DISTRIBUTION OF GAS HYDRATE IN SHENHU AREA: IDENTIFIED WITH WELL LOG AND SEISMIC MULTI-ATTRIBUTES
-
摘要: 我国在神狐海域钻探发现了高饱和度天然气水合物,由于该地区受迁移峡谷影响,水合物在空间的分布变化较大。本文把测井数据和地震数据相结合识别了BSR并解释了侵蚀面等层位,沿水合物稳定带底界提取多种属性,并对属性结果进行优化分析。发现振幅类属性对水合物显示较为敏感,不同站位水合物矿体展布特征不同。在W19井和SC-02井水合物矿体呈马蹄状分布,W18井矿体呈斑点状分布,分别位于埋藏水道天然堤的局部高点和水道头部高点上,矿体形态与构造高点形态一致。测井异常指示的水合物层在SC-02井伽马值较高,而W18和W19井水合物层伽马值较低,表明不同站位含水合物层泥质含量不同。而地震解释和属性分析发现水合物层位于一个规模较大的气烟囱构造上部,流体运移是控制该区域水合物成藏的重要条件,气体组成分析表明热成因气为水合物的成藏提供重要气源。Abstract: High quality gas hydrate samples have been successfully recovered from the Shenhu area, the northern slope of South China Sea. The spatial distribution of gas hydrate varies greatly owing to the complex fluid movement caused by lateral migration of canyons and gas chimneys. In this paper, we identified the BSR and erosional canyon surface with well logging and seismic data and the extracted multiple seismic attributes along the theoretical base of the gas hydrate stability zone (BGHSZ). It is found that the amplitude type of attributes are sensitive to gas hydrate after optimization of all extractable seismic attributes. Description of gas hydrate bodies suggests that the distribution pattern of gas hydrate changes from site to site. It is horseshoe-shaped at Site W19 and U-shaped and point-shaped at Site W18 respectively, depending upon the topography of the local structural high. Gas hydrate occurrences are inconsistent with lithology according to well log data. It is mainly distributed at the top of a large gas chimney structure. Fluid flow is an essential element for gas hydrate deposition in this area, and thermogenic gas contributes to higher gas hydrate saturation.
-
Keywords:
- gas hydrate /
- attribute analysis /
- spatial distribution /
- erosion surface /
- Shenhu area
-
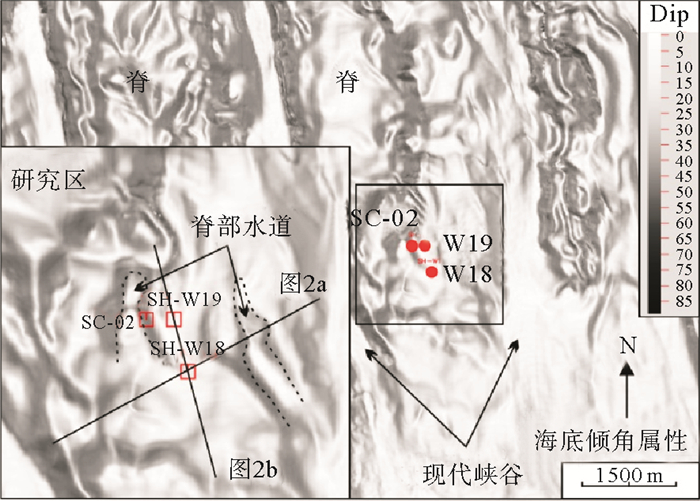
天然气水合物是在低温、高压环境下形成的类似于冰的固态化合物,近年来,由于天然气水合物在能源、气候变化及水合物分解对海底稳定性的影响而成为国际研究热点[1-7]。自2007年开始,我国在南海北部神狐海域先后进行了3次水合物钻探项目(GMGS-01,03和04),大量随钻测井数据的研究发现该区域不同站位水合物厚度、赋存状态不同,不仅发现了热成因天然气水合物,而且在局部位置发现了饱和度达60%以上的水合物层[8, 9](图 1)。前人研究表明神狐海域热流体活动、沉积构造演化、峡谷迁移、气烟囱、断层等流体运移构造以及储层条件等都对水合物成藏有较为明显的控制作用[10-14],但是神狐海域水合物层砂质含量并不高,岩性主要为泥质粉砂岩[8]。近年来在国际多个海域都进行了大量水合物钻探,并在多个盆地发现了砂质高饱和度水合物层,如日本南海海槽、印度海域、韩国郁陵盆地、美国墨西哥湾、水合物脊等地区[15-19],但是不同海域发现的砂质储层水合物厚度、饱和度等差异较大,并不是砂质储层都含有水合物和形成的水合物都具有高饱和度特点, 韩国郁陵盆地发现的砂质水合物储层饱和度较低[20, 21]。从识别不同类型水合物的测井异常看,砂质水合物储层具有高纵波速度、高电阻率异常(几Ωm至上百Ωm)[21-23]。神狐海域发育了大量的迁移峡谷,位于峡谷脊部W18、SC-02和W19井,水合物赋存状态相差不大,但是水合物分布厚度明显不同,从随钻成像测井来看,水合物层多是由多期厚层状水合物和分散状水合物的旋回组成[10]。由于珠江口盆地独特地质构造背景,该区域峡谷水道与国际上在浊流水道发现砂质储层高饱和度水合物并不完全相同。因此,对该地区典型站位进行水合物层厚度、空间分布的精细刻画,分析控制水合物层厚度差异控制因素的研究具有重要意义。
测井数据能够提供井位附近含水合物层的垂向变化,但是难以描述水合物层在横向上的变化,通过合成地震记录将地震与测井相结合能够描述水合物空间分布,而地震属性分析是描述水合物空间分布特征的一种重要的技术。在神狐研究区,前人结合钻井数据利用最大振幅属性、最小振幅属性和波阻抗等对水合物层和游离气层分布特征进行描述[13, 24],发现水合物分布呈条带状水道特征[13]。而韩国郁陵盆地水合物敏感的地震属性研究发现频谱分解、反射强度、瞬时频率以及P波速度对水合物层有较好响应[25-27]。在新西兰南部的珀伽索斯盆地中,瞬时相位和瞬时频率属性对水合物层较为敏感,P波及S波反演对水合物层分辨较好[28]。墨西哥湾盐底辟发育的水合物分布区反射强度、速度反演等对水合物识别较为有效[29, 30]。
本文围绕水合物钻探GMGS-03航次的W18、W19井及GMGS-04航次SC-02井,通过对测井数据分析识别水合物层,通过合成地震记录将测井上识别的水合物层与地震反射特征与属性异常进行对比研究,利用高分辨率三维地震资料描述水合物层分布范围,分析了水合物层形成的主要控制因素。
1. 水合物层地球物理响应特征
1.1 BSR识别
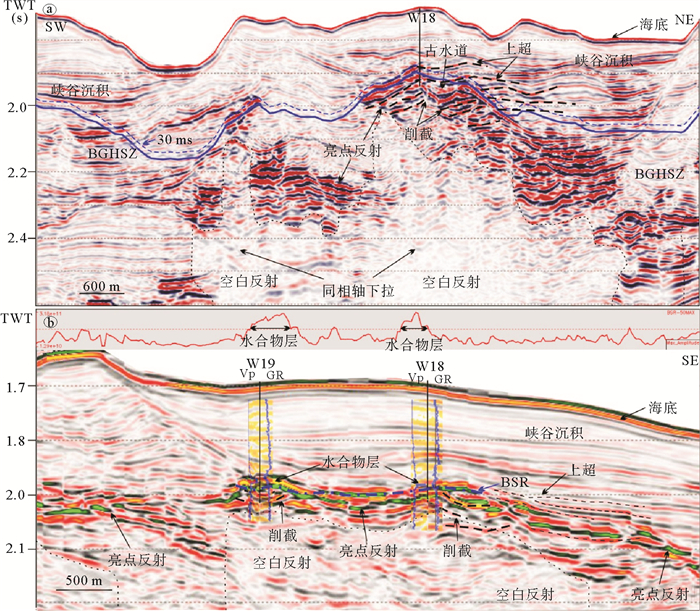
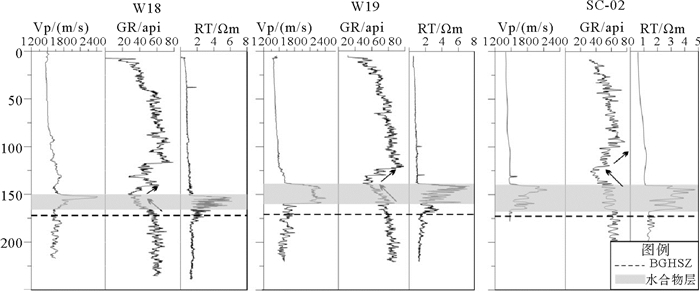
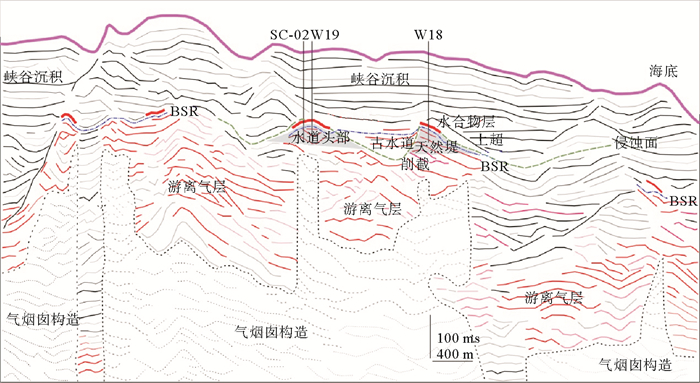
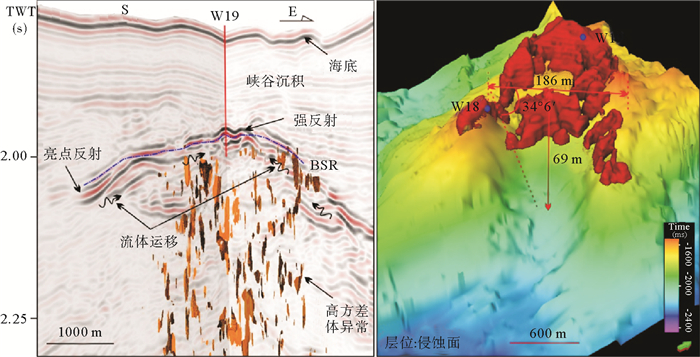
在地震剖面上,BSR一般为与海底近似平行、极性相反且与地层斜交的地震反射特征[31, 32]。SC-02井附近BSR为连续、强反射、斜穿地层且与海底平行特征,位于峡谷底部较近一期侵蚀面的下部,而W18和W19井附近BSR为连续、强反射、与海底并不完全平行,局部与侵蚀面平行,受侵蚀面控制作用明显,在构造高点处BSR深度明显变浅(图 2a, b)。据统计研究区附近BSR面积为8.18 km2,统计区面积为20.17 km2,占统计范围的40%,BSR分布范围较广。基于测量的地温梯度与海底温度,利用天然气水合物相平衡计算的稳定带底界(BGHSZ)深度变化不大,在W18、W19和SC-02井分别为171、172和173 m(图 3)
![]() 图 3 W18井、W19井和SC-02井纵波速度、伽马和电阻率测井曲线[36]Figure 3. The well logs of sites W18, W19 and SC-02 showing the P-wave velocity, gamma ray, and resistivity
图 3 W18井、W19井和SC-02井纵波速度、伽马和电阻率测井曲线[36]Figure 3. The well logs of sites W18, W19 and SC-02 showing the P-wave velocity, gamma ray, and resistivity1.2 水合物层识别
含水合物层具有高纵波速度、高电阻率等测井异常[33-35]。从W19井测井资料看,水合物层测井曲线呈漏斗型测井异常,电阻率和纵波速度均为向上增大趋势,纵波速度达到2 400 m/s, 电阻率达6 Ωm,远高于背景纵波速度与电阻率值,伽马测井呈低值异常,而密度测井无明显变化,表明该井存在水合物且沉积环境与下覆地层略微不同,沉积物粒度向上为由细变粗,含水合物层厚度大约为23 m。W18井与W19井具有相似处,而伽马测井异常的厚度比W19井大,水合物层纵波速度和电阻率测井值明显增高,但是厚度小于W19井,大约为16 m。SC-02井距W19井约200 m左右,该井纵波速度和电阻率测井明显增大,但伽玛测井显示该层岩性无明显变化,水合物层厚度达约28 m(图 3)。W18,W19井及SC-02井,伽马测井均向上变小呈漏斗形态,指示含水合物层的沉积物粒度向上逐渐变粗,通常指示天然堤或者决口扇。不同站位对比发现伽马异常出现的地层与存在水合物层并不一一对应[36],尤其是SC-02井,水合物层对应的地层伽马值相对较高,指示可能岩性相对较细。从合成地震记录来看,水合物层为BSR上部与海底极性一致的强振幅反射(图 2b)。
1.3 游离气层识别
从地震资料看,在W18井、19井和SC-02井BSR下存在大量厚度不等的亮点反射,沿地层方向展布,与BSR呈斜交,且下部与空白反射相伴生(图 2a,b)。在BSR下方伽马值较大且无明显变化,表明沉积物粒度逐渐变细,该段地层可能泥质含量较高。BSR下地层出现空白反射和同相轴下拉现象,是由于地层含有气体导致纵波速度降低。BSR下部的亮点反射与BSR上反映水合物的强反射相伴生,亮点反射大多圈闭在峡谷或水道的侵蚀面之下,较深部地层中的空白反射两侧也可能伴有亮点反射的发育(图 2a,b)。
2. 埋藏水道
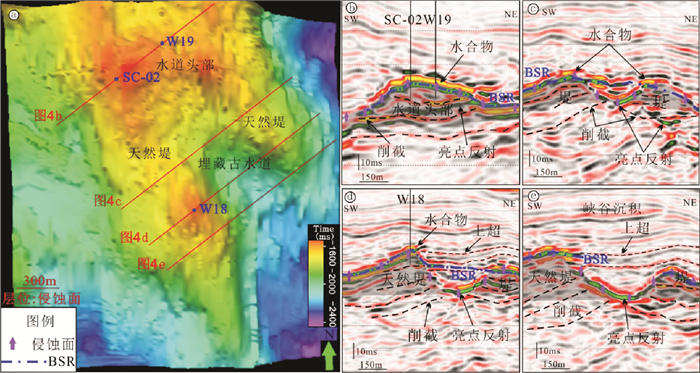
基于高分辨率三维地震数据解释,在水合物层附近存在一期峡谷侵蚀面,在侵蚀面上部和下部分别出现上超和削截等反射终止现象(图 2,图 4)。削截出现在侵蚀面下部,是下部倾斜地层受到侵蚀并再次受到沉积埋藏形成,而侵蚀面上部出现地层上超,反映峡谷沉积对可容纳空间的持续充填作用[37, 38]。侵蚀面时间图我们可以清楚看到研究区侵蚀面中间位置一个古水道的发育,水道规模不大,呈喇叭状开口,在W18井处,水道宽度大约为186 m,深度大约为69 m,天然堤倾角较大为34°6′(图 4)。水道横切剖面可以看到水道头部和天然堤上部以及水道内部的BSR上部都有代表水合物发育的强反射。侵蚀面下部均有代表游离气分布的亮点反射,向上截止于BSR。峡谷沉积主要呈中-弱振幅、中-强连续性反射,W18井、W19井及SC-02井上部主要为东部峡谷的沉积物(图 2a,b)。
3. 地震属性分析
地震信号中包含各种由岩性变化、所含流体成分、构造变形等地质现象造成的异常信息,利用振幅类属性、瞬时类属性和频谱类属性等,提取剖面属性、层位属性、三维体属性提取与敏感分析能够对储层特征、构造要素、沉积相及沉积环境等研究[39, 40]。通过对各种属性进行优化筛选,对水合物目标层进行反映,发现最大振幅属性、弧长属性、倾角时间切片及均方根振幅属性对水合物较为敏感。
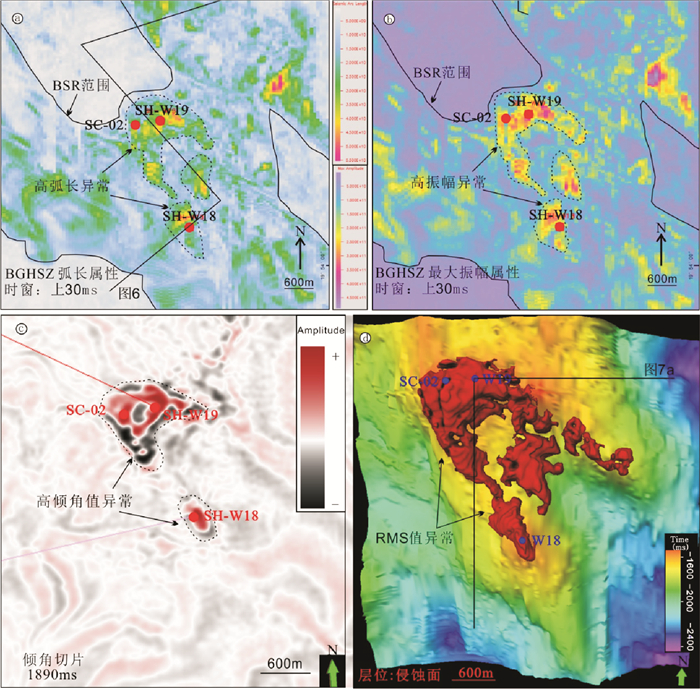
图 5a为对BGHSZ向上30 ms提取的弧长属性,该属性将显示水合物的强振幅与不含水合物层的弱振幅区分,也可以区分高频与反映游离气的低频信号,是一种频率与振幅的混合属性。含水合物地层为高弧长异常显示,对钻井附近弧长值异常进行圈定可以显示水合物分布范围。图 5b为沿BGHSZ向上30 ms时窗提取的最大振幅属性,水合物层为红色及黄色的最大振幅属性高值异常,从图 2b的剖面也可以看到,井孔处水合物层的最大振幅值异常增大。图 5c为计算的倾角地震数据体沿1 890 ms的时间切片,时间切片反映了在1 890 ms时间处水合物分布造成的振幅信息异常和构造高点的形态,水合物为高振幅响应,与周围地层有明显界线。图 5d是均方根振幅属性体提取高值异常与下部埋藏水道的分布关系,红色块体为均方根振幅异常反映的水合物层分布情况。
![]() 图 5 a:BGHSZ层位向上30 ms提取弧长属性;b:BGHSZ层位向上30 ms提取最大振幅属性;c:倾角体1 890 ms时间切片;d:RMS属性刻画的水合物分布范围Figure 5. a:The maximum amplitude attribute map extracted for a time window 30 ms above the BGHSZ; b: The arc length attribute map extracted for a time window 30 ms above the BGHSZ; c: 1 890 ms time slide from dip cube; d: The RMS displays the distribution of gas hydrate
图 5 a:BGHSZ层位向上30 ms提取弧长属性;b:BGHSZ层位向上30 ms提取最大振幅属性;c:倾角体1 890 ms时间切片;d:RMS属性刻画的水合物分布范围Figure 5. a:The maximum amplitude attribute map extracted for a time window 30 ms above the BGHSZ; b: The arc length attribute map extracted for a time window 30 ms above the BGHSZ; c: 1 890 ms time slide from dip cube; d: The RMS displays the distribution of gas hydrate水合物在沉积物孔隙中发生充填,会造成沉积物声波速度增大,而沉积物密度不变或略微降低[33],这就导致波阻抗值的提高,在地震数据中体现在同相轴振幅的异常增强、且极性与海底极性一致,因此振幅类属性对水合物层都较为敏感。弧长属性比最大振幅属性圈定的水合物层范围略大,可能是其引入地震频率属性后对水合物层更敏感。时间切片由于其单一时间层位的限制,无法对水合物范围完全显示。通过对不同地震属性综合分析,发现W18井与W19井、SC-02井附近水合物范围不同,W19井和SC-02井附近水合物矿体呈马蹄型展布,分布于水道头部高点,且与构造高点形态一致;W18井附近水合物为斑状分布,位于水道西部天然堤的局部构造高点上;另外水道内部同样存在少量水合物层的分布。对均方根振幅属性刻画的水合物矿体计算,W19和SC-02井矿体呈东北—西南向长度大约为560 m,西北—南东向宽度大约为365 m。W18井呈东北—西南向长度大约为210 m,西北-东南向宽度大约为200 m(图 5a,b,d)。
4. 讨论
大量研究表明天然气水合物成藏与温度压力条件、气源、气体运移、储层条件、生成时间和水等有关[41]。神狐海域水合物成藏地质条件与成藏系统前人进行了大量研究[5, 9-12, 29],发现相对高饱和度水合物层与富含有孔虫的储层条件、深部热成因气气源、流体运聚体系等密切相关[42-44]。从W18井、W19井及SC-02井识别的水合物层看,水合物层均位于被峡谷沉积埋藏的古构造高点之上,W19井和SC-02井位于古水道头部,而W18井位于古水道-天然堤的局部构造高点,但水合物层的岩性存在较大差异,均位于侵蚀面附近,而下部发育一个较大规模烟囱构造,水合物层均位于靠近稳定带底界上方的地层(图 6)。
4.1 储层条件
从水合物层分布看,研究区三口测井资料表明在W18井和W19井并不是所有低伽玛值地层都出现含水合物的测井异常,仅在稳定带底界上方低伽马值的局部地层含有水合物,而SC-02井水合物层出现在稳定带上方的伽马值较大层位,而伽马值相对较低地层不含水合物(图 3)。伽马测井常用来识别泥岩地层与非泥岩层,砂岩地层与碳酸盐地层伽马测井值较低[45],由于缺乏岩心分析资料,不确定低伽马值是否为砂质地层,但是峡谷侵蚀面的存在往往伴随着侵蚀面上部河道滞留等粗粒沉积的发育[46],从地震合成地震记录来看(图 2b),W19井与W18井低伽马值层对应地震剖面中侵蚀面上部反射杂乱层位,侵蚀-沉积作用造成的岩性变化也可能是导致测井目标区低伽马值异常的原因。W18井和W19井的水合物可能储集在粉砂质-砂质含量较高的地层中,而SC-02井水合物层则形成在相对富泥地层中,而浅部岩性变粗的地层中缺少水合物发育,这也表明该区域形成水合物岩性并不是控制水合物富集的最关键因素[36]。
4.2 流体运移
大量研究表明白云凹陷内发育大量气烟囱构造,气烟囱构造与水合物成藏密切相关[12, 34],而且在空间上气烟囱与BSR相叠覆[7]。在W18、SC-02和W19井下部发育花冠状气烟囱构造,直径最大达到360 m(图 7a)。气烟囱顶部及侧向地层中均伴有亮点反射,表明局部地层圈闭了游离气。
从W18井及W19井的伽马测井和合成地震记录分析,两口测井中伽马值最低层位对应侵蚀面位置,侵蚀面附近出现亮点反射(图 4b-d),而且天然堤坡度较大,侵蚀面对流体侧向运移起到良好的疏导作用。流体沿侵蚀面的运移作用使稳定带下部的气体能够向构造高点汇聚运移,为构造高点上水合物成藏提供充足的气源条件(图 7a, b)。属性分析显示水道内部也局部发育水合物,这可能是下部气烟囱构造供给的气体通量较大,能够提供水道内水合物所需的气源,但是可能受垂向上气体运移的限制,水合物量和矿体规模不大。
从3口井来看,水合物主要分布在靠近稳定带底界的上部地层,由于水合物层形成造成地层渗透率降低,影响气体垂向运移,使稳定带内向浅部地层运移的气体通量大大降低,即使岩性较好的浅部地层由于缺少气源的供给而难以形成水合物。因此,气体运移可能是造成浅部地层缺少水合物发育的关键因素。
4.3 气源条件
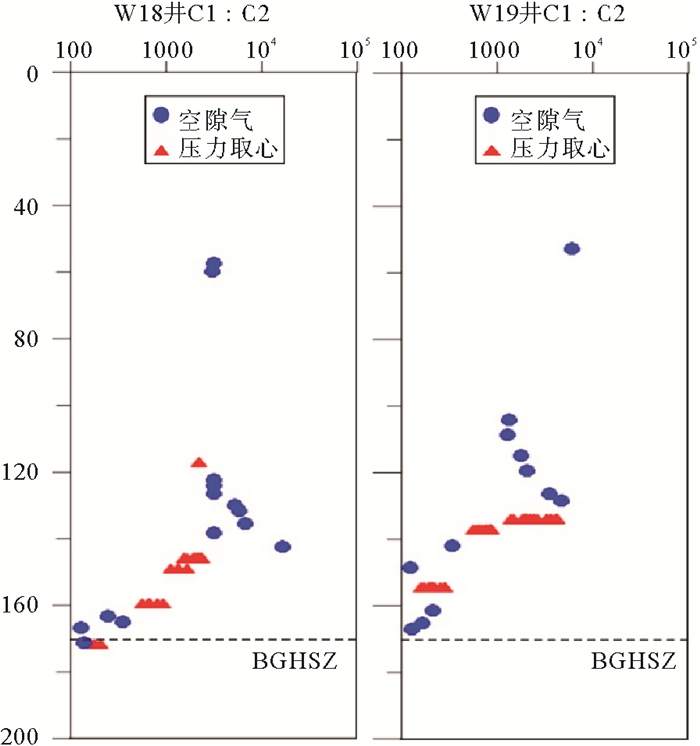
大量研究发现形成水合物的气源主要为生物成因气和热成因气[41, 47],在神狐钻探区发现了热成因水合物[8]。从W18井和W19井气体组成看(图 8),浅部缺少水合物的地层中,C1/C2比值大于1 000,说明烃类气体中甲烷含量高,是典型的生物成因气指标。而在电阻率和纵波速度出现异常地层C1/C2值大幅度降低,局部地层C1/C2比值接近100,表明热成因气对水合物的形成具有重要贡献。同样,地震资料分析显示研究区内3口钻井下部为同一个气烟囱构造,稳定带下部热成因气可能沿气烟囱运移到浅部地层,为水合物形成提供气源。
5. 结论
通过对神狐目标区W18、W19及SC-02井的随钻测井资料和三维地震数据多属性综合分析研究,发现不同站位水合物的平面展布形态不同,控制因素相似。三维地震资料显示该目标区水合物层主要分布在水道-天然堤处,在W19和SC-02井水合物在空间上呈马蹄状分布,而W18井呈斑状分布,均方根振幅属性、最大振幅属性、弧长属性以及倾角时间切片能够反映水合物空间分布,但是该目标区振幅类属性对水合物层的显示较为敏感。在垂向上,3口井水合物层位于稳定带底界上方地层中,局部水合物层位于水道-天然堤内,但是水道-天然堤内并没有都形成水合物,水合物主要分布在相对构造高点。水合物层下部发育了气烟囱构造和侵蚀面,稳定带下方出现大量亮点反射指示地层含有游离气,同时甲烷与乙烷比在水合物层呈明显降低趋势,表明深部热成因气为水合物的形成提供重要气体来源。
-
图 3 W18井、W19井和SC-02井纵波速度、伽马和电阻率测井曲线[36]
Figure 3. The well logs of sites W18, W19 and SC-02 showing the P-wave velocity, gamma ray, and resistivity
图 5 a:BGHSZ层位向上30 ms提取弧长属性;b:BGHSZ层位向上30 ms提取最大振幅属性;c:倾角体1 890 ms时间切片;d:RMS属性刻画的水合物分布范围
Figure 5. a:The maximum amplitude attribute map extracted for a time window 30 ms above the BGHSZ; b: The arc length attribute map extracted for a time window 30 ms above the BGHSZ; c: 1 890 ms time slide from dip cube; d: The RMS displays the distribution of gas hydrate
-
[1] Schmuck E A, Paull C K. Evidence for gas accumulation associated with diapirism and gas hydrates at the head of the Cape Fear Slide[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1993, 13(3): 145-152. doi: 10.1007/BF01593187
[2] Zhang Z G, Wang Y, Gao L F, et al. Marine gas hydrates: future energy or environmental killer?[J]. Energy Procedia, 2012, 16: 933-938. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2012.01.149
[3] Chong Z R, Yang S H B, Babu P, et al. Review of natural gas hydrates as an energy resource: prospects and challenges[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 1633-1652. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.061
[4] Zhao J F, Song Y C, Lim X L, et al. Opportunities and challenges of gas hydrate policies with consideration of environmental impacts[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 70: 875-885. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.269
[5] Zhang G X, Liang J Q, Lu J G, et al. Geological features, controlling factors and potential prospects of the gas hydrate occurrence in the east part of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 67: 356-367. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.05.021
[6] Buffett B, Archer D. Global inventory of methane clathrate: sensitivity to changes in the deep ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 227(3-4): 185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.09.005
[7] Chen D X, Wang X J, Volker D, et al. Three dimensional seismic studies of deep-water hazard-related features on the northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 1125-1139. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.012
[8] Yang S X, Zhang M, Liang J Q, et al. Preliminary results of china's third gas hydrate drilling expedition: a critical step from discovery to development in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, 2015, 15(2): 1-21. https://www.resilience.org/stories/2016-08-11/methane-hydrates-the-next-shale-gas/
[9] 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 陆敬安, 等.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏特征及主控因素新认识[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(2): 1-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201704001 YANG Shengxiong, LIANG Jinqiang, LU Jing'an, et al. New understandings on the characteristics and controlling factors of gas hydrate reservoirs in the shenhu area on the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(2): 1-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201704001
[10] 吴能友, 梁金强, 王宏斌, 等.海洋天然气水合物成藏系统研究进展[J].现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 356-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.003 WU Nengyou, LIANG Jinqiang, WANG Hongbin, et al. Marine gas hydrate system: state of the art[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 356-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.003
[11] 吴能友, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等.南海北部陆坡神狐海域天然气水合物成藏的流体运移体系[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.06.027 WU Nengyou, YANG Shengxiong, WANG Hongbin, et al. Gas-bearing fluid influx sub-system for gas hydrate geological system in Shenhu Area, Northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.06.027
[12] 乔少华, 苏明, 杨睿, 等.运聚体系-天然气水合物不均匀性分布的关键控制因素初[J].新能源进展, 2013, 1(3): 245-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2013.03.008 QIAO Shaohua, SU Ming, YANG Rui, et al. Migration and accumulation system: the key control factors of heterogeneous distribution of gas hydrate[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 2013, 1(3): 245-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2013.03.008
[13] Wang X J, Qiang J, Collett T S, et al. Characterization of gas hydrate distribution using conventional 3D seismic data in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea[J]. Interpretation, 2016, 4(1): SA25-SA37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fe89cb6824f1ebc15420e0ac14562181
[14] Hui G G, Li S Z, Guo L L, et al. Source and accumulation of gas hydrate in the northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 69: 127-145. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.10.009
[15] Horozal S, Kim G Y, Bahk J J, et al. Core and sediment physical property correlation of the second Ulleung Basin Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition (UBGH2) results in the East Sea (Japan sea)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 535-562. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.09.019
[16] Collett T S, Boswell R, Cochran J R, et al. Geologic implications of gas hydrates in the offshore of India: results of the national gas hydrate program expedition 01[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58: 3-28. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.021
[17] Boswell R, Collett T S, Frye M, et al. Subsurface gas hydrates in the northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 4-30. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.10.003
[18] Ruppel C, Boswell R, Jones E. Scientific results from gulf of mexico gas hydrates joint industry project leg 1 drilling: introduction and overview[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2008, 25(9): 819-829. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.02.007
[19] Kumar P, Collett T S, Boswell R, et al. Geologic implications of gas hydrates in the offshore of India: Krishna-Godavari Basin, Mahanadi Basin, Andaman Sea, Kerala-Konkan Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58: 29-98. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.031
[20] Bahk J J, Kim G Y, Chun J H, et al. Characterization of gas hydrate reservoirs by integration of core and log data in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.05.007
[21] Lee M W, Collett T S. Scale-dependent gas hydrate saturation estimates in sand reservoirs in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea of Korea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.09.004
[22] Collett T S, Lee M W, Zyrianova M V, et al. Gulf of Mexico gas hydrate joint industry project leg Ⅱ logging-while-drilling data acquisition and analysis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 41-61. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.08.003
[23] Lee M W, Collett T S. Pore-and fracture-filling gas hydrate reservoirs in the gulf of Mexico gas hydrate joint industry project leg Ⅱ green canyon 955 H well[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.08.002
[24] 杨睿, 吴能友, 雷新华, 等.波阻抗反演在南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物勘探中的应用[J].现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 495-500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.012 YANG Rui, WU Nengyou, LEI Xinhua, et al. Impedance inversion and its application in gas hydrate exploration in shenhu area, northern South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(3): 495-500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.012
[25] Kim K J, Yi B Y, Kang N K, et al. Seismic attribute analysis of the indicator for gas hydrate occurrence in the northwest Ulleung Basin, East Sea[J]. Energy Procedia, 2015, 76: 463-469. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2015.07.882
[26] Yoo D G, Kang N K, Yi B Y, et al. Occurrence and seismic characteristics of gas hydrate in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 236-247. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.07.001
[27] Ryu B J, Collett T S, Riedel M, et al. Scientific results of the second gas hydrate drilling expedition in the ulleung basin (UBGH2)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.07.007
[28] Fraser D R A, Gorman A R, Pecher I A, et al. Gas hydrate accumulations related to focused fluid flow in the Pegasus Basin, southern Hikurangi Margin, New Zealand[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.06.025
[29] Zhang Z J, McConnell D R, Han D H. Rock physics-based seismic trace analysis of unconsolidated sediments containing gas hydrate and free gas in Green Canyon 955, Northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.11.004
[30] Simonetti A, Knapp J H, Sleeper K, et al. Spatial distribution of gas hydrates from high-resolution seismic and core data, Woolsey Mound, Northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 44: 21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.04.004
[31] Lin C C, Lin A T, Liu C S, et al. Geological controls on BSR occurrences in the incipient arc-continent collision zone off southwest Taiwan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(7): 1118-1131. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.11.002
[32] Popescu I, De Batist M, Lericolais G, et al. Multiple bottom-simulating reflections in the Black Sea: potential proxies of past climate conditions[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 227(3-4): 163-176. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.12.006
[33] Wang X J, Lee M, Collett T, et al. Gas hydrate identified in sand-rich inferred sedimentary section using downhole logging and seismic data in Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 51: 298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.01.002
[34] Wang X J, Collett T S, Lee M W, et al. Geological controls on the occurrence of gas hydrate from core, downhole log, and seismic data in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357: 272-292. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.09.040
[35] 陆敬安, 杨胜雄, 吴能友, 等.南海神狐海域天然气水合物地球物理测井评价[J].现代地质, 2008, 22(3): 447-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.015 LU Jing'an, YANG Shengxiong, WU Nengyou, et al. Well logging evaluation of gas hydrates in Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 447-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.015
[36] Yang S X, Liang J Q, Lei Y, et al. GMGS4 gas hydrate drilling expedition in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice, 2017, 17(1): 7-11.
[37] 钟广法.巽他陆架晚新生代地震超覆层序与海平面变化研究[D].同济大学博士学位论文, 2002. ZHONG Guangfa. Late cenozoic seismic onlap-offlap sequences and sea level changes on the northern sunda shelf, South China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Tongji University, 2002.
[38] 葛黄敏, 李前裕, 钟广法, 等.南海北部第四纪高分辨率地震层序地层与古环境演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4): 49-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201204007 GE Huangmin, LI Qianyu, ZHONG Guangfa, et al. High resolution quaternary seismic sequence stratigraphy and paleoenvironmental evolution in the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 49-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201204007
[39] 张军华, 周振晓, 谭明友, 等.地震切片解释中的几个理论问题[J].石油地球物理勘探, 2007, 42(3): 348-352, 361. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2007.03.022 ZHANG Junhua, ZHOU Zhenxiao, TAN Mingyou, et al. Several theoretical issues about interpretation of seismic slices[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 42(3): 348-352, 361. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2007.03.022
[40] Chopra S. Interpreting fractures through 3D seismic discontinuity attributes and their visualization[C]//8th Biennial International Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, 2009: 1-13.
[41] Collett T S, Johnson A H, Knapp C C, et al. Natural Gas Hydrates: A Review[M]. Tulsa: AAPG, 2009: 146-219.
[42] Sun Q L, Wu S G, Cartwright J, et al. Shallow gas and focused fluid flow systems in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 315-318(4): 1-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6ab647482948e848eb254ec0452515a4
[43] 张辉, 卢海龙, 梁金强, 等.南海北部神狐海域沉积物颗粒对天然气水合物聚集的主要影响[J].科学通报, 2016, 61(3): 388-397. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201603014 ZHANG Hui, LU Hailong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. The methane hydrate accumulation controlled compellingly by sediment grain at Shenhu, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(3): 388-397. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201603014
[44] 陈芳, 周洋, 苏新, 等.南海神狐海域含水合物层粒度变化及与水合物饱和度的关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105014 CHEN Fang, ZHOU Yang, SU Xin, et al. Gas hydrate saturation and its relation with grain size of the hydrate-bearing sediments in the Shenhu area of Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105014
[45] Hunt J K. Identifying and quantifying erosion beneath the deposits of long-runout turbidity currents along their pathway[J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 389(1): 32-51. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1d08d4cd770a484195b89882e903bb73
[46] Schnyder J, Ruffel A, Deconinck J F, et al. Conjunctive use of spectral gamma-ray logs and clay mineralogy in defining late jurassic-early Cretaceous palaeoclimate change (Dorset, U.K.)[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 229(4): 303-320. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.027
[47] 沙志彬, 郭依群, 杨木壮, 等.南海北部陆坡区沉积与天然气水合物成藏关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5): 89-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200905012 SHA Zhibin, GUO Yiqun, YANG Muzhuang, et al. Relation between sedimentation and gas hydrate reservoirs in the northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5): 89-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200905012
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 彭文睿,邢磊,李倩倩,王旭. CO_2海底咸水层封存波及范围地震监测方法研究:以Sleipner CCS项目为例. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2025(01): 210-224 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张旭东,曾凡祥. 南海北部琼东南海域天然气水合物地球物理特征及运聚成藏模式. 地质学报. 2024(09): 2619-2629 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 谢莹峰,任金锋,邓炜,陆敬安,匡增桂,康冬菊,曲长伟. 琼东南盆地渗漏型天然气水合物识别与差异成藏特征. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2024(06): 1-11 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. Jiapeng JIN,Xiujuan WANG,Zhenyu ZHU,Pibo SU,Lixia LI,Qingping LI,Yiqun GUO,Jin QIAN,Zhendong LUAN,Jilin ZHOU. Physical characteristics of high concentrated gas hydrate reservoir in the Shenhu production test area, South China Sea. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology. 2023(02): 694-709 .  必应学术
必应学术
5. 徐海良,蒋昌健,杨放琼,孙思聪. 基于分形理论的水合物回波特征提取及分类识别. 中南大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(03): 899-908 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 雷亚妮,吴时国,孙金,王广建. 海洋天然气水合物综合地球物理识别方法评述. 中南大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(03): 864-878 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. Shu-yu Wu,Jun Liu,Hua-ning Xu,Chang-ling Liu,Fu-long Ning,Hong-xian Chu,Hao-ran Wu,Kai Wang. Application of frequency division inversion in the prediction of heterogeneous natural gas hydrates reservoirs in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. China Geology. 2022(02): 251-266 .  必应学术
必应学术
8. 王辉,修宗祥,孙永福,刘绍文,宋玉鹏,董立峰,宋丙辉. 考虑天然气水合物上覆层不排水抗剪强度深度变化的海底斜坡稳定性影响分析. 高校地质学报. 2022(05): 747-757 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李彦龙,陈强,刘昌岭,吴能友,孙建业,申志聪,张民生,胡高伟. 水合物储层工程地质参数评价系统研发与功能验证. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2020(05): 192-200 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 吴淑玉,徐华宁,刘俊,杨睿,宁伏龙. 南海神狐海域非均质性天然气水合物储层的分频反演. 海洋地质与第四纪地质. 2020(06): 106-120 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 李杰,何敏,颜承志,李元平,张俊斌,钱进,靳佳澎,李方. 南海北部荔湾3区块天然气水合物分布特征及目标识别. 海洋科学. 2019(05): 81-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. Yan-long Li,Yi-zhao Wan,Qiang Chen,Jia-xin Sun,Neng-you Wu,Gao-wei Hu,Fu-long Ning,Pei-xiao Mao. Large borehole with multi-lateral branches: A novel solution for exploitation of clayey silt hydrate. China Geology. 2019(03): 333-341 .  必应学术
必应学术
13. 鲍祥生,周海燕,李丽霞,马飞英,陈振亚. 海域天然气水合物分布地震预测技术研究现状及展望. 广东石油化工学院学报. 2018(04): 5-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 吴景鑫,郭秀军,孙翔,李宁. 神狐海域天然气水合物层分解井中电学监测效果模拟与分析. 海洋与湖沼. 2018(06): 1211-1219 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: