STUDY ON SAND PRODUCTION IN A NATURAL GAS HYDRATE PRODUCTION WELL
-
摘要: 天然气水合物是一种重要的非常规能源,但水合物开采出砂问题成为制约其走向商业化开发的关键因素。南海北部陆坡是我国天然气水合物的重要赋存区,其水合物主要以分散状弱胶结方式赋存,研究其出砂问题显得极为迫切。研究表明储层出砂的根本原因是储层介质强度降低,而水合物储层介质强度受到水合物胶结模式、水合物饱和度、孔隙流体压力、流速及生产压差等影响。本文在对比分析天然气水合物储层出砂与常规油气藏出砂特征的基础上,总结了弱胶结疏松砂岩油藏出砂研究方法,为天然气水合物储层开采井孔出砂的研究提供思路和参考。Abstract: Natural gas hydrate has been proved significant as a kind of unconventional energy source. However, the sand production from gas hydrate-bearing deposits has remained a nightmare to the commercial development of the resource. The northern slope of the South China Sea is an important natural gas hydrate area in China. The natural gas hydrate there is distributed mainly in a scattered pattern by weakly cemented deposits and it really is urgent to study the mechanism of sand production for sustainable development of the resource. The fundamental reason of sand production is the decrease in the strength of reservoir medium, which is cemented by hydrate, and effected by the factors of hydrate saturation, pore fluid pressure, flow rate, production pressure and so on. Based on the comparison of sand production from the natural gas hydrate reservoir to the conventional oil and gas reservoir, this paper summarizes the up-to-date research results of sand production in weakly cemented sandstone reservoirs, and taking it as a reference we studied the sand production in natural gas hydrate reservoirs.
-
天然气水合物储量巨大[1],燃烧污染小[2],被视为21世纪最具有潜力的战略资源[3]。天然气水合物主要赋存在大陆边缘陆坡带,南海海域是我国重要的天然气水合物赋存区,储量巨大且分布广泛。总结国内外试采经验,结合南海天然气水合物赋存状态,水合物储层在商用期间可能发生严重出砂事故,影响开采效率,这是我国天然气水合物商业化开采面临的重要问题。
目前已开展短期试采工作的地区包括加拿大Mallik[4],美国阿拉斯加北坡Mount Elbert[5]和Ignik Sikumi[6]、日本南海海槽[7]以及中国南海神狐海域(2017)。除日本水合物试采由于出砂被迫终止外[8],冻土区开采也面临严重出砂问题[9, 10]。这些试采工程均以降压为主进行开采,大部分地区的开采过程中均出现不同程度的出砂现象。值得注意的是,2013年和2017年日本南海海槽进行的两次海域天然气水合物试采均因井筒大量出砂而被迫中止,这一事件表明了井孔出砂问题对海洋天然气水合物开采中天然气稳定持续产出有严重影响。而我国南海水合物资源开发也同样面临出砂难题,南海北部陆坡天然气水合物主要以分散状弱胶结方式赋存于细砂泥质地层中,颗粒较国外砂岩地层颗粒小,解决出砂问题有利于水合物资源商业化利用。表 1介绍了我国与日本在天然气水合物试采工程方面的情况对比。
日本 中国 首次海域试采 第二次海域试采 首次海域试采 时间 2013年 2017年 2017年 作业区域 第二渥美海丘 第二渥美海丘 南海神狐海域 作业水深 约1 000 m 约1 000 m 1 266 m 储层深度 海底以下约300 m 海底以下约350 m 海底以下203~277 m 储层条件 砂质 砂质 泥质粉砂 开采方法 降压法 降压法 基于降压的地层流体抽取法 产气持续时间 6 d 第一口井12 d;第二口井24 d 60 d 累计产气量 12万m3 第一口井3.5万m3;第二口井20万m3 30.9万m3 日均产气量 2万m3 第一口井0.292万m3;第二口井0.833万m3 0.515万m3 日均最高产气 约2.5万m3 — 3.5万m3 停产原因 出砂堵塞 第一口井出砂堵塞 主动关井 技术上,出砂问题是制约水合物商业化生产的关键障碍[11],要实现长期稳定的商业开采,必须攻克出砂问题。安全上,储层出砂是地层结构受到破坏的表现[12],大量出砂使地层压力亏空[13],地应力重新分布[14],地层强度降低[15],增加地质灾害发生的风险[16]。因此,无论从技术上还是安全上,研究海洋天然气水合物开采井孔出砂力学机理,建立出砂数学模型,研究防砂对策,设计防砂完井方式具有重要意义。
水合物出砂问题与弱固结储层介质息息相关,而储层介质强度受到水合物分布模式、孔隙流体压力等的影响。当前,针对海域天然气水合物开采出砂方面的研究相对较少,参考常规油气开采过程,特别是在弱胶结疏松砂岩油藏中井孔出砂的研究成果,对于水合物开采出砂研究具有借鉴意义。针对水合物储层的特殊性,本文在对比分析天然气水合物开采储层出砂与常规油气藏出砂特征的基础上,总结了影响储层介质强度的相关因素以及弱胶结疏松砂岩油藏出砂研究方法,为天然气水合物开采储层出砂研究提供参考。
1. 出砂机理及其影响因素
水合物开采储层出砂与常规油气藏出砂的根本区别在于前者出砂过程中存在相态变化(固态水合物分解为气和水),而开采中的许多因素都会影响水合物分解过程。水合物开采储层出砂是一个多相态变化、多物理场耦合的复杂过程,与常规油气藏出砂具有明显区别。
水合物储层出砂特殊性具体表现为3点:一是天然气水合物可作为胶结物或骨架赋存于沉积层,固态水合物分解为可流动气水混合物,导致沉积颗粒间粘结力减弱,骨架砂向流砂转化;而常规油气以孔隙流体的形式存在,无相变问题;二是水合物分解释放大量气体[17],导致孔隙压力急剧增高;而常规油气一般不会出现这种现象。根据Terzaghi有效应力原理[18],储层所受压力由岩石骨架和孔隙流体共同承担,当孔隙压力急剧增大时,岩石骨架所承担的有效应力就会急剧下降,导致砂土液化;沉积颗粒间接触力及相互间摩擦力下降,剪切破坏增强[19];第三,水合物开采出砂为水、气、砂三相产出;而常规油气开采出砂一般是油、砂或气、砂两相,气体粘度小且对压力变化敏感,携砂能力弱,两者出砂特征不同。
水合物层出砂的根本原因在于储层结构破坏,储层介质强度降低。因此,凡是能影响储层介质强度的因素都会影响水合物出砂。从宏观角度来看,储层强度受到储层岩性、水合物胶结模式、水合物饱和度等因素影响。从微观角度来看,岩石颗粒受到微粒间的接触力和胶结物间的粘结力作用,而岩石颗粒间的粘结力主要受水合物胶结模式控制。根据对原位储层的地质条件及开发环节进行分析,可将影响水合物开采出砂问题的因素分为水合物分布模式、水合物饱和度、孔隙流体和生产压差等。
1.1 水合物分布模式的影响
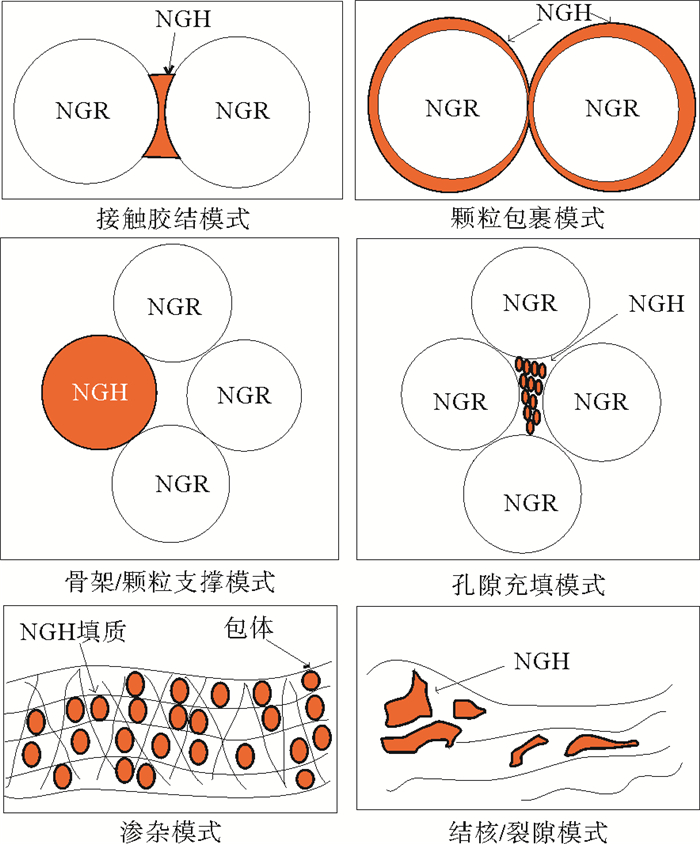
矿物颗粒间孔隙为水合物的形成提供空间,水合物形成加强矿物颗粒间的联系,提高沉积物胶结强度。对水合物分布模式的研究表明,不同分布模式的含水合物沉积体具有不一样的弹性波速度[21]。根据含水合物沉积物弹性波速度的不同,可将水合物的分布模式分成孔隙流体型和土骨架型。此外,斯伦贝谢根据水合物分布类型将水合物分布模式详细分为6类[22]:接触胶结模式、骨架/颗粒支撑模式、掺杂模式、颗粒包裹模式、孔隙充填模式以及结核/裂隙充填模式(图 1)。水合物储层通常埋藏较浅,一般只经历过压实作用和较弱的胶结作用,因此,含水合物沉积介质的强度主要受胶结物含量及分布模式控制。孔隙充填形式的沉积物颗粒并未胶结,结构最疏松;接触胶结模式的含水合物沉积层结构强度高于孔隙充填模式;包裹模式又强于接触胶结模式。
借鉴常规油气出砂观点,水合物开采过程中胶结物随水合物分解减少,砂粒受到的运动学约束减弱,胶结强度不断下降。砂粒从骨架中分离出来成为游离砂,游离砂产出受吼道直径和几何形态控制,可产生“负表皮效应”;而骨架砂产出在减少流体运输阻力的同时破坏了储层稳定性。实际地层条件下的水合物赋存特征极其复杂,故将水合物分布模式分为接触胶结模式和骨架支撑模式有利于简化出砂模型,降低对其数学描述上的复杂度。
1.2 水合物饱和度的影响
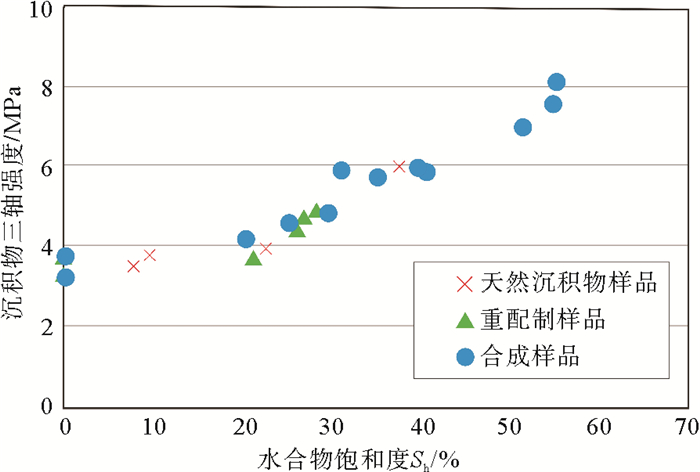
天然气水合物饱和度代表沉积物孔隙中的水合物含量,而水合物含量与沉积介质强度息息相关。图 2表示了天然沉积物样品和合成样品的三轴力学试验结果,结果表明当水合物饱和度低于20%时,天然气水合物对沉积物刚度影响较小[23],这主要是由于该饱和度下水合物在多孔介质中以充填为主,对颗粒间胶结作用贡献不大;而当水合物饱和度超过40%时,水合物的剪切强度明显增强[24]。水合物饱和度影响水合物在孔隙结构中的赋存形态,而不同的赋存形式对沉积物力学性能影响存在差异。室内试验表明[25],随着水合物饱和度增加,其沉积物力学性能相应增强[26, 27],含水合物沉积物的粘聚力和内摩擦角也增大[28],而水合物饱和度对沉积物泊松比影响不大。
1.3 孔隙流体的影响
对于欠压实弱固结地层,孔隙压力在平衡上覆地层压力和水平构造应力中起到了重要作用[22]。从宏观角度,根据Biot三维固结理论[30],地层所受应力由土骨架和孔隙中能够有效传递流体压力的那部分承担。其数学关系由如下方程给出:
$$ \sigma {{'}_{ij}}={{\sigma }_{i, j}}-{{\delta }_{ij}}u $$ (1) $$ \begin{align} & \frac{\kappa }{{{\gamma }_{w}}~}{{\nabla }^{2}}u=~\frac{\partial {{\mathit{\varepsilon }}_{\mathit{v}}}}{\partial t}~=~~\frac{\partial }{\partial t}\text{ }\left( \text{ }\frac{1-2v}{E}\theta ' \right)= \\ & \frac{1-2v}{E}\frac{\partial }{\partial t}\left( \theta -3u \right) \\ \end{align} $$ (2) 其中σij为地层总应力,σij′为土骨架应力(即有效应力),u为超静水压力,δi,j为Kronecker符号,δi,j=$\left[ \begin{align} & 1\ 0\ 0 \\ & 0\ 1\ 0 \\ & 0\ 0\ 1 \\ \end{align} \right]$γw为水的体积力,κ为渗透系数,εv为体积应变,t为时间,θ′表示除去超静水压力的应力和函数有效值,θ′=θ-3u,其中θ=σx+σy+σz,σx、σy、σz为x、y、z三个方向的总应力,v、E为弹性参数。Biot三维固结理论考虑了土骨架变形对孔隙压力的影响。在钻井过程中,若发生水合物分解,孔隙流体压力短时间内增大,沉积物骨架有效应力降低。当孔隙流体压力进一步增大,骨架有效应力降低至零时,岩石颗粒处于“悬浮”状态,储层力学强度降低,此时地层易发生液化。随着水合物分解及气、水两相排出,有效应力超过储层强度导致储层破坏,进而表现为水合物开采井孔出砂。
从细观角度,砂粒从骨架上脱离受到胶结物分解和地层流体冲刷的影响[31]。后者影响出砂的根本原因在于流体压力梯度和拖拽力(即粘滞力)超过胶结力、吸附力及颗粒间接触力共同产生的阻力[32],从而为颗粒脱离壁面提供启动动力。流体拖拽力和压力梯度描述由如下关系给出:
$$ {{f}_{\text{in}{{\text{t}}_{_{j}}}}}={{\beta }_{in{{t}_{_{j}}}}}\left( \overline{v}{{~}_{j}}-{{u}_{j}} \right)~ $$ (3) $$ \begin{align} & \nabla {{p}_{j}}\left( 150\frac{{{\left( 1-n \right)}^{2}}}{~{{n}^{2}}\overline{d}~_{p}^{2}}~{{\mu }_{f}}+1.75\frac{\left( 1-n \right)\text{ }{{\rho }_{f}}}{{{n}^{2}}~{{\overline{d}}_{p}}}\left| \overline{v}-{{u}_{j}} \right| \right) \\ & (~{{\overline{v}}_{j}}-{{u}_{j}}) \\ \end{align} $$ (4) 式中fintj为单位拖拽力,βintj为拖拽力系数,βintj=150$\frac{{{\left( 1-n \right)}^{2}}}{n\overline{{{d}_{p}}}}\mu f+1.75\frac{\left( 1-n \right)\rho f}{{{n}^{2}}\overline{{{d}_{p}}}}\left| {{\overline{v}}_{j}}-{{u}_{j}} \right|$,vj和uj分别为颗粒平均速度和流体流动速度,dp为颗粒平均直径,pj为流体压力梯度,μf、ρf为流体运动粘滞系数和密度,n为孔隙度。拖拽力受流体粘度和流速的影响:粘度影响携砂能力,流速影响冲刷效果。随着水合物分解产水,颗粒间界面张力降低,流动性增强,出砂几率增大[33]。
1.4 生产压差的影响
降压法是目前水合物开采试验中最常用的方法[34-36],例如2002和2007年加拿大Mallik[4]、2007美国阿拉斯加北坡Mount Elbert[5]、2013和2017日本南海海槽[7]以及2017中国南海神狐海域均是基于降压法开采。生产压差对水合物开采井孔出砂的影响包括3方面。首先生产压差通过影响水合物分解影响储层的稳定性,当储层压力低于水合物相平衡压力时,水合物稳定性被破坏而发生分解,储层介质胶结强度降低。因此,提高生产压差加速了水合物的分解,但同时增加了出砂的可能性。其次,上覆岩层压力依靠孔隙流体和岩石骨架共同平衡[37],过大的生产压差使孔隙流体压力迅速降低,骨架有效应力急速增大,储层可能受到剪切破坏。此外,出砂是由于井孔环壁出现较高的压力梯度。在压力梯度和流体冲刷的作用下井壁附近砂粒稳定性最为薄弱,受流体粘滞力作用易于剥离,造成井孔出砂。如2002年加拿大Mallik区降压试采中MDT-4层段出现出砂现象[38]。借鉴常规油气出砂理论,可认为水合物层出砂存在门限压差和临界压差,使水合物中未胶结砂粒运动的压差为门限压差,使骨架砂脱离骨架变为自由砂时的压差为临界压差,同样可定义门限流速和临界流速,以此判断水合物储层开发是否出砂。
2. 出砂问题研究方法
目前针对天然气水合物开采储层出砂问题的研究较少,而弱胶结疏松砂岩储层的物性与水合物储层性质较为接近,其出砂理论和防砂工艺研究都较为充分,可以借鉴其研究方法和相关理论,为水合物开采储层出砂机理的研究提供参考。关于砂岩油藏出砂研究的方法主要分为3类:基于岩石力学的宏观模型、砂拱稳定模型和砂粒脱离的细观模型。
2.1 岩石力学宏观模型
出砂问题源于井壁稳定性分析[39],通过借鉴岩石力学理论,建立了宏观的岩石力学模型[40]。这种模型在推导控制微分方程的过程中认为介质是连续体,采用线-弹性模型[41]、弹-塑性模型[42, 43]等来刻画出砂行为。通过强度判别准则,主要包括Mohr-Coulomb破坏准则、Drucker-Prager破坏准则、Duncan-Chang破坏准则、Hoek-Brown破坏准则、极限塑性应变准则等,来判断其出砂条件。
弹-塑性力学模型[42, 44, 45]认为,出砂的前提条件是岩石强度退化,而介质强度的退化与局部集中塑性变形相关,塑性状态下的材料仍能抵抗一定载荷[46];只有当岩石应变超过其极限值后地层才发生破坏。其塑性区域应力状态分布的数学描述如下:
$$ \begin{align} & {{\sigma }_{r}}={{P}_{i}}+\frac{\mu q}{2\pi h\kappa }~{\rm ln}r/{{R}_{i}}+\text{ }\frac{1}{{{\left( {\rm tan}\alpha \right)}^{2}}-1}\text{ }(2{{S}_{0}}{\rm tan}\alpha - \\ & ~\frac{\mu q}{2\pi hk})\cdot \text{ }\left[ {{\left( \frac{r}{{{R}_{i}}} \right)}^{{{~}^{{{\left( {\rm tan}\alpha \right)}^{2}}-1}}}}-1 \right]\text{ } \\ \end{align} $$ (5) $$ \begin{align} & {{\sigma }_{z}}={{P}_{i}}+\frac{\mu q}{2\pi h\kappa }\left( 1+\text{lnr}/{{R}_{i}} \right)+ \\ & \frac{1}{{{\left( \text{tan }\!\!\alpha\!\!\text{ } \right)}^{2}}-1\text{ }}\text{ }\left( 2{{S}_{0}}\text{tan}\alpha -\frac{\mu q}{2\pi hk} \right)\cdot \text{ }\left[ {{\left( \frac{r}{{{R}_{i}}} \right)}^{^{{{\left( t\text{an }\!\!\alpha\!\!\text{ } \right)}^{2}}-1}}}{{\left( \text{tan }\!\!\alpha\!\!\text{ } \right)}^{2}}-1~ \right]\text{ } \\ \end{align} $$ (6) 式中σr为径向应力,σz为垂向应力,r为距井轴的距离,Ri为井孔半径,Pi为井内水压力,μ为流体粘度,q为流量,S0为抗剪强度,h为模型高度,α为破裂角,k为渗透率。该模型在Biot模型的基础上引入流体压力分布,将流体压力与岩石强度联系起来,故该模型能更精细地刻画砂岩应力分布状态。地层出砂除受到地层自身强度和流体性质的影响外,还同时受剪切应力对地层破坏的作用,即张应力破坏是由于地层流体流速过高引起,而剪应力破坏由井底压力下降引起,这两者也是造成水合物储层出砂的原因,如果将水合物储层视为良好固结岩体,可采用该模型进行研究。根据油藏出砂的力学特征,可将疏松砂岩油藏出砂问题分为[44]:弱胶结地层出砂、中等胶结强度但易出水地层出砂、油藏压力衰竭的良好胶结地层出砂、高水平构造应力的良好胶结地层出砂以及井壁周围高压力梯度出砂。水合物开采储层出砂与砂岩油藏出砂中的弱胶结地层出砂相似,这类储层出砂多是由于剪切破坏造成。
应变硬化/软化-塑性模型[45]在考虑地质力学和流体运移基础上,采用双线性莫尔-库伦流动理论,研究了砂岩的应力应变行为。其应变张量和屈服函数如下:
$$ \text{ }\varepsilon {{}_{ij}}=\text{ }\varepsilon _{ij}^{e}+\text{ }\varepsilon _{ij}^{p} $$ (7) $$ f=\left| \sigma {{'}_{Z}}-\sigma {{'}_{r}} \right|/\sqrt{3}\text{ }-\text{ }\left[ Q+\left( \sigma {{'}_{z}}+2\sigma {{'}_{r}} \right)/3\text{ } \right]~\eta =0 $$ (8) 其中εij、εije、εijp分别表示总应变、应变弹性部分和应变塑性部分。σ′z、σ′r分别为有效垂向应力和有效径向应力。$\eta =\frac{2\sqrt{2} sin \varnothing }{2- sin \varnothing }, \varnothing $为摩擦角,Q为张力极限值。该模型完善了经典弹塑性模型中存在尺寸效应的缺陷,考虑了渗透率对岩石变形及应力释放的影响。可通过施加低围压的三轴力学实验来模拟低应力状态下试样强度;而在高有限应力状态下通过增加围压来模拟试样的破坏情况。含天然气水合物储层力学测试也借鉴了类似的研究方法,三轴试验表明[47, 48],相对于完全不含水合物的样品而言,含水合物的样品的剪切强度更大,表现为塑性破坏,且含水合物沉积物的强度与围压呈正相关关系。
疏松砂岩油藏出砂研究[49]发现,当生产压差或生产流速超过临界值时地层出砂,出砂速率是负载因子和雷诺数的函数,可通过该函数预测当达到出砂临界条件时连续产砂的速率问题。这对研究水合物出砂具有借鉴意义,因为流体动力学特征作为颗粒脱落启动力在天然气水合物开采出砂过程中亦扮演重要角色。
天然气水合物开采井孔出砂可认为是岩体破坏和流体压力传递失效共同作用的结果。砂岩油藏实验表明,这两种基本作用可导致裂缝的发展[50],并随裂缝的生长诱发储层损伤演化,而这又反过来影响储层流体动力学行为和储层介质强度[51, 52]。
岩石力学宏观模型与水合物开采井孔出砂模型的区别在于海洋天然气水合物通常赋存于海底浅层、结构疏松的沉积体中,将水合物储层视为岩石块体研究与实际情况存在一定差异。
2.2 砂拱稳定模型
砂拱是在油层套管封固产层后,通过射孔弹将套管、水泥环和储层射穿,使储层裂隙发育,为油气流通提供通道。在此过程中,射孔炮眼周围的岩石破碎坍塌,形成似球形空间,并由于岩石颗粒间的接触力、摩擦力以及地层流体与颗粒间的表面张力而保持稳定。当孔隙流体压力和地层有效应力超过砂拱的稳定极限,或者地层流体流速过大时,砂拱坍塌从而导致大量出砂。
在砂拱力学稳定性方面,三轴试验[53]表明岩石的力学性质与不同润湿相之间存在影响关系,颗粒在一定的润湿相浓度范围内保持稳定。过低的润湿相浓度不能形成砂拱,过高的润湿相浓度使砂拱强度大大降低,容易坍塌。这是因为砂粒间的粘附强度及摩擦力是砂拱稳定的重要因素,而粘附强度受润湿相与砂粒间表面张力影响。出砂样品的CT扫描显示,在较低的流体流速下,随着出砂的发展,砂粒沉积从而在地层中形成稳定结构,出砂缓解。地层流体流速同样影响砂拱稳定,流速增大砂拱体积增大,流速过高砂拱被破坏,这一观点对水合物出砂同样适用,因为流体对含水合物沉积物中砂粒的剥离作用与疏松砂岩油藏是相似的。此外井孔压降[54]通过对流体流速的控制间接影响砂拱稳定。
理论模型方面通过考虑砂粒应力状态[55]和流体流动的影响,研究由于产液流动而产生的剪切膨胀区[55],该区域存在如下关系:
$$ \begin{align} & \left[ \frac{{{\mathit{s}}_{\mathit{0}}}}{\text{tan}\mathit{\varphi }} \right]~\text{ }+{{\sigma }_{r}}-\frac{\mu q}{4\pi k{{R}_{i}}~}\left( 1-\frac{4sin\varphi }{\text{ }1+2sin\varphi } \right)\text{ } \\ & \left( \frac{4sin\varphi }{1-sin\varphi } \right)\text{ }\frac{\text{d}r}{\text{d}{{R}_{i}}}~~=0 \\ & ~ \\ \end{align} $$ (9) 式中S0为抗剪强度,φ为内摩擦角,σr为径向应力。模型认为当疏松砂岩产砂时,砂拱可以在射孔开口后继续生长,砂拱临界流量与其半径成正比。此外,基于弹塑性理论[56],对外荷载作用下径向和切向应力变化趋势的研究表明,井周各点应力随转角而变化,当井壁受挤压应力最大时易发生剪切破坏。
砂拱稳定模型的应用具有一定的局限性,它主要适用于采用射孔方式完井的储层,对于非射孔完井,砂拱稳定模型不适用。
2.3 砂粒脱离细观模型
随着对出砂影响因素的考虑越来越全面,以岩石块体为研究对象的宏观粗略模型已经不能很好地解释储层出砂的发生和发展。为了全面反映出砂机制,出砂研究方法从借鉴岩石力学的宏观模型逐步发展到以分析单个砂粒的受力状态和运动状态的细观模型[57, 58]。
这类模型[58-60]通过超临界离散元方法(PFC)和Darcy流体流动理论等来模拟常规油井产砂过程,研究储层在压实作用下应力路径的非线性演变和剪切带的形成,结果表明多孔岩石的破坏模式将随着围压的变化而变化。平行黏结模型[61]从细观角度,运用几何学的方法研究了油井出砂机理,分析发现井孔周围塑性区随着流体运动逐步增大,塑性范围的增大进一步削弱砂粒之间粘结关系,胶结破坏增强[62]。而含水合物沉积物细观胶结状态[62]对水合物储层强度及剪切带的形成有重要影响。水合物出砂同样可视为塑性边界砂粒脱离过程,因此,这一研究方法对水合物储层出砂具有重要意义。
此外,Uchida等[63]认为水合物开采井孔出砂过程是传热-流动-力学的耦合过程,提出了一个关于水合物出砂的显式耦合模型,其模型的本构数学描述如下:
$$ \begin{align} & d{{\sigma }^{\prime }}=\left[ D_{hs}^{e}-\frac{D_{hs}^{e}\frac{\partial g\partial {{f}^{\text{T}}}}{\partial {{\sigma }^{\prime }}\partial {{\sigma }^{'}}}D_{hs}^{e}}{{{\Lambda }_{den}}} \right]\text{d}\epsilon + \\ & \left[ D_{ho}^{e}{{\left[ D_{hs}^{e} \right]}^{-1}}\left( {{\sigma }^{\prime }}-\sigma _{0}^{\prime } \right)- \right. \\ & \left. \frac{D_{hs}^{e}\frac{\partial g\partial {{f}^{\top }}}{\partial {{\sigma }^{\prime }}\partial {{\sigma }^{\top }}}D_{ho}^{e}{{\left[ D_{hs}^{e} \right]}^{-1}}\left( {{\sigma }^{\prime }}-\sigma _{0}^{\prime } \right)}{{{\Lambda }_{den}}}-\frac{D_{hs}^{e}\frac{\partial g\partial {{f}^{\top }}}{\partial {{\sigma }^{\prime }}\partial {{\xi }_{h}}}}{{{\Lambda }_{den}}} \right]\text{d}{{S}_{h}} \\ & -\left[ D_{hs}^{e}-\frac{D_{ho}^{e}\frac{\partial g\partial {{f}^{\text{T}}}}{\partial {{\sigma }^{\prime }}\partial {{\sigma }^{'}}}D_{hs}^{e}}{{{\Lambda }_{den}}} \right]\frac{\delta }{3}\beta \cdot dT \\ & D_{hs}^{e}-\frac{D_{hs}^{e}\frac{\partial g\partial {{f}^{\text{T}}}}{\partial {{\sigma }^{\prime }}\partial {{\sigma }^{\prime }}}D_{hs}^{e}}{{{\Lambda }_{den}}}]{{\left[ D_{hs}^{e} \right]}^{-1}}{{\sigma }^{\prime }}{{\omega }_{1}}\frac{d{{m}_{\mathit{ssi}}}}{{{m}_{si}}} \\ & {{\Lambda }_{\text{den}}}=\frac{\partial {{\text{f}}^{\text{T}}}}{\partial {{\sigma }^{\prime }}}\text{D}_{\text{hs}}^{\text{e}}\frac{\partial \text{g}}{\partial {{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\prime }}}-\frac{\partial \text{f}}{\partial \text{ }\!\!\xi\!\!\text{ }}\frac{\partial {{\text{ }\!\!\xi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{T}}}}{\partial {{\epsilon }^{\text{p}}}}\frac{\partial \text{g}}{\partial {{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\prime }}} \\ \end{align} $$ (10) 式中σ′为有效应力,σ′0为土骨架初始有效应力,Dhs?为含水合物土体的弹性刚度矩阵,Dhoe为水合物弹性刚度矩阵,g为塑性流动势能,f为屈服函数,Λ为塑性增量,?、?p分别为总应变矢量和塑性应变矢量,ξ为硬化参数,Sh为水合物饱和度,n为孔隙度,β*为颗粒和水合物热膨胀系数的体积平均值,β*=(1-n)βs+nShβh,βs、βh分别为砂颗粒和水合物的热膨胀系数,δ=[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]T。T为温度,ω1为应力降低因子,mssi为未扰动原始土体质量,mssi=ms-mfs-msst,ms为固体颗粒总质量,mfs为处于流动状态的固体颗粒质量,msst为由于水力梯度降低而沉降的土颗粒。
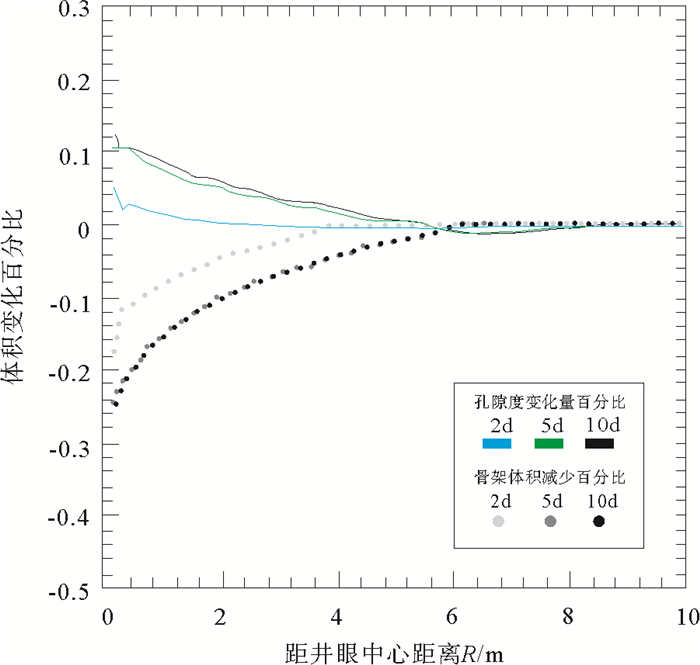
模型根据砂粒运动状态将其分为流动砂、沉降砂以及原状砂,认为砂粒状态的变化本身并不改变总体质量,而流动砂运移至井筒中时才发生质量变化。当水力梯度不足以携砂至井筒时将产生沉降砂。图 3给出了砂体变化量随时间和距离的变化关系,其中d表示天数。在出砂初期,井眼附近出现较高的水力梯度,砂体迅速脱离骨架,流化颗粒量迅速增多,孔隙度在井眼附近随之也发生较大变化。随着距离的增加,水利梯度降低,且应力传播下降,出砂量和孔隙度变化均减小。随着开采时间的延长,压力梯度进一步降低,出砂量趋于稳定。值得注意的是,随着出砂量增加,储层产生剪切变形,而塑性变形将增加砂粒脱离的可能性。此外,温度和压力的分布状态受到流体产出的影响,从而改变水合物的分解状态。通过数值模拟研究发现,压力梯度是井孔出砂的主要影响因素,过高的压力梯度会在生产初期造成大量出砂,通过降低降压速率能够最有效地减少出砂量。
![]() 图 3 单位体积变化百分比随时间和距离变化关系[64]Figure 3. The percentage of unit volume change with time and distance
图 3 单位体积变化百分比随时间和距离变化关系[64]Figure 3. The percentage of unit volume change with time and distance常规砂粒脱离模型能够较好地从细观角度描述出砂过程,但该模型缺少对水合物分解特性的考虑。在借鉴该模型的基础上,应当考虑水合物分解动力学特征以及储层自身物性的变化,以更好地反映水合物藏的产气和出砂问题。
3. 讨论
天然气水合物开采是一个多相态变化、多物理场耦合的复杂过程,其出砂问题与常规油藏出砂存在较大差异。在借鉴砂岩油藏出砂研究方法的过程中,必须考虑海洋天然气水合物储层的特殊性,例如未固结沉积体天然气水合物赋存状态、海洋水合物分解特征、沉积物强度随饱和度增加等。
储层出砂主要受地层有效应力和孔隙流体压力的影响。岩石力学宏观模型应用广泛,但对于天然气水合物储层的应用具有一定局限性。这类模型以井壁或射孔周围的岩石块体为研究对象,认为地层是各向均一的连续介质,而海洋天然气水合物储层一般位于海底浅表层,未固结成岩,结构非常疏松,因此,在借鉴岩石力学的相关理论和参数时应当考虑水合物储层的固结特性。
砂拱稳定模型主要用于研究射孔周围砂拱稳定性。这类模型通常采用室内三轴试验与弹塑性理论模型相结合的方法来研究,出砂影响因素主要包括润湿相类型、润湿相浓度以及地层流体流速等。该模型是否适用于水合物出砂研究决定于水合物开采所采用的完井方式,砂拱模型应用场景有限。根据国外水合物试采资料,2007年加拿大Mallik2L-38天然气水合物测试井,即采用射孔方式完井,未采取防砂措施,后由于大量出砂导致试采中止,该完井方式下可以借鉴砂拱稳定模型进行研究。而2017年日本南海海槽海域水合物试采采用GeoFORM防砂系统,不适用砂拱稳定模型。
砂粒脱离细观模型能够较好的描述出砂的发生过程。这类模型通常采用非连续介质理论,运用离散元方法(PFC)来考虑砂粒从骨架上的脱离与在流体中的运动,并将影响出砂的细观因素归于流体压力梯度与流体拖拽力两方面。但该模型缺少对水合物分解特性的考虑。因此,在借鉴砂粒脱离细观模型用于研究海洋天然气水合物井孔出砂问题的过程中应当考虑水合物分解效应。此外,水合物分解是一个动态过程,储层应力与水合物分解间存在相互作用[64],一方面水合物分解使储层孔隙度增加,改变储层结构特征和应力分布;另一方面储层在应力作用下的变形及损伤对水合物渗流场产生影响。因此在借鉴颗粒脱离细观模型的基础上还应当考虑出砂过程中的流固耦合作用。
综合对比3种研究方法,可以发现砂粒脱离细观模型能更为细致地考虑出砂问题,可借鉴应用到天然气水合物储层出砂研究之中。
4. 结论
天然气水合物开采井孔出砂是制约水合物商业化开发的关键因素。我国南海北部陆坡天然气水合物主要以分散状弱胶结方式赋存于细砂泥质沉积层中,研究水合物开采出砂问题极为迫切。
(1) 水合物开采井孔出砂问题受多种因素影响:水合物胶结模式和水合物饱和度影响储层胶结强度;孔隙流体压力和流速影响储层受力状态,生产压差控制水合物分解及储层应力变化。因此,在研究天然气水合物开采出砂问题过程中应当注意这些因素的影响。
(2) 常规油气藏出砂研究中的岩石力学宏观模型应用广泛,但仅能用于预测出砂发生时岩石力学不稳定状态及局部强度的退化,不能较好地反映出砂量的变化,且该模型认为储层介质是胶结良好的岩体,这可能过高地估计了水合物储层的出砂条件。
(3) 通过对比分析弱胶结疏松砂岩油藏出砂研究的3种方法,发现以砂体受力状态作为切入点的砂粒脱离细观模型具有借鉴意义。由于水合物出砂过程中存在相变,因此,在借鉴砂粒脱离细观模型的基础上还应当考虑水合物的分解特性以及出砂过程中的流固耦合作用。
-
图 3 单位体积变化百分比随时间和距离变化关系[64]
Figure 3. The percentage of unit volume change with time and distance
日本 中国 首次海域试采 第二次海域试采 首次海域试采 时间 2013年 2017年 2017年 作业区域 第二渥美海丘 第二渥美海丘 南海神狐海域 作业水深 约1 000 m 约1 000 m 1 266 m 储层深度 海底以下约300 m 海底以下约350 m 海底以下203~277 m 储层条件 砂质 砂质 泥质粉砂 开采方法 降压法 降压法 基于降压的地层流体抽取法 产气持续时间 6 d 第一口井12 d;第二口井24 d 60 d 累计产气量 12万m3 第一口井3.5万m3;第二口井20万m3 30.9万m3 日均产气量 2万m3 第一口井0.292万m3;第二口井0.833万m3 0.515万m3 日均最高产气 约2.5万m3 — 3.5万m3 停产原因 出砂堵塞 第一口井出砂堵塞 主动关井 -
[1] Kvenvolden K A. A primer on the geological occurrence of gas hydrate[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1998, 137(1): 9-30. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1998.137.01.02
[2] Liu Y, Gamwo I K. Comparison between equilibrium and kinetic models for methane hydrate dissociation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 69(1): 193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2011.10.020
[3] Sum A K, Koh C A, Sloan E D. Clathrate hydrates: from laboratory science to engineering practice[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(16): 7457-7465. doi: 10.1021/ie900679m
[4] Kurihara M, Sato A, Funatsu K, et al. Analysis of production data for 2007/2008 mallik gas hydrate production tests in Canada[C]//International Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition in China. Beijing, China: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2010.
[5] Hunter R B, Collett T S, Boswell R, et al. Mount elbert gas hydrate stratigraphic test well, Alaska north slope: overview of scientific and technical program[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(2): 295-310. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.02.015
[6] Kvamme B. Feasibility of simultaneous CO2 storage and CH4 production from natural gas hydrate using mixtures of CO2 and N2[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 93(8): 897-905. doi: 10.1139/cjc-2014-0501
[7] Terao Y, Duncan M, Hay B, et al. Deepwater methane hydrate gravel packing completion results and challenges[C]//Offshore Technology Conference 2014. Houston, Texas, USA: Offshore Technology Conference, 2014.
[8] Yoshihiro T, Duncan M W, Hay W J, et al. Deepwater methane hydrate gravel packing completion results and challenges[C]//Offshore Technology Conference 2014. Houston, Texas: Offshore Technology Conference, 2014.
[9] Kurihara M, Sato A, Funatsu K, et al. Analysis of 2007 and 2008 Gas Hydrate Production Tests on the Aurora/JOGMEC/NRCan Mallik 2L-38 Well Through Numerical Simulation[M]//Dallimore S R, Yamamoto K, Wright J F, et al. Scientific Results from the JOGMEC/NRCan/Aurora Mallik 2007-2008 Gas Hydrate Production Research Well Program, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada. Mackenzie Delta: Natural Resources Canada, 2012.
[10] Hancock S H, Collett T S, Dallimore S R, et al. Overview of Thermal-Stimulation Production-Test Results for the JAPE X/JNOC/GSC et al. Mallik 5L-38 Gas Hydrate Production Research Well[M]//Dallimore S R, Collett T S. Scientific Results from the Mallik 2002 Gas Hydrate Production Research Well Program, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada. Ottawa: Geological Survey of Canada, 2005.
[11] 李彦龙, 刘乐乐, 刘昌岭, 等.天然气水合物开采过程中的出砂与防砂问题[J].海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(7): 36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201607005 LI Yanlong, LIU Lele, LIU Changling, et al. Sanding prediction and sand-control technology in hydrate exploitation: a review and discussion[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(7): 36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201607005
[12] Rahmati H, Jafarpour M, Azadbakht S, et al. Review of sand production prediction models[J]. Journal of Petroleum Engineering, 2013, 2013: 864981.
[13] 宁伏龙, 蒋国盛, 张凌, 等.影响含天然气水合物地层井壁稳定的关键因素分析[J].石油钻探技术, 2008, 36(3): 59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2008.03.014 NING Fulong, JIANG Guosheng, ZHANG Ling, et al. Analysis of key factors affecting wellbore stability in gas hydrate formations[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2008, 36(3): 59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2008.03.014
[14] Rutqvist J, Moridis G J, Grover T, et al. Geomechanical response of permafrost-associated hydrate deposits to depressurization-induced gas production[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2009, 67(1-2): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2009.02.013
[15] 吴时国, 陈珊珊, 王志君, 等.大陆边缘深水区海底滑坡及其不稳定性风险评估[J].现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 430-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.013 WU Shiguo, CHEN Shanshan, WANG Zhijun, et al. Submarine landslide and risk evaluation on Its instability in the deepwater continental margin[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 430-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.013
[16] Sultan N, Cochonat P, Foucher J P, et al. Effect of gas hydrates melting on seafloor slope instability[J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 213(1-4): 379-401. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.10.015
[17] Sloan E D Jr, Koh C A. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases[M]. Florida: CRC Press, 2007.
[18] 曹宇春.考虑骨架压缩效应的饱和土有效应力原理[J].施工技术, 2013, 42(S1): 7-11. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90566A/2013S1/1005610185.html CAO Yuchun. Effective stress principle of saturated soils in terms of skeleton compressibility[J]. Construction Technology, 2013, 42(S1): 7-11. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90566A/2013S1/1005610185.html
[19] Kennett J, Cannariato K, Hendy I L, et al. Carbon isotopic evidence for methane hydrate instability during quaternary interstadials[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5463): 128-133. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5463.128
[20] 邵明娟, 张炜.海洋地质信息(天然气水合物勘查与试采专刊)[R].北京: 中国地质图书馆, 2017. SHAO Mingjuan, ZHANG Wei. Marine Geology Information (Natural gas hydrate exploration and test)[R]. Beijing: China Geological Library, 2017.]
[21] Ecker C, Dvorkin J, Nur A M. Estimating the amount of gas hydrate and free gas from marine seismic data[J]. Geophysics, 2000, 65(2): 565-573. doi: 10.1190/1.1444752
[22] 宁伏龙.天然气水合物地层井壁稳定性研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-2006053409.htm NING Fulong. Research on wellbore stability in gas hydrate formation[D]. Beijing: Doctoral Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-2006053409.htm
[23] Kingston E, Clayton C, Priest J. Emily Kingston, Chris Clayton and Jeff Priest School of Civil Engineering and the Environment University of Southampton Highfield, Southampton, SO17 1BJ UNITED KINGDOM[J]. Hydrate Morphology, 2008.
[24] Waite W F, Santamarina J C, Cortes D D, et al. Physical properties of hydrate‐bearing sediments[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2009, 47(4): RG4003. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_5762815b05ef1bf0ed9be6fc1d599e2c
[25] Yan R T, Wei C F. Constitutive model for gas hydrate-bearing soils considering hydrate occurrence habits[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 17(8): 04017032. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000914
[26] Hyodo M, Nakata Y, Yoshimoto N, et al. Basic research on the mechanical behavior of methane hydrate-sediments mixture[J]. Journal of the Japanese Geotechnical Society, 2005, 45(1): 75-85.
[27] 魏厚振, 颜荣涛, 陈盼, 等.不同水合物含量含二氧化碳水合物砂三轴试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2011, 32(S2): 198-203. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7528604 WEI Houzhen, YAN Rongtao, CHEN Pan, et al. Deformation and failure behavior of carbon dioxide hydrate-bearing sands with different hydrate contents under triaxial shear tests[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(S2): 198-203. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7528604
[28] Grozic J, Ghiassian H. Undrained shear strength of methane hydrate-bearing sand; preliminary laboratory results[C]//Proceeding of 6th Canadian Permafrost Conference and 63rd Canadian Geotechnical Conference. Calgary, 2010.
[29] Masui A, Haneda H, Ogata Y, et al. Effects of methane hydrate formation on shear strength of synthetic methane hydrate sediments[C]//The Fifteenth International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. Seoul, Korea: International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers, 2005.
[30] 印兴耀, 刘欣欣, 曹丹平.基于Biot相洽理论的致密砂岩弹性参数计算方法[J].石油物探, 2013, 52(5): 445-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2013.05.001 YIN Xingyao, LIU Xinxin, CAO Danping. Elastic parameters calculation for tight sand reservoir based on Biot-consistent theory[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2013, 52(5): 445-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2013.05.001
[31] Vaziri H H, Nouri A, Hovem K A, et al. Computation of sand production in water injectors[J]. SPE Production and Operations, 2008, 23(4): 518-524. doi: 10.2118/107695-PA
[32] 徐守余, 王宁.油层出砂机理研究综述[J].新疆地质, 2007(3): 283-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2007.03.011 XU Shouyu, WANG Ning. Research on reservoir sand production mechanism[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2007(3): 283-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2007.03.011
[33] Wu B L, Tan C P, Lu N. Effect of water-cut on sand production-an experimental study[J]. SPE Production and Operations, 2006, 21(3): 349-356. doi: 10.2118/92715-PA
[34] Huang L, Su Z, Wu N Y. Evaluation on the gas production potential of different lithological hydrate accumulations in marine environment[J]. Energy, 2015, 91: 782-798. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2015.08.092
[35] Konno Y, Masuda Y, Akamine K, et al. Sustainable gas production from methane hydrate reservoirs by the cyclic depressurization method[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 108: 439-445. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2015.11.030
[36] Jin G R, Xu T F, Xin X, et al. Numerical evaluation of the methane production from unconfined gas hydrate-bearing sediment by thermal stimulation and depressurization in Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 33: 497-508. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.05.047
[37] 沈海超, 程远方, 胡晓庆.天然气水合物藏降压开采近井储层稳定性数值模拟[J].石油钻探技术, 2012, 40(2): 76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2012.02.015 SHEN Haichao, CHENG Yuanfang, HU Xiaoqing. Numerical Simulation of near wellbore reservoir stability during gas hydrate production by depressurization[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2012, 40(2): 76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2012.02.015
[38] 肖钢, 白玉湖, 董锦.天然气水合物综论[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2012: 156. XIAO Gang, BAI Yuhu, DONG Jin. A Comprehensive Review of Natural Gas Hydrates[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2012.
[39] 何湘清.弱胶结砂岩油藏出砂机理研究[D].成都: 西南石油学院博士学位论文, 2002. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10615-2003051292.htm HE Xiangqing. Study on the mechanism of sand production for weakly consolidated sand formation[D]. Chengdu: Doctoral Dissertation of Southwest Petroleum University, 2002. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10615-2003051292.htm
[40] Coates G R, Denoo S. Mechanical properties program using borehole analysis and Mohr's circle[C]//SPWLA 22nd Annual Logging Symposium. Mexico: Society of Petrophysicists and Well-Log Analysts, 1981.
[41] Nordgren R P. Strength of well completions[C]//The 18th U.S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS). Golden, Colorado: American Rock Mechanics Association, 1977.
[42] Morita N, Whitfill D L, Massie I, et al. Realistic sand-production prediction: Numerical Approach[J]. SPE Production Engineering, 1989, 4(1): 15-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLHY/NSTL_HYCC025654707/
[43] Rahmati H, Nouri A, Vaziri H, et al. Validation of predicted cumulative sand and sand rate against physical-model test[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology, 2012, 51(5): 403-410. doi: 10.2118/157950-PA
[44] Morita N, Whitfill D L, Fedde O P, et al. Parametric study of sand-production prediction: analytical approach[J]. SPE Production Engineering, 1989, 4(1): 25-33.
[45] Nouri A, Kuru E, Vaziri H. Elastoplastic modelling of sand production using fracture energy regularization method[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology, 2009, 48(4): 64-71. doi: 10.2118/09-04-64
[46] Jafarpour M, Rahmati H, Azadbakht S, et al. Determination of mobilized strength properties of degrading sandstone[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2012, 52(4): 658-667. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2012.07.007
[47] 张旭辉, 王淑云, 李清平, 等.天然气水合物沉积物力学性质的试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2010, 31(10): 3069-3074. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.10.007 ZHANG Xuhui, WANG Shuyun, LI Qingping, et al. Experimental study of mechanical properties of gas hydrate deposits[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(10): 3069-3074. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.10.007
[48] Winters W J, Pecher I A, Waite W F, et al. Physical properties and rock physics models of sediment containing natural and laboratory-formed methane gas hydrate[J]. American Mineralogist, 2015, 89(8): 1221-1227. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.2138/am-2004-8-909
[49] Willson S M, Moschovidis Z A, Cameron J R, et al. New model for predicting the rate of sand production[C]//SPE/ISRM Rock Mechanics Conference. Irving, Texas: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2002.
[50] Detournay C. Numerical modeling of the slit mode of cavity evolution associated with sand production[J]. SPE Journal, 2009, 14(4): 797-804. doi: 10.2118/116168-PA
[51] 蒋官澄, 毕彩丰, 史源清.疏松砂岩油藏出砂状况模拟技术研究[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2005, 29(4): 64-67. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sydxxb200504015 JIANG Guancheng, BI Caifeng, SHI Yuanqing. Study on simulating sand production in unconsolidated sandstone reservoir[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural science, 2005, 29(4): 64-67. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sydxxb200504015
[52] 吴建平, 孙辉, 高斌, 等.低渗透油藏出砂机理研究——以雁木西油田为例[J].油气地质与采收率, 2003, 10(6): 70-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2003.06.025 WU Jianping, SUN Hui, GAO Bin, et al. Study on sanding mechanism in low permeability oil reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2003, 10(6): 70-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2003.06.025
[53] Hall C D Jr, Harrisberger W H. Stability of sand arches: a key to sand control[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1970, 22(7): 820-829.
[54] 张建国, 程远方.砂拱及其稳定模型的推导及验证[J].石油钻探技术, 1999, 27(1): 40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.1999.01.017 ZHANG Jianguo, CHENG Yuanfang. Sand arch stability model and its verification[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 1999, 27(1): 40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.1999.01.017
[55] Bratli R K, Risnes R. Stability and failure of sand arches[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1981, 21(2): 236-248. doi: 10.2118/8427-PA
[56] Risnes R, Bratli R K, Horsrud P. Sand stresses around a wellbore[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1982, 22(6): 883-898. doi: 10.2118/9650-PA
[57] Jing LR, Stephansson O. Fundamentals of Discrete Element Methods for Rock Engineering: Theory and Applications[M]. Rotterdam: Elsevier, 2007.
[58] Li L, Papamichos E, Cerasi P. Investigation of Sand Production Mechanisms Using DEM with Fluid Flow[M]//Van Cotthem A, Charlier R, Thimus J F, et al. Eurock 2006: Multiphysics Coupling and Long Term Behaviour in Rock Mechanics. Liège, Belgium: Taylor and Francis, 2006: 67-69.
[59] Preece D S, Jensen R P, Perkins E D, et al. Sand production modeling using superquadric discrete elements and coupling of fluid flow and particle motion[C]//Vail Rocks 1999, The 37th U.S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS). Vail, Colorado: American Rock Mechanics Association, 1999.
[60] Li L, Holt R M. Particle Scale Reservoir Mechanics[J]. Oil and Gas Science and Technology, 2002, 57(5): 525-538. doi: 10.2516/ogst:2002035
[61] 刘先珊, 许明.基于柱坐标系的油井出砂三维数值模型设计与研究[J].岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(5): 871-878. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytgcxb201305010 LIU Xianshan, XU Ming. 3-Dimensional numerical model for sand production in oil wellbore based on cylindrical coordinate system[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(5): 871-878. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytgcxb201305010
[62] 蒋明镜, 彭镝, 申志福, 等.深海能源土剪切带形成机理离散元分析[J].岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(9): 1624-1630. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201409010 JIANG Mingjing, PENG Di, SHEN Zhifu, et al. DEM analysis on formation of shear band of methane hydrate bearing soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(9): 1624-1630. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201409010
[63] Uchida S, Klar A, Yamamoto K. Sand production model in gas hydrate-bearing sediments[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2016, 86: 303-316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.04.009
[64] 程远方, 沈海超, 李令东, 等.天然气水合物藏物性参数综合动态模型的建立及应用[J].石油学报, 2011, 32(2): 320-323. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201102021 CHENG Yuanfang, SHEN Haichao, LI Lingdong, et al. Comprehensive and dynamical modeling for physical parameters of natural gas hydrate reservoirs and its application[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 320-323. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201102021
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 吴霞,王晓丽,乌音嘎,阿如汗,虹霞. 黄河内蒙古段甲烷通量变化特征及甲烷功能菌群落对通量的影响. 生态学报. 2024(16): 7105-7118 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴艺,毛旭锋,宋秀华,于红妍,唐文家,谢顺邦,刘泽碧,丁启智. 黄河上游梯级水库产甲烷菌的群落特征及影响因素研究. 环境工程. 2024(12): 8-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李晋,梁家豪,马文峰,郭绍辉,王庆宏,陈春茂. 热-碱渣预处理强化炼厂剩余活性污泥厌氧消化性能. 化工进展. 2023(12): 6609-6619 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: