APPLICATION OF MONTE CARLO MODEL TO SIMULATION OF COMPACTION RATES OF SHALLOW SEDIMENTS IN THE MODERN YELLOW RIVER DELTA
-
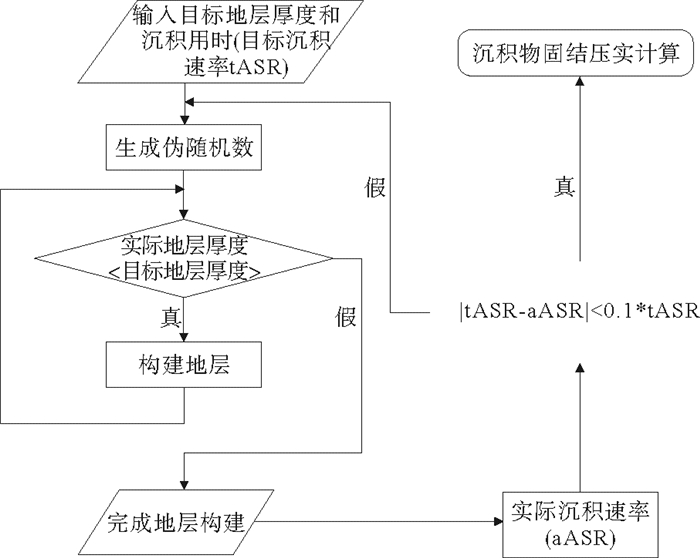
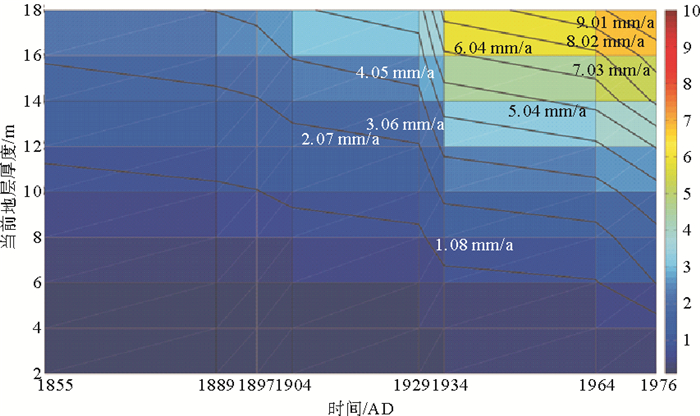
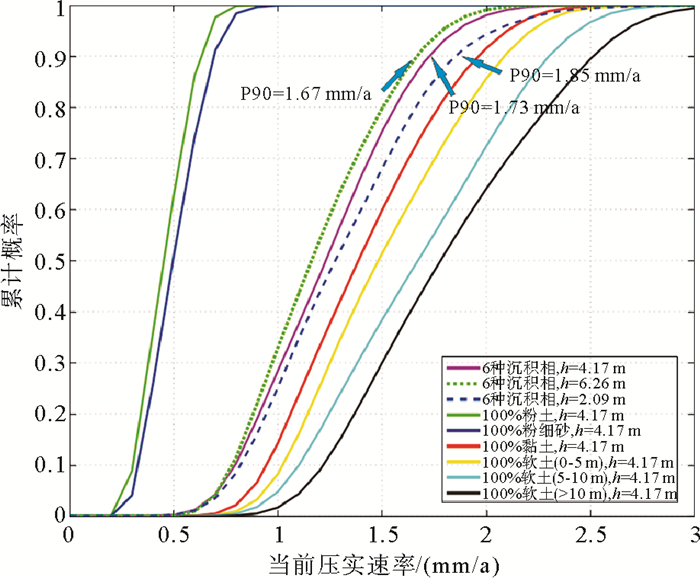
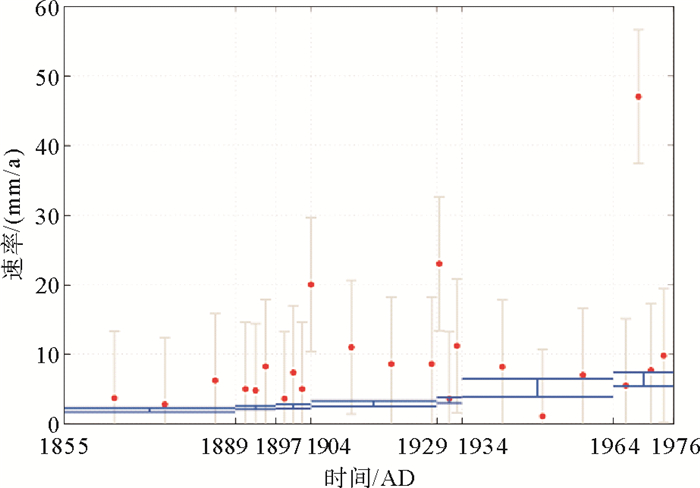
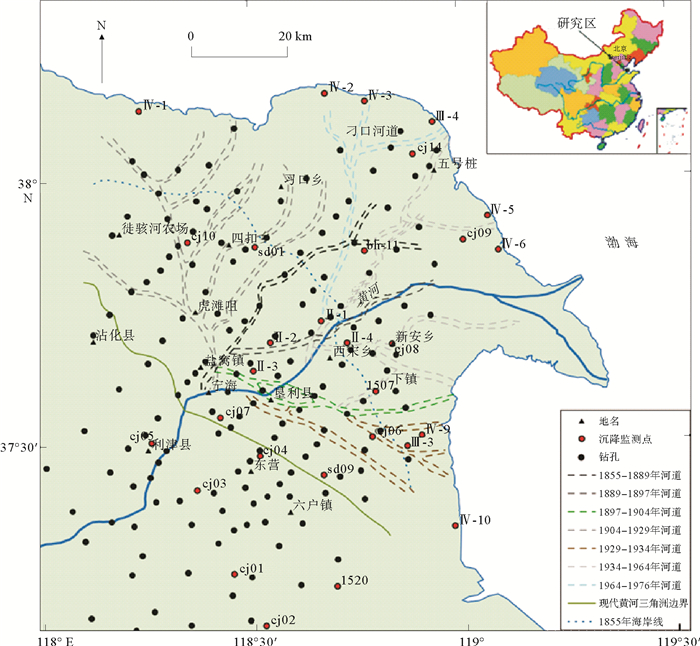
摘要: 在进行黄河三角洲浅层沉积物固结压实研究中,过去传统的方法通常基于钻孔和剖面,进行局部计算分析。为克服钻孔分布不均的局限性需研究整个现代黄河三角洲地区浅层沉积物的压实沉降特征,基于1987年黄河三角洲地区综合工程地质勘察获取的钻孔资料,采用了数学地质中的蒙特卡洛方法,结合土力学的分层总和法对整个现代黄河三角洲浅层沉积物的压实速率进行模拟,并分析了压实模拟的具体影响因素。结果表明当前浅层沉积物的90%累积概率(P90)的压实速率变化范围为0.18~9.07 mm/a,影响模拟沉积层的压实速率主要因素为沉积物的初始孔隙比、压缩系数和平均沉积速率,上述要素均与压实速率呈显著正相关,软土层应是浅沉积地层压实沉降的主要贡献层。提出按照时间序列分别对不同流路时期叶瓣进行模拟,更符合现代黄河三角洲地区的沉积环境和历史,并对比23个地面沉降水准监测数据,定量分离了浅层沉积物固结压实分量,其约占沉降总量的13%。Abstract: The traditional methods used in the study of shallow sediment compaction, which is one of the important contributors to land subsidence, are usually based on drillings and profile measurement with local computation in the Yellow River Deltaic area. In order to overcome the methodological limitation and restriction in past studies, the Monte Carlo approach and the stratified summation method are adopted. With the borehole data obtained from the Project on Comprehensive Engineering Geological and Hydrogeological Survey in 1987, we numerically modeled the shallow sediments of the whole delta, calculated the compaction rates and analyzed the influence factors of compaction simulation. The results show that the present compaction rates vary in a range from 0.18mm/a to 9.07mm/a. The influence factors of compaction rates are mainly the geotechnical parameters, such as initial porosity and compressibility and the average net accumulation rates, both of which are significantly and positively correlated with the present compaction rates, and the soft layer is the major contributor to the sediment compaction and land subsidence. The results are fit to the history of the Yellow River delta if simulations are made for lobes with time. Combined with the ground subsidence level monitoring data, it is found that the contribution of consolidation and compaction of shallow sediments accounts for about 13% of the total settlement.
-
Keywords:
- lobe /
- compaction /
- Monte Carlo simulations /
- the Modern Yellow River Delta
-
-
表 1 沉积物工程地质参数[12]
Table 1 Geotechnical parameters of sediments
地层 粉土 粉细砂 黏土 软土0~5 m 软土5~10 m 软土>10 m 有效重度/kN·m-3 9.1 9.1 8 8.15 8.6 8.95 初始孔隙比 0.79 0.74 1.135 1.36 1.36 1.43 压缩系数/MPa-1 0.16 0.17 0.67 0.78 0.805 0.875 说明:统一取地下水埋深为2 m,表 1中黏土有效重度值为干容重与含水率换算得出,较饱和重度略小。 表 2 不同模拟次数下的精度和用时
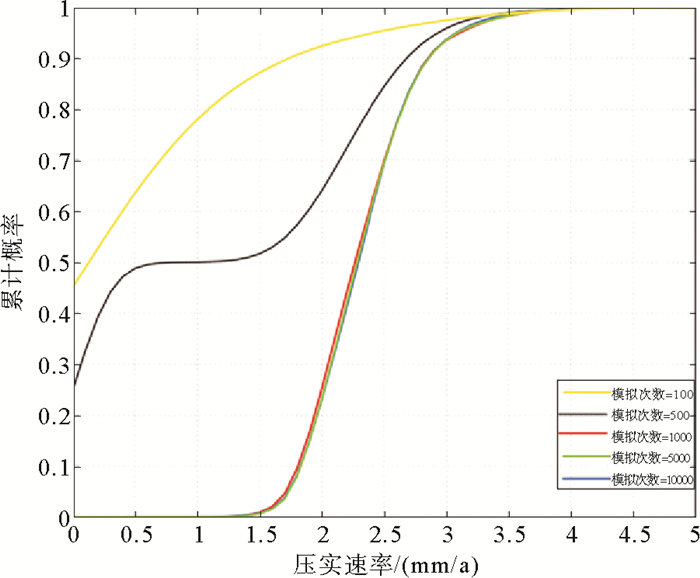
Table 2 The accuracy and time consuming under different simulation times
模拟次数 P90/(mm·a-1) 用时/s 100 1.743 0.075 706 500 2.684 0.300 654 1 000 2.854 0.701 427 5 000 2.862 9.789 145 10 000 2.859 15.459 052 -
[1] 黄海军, 李凡, 庞家珍, 等.黄河三角洲与渤、黄海陆海相互作用研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2005:61-64. HUANG Haijun, LI Fan, PANG Jiazhen, et al.Study on Land-ocean Interation in Yellow River Delta with Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2005:61-64.
[2] 李胜男, 王根绪, 邓伟, 等.水沙变化对黄河三角洲湿地景观格局演变的影响[J].水科学进展, 2009, 20(3):325-331. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2009.03.003 LI Shengnan, WANG Genxu, DENG Wei, et al.Effects of runoff and sediment variation on landscape pattern in the Yellow River delta of China[J].Advances in Water Science, 2009, 20(3):325-331. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2009.03.003
[3] 任美锷.黄河长江珠江三角洲近30年海平面上升趋势及2030年上升量预测[J].地理学报, 1993, 48(5):385-393. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1993.05.001 REN Meie.Relative sea level rise in Huanghe, Changjiang and Zhujiang delta over the last 30 years predication for the next 40 years (2030) [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1993, 48(5):385-393. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1993.05.001
[4] 李广雪, 庄克琳, 姜玉池.黄河三角洲沉积体的工程不稳定性[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(2):21-26. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200002004 LI Guanxue, ZHUANG Kelin, JIANG Yuchi.Engineering instability of the deposition bodies in the Yellow River delta[J].Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(2):21-26. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200002004
[5] 师长兴, 尤联元, 李炳元, 等.黄河三角洲沉积物的自然固结压实过程及其影响[J].地理科学, 2003, 23(2):175-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.02.008 SHI Changxing, YOU Lianyuan, LI Bingyuan, et al.Natural consolidation of deposits and its consequences at the Yellow River delta[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 23(2):175-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.02.008
[6] 别君, 黄海军, 樊辉, 等.现代黄河三角洲地面沉降及其原因分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4):29-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200604005 BIE Jun, HUANG HaiJun, FAN Hui, et al.Ground subsidence of modern Yellow River delta and its causes[J].Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(4):29-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200604005
[7] 秦伟颖, 庄新国, 黄海军.现代黄河三角洲地区地面沉降的机理分析[J].海洋科学, 2008, 32(8):38-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200808010 QIN Weiying, ZHUANG Xinguo, HUANG Haijun.Mechanism analysis of land surface subsidence in the modern Yellow River Delta[J].Marine Science, 2008, 32(8):38-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200808010
[8] Liu Y, Huang H.J.Characterization and mechanism of regional land subsidence in the Yellow River Delta, China[J].Natural Hazards, 2013, 68(2):687-709. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0648-4
[9] Timothy H D, Falk A, Alessandro F, et al. Subsidence and flooding in New Orleans[J]. Nature, 2006, 441(7093): 587-588. doi: 10.1038/441587a
[10] Shi C, Zhang D, You L, et al.Land subsidence as a result of sediment consolidation in the Yellow River Delta[J].Journal of Coastal Research, 2007, 23(1):173-181. doi: 10.2112-39951.1/
[11] 高茂生, 薛春汀, 叶思源, 等.现代黄河三角洲沉积层压实下沉的计算分析[J].海洋学报, 2010, 32(5):34-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201005005 GAO Maosheng, XUE Chunting, YE Siyuan, et al.The computation and analysis of compactional subsidence of sediments in the modern Huang River Delta[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(5):34-40] http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201005005
[12] 谭晋钰, 黄海军, 刘艳霞.黄河三角洲沉积物压实固结及其对地面沉降贡献估算[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(5):33-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405004 TAN Jinyu, HUANG Haijun, LIU Yanxia. Estimation of sediment compaction and its contribution to land subsidence in the Yellow River Delta[J].Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(5):33-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201405004
[13] Metropolis N, Ulam S.The Monte Carlo method[J].Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1949, 44(247): 335-341. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1949.10483310
[14] Schwarzacher W.Sedimentation Models and Quantitative Stratigraphy[M].Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1975:382.
[15] Dacey M F.Models of bed formation[J].Mathematical Geology, 1979, 11(6):655-668. doi: 10.1007/BF01031890
[16] Jensen J L, Lake L W, Corbett P W, et al.Statistics for Petroleum Engineers and Geoscientis-ts[M].The Netherlands Linacre House, Jordan Hill, 2008:56-58.
[17] Wilkinson B H, Merrill G K, Kivett S J.Stratal order in Pennsylvanian Cyclothems[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2003, 115(9):1069-1087. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8b7c83fe41be10bda25422c6cb6a3293
[18] Meckel T A, Ten Brink U, Williams S J.Current subsidence rates due to compaction of Holocene sediments in Southern Louisiana[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33, L11403. doi: 10.1029/2006GL026300
[19] Meckel T A, Ten Brink U, Willianms S J.Sediment compaction rates and subsidence in Deltaic plains:numerical constraints and stratigraphic influences[J].Basin Research, 2007, 19:19-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2006.00310.x
[20] 成国栋, 薛春汀.黄河三角洲沉积地质学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1997. CHENG Guodong, XUE Chunting. The Yellow River Delta Sedimentary Geology [M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1973.
[21] 田洪水, 肖俊华, 赵淑慧, 等.黄河三角洲软土的特征及地基处理方法[J].山东建筑工程学院学报, 2003, 18(4):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7644.2003.04.007 TIAN Hongshui, XIAO Junhua, ZHAO Shuhui, et al.Study of characteristics and foundation treatment of soft soil in the Yellow River Delta[J].Iournal of Shandong University Architecture and Engineering, 2003, 18(4):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7644.2003.04.007



 下载:
下载: