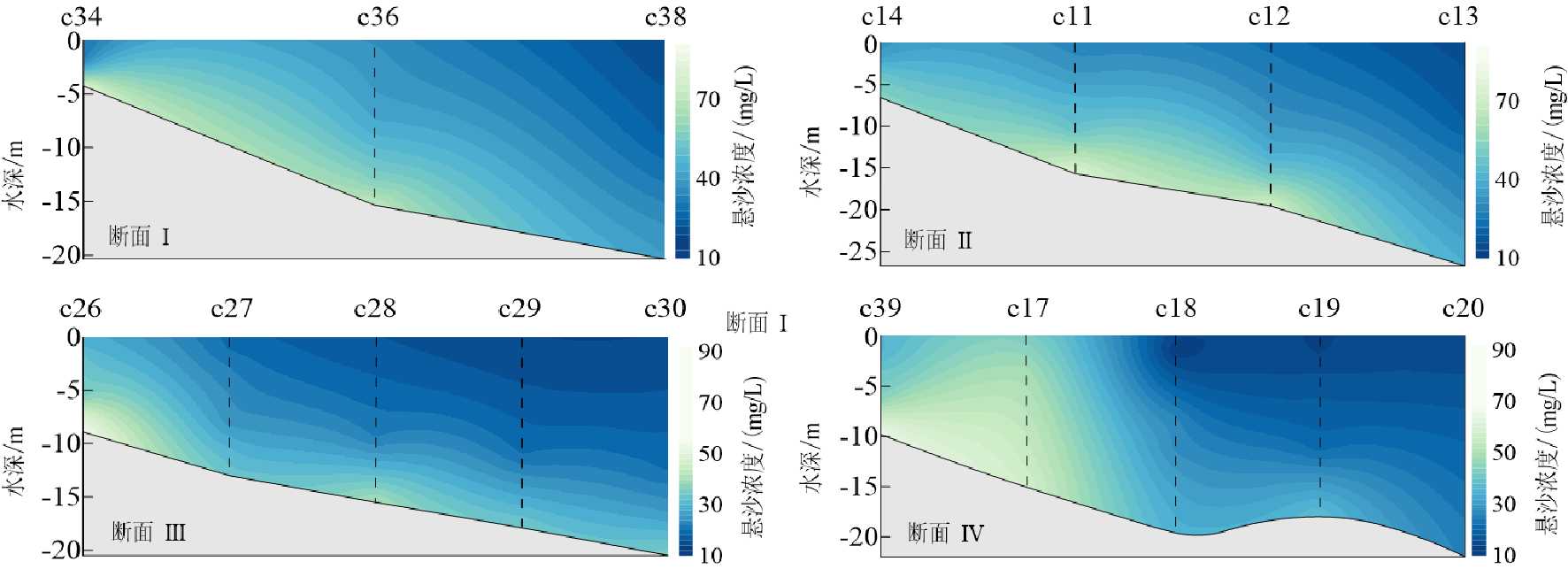
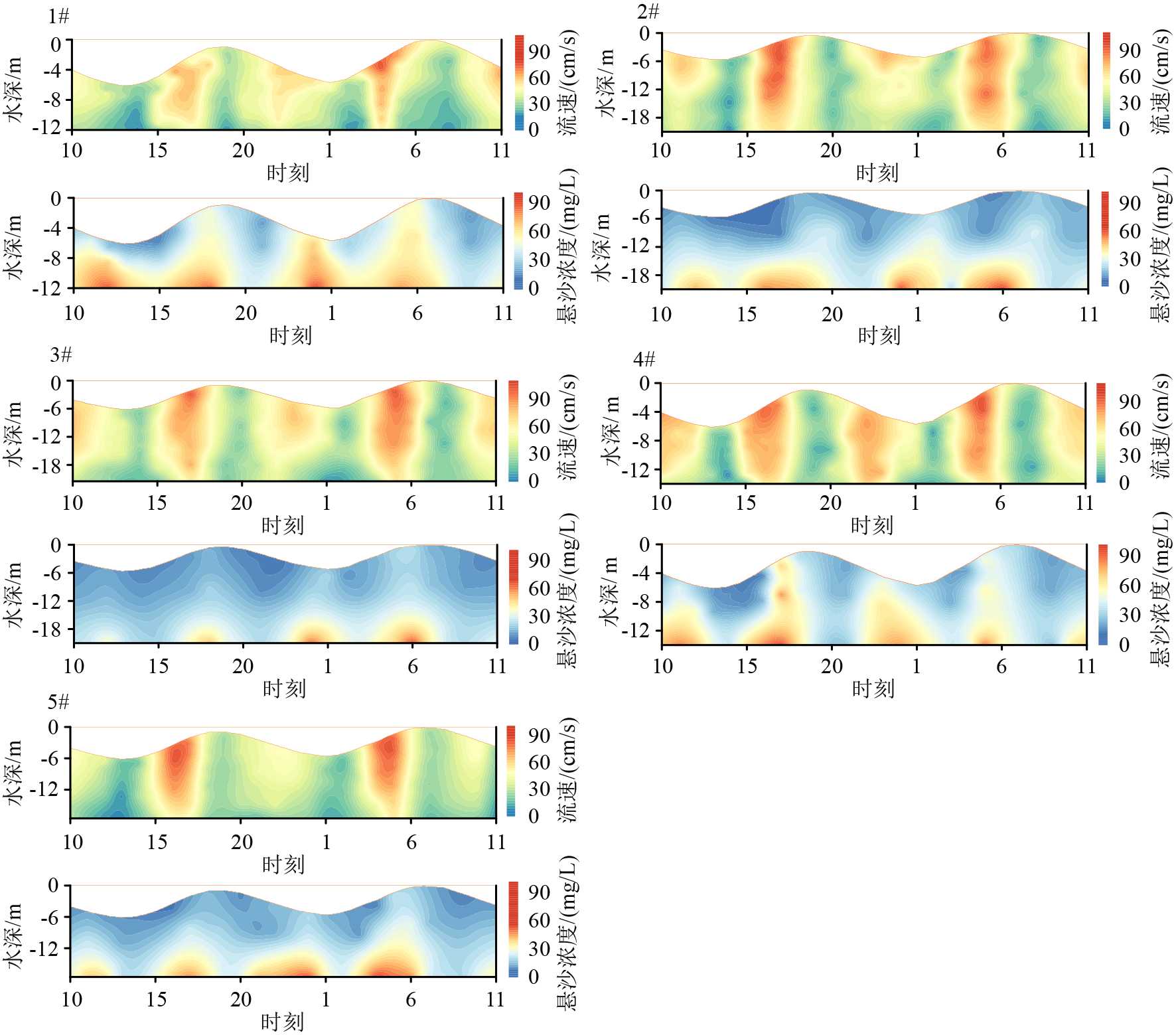
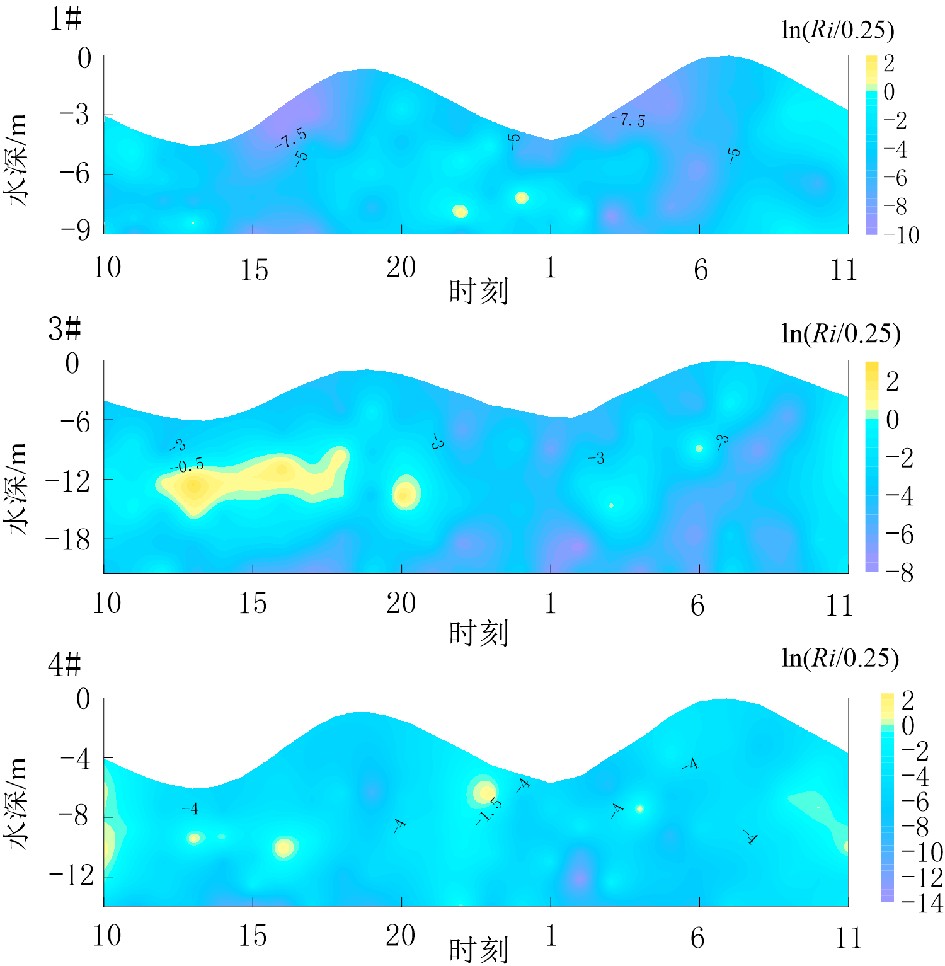
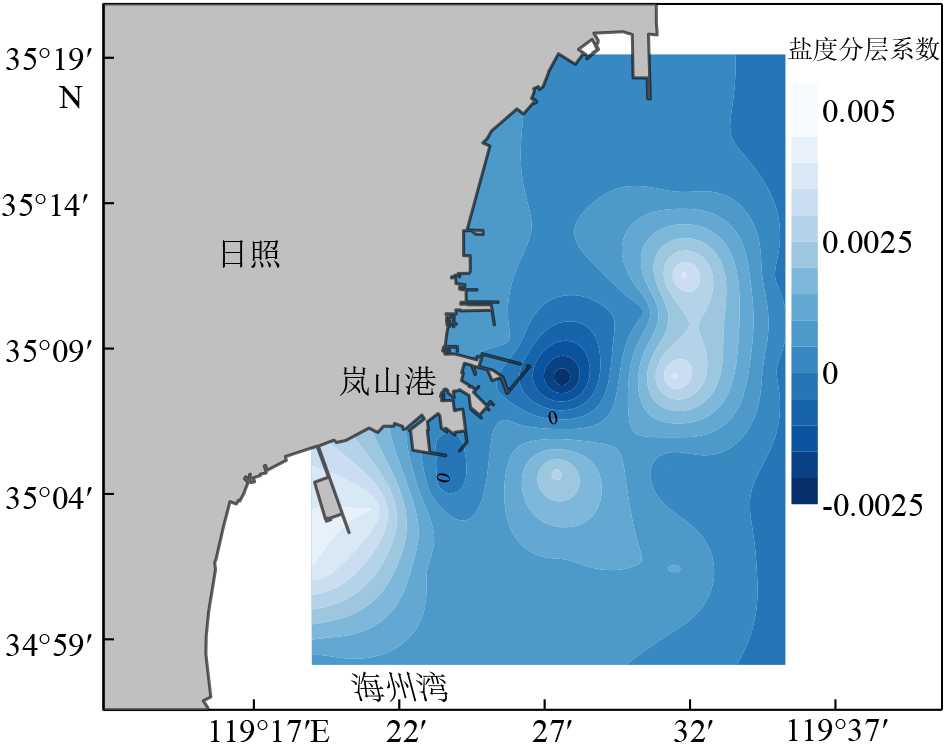
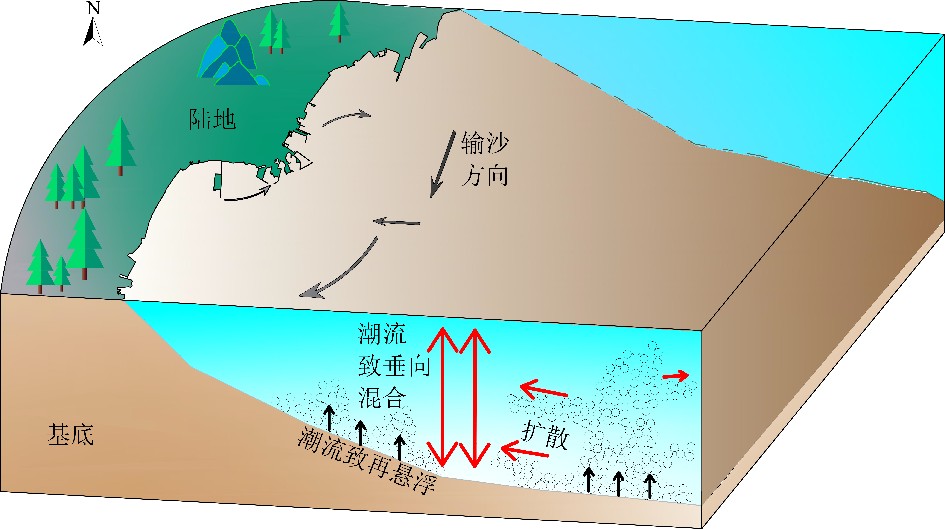
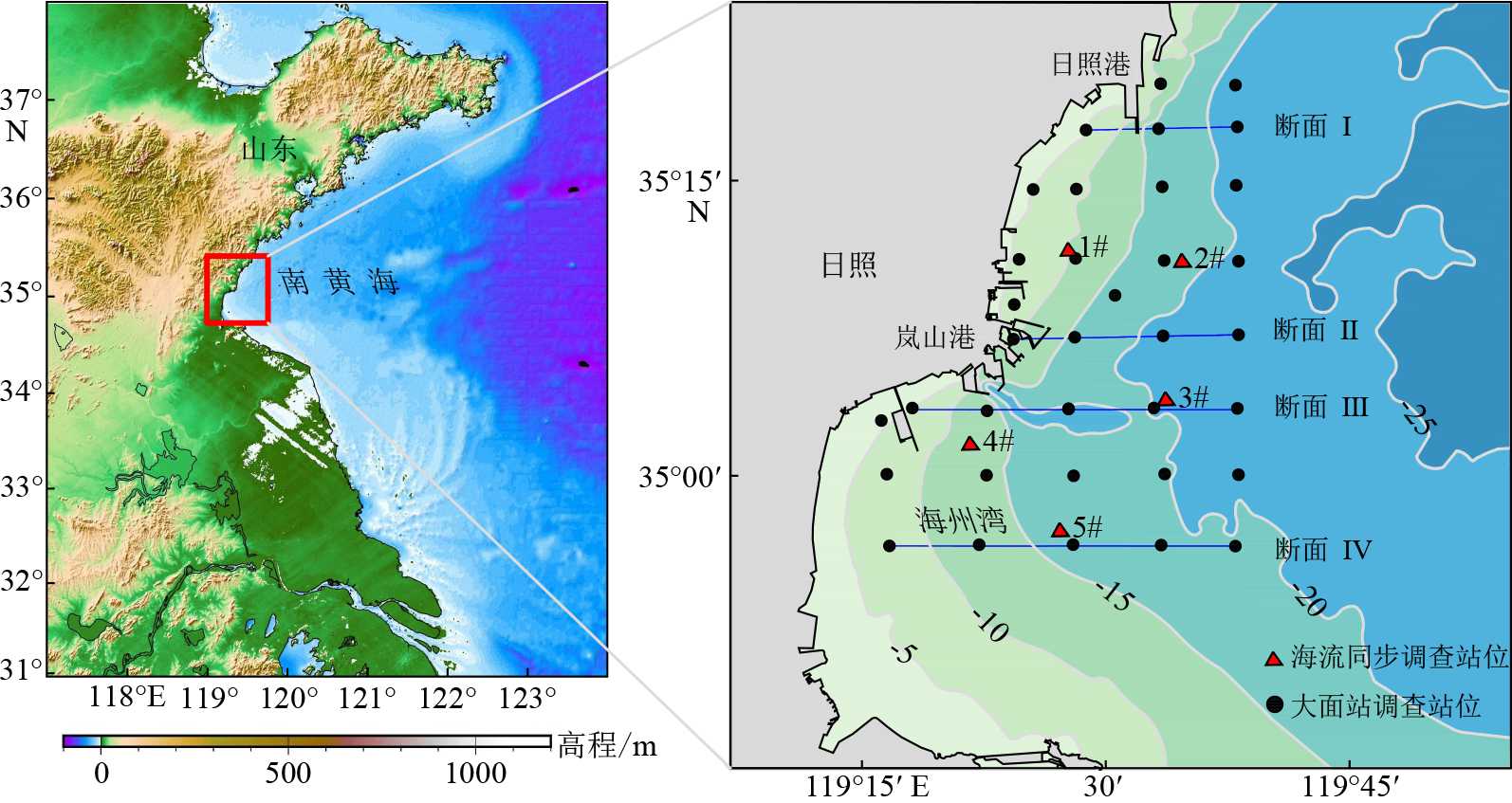
摘要: 基于2020年10月日照近岸海域大潮期水文泥沙观测资料,研究了海流和悬浮泥沙时空分布特征,利用单宽通量机制分解等方法,探讨了悬浮泥沙输运机制和控制因素。结果表明,日照近岸海域悬浮泥沙浓度平面上呈由岸向海逐渐降低的分布特征,垂向上呈由表层至底层逐渐升高的趋势。悬浮泥沙浓度变化与潮周期流速变化趋势总体一致,但具有滞后效应。研究区单宽净输沙率为4.72~24.68 g/(s·m),近岸单宽净输沙率明显大于远岸输沙率。悬浮泥沙输运以平流输运为主,其次为潮泵效应或垂向净环流输运。研究区水体垂向混合均匀,对悬浮泥沙垂向分布影响微弱。潮流引起研究区悬浮泥沙浓度的潮周期变化,南黄海西部近海悬浮泥沙净输运方向和潮余流方向大体相同,在远岸开阔海域总体呈向南的净输运趋势。研究成果有利于完善南黄海西部近海泥沙输运规律理论成果,对日照近岸工程建设具有一定的指导意义。Abstract: In this paper, based on the hydrological and sediment observation data collected from the coastal area of Rizhao in October 2020 during the spring tide, the spatial and temporal distribution pattern of ocean current and suspended sediment are studied, and the transport mechanism and controlling factors of the suspended sediment discussed by means of single wide flux mechanism decomposition. The results show that the concentration of suspended sediment in the studied coastal area decreases gradually from shore to sea laterally, and increases gradually from top to bottom vertically. The variation trend of suspended sediment concentration is consistent with the velocity change of tidal cycle, except for the hysteresis effect. The net sediment transport rate per width in the study area varies between 4.72 and 24.68 g/(s·m), and the net sediment transport rate per width near shore is significantly higher than that offshore. The main transport of suspended sediment is advection, followed by tidal pump effect or vertical net circulation. The vertical mixing of water body in the study area is uniform, and its effect on vertical distribution of suspended sediment is rather weak. Tidal current is the major process to cause the tidal cycle change of suspended sediment concentration in the study area. The net transport direction of suspended sediment and tidal residual current are roughly the same in the west coast of the South Yellow Sea, and there is southward net transport trend in general in the far shore area of the open sea. The research results are beneficial to improve the theoretical results of sediment transport pattern in the west of the South Yellow Sea and have certain guiding significance to the engineering construction in the Rizhao coast.
-
Keywords:
- control factors /
- suspended sediment /
- transport mechanism /
- Rizhao /
- South Yellow Sea
-
-
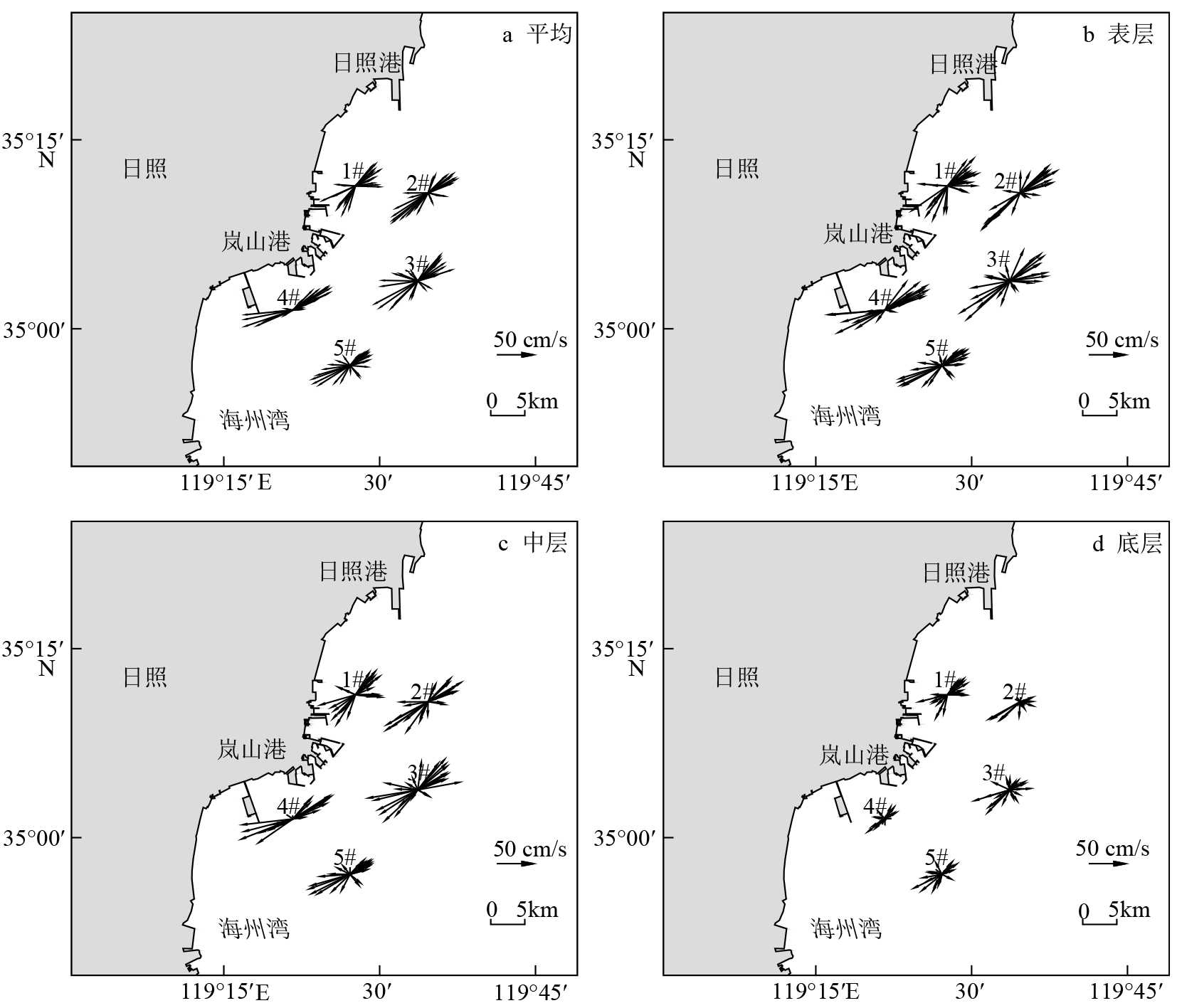
表 1 各站位海流观测结果
Table 1 Marine current observation results at each station
涨潮 落潮 站位 层位 最大 平均 最大 平均 流速/(cm/s) 流向
/(°)流速/(cm/s) 流向
/(°)流速/(cm/s) 流向
/(°)流速/(cm/s) 流向
/(°)1# 表层 78.78 274.2 51.69 223.14 67.93 108.4 45.03 68.19 中层 66.50 294.5 46.22 239.22 56.21 97.1 41.26 58.04 底层 53.43 271.3 32.06 233.10 40.90 91.3 29.89 59.91 2# 表层 94.56 277.9 55.50 216.15 77.60 134.1 50.55 65.71 中层 92.17 351.7 55.36 242.51 69.24 181.6 42.47 66.52 底层 63.54 267.2 44.16 228.07 44.79 123.3 28.25 69.73 3# 表层 105.80 345.9 58.30 255.99 75.60 152.5 52.13 74.80 中层 89.95 336.9 55.27 256.61 77.48 120.0 53.53 61.68 底层 67.35 355.1 32.76 267.59 45.89 113.9 28.50 47.94 4# 表层 96.21 279.0 58.30 254.57 79.06 105.6 49.91 60.66 中层 85.10 303.0 52.24 261.03 75.26 135.5 47.65 59.28 底层 61.33 277.0 34.50 248.25 67.88 103.9 31.84 61.78 5# 表层 83.70 347.5 53.89 260.53 52.00 144.3 38.11 70.11 中层 78.60 320.4 51.30 257.51 44.60 140.9 33.85 63.83 底层 57.10 308.1 33.22 251.34 31.70 135.5 20.36 90.33 表 2 各站位垂向余流特征值
Table 2 Vertical residual power flow characteristic values at each station
站位 表层 中层 底层 流速/(cm/s) 流向
/(°)流速/(cm/s) 流向
/(°)流速/(cm/s) 流向
/(°)1# 10.1 107.0 7.5 56.6 6.6 71.9 2# 4.9 140.8 4.7 193.9 5.6 198.6 3# 3.8 264.5 5.4 312.4 3.4 324.5 4# 8.9 14.6 8.7 15.8 5.5 34.6 5# 3.3 297.0 2.5 279.7 3.9 241.3 表 3 各海流观测站位平均悬浮泥沙浓度垂向变化统计
Table 3 Statistical table of vertical variation of average suspended sediment concentration at each current observation station
mg/L 站位 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# 表层 34.92 12.92 12.62 30.55 12.67 中层 44.61 19.06 16.30 39.12 17.61 底层 63.00 38.25 35.32 59.61 35.19 表 4 悬浮泥沙浓度特征值
Table 4 List of characteristic values of suspended sediment concentration
mg/L 表层 中层 底层 最小值 14.79 19.43 33.25 最大值 45.22 53.85 85.53 平均值 23.97 30.22 50.19 表 5 1#、3#、4#站位温度、盐度特征值
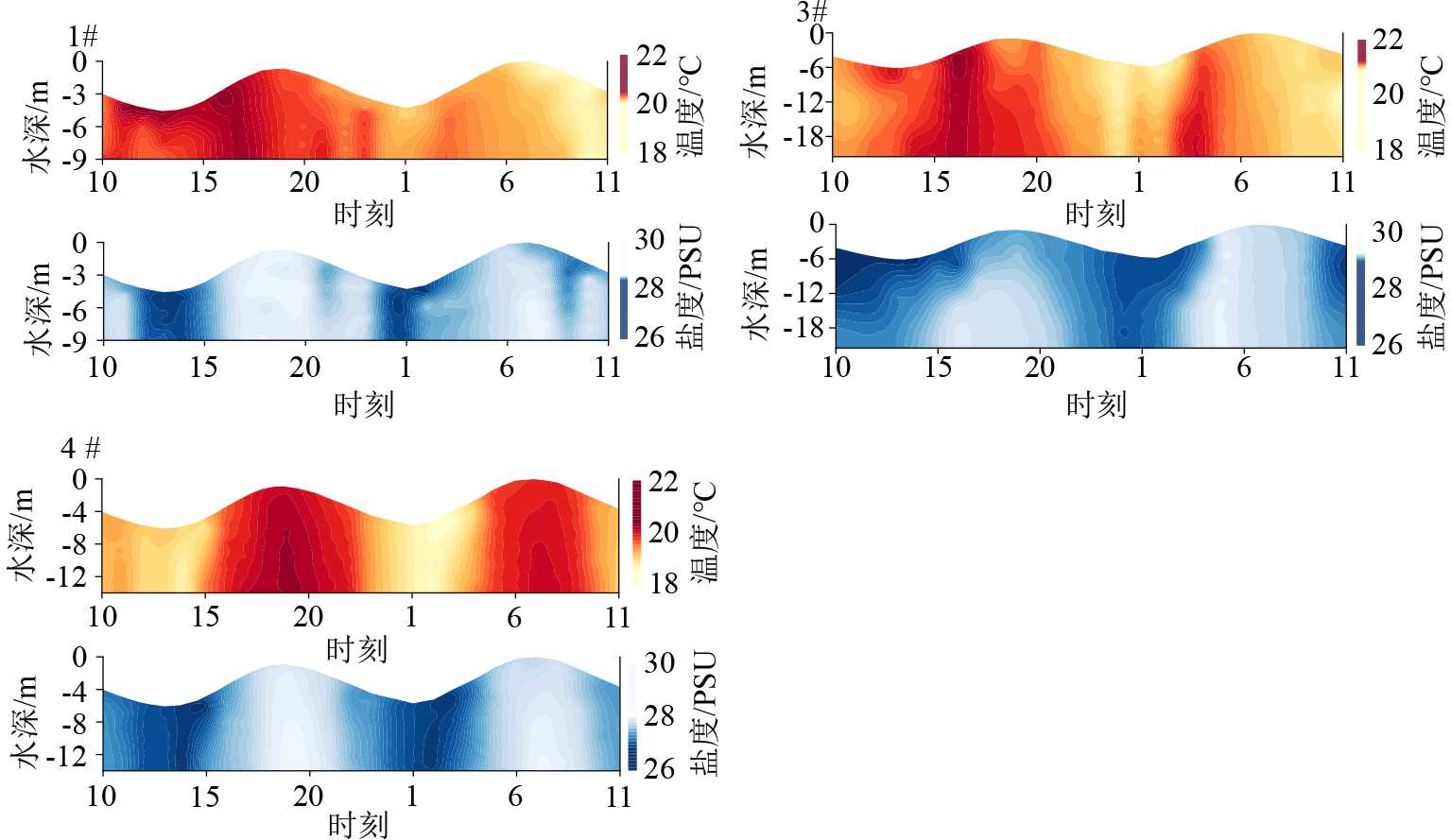
Table 5 The characteristic values of temperature and salinity at stations 1, 3 and 4
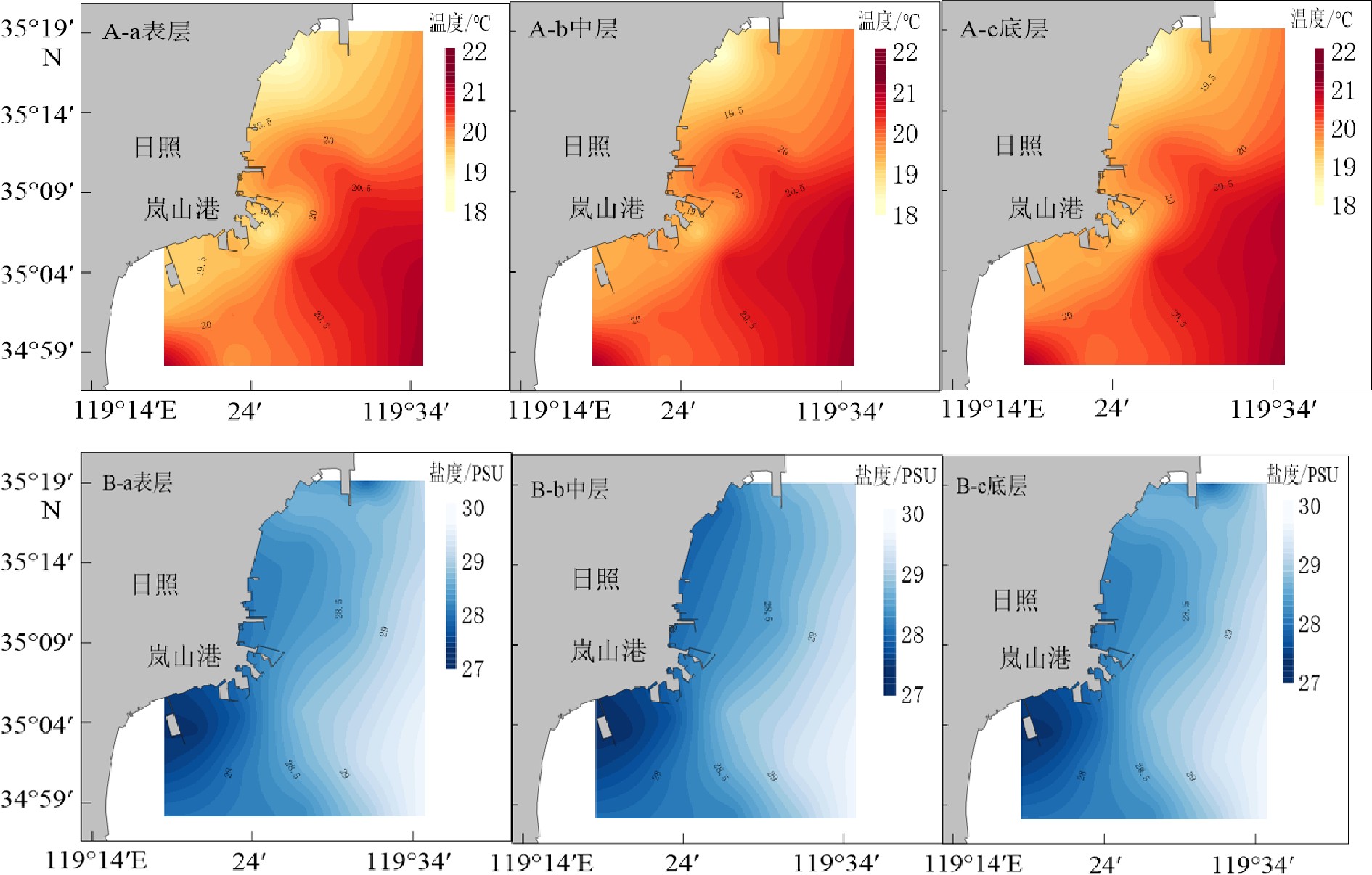
站位 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 1# 20.01 20.51 20.29 28.45 28.65 28.57 3# 20.93 21.28 21.10 28.99 29.31 29.15 4# 18.66 20.32 19.54 26.85 28.02 27.44 表 6 大面站温度、盐度特征值
Table 6 Table of characteristic values of temperature and salinity of the main surface station
层位 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 表层 18.70 21.22 20.07 27.38 29.69 28.60 中层 18.30 21.23 20.08 27.46 29.70 28.61 底层 18.42 21.23 20.09 27.49 29.68 28.63 表 7 悬浮泥沙输运项及单宽净输沙率
Table 7 Suspended sediment transport items and net sediment transport rate per width
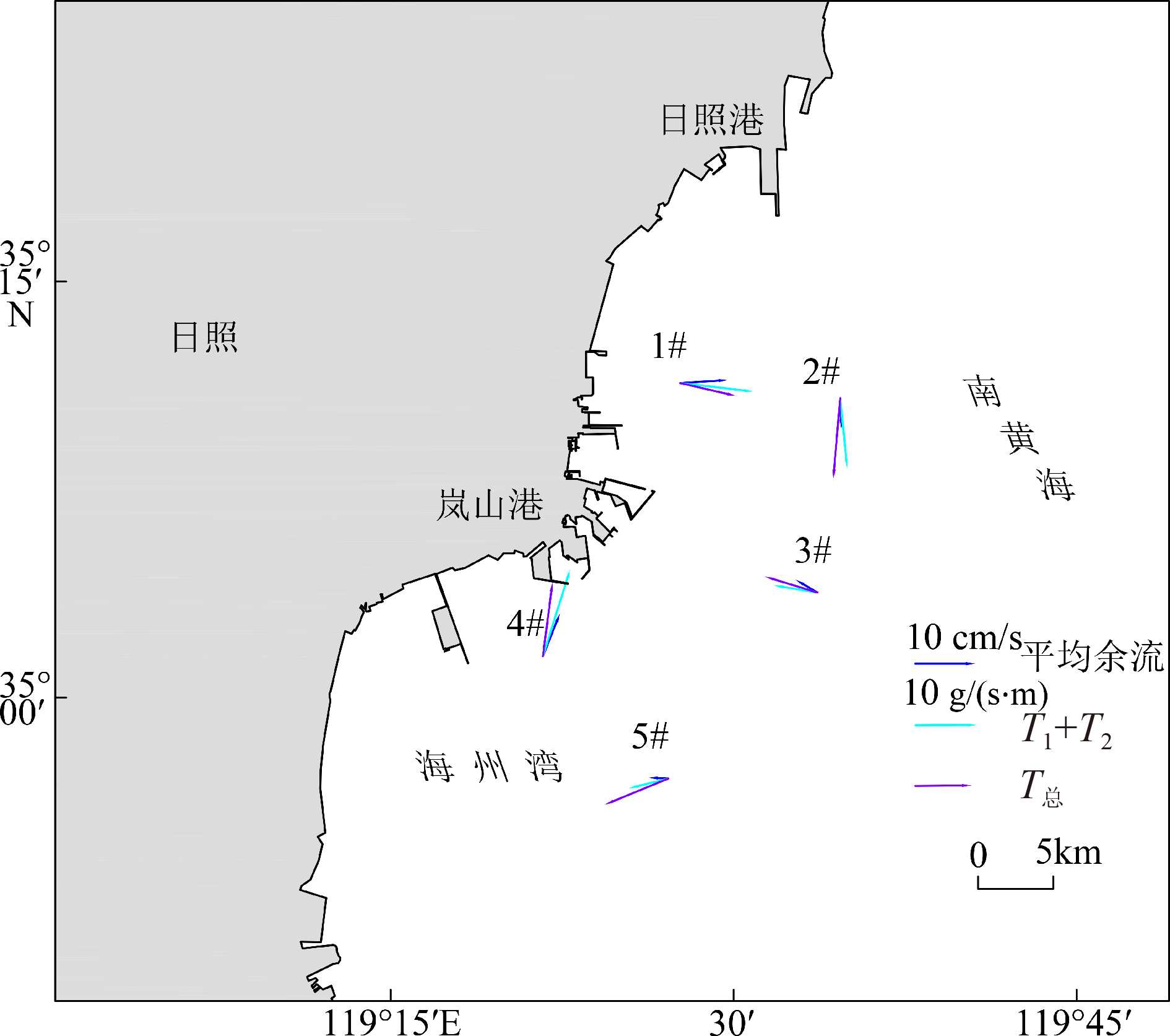
站位 输沙项 T1 T2 T3+T4 T5 T6+T7+T8 T1+T2 T总 1# 输沙率/(g/(s·m)) 30.38 9.82 5.31 2.15 0.47 24.46 19.12 方向/(°) 80.09 214.97 232.65 308.18 31.32 96.62 103.02 2# 输沙率/(g/(s·m)) 7.90 8.39 0.37 3.75 1.06 11.64 13.42 方向/(°) 128.20 217.06 178.32 234.00 42.02 174.31 184.97 3# 输沙率/(g/(s·m)) 7.66 7.11 2.10 2.13 1.21 7.33 9.11 方向/(°) 335.83 215.20 232.30 340.35 49.06 279.22 286.92 4# 输沙率/(g/(s·m)) 38.96 9.95 7.34 1.98 0.55 30.25 24.68 方向/(°) 25.47 230.62 248.42 187.12 48.33 17.44 5.61 5# 输沙率/(g/(s·m)) 4.36 3.75 1.70 1.97 0.43 4.45 7.62 方向/(°) 304.62 190.64 241.68 234.14 50.10 254.26 247.69 表 8 各悬浮泥沙输运项在单宽净输沙率中占比
Table 8 Proportion of suspended sediment transport terms in net sediment transport rate per width %
站位 T1 T2 T3+T4 T5 T6+T7+T8 T1+T2 1# 158.88 51.37 27.77 11.26 2.47 129.72 2# 58.88 58.88 2.76 27.98 7.92 86.73 3# 84.12 78.13 23.06 23.39 13.34 80.52 4# 157.89 40.31 29.73 8.04 2.22 122.6 5# 57.27 49.24 22.36 25.86 5.68 58.42 注:各悬浮泥沙输运项为具有方向的矢量值,因此,部分悬浮泥沙输运项在净输沙率中占的比例大于100%。 表 9 各站位涨落潮悬浮泥沙输运通量
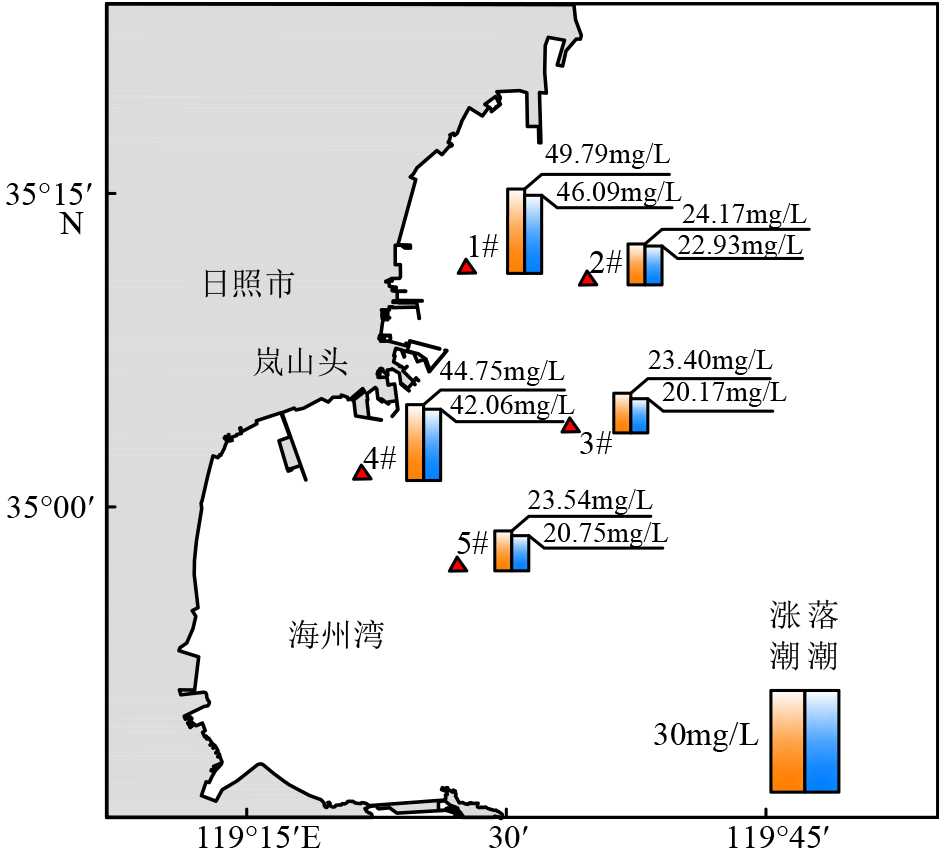
Table 9 Suspended sediment transport at each station at ebb and flow tide
站名 输沙率/(g/(s·m)) 输沙方向/(°) 涨潮 落潮 涨潮 落潮 1# 207.86 153.78 229.68 60.97 2# 189.41 111.06 238.50 69.08 3# 212.53 104.16 252.23 59.36 4# 290.63 205.09 255.72 59.24 5# 150.73 71.60 248.22 63.59 -
[1] Bian C W, Jiang W S, Quan Q, et al. Distributions of suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea based on field surveys during the four seasons of 2011 [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2013, 121-122: 24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.03.013
[2] Bouchez J, Gaillardet J, France-Lanord C, et al. Grain size control of river suspended sediment geochemistry: clues from Amazon River depth profiles [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2011, 12(3): Q03008.
[3] Bian C W, Jiang W S, Greatbatch R J, et al. The suspended sediment concentration distribution in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2013, 12(3): 345-354. doi: 10.1007/s11802-013-1916-3
[4] Ma M, Feng Z, Guan C, et al. DDT, PAH and PCB in sediments from the intertidal zone of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2001, 42(2): 132-136. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00118-1
[5] Zhang J, Liu S M, Xu H, et al. Riverine sources and estuarine fates of particulate organic carbon from North China in late summer [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 46(3): 439-448. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1997.0277
[6] 韦钦胜, 刘璐, 臧家业, 等. 南黄海悬浮体浓度的平面分布特征及其输运规律[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(2):73-83 WEI Qinsheng, LIU Lu, ZANG Jiaye, et al. The distribution and transport of suspended matter in the Southern Huanghai Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(2): 73-83.
[7] 刘芳, 黄海军, 郜昂. 春、秋季黄东海海域悬浮体平面分布特征及海流对其分布的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 2006, 30(1):68-72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2006.01.014 LIU Fang, HUANG Haijun, GAO Ang. Distribution of suspended matter on the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea and effect of ocean current on its distribution [J]. Marine Sciences, 2006, 30(1): 68-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2006.01.014
[8] 蔡德陵, 石学法, 周卫健, 等. 南黄海悬浮体和沉积物的物质来源和运移: 来自碳稳定同位素组成的证据[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(S1):21-29 doi: 10.1007/BF02900936 CAI Deling, SHI Xuefa, ZHOU Weijian, et al. Sources and transportation of suspended matter and sediment in the southern Yellow Sea: evidence from stable carbon isotopes [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(S1): 21-29. doi: 10.1007/BF02900936
[9] 范恩梅, 陈沈良, 张国安. 连云港海域水文泥沙运动特征[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2009, 31(4):703-707 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2009.04.040 FAN Enmei, CHEN Shenliang, ZHANG Guoan. The hydrological and sediment characteristics in Lianyungang coastal waters [J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 2009, 31(4): 703-707. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2009.04.040
[10] 郭瑜璇. 渤、黄、东海悬浮物传输过程和机制的数值模拟[D]. 自然资源部第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2019. GUO Yuxuan. Numerical simulation of suspended sediment transport process and its mechanism of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of the First Institute of Oceanography, 2019.
[11] 庞重光, 杨扬, 刘志亮. 黄东海悬浮泥沙输运结构及其形成机制[J]. 泥沙研究, 2010(3):24-30 PANG Chongguang, YANG Yang, LIU Zhiliang. Transportation pattern of suspended sediment and its forming mechanism in the Yellow and East China Sea [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2010(3): 24-30.
[12] 余佳, 王厚杰, 毕乃双, 等. 基于MODIS L1B数据的黄海悬浮体季节性分布的反演[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1):1-9 YU Jia, WANG Houjie, BI Naishuang, et al. Seasonal distribution and variation of suspended sediment in the Yellow Sea in 2010 based on retrieved monthly data from Modis L1B imagery [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(1): 1-9.
[13] 李文建, 王珍岩, 黄海军. 夏季南黄海悬浮体粒度分布及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(6):49-60 LI Wenjian, WANG Zhenyan, HUANG Haijun. Grain size distribution pattern and influencing factors of suspended matters in the Southern Yellow Sea during summer season [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(6): 49-60.
[14] 仲毅, 乔璐璐, 王震, 等. 南黄海中部悬浮体垂直分布及其季节变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(3):518-526 ZHONG Yi, QIAO Lulu, WANG Zhen, et al. Vertical distribution and seasonal variation of suspended particulate matter in the central South Yellow Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(3): 518-526.
[15] 李建超, 乔璐璐, 李广雪, 等. 基于LISST数据的冬季南黄海悬浮体分布[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(5):13-25 LI Jianchao, QIAO Lulu, LI Guangxue, et al. Distribution of winter suspended particulate matters in the South Yellow Sea based on LISST data [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(5): 13-25.
[16] 高建华, 高抒, 董礼先, 等. 鸭绿江河口地区沉积物特征及悬沙输送[J]. 海洋通报, 2003, 22(5):26-33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005 GAO Jianhua, GAO Shu, DONG Lixian, et al. Sediment distribution and suspended sediment transport in Yalu River Estuary [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2003, 22(5): 26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
[17] 刘运令, 汪亚平, 吴祥柏, 等. 南黄海苏北近岸西洋水道水沙输运机制分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(11):120-127 LIU Yunling, WANG Yaping, WU Xiangbai, et al. Mechanism of water and suspended sediment transport in the Xiyang Channel along the Southwestern Yellow Sea coast [J]. Marine Sciences, 2011, 35(11): 120-127.
[18] 英晓明, 丁平兴. 洋山港海域水体和悬沙输运机制研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(2):135-140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.02.003 YING Xiaoming, DING Pingxing. Research on transport mechanism of water and suspended sediment in the Yangshan harbor waters [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30(2): 135-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.02.003
[19] Liu J H, Yang S L, Zhu Q, et al. Controls on suspended sediment concentration profiles in the shallow and turbid Yangtze Estuary [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.01.021
[20] 杜家笔, 裴艳东, 高建华, 等. 弱动力浅海中的悬沙输运机制: 以天津港附近海域为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(1):136-144 DU Jiabi, PEI Yandong, GAO Jianhua, et al. The suspended sediment transport associated with low flow patterns in shallow waters: a case study from the Tianjin subtidal area [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(1): 136-144.
[21] 孟令鹏, 胡日军, 李毅, 等. 福宁湾海域冬季大潮期悬浮泥沙输运特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):61-73 MENG Lingpeng, HU Rijun, LI Yi, et al. Transport characteristics of suspended sediment in Funing Bay during spring tide in winter [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 61-73.
[22] 刘伟, 范代读, 涂俊彪, 等. 椒江河口春季悬沙输运特征及通量机制研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(1):41-51 LIU Wei, FAN Daidu, TU Junbiao, et al. Suspended transportation and flux mechanism of sediment in the Jiaojiang Estuary in spring [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(1): 41-51.
[23] 秦亚超, 高飞, 苏大鹏, 等. 南黄海西部日照至连云港海域的春季温跃层和化学跃层[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(3):22-32 QIN Yachao, GAO Fei, SU Dapeng, et al. Late spring thermocline and chemoclines in the area off the Rizhao–Lianyungang coast, western South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(3): 22-32.
[24] 宋红瑛, 刘金庆, 印萍, 等. 日照近海表层沉积物粒度特征与沉积环境[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2016, 46(3):96-104 SONG Hongying, LIU Jinqing, YIN Ping, et al. Grain size characteristics of the surface sediment and sedimentary environment in Rizhao offshore [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(3): 96-104.
[25] 薛刚. 岚山港西突堤工程对海底冲淤影响预测[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2007. XUE Gang. Prediction on erosion and accumulation of the seabed by the project of western jetty of Lanshan Harbor[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2007.
[26] Dyer K R. The salt balance in stratified estuaries [J]. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science, 1974, 2(3): 273-281. doi: 10.1016/0302-3524(74)90017-6
[27] Ingram R G. Characteristics of the great Whale River Plume [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1981, 86(C3): 2017-2023. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC03p02017
[28] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary [J]. Estuaries, 1985, 8(3): 256-269. doi: 10.2307/1351486
[29] Trowbridge J H. A simple description of the deepening and structure of a stably stratified flow driven by a surface stress [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1992, 97(C10): 15529-15543. doi: 10.1029/92JC01512
[30] Prandle D. On salinity regimes and the vertical structure of residual flows in narrow tidal estuaries [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1985, 20(5): 615-635. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(85)90111-8
[31] 陈斌, 周良勇, 刘健, 等. 废黄河口海域潮流动力与悬沙输运特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(5):73-81 CHEN Bin, ZHOU Liangyong, LIU Jian, et al. The relationship between the suspended sediment movement and tidal current dynamic characteristic in Old Yellow River Delta [J]. Marine Sciences, 2011, 35(5): 73-81.
[32] 鲁号号, 杨旸, 唐杰平, 等. 南黄海废黄河口近岸海域近底部悬沙输运观测[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(1):38-48 LU Haohao, YANG Yang, TANG Jieping, et al. Observation of near-bottom transport of suspended sediment in the offshore area of abandoned Yellow River mouth [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(1): 38-48.
[33] 周良勇, 陈斌, 刘健, 等. 江苏废黄河口外夏季悬浮泥沙运动[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(6):17-24 ZHOU Liangyong, CHEN Bin, LIU Jian, et al. Observation of currents and suspended sediment concentration off Northern Jiangsu Coast, China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(6): 17-24.
[34] 杨林, 杨红, 吉新磊, 等. 废黄河口海域悬沙输运特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2018(6):1-8 YANG Lin, YANG Hong, JI Xinlei, et al. Sediment transportation in the Abandoned Yellow River Delta [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2018(6): 1-8.
[35] 徐粲, 高建华, 杨旸, 等. 南黄海辐射沙脊群潮汐水道的悬沙输运特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(11):150-162 XU Can, GAO Jianhua, YANG Yang, et al. Suspended sediment transport patterns in the tidal channels in the southwestern Yellow Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 36(11): 150-162.
[36] 庞重光, 白学志, 胡敦欣. 渤、黄、东海海流和潮汐共同作用下的悬浮物输运、沉积及其季节变化[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 2004(46):32-41 PANG Chongguang, BAI Xuezhi, HU Dunxin. The transport and sedimentation of suspended matter and their seasonal variation are affected by circulation and tide current in the Bohai Sea, the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea [J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 2004(46): 32-41.
[37] 陈沈良, 张国安, 杨世伦, 等. 长江口水域悬沙浓度时空变化与泥沙再悬浮[J]. 地理学报, 2004, 59(2):260-266 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.02.012 CHEN Shenliang, ZHANG Guoan, YANG Shilun, et al. Temporal and spatial changes of suspended sediment concentration and resuspension in the Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent waters [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2004, 59(2): 260-266. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.02.012
[38] 曹祖德, 王桂芬. 波浪掀沙、潮流输沙的数值模拟[J]. 海洋学报, 1993, 15(1):107-118 CAO Zude, WANG Guifen. Numerical simulation of wave lifting sand and tidal current transporting sand [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1993, 15(1): 107-118.
[39] 邢飞, 汪亚平, 高建华, 等. 江苏近岸海域悬沙浓度的时空分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(3):459-468 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201003025025 XING Fei, WANG Yaping, GAO Jianhua, et al. Seasonal distributions of the concentrations of suspended sediment along Jiangsu coastal sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(3): 459-468. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201003025025
[40] 秦蕴珊, 李凡, 郑铁民, 等. 南黄海冬季海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋科学, 1986, 10(6):1-7 QIN Yunshan, LI Fan, ZHENG Tiemin, et al. Study on suspended matter of the South Yellow Sea in winter [J]. Marine Science, 1986, 10(6): 1-7.
[41] 秦蕴珊, 李凡, 徐善民, 等. 南黄海海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1989, 20(2):101-112 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1989.02.002 QIN Yunshan, LI Fan, XU Shanmin, et al. Suspended matter in the south Yellow Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1989, 20(2): 101-112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1989.02.002
[42] 左书华, 庞启秀, 杨华, 等. 海州湾海域悬沙分布特征及运动规律分析[J]. 山东科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 32(1):10-17 ZUO Shuhua, PANG Qixiu, YANG Hua, et al. Analysis on the distribution and movement of suspended sediment in Haizhou Bay sea area [J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology:Natural Science, 2013, 32(1): 10-17.
[43] 赵季伟, 李占海, 徐圣, 等. 长江口北港上段河道枯季悬沙浓度垂向分布特征研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(9):2207-2218 ZHAO Jiwei, LI Zhanhai, XU Sheng, et al. Vertical profile of suspended sediment concentration in the upper reach of north channel in the Changjiang Estuary during the dry season [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(9): 2207-2218.
[44] 郑铁民, 赵一阳, 李凡, 等. 南黄海夏季海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1990, 12(6):749-757,806 ZHENG Tiemin, ZHAO Yiyang, LI Fan, et al. A study on total suspended matter in winter in the south Yellow Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1990, 12(6): 749-757,806.
[45] Dyer K R. Coastal and Estuarine Sediment Dynamics[M]. Chichester: Wiley, 1986.
[46] 文明征, 陈天, 胡云壮, 等. 波流作用下海底边界层沉积物再悬浮与影响因素研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(3):97-106 WEN Mingzheng, CHEN Tian, HU Yunzhuang, et al. Sediment resuspension of bottom boundary layer under waves and currents [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2020, 42(3): 97-106.



 下载:
下载: