GAS SOURCE ANALYSIS FOR GAS HYDRATE IN MULI PERMAFROST AREA OF THE SOUTHERN QILIAN BASIN
-
摘要: 南祁连盆地木里冻土区天然气水合物的气体成因或来源存在不同观点,目前还没有统一认识,这直接影响到水合物的资源评价及下一步勘探方向。文章依托前人研究成果及新近钻探木参1井、木参2井及SK-0井资料,对比分析中侏罗统与上三叠统尕勒得寺组两套烃源岩,结合天然气水合物气体组成与碳氢同位素特征进行综合研究,结果表明:南祁连盆地木里冻土区天然气水合物的气体以轻烃为主,具湿气特征,其同位素表现为正碳同位素系列,为有机成因,成气母质主要为腐泥型干酪根的油型气,是热演化程度较低的原油伴生气;少量与微生物成因气有关,与煤层气关系不大。中侏罗统有机质丰度高、类型较好,镜质体反射率Ro在0.48%~1.14%之间,处于生油高峰期,生油过程中原油伴生气为天然气水合物的主要气体来源;上三叠统尕勒得寺组有机质丰度较高、类型较好,但成熟度高,处于生凝析气或裂解气阶段,总体生排烃能力差,从气源对比分析来看对天然气水合物气体来源贡献不大。Abstract: There are hot debates on the gas source of gas hydrate in the Muli permafrost area of the Southern Qilian Basin. The understanding of gas source directly affects the gas hydrate resource evaluation and exploration. Based on the previous research results and the newly acquired data from the Wells of Mucan 1, Mucan 2 and SK-0, the authors have made a comparison of the source rocks in the Middle Jurassic and Upper Triassic Galedesi Formation. Comprehensive studies on gas compositions as well as carbon and hydrogen isotopic characteristics were also performed. The results show that the gases in the Muli permafrost area of southern Qilian Basin is mainly composed of light hydrocarbon and characterized by wet gases. The isotopic composition of the gas hydrate, which is characterized by positive carbon isotopic series, indicates that the gas is formed by pyrolysis of organic matter and the parent gas is a kind of sapropelic kerogen oil-based gas with low thermal evolution. It is mainly oil associated gas with a small amount of microbial gas and coal-bed methane. The organic matter in the Middle Jurassic is of high abundance and good type, of which the vitrinite reflectivity Ro is between 0.48% and 1.14%, indicating that it is in the peak period of oil generation. The oil associated gas is the main source of the gas hydrate. The organic matter is also abundant and of good type in the Galedesi Formation of Upper Triassic, but the maturity is too high. It remains in the stages of condensate gas or pyrolytic gas, and the total hydrocarbon generation and discharge are poor. As a source of hydrate gas, its contribution is little.
-
天然气水合物是由气体分子(烃类气体如CH4、C2H6、C3H8等和非烃气体如CO2、H2S等)与水分子在一定温度压力下形成的笼型化合物,由于其外形呈冰状,又称“可燃冰”,广泛分布于大陆边缘海水深300 m以下的海底沉积物及陆地的永久冻土区[1, 2]。迄今已在全球发现天然气水合物产地132处,其中海底及湖底沉积物123处,陆地冻土区9处[3, 4]。一般认为全球天然气水合物中所含的天然气资源量远远超过全球已探明的天然气储量[5]。天然气水合物因其能量密度高、分布广、规模大、埋藏浅,已被视为21世纪的一种潜在能源[6, 7]。
青海省祁连山地区多年冻土面积达10×104 km2,年平均气温低于-2 ℃,冻土层厚度为50~139 m[8],冻土区内不仅有丰富的气源条件,而且具备形成天然气水合物的温压条件[9]。2008年以来,中国地质调查局在南祁连盆地木里冻土区共完成天然气水合物科学钻探试验井15口(DK1、DK2、DK3、DK4、DK5、DK6、DK7、DK8、DK9、DK10、DK11、DK12、SK-0、SK-1、SK-2),其中钻到水合物样品的钻井为DK1、DK2、DK3、DK7、DK8、DK9、DK12、SK-0、SK-1、SK-2,分布较为集中,相距较远的DK5、DK6、DK10、DK11等井并未钻遇水合物,只观察到与水合物相关的异常现象。2013—2014年神华集团青海能源发展有限责任公司投资项目在调查工作区施工钻探14口井,仅有DK13-11、DK12-13、DK11-14和DK8-19井钻获天然气水合物实物样品。这一方面说明天然气水合物分布较为复杂,另一方面说明天然气水合物的成藏控制因素等基础性认识远远不够。目前,对天然气水合物的气体成因或来源存在不同观点,自2008年在调查区发现天然气水合物以来,随着勘查工作的不断深入,不同学者对其气源提出不同认识,可归纳为以下3种主要认识:(1)认为水合物气源属于煤成气,且气源主要来自于木里煤田中侏罗统江仓、木里组的煤层及其附近的碳质泥岩[10, 11];(2)认为天然气水合物属于混合型气源,即煤成气和油型气都有,煤成气来自于侏罗系的煤层,油型气可能来自于下伏上三叠统尕勒得寺组、中二叠统草地沟组、石炭系暗色泥岩[12-15];(3)除少量浅层岩心烃类气体可能含有少量生物成因气外,天然气水合物样品的气源组成均以热解成因气为主,为典型的有机成因烃类气体[16, 17]。
依托研究区已有钻探成果及新近钻探木参1井、木参2井及试采SK-0井,对可能烃源岩(中侏罗统和三叠系尕勒得寺组)进行系统取样,并进行有机显微组分观察、镜质体发射率测定、总有机碳含量测定、生油岩热解分析、有机质碳氢同位素分析、氯仿抽提、族组分分析及色谱-质谱分析。另外通过收集气测录井资料和天然气水合物样品分解测试资料,尝试从天然气水合物的气体地球化学及同位素地球化学特征入手,分析天然气水合物的气体成因或来源,探讨祁连山冻土区天然气水合物的气体与煤层气、微生物成因气、热成因气等之间的可能关系,明确天然气水合物气源。研究认为木里冻土区天然气水合物来源为淡水环境中形成的有机热解成因气,且为热演化程度较低的原油伴生气,中侏罗统烃源岩成熟度中等,为生油高峰期,伴生大量原油伴生气,为天然气水合物主力生烃层系;上三叠统烃源岩有机质成熟度高,生排烃能力差,对天然气水合物成藏贡献不大,南祁连盆地天然气水合物勘查应着重考虑侏罗系地层的分布情况。
1. 基本地质特征
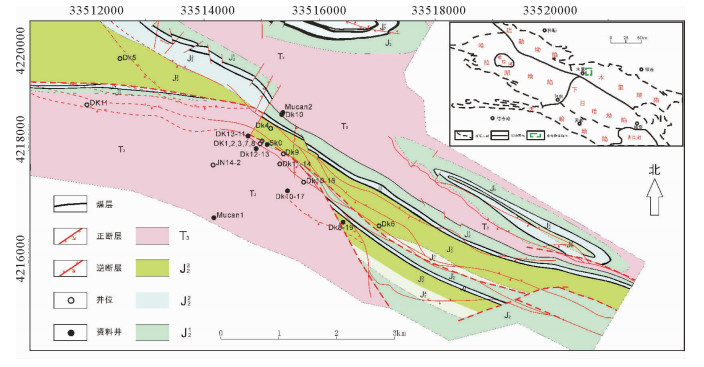
南祁连盆地地处青藏高原东北缘,北侧与广泛发育前寒武系的中祁连山体相邻,南部以宗务隆山与柴达木盆地相邻。自震旦纪以来,祁连山先后经历了大陆裂谷阶段(震旦—中寒武世)、洋底扩张及沟弧盆体系阶段(晚寒武—中奥陶世)、造山阶段(中奥陶世之后经历了俯冲造山、碰撞造山和陆内造山作用)等演化阶段,形成了现今的地质构造格局。盆地被分割为多个近北西向展布的坳陷,从西向东依次为哈拉湖坳陷、疏勒坳陷、下日哈坳陷和木里坳陷(图 1)。
木里冻土区位于木里坳陷内,地理位置处于青海省北部高寒地区,青海湖以北、祁连山南麓的狭长区域内,海拔4 100~4 300 m,年平均气温-5.1 ℃。坳陷内多年冻土层广泛发育,呈岛状分布,平均厚度约80 m,部分地区冻土层厚度大于100 m[18]。木里坳陷自下而上主要发育4套烃源岩:石炭系暗色泥(灰)岩、下二叠统草地沟组暗色灰岩、上三叠统尕勒得寺组暗色泥岩、侏罗系暗色泥页岩。研究区出露的地层除第四系外,主要包括中侏罗统江仓组和木里组[19, 20],以及部分上三叠统地层,并普遍缺失上白垩统和古近系。该区中侏罗统为含煤地层,是在温暖湿润、还原环境中沉积的一套山间河湖沼泽相含煤碎屑岩建造,而其中深灰、灰黑色泥岩、油页岩为半深湖、深湖相建造,侏罗系含煤岩系是木里煤田主要的勘探开采层系。
2. 烃源岩有机地球化学特征
本次在南祁连盆地木里冻土区共采集到3口井的烃源岩岩心样品,分别为木参1井、木参2井和SK-0井(图 1)。岩心样品均来自中侏罗统江仓组、木里组和上三叠统尕勒得寺组。木参1井采集岩心样品16件,岩屑样品27件;木参2井岩心样品12件,岩屑样品29件;SK-0井岩心样品22件。共进行化验分析511样次,主要针对总有机碳含量(TOC)、生油岩热解(RockEval)、氯仿沥青“A”、族组分、干酪根有机显微组分及镜质组反射率等项目进行了分析。其中,总有机碳含量测试依据GB/T19145-2003标准,检测仪器为美国力克公司CS-230碳硫测定仪,测试条件为常温常压;热解测试依据GB/T18602-2012标准,检测仪器为OGE-Ⅱ岩石热解仪,测试条件为温度20 ℃,湿度40%;干酪根分离鉴定依据GB/T19144-2010标准,使用仪器为LXJ-Ⅱ离心沉淀机、烘箱,测试条件为常温常压;干酪根类型鉴定依据SY/T5125-1996标准,使用仪器为LEICA DM-4500P研究型显微镜,测试条件为温度25 ℃,湿度65%;镜质体反射率的测定依据SY/T5154-2012标准,使用仪器为DMLP with MSP200镜质体反射率测定仪,测试条件为温度23 ℃,湿度50%;干酪根元素分析依据SY/T 5122-1986标准,使用仪器为美国CE-440有机元素分析仪,精度满足0.1%要求;干酪根碳同位素鉴定依据GB/T18340.2-2010标准,使用仪器为DELTA V ADV同位素质谱仪,系统稳定性小于10 ×10-6;氯仿沥青“A”测定依据SY/T5118-2005标准,使用仪器为YS全自动多功能抽提仪。
2.1 有机质丰度
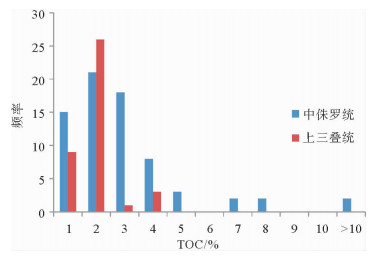
化验分析结果显示,研究区中侏罗统TOC含量较高,几乎所有样品都大于0.4%,大于1%的样品占总数78.9%,大于2%的样品占总数的49.7%,为好和很好烃源岩。上三叠统所有样品TOC都大于0.4%,主要分布在1%~2%之间,占样品总数的66.7%,仅4个样品大于2%,大部分为好烃源岩。从总有机碳含量看,中侏罗统烃源岩明显优于上三叠统烃源岩。
中侏罗统氯仿沥青“A”含量所有样品都大于0.01%,其中氯仿沥青“A”大于0.1%占样品总数的72.2%,为非常好的烃源岩。上三叠统所有样品氯仿沥青“A”分析结果均小于0.05%,其中小于0.01%的非烃源岩样品占总数的41.2%,位于0.01%~0.05%之间的差烃源岩样品占样品总数的58.8%,大部分为差烃源岩或非烃源岩。氯仿沥青“A”分析结果显示,中侏罗统为好的烃源岩,而上三叠统尕勒得寺组烃源岩为差烃源岩或非烃源岩(图 2)。
2.2 有机质类型
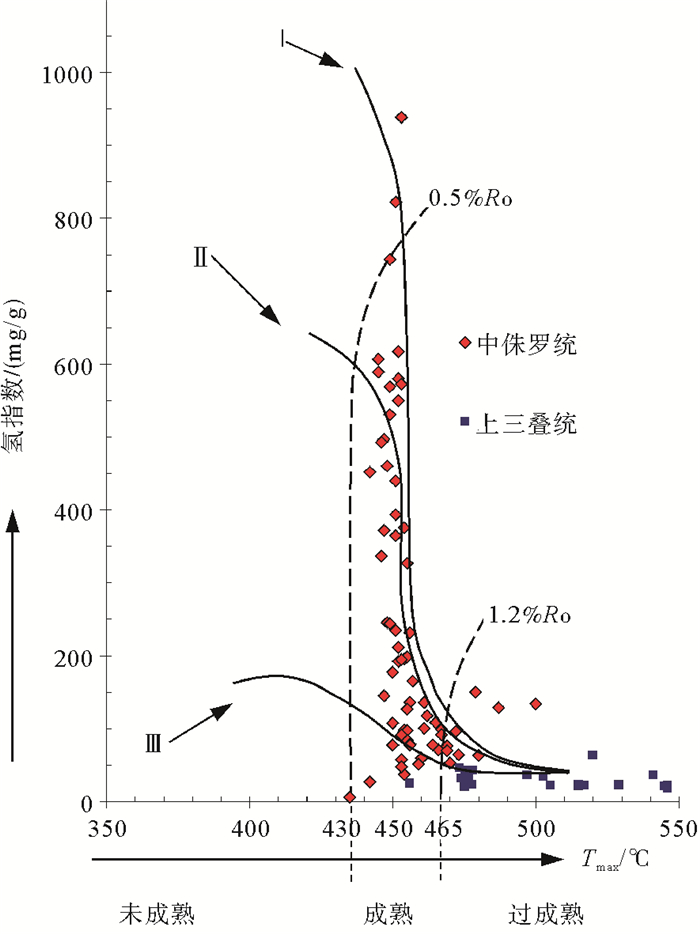
岩石热解氢指数(Ih)与最高热解峰温(Tmax ℃)投点成图分析(图 3),可以看出在中侏罗统有机质类型既有Ⅰ型,也有Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型[21-23],且以Ⅱ型(Ⅱ1型和Ⅱ2型)为主,其中Ⅱ1型比Ⅱ2型略占优势,Ⅲ型次之,Ⅰ型也有一定数量的分布。而上三叠统有机质类型以Ⅲ型最多,其次为Ⅱ1型,Ⅱ2型最少,基本没有Ⅰ型有机质类型。
2.3 有机质热演化程度
烃源岩有机质成熟度是烃类形成的关键因素,判别指标有干酪根的镜质体反射率Ro、岩石热解峰温度(Tmax)、热变指数(TAI)、干酪根红外光谱、孢粉颜色指数(SCI)、奇偶优势指数(OEP)、可溶有机质的演化以及生物标志化合物等[24, 25]。本文重点对镜质体反射率进行讨论,其测定结果显示:中侏罗统烃源岩Ro值介于0.48%~1.14%之间,上三叠统烃源岩Ro值介于1.12%~1.77%之间。依据中国石油天然气总公司1995年发布的行业标准,将有机质热演化程度分为5个阶段,即未成熟阶段、低成熟阶段、成熟阶段、高成熟阶段、过成熟阶段,分别对应镜质体反射率(Ro) < 0.5%,0.5%~0.7%,0.7%~1.2%,1.2%~2.0%,>2.0%。中侏罗统烃源岩正处于有机质成熟阶段,为生油高峰期和生湿气阶段,在原油生成的过程中,产生大量的原油伴生气。上三叠统处于有机质高成熟阶段,以生凝析气和油型裂解气为主。
2.4 烃源岩生烃潜能评价
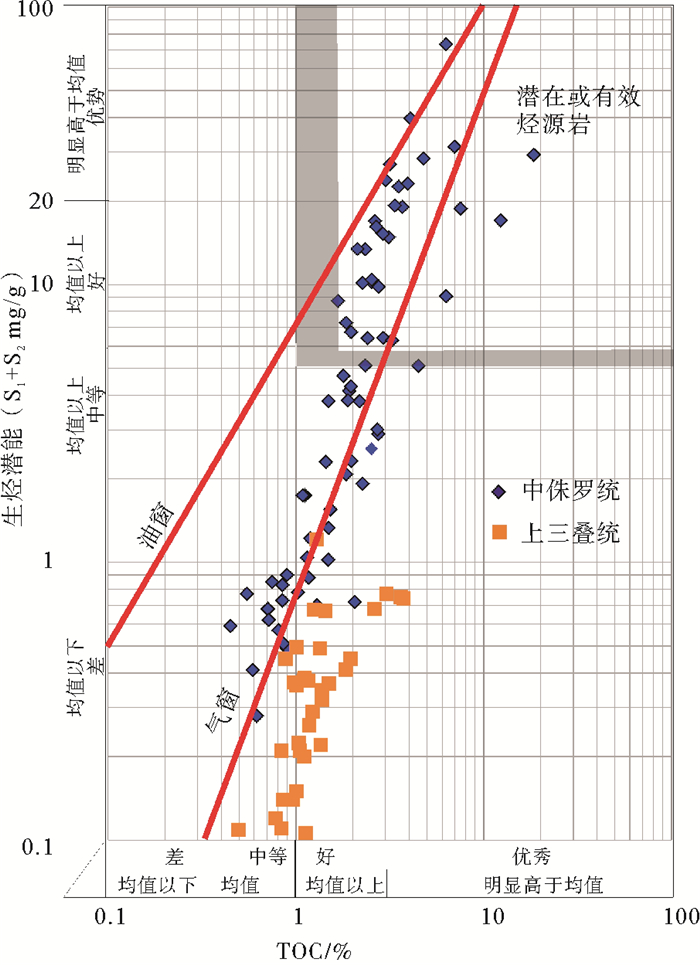
生烃潜量(S1+S2)是衡量烃源岩生油生气能力的重要指标,可以更加直接和客观地体现烃源岩的生烃能力。生烃潜量用来表示单位质量烃源岩的产油潜能,其中,S1表示岩石中游离烃的热蒸发量,S2表示有机质的热解烃量。以生烃潜量值2、6、20 mg/g为评价分界点,将泥岩和油页岩分为差、中等、好、最好4个级别。生烃潜量与总有机碳含量(TOC)的交会图显示(图 4),中侏罗统烃源岩大部分样品总有机碳(TOC)含量多大于1%,生烃潜量大于2 mg/g,71个样品生烃潜量均值为8.8 mg/g,属于中等到最好样品级别,为潜在或有效的烃源岩。而上三叠统烃源岩总有机碳含量(TOC)多处于1%~3%之间,总体有机碳含量较高,但生烃潜量多低于1 mg/g,本次分析39个样品测试结果其均值仅为0.35 mg/g,属于非烃源岩到差烃源岩的范围。
综上文所述,研究区中侏罗统烃源岩有机质丰度较高,TOC含量大于1%样品占78.9%;氯仿沥青“A”大于0.1%占样品总数的72.2%;有机质类型以Ⅱ2型为主;镜质体反射率Ro多介于0.7%~1.2%之间;氢指数HI均值256 mg/g;生烃潜量(S1+S2)均值8.8 mg/g,总体处于生烃高峰期的生油阶段或凝析油阶段,属于好、很好烃源岩。上三叠统尕勒得寺组亦为煤系地层烃源岩,TOC含量大于1%样品占76.9%,氯仿沥青“A”小于0.05%,有机质类型以Ⅲ型为主;镜质体反射率Ro介于1.1%~2.4%之间;总体处于生湿气或干气阶段,但由于构造抬升影响其氢指数HI均值仅21.5 mg/g;生烃潜量(S1+S2)均值仅0.35 mg/g,整体生、排烃能力较差,为较差烃源岩。
3. 天然气水合物地球化学特征
3.1 气体组分特征
通过收集气测录井资料和天然气水合物样品分解测试资料[15-17],对研究区气体组成特征进行系统对比分析,探讨天然气水合物的气体来源。
本区气测录井采用Agilent7890A色谱仪进行百分浓度含量的连续分析,该色谱最小检测浓度为4×10-6检测范围是C1~nC5,重复性误差小于1%。天然气水合物样品气体分析测试方法为:气体成分(C1~C6+、CO2)采用氢火焰离子化检测器(FID)和热导检测器(TCD)并联气相色谱法(GC-FID/TCD)测定,方法检出限为0.000 3~0.046 0 mol/mol。收集煤层段气测显示样品21个(DK9、DK11、DK12、木参1井)(图 1),DK10井浅层气显示样品4个,木参1井泥页岩气测异常段显示样品6个,DK9油气层段气测显示样品2个,DK9、DK12井水合物层段气测显示样品9个。实验室分析水合物显示样品26个。将所有测试数据剔除掉氧气、氮气组分后,气体组分按含量100%归一化来进行换算,统计了甲烷、乙烷和丙烷的含量及气体成分比即C1/(C2+C3)(也称干燥系数)(表 1)。
井名 样品 深度
/m甲烷
/%乙烷
/%丙烷
/%C1/
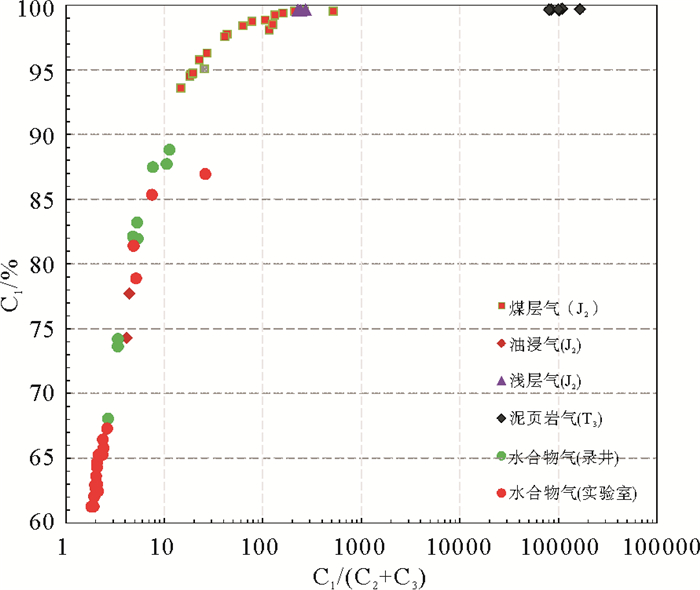
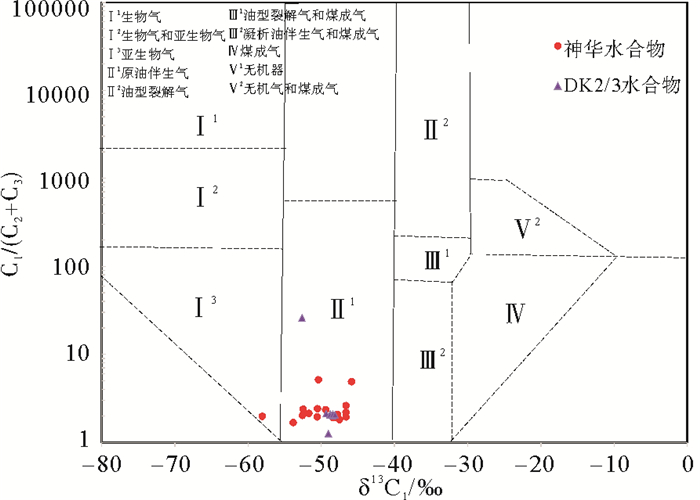
(C2+C3)DK9 煤层气(J2m) 56 99.4 0.6 0.0 160.4 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 63 99.2 0.7 0.0 132.0 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 81 98.7 1.3 0.0 77.7 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 112 99.6 0.4 0.0 243.6 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 118 99.5 0.5 0.0 209.7 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 586 98.4 1.5 0.1 62.9 DK12 煤层气(J2m) 216 98.1 0.7 0.1 116.1 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 149 94.7 4.6 0.5 18.4 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 207 97.8 2.1 0.2 43.6 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 237 96.3 3.4 0.1 27.1 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 281 95.8 4.1 0.2 22.6 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 406 97.6 2.3 0.1 40.9 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 234 93.6 6.3 0.0 14.7 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 331 94.5 5.1 0.1 18.2 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 335 94.7 4.8 0.1 19.2 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 338 94.7 4.8 0.1 19.5 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 357 95.1 3.6 0.2 25.5 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 427 98.9 0.6 0.3 105.7 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 434 99.5 0.3 0.1 263.1 DK12 煤层气(J2m) 587 98.5 0.7 0.1 125.4 DK12 煤层气(J2m) 174 99.5 0.1 0.0 518.5 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 50 99.6 0.4 0.0 224.1 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 51 99.6 0.4 0.0 242.6 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 52 99.6 0.4 0.0 230.5 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 53 99.6 0.4 0.0 271.8 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 678 99.7 0.0 0.0 108 522.6 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 694 99.7 0.0 0.0 84 346.3 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 740 99.7 0.0 0.0 165 218.9 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 769 99.6 0.0 0.0 101 410.4 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 795 99.6 0.0 0.0 80 339.4 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 825 99.7 0.0 0.0 99 519.5 DK9 油浸气(J2m) 364 77.7 6.1 11.5 4.4 DK9 油浸气(J3m) 366 74.3 7.1 10.8 4.1 DK9 水合物气(录井) 188 87.5 4.1 7.3 7.7 DK9 水合物气(录井) 192 82.1 10.8 6.3 4.8 DK9 水合物气(录井) 197 83.2 8.2 7.4 5.3 DK9 水合物气(录井) 259 73.6 9.0 12.8 3.4 DK9 水合物气(录井) 271 74.2 8.9 13.0 3.4 DK9 水合物气(录井) 300 81.9 8.5 6.8 5.4 DK12 水合物气(录井) 339 68.1 12.5 12.8 2.7 DK12 水合物气(录井) 558 88.8 4.5 3.3 11.3 DK12 水合物气(录井) 560 87.7 4.8 3.5 10.6 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 116.0 62.9 8.0 23.7 2.0 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 120.0 57.3 13.9 20.1 1.7 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 126.1 64.7 8.8 22.5 2.1 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 129.2 78.9 7.7 7.6 5.2 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 143.9 63.6 10.0 21.2 2.0 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 182.0 65.3 9.2 21.4 2.1 DK10-17 水合物(实验室) 487.3 62.0 14.9 16.9 2.0 DK11-14 水合物(实验室) 293.4 35.8 3.8 12.5 2.2 DK11-14 水合物(实验室) 322.2 61.3 6.8 25.2 1.9 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 202.8 65.8 6.3 2.4 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 203.3 85.3 3.9 7.5 7.5 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 204.8 65.3 5.7 22.0 2.4 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 262.9 62.1 9.4 22.4 2.0 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 295.6 81.4 6.2 10.4 4.9 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 302.5 61.3 8.4 25.3 1.8 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 312.6 64.3 9.8 21.2 2.1 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 316.9 67.3 9.9 15.7 2.6 DK13-11 水合物(实验室) 267.2 66.4 6.5 21.3 2.4 DK2 水合物(实验室) 149.0 34.9 6.6 21.2 1.3 DK2 水合物(实验室) 253.0 62.6 8.6 22.4 2.0 DK2 水合物(实验室) 266.8 62.5 8.7 20.7 2.1 DK2 水合物(实验室) 336.0 63.0 9.2 21.0 2.1 DK2 水合物(实验室) 363.0 59.0 8.9 19.8 2.1 DK2 水合物(实验室) 372.6 62.5 8.9 21.2 2.1 DK3 水合物(实验室) 142.0 52.2 8.7 16.6 2.1 DK3 水合物(实验室) 395.0 87.0 2.9 0.5 26.0 一般认为甲烷含量在90%以上的叫干气,而乙烷、丙烷等烷烃的含量或其含量之和在10%以上的叫湿气。研究区中侏罗统煤层段甲烷气体含量均大于93%,最大值为99.6%,均值为97.3%,基本为干气(表 1);DK10井中侏罗统浅层气甲烷含量为99.6%,为干气;木参1井较好气测显示的三叠系尕勒得寺组烃源岩段甲烷含量为99.6%~99.7%,亦为干气。天然气水合物甲烷含量最大值为88.8%,最小值为34.9%,平均为68.0%,乙烷、丙烷含量之和大于10%,呈现出明显的湿气特征,与DK9井油浸气甲烷组分均值76.0%较为接近。
从35个样品测试数据来看,水合物岩心气体干燥系数多小于10,其均值仅4.1,与DK9井中侏罗统油浸气干燥系数均值4.3较为接近,显示湿气特征。而中侏罗统煤层气干燥系数多大于15,均值为107.9;DK10井浅层气干燥系数均值242.3;木参1井三叠系尕勒得寺组泥页岩气干燥系数均值为106 559.5,均呈现明显干气特征。从干燥系数和甲烷百分含量的交汇图上看(图 5),天然气水合物气测录井和实验室测定结果相关性较好,与DK9井油浸气处于同一区域内,其甲烷含量多小于90%。与煤层气、DK10井浅层气和木参1井三叠系泥页岩气明显处于不同区域。
从气体组分特征来看,木里冻土区天然气水合物气体与煤层气、三叠系尕勒得寺组油页岩气差别大,应属不同的气体来源,而与DK9井油浸气气体组分类似,具有较好的对比关系,可能为统一的气体来源。
3.2 气体碳氢同位素特征
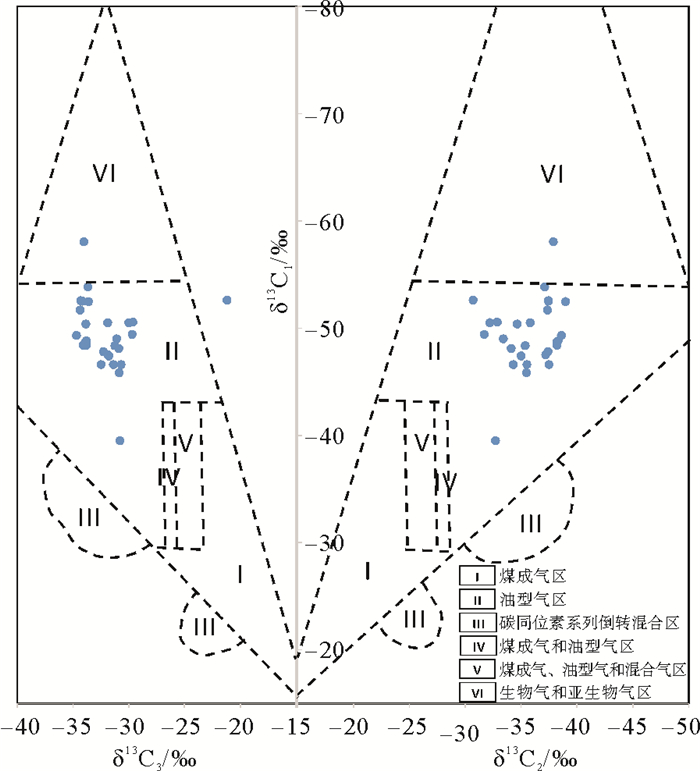
烷烃气体碳同位素组成分析(表 2):研究区天然气水合物气体甲烷碳同位素(δ13C1)值在-58.04‰~-39.5‰之间变化,平均为-49.35‰;乙烷碳同位素(δ13C2)值在-38.97‰~-30.7‰之间变化,平均为-35.84‰;丙烷碳同位素(δ13C3)值在-34.7‰~-21.2‰之间变化,平均为-32.01‰。所有样品都表现出δ13C1 < δ13C2 < δ13C3的特征,属正碳同位素系列,是典型的有机成因烃类气体[16, 17],气体成因相对简单,没有明显受到次生改造作用的影响。
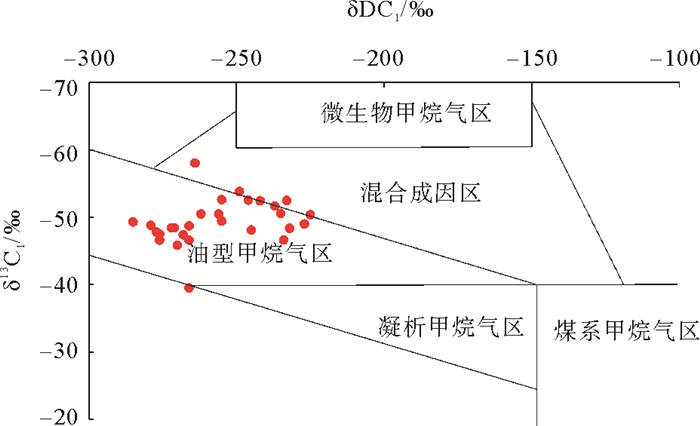
井名 井深/m δ13/‰(VPDB) δD/‰(VSMOW) δ13C1/‰ δ13C2/‰ δ13C3/‰ CO2/‰ C1/‰ C2/‰ C3/‰ DK1 134 -50.5 -35.8 -31.9 -18 -262 -240 DK1 143 -39.5 -32.7 -30.8 -18 -266 DK1 143 -47.4 -35 -31.8 -17 -268 -254 DK2 149 -49 -33.4 -31.1 2.3 -227 -236 -198 DK2 253 -48.4 -38.2 -33.8 -24.9 -272 -265 -240 DK2 266.8 -49.3 -38.6 -34.7 -14.8 -285 -276 -247 DK2 336 -48.7 -38.2 -33.9 -27.9 -266 -276 -243 DK2 363 -48.8 -38.3 -33.8 -19.3 -279 -271 -244 DK2 372.6 -48.4 -38.2 -34.1 -18.6 -271 -271 -228 DK3 142 -48.1 -34.1 -30.9 -9.2 -245 -249 -200 DK3 395 -52.6 -30.7 -21.2 16.7 -255 nd nd DK8-19 116 -58.04 -37.88 -34.04 -17.7 -264 -274 -246 DK8-19 120 -53.82 -37.1 -33.67 -20.34 -249 -271 -246 DK8-19 126.1 -52.49 -37.43 -34.15 -20.45 -233 -276 -247 DK8-19 129.2 -50.38 -34.64 -33.86 -25.52 -225 -266 -248 DK8-19 143.9 -52.54 -37.42 -34.32 -18.9 -246 -276 -253 DK8-19 182 -51.67 -37.34 -34.38 -24.38 -237 -274 -252 DK10-17 487.3 -50.54 -32.85 -29.64 -17.28 -235 -228 -179 DK11-14 293.4 -46.6 -34.3 -30.7 -10.2 -234 -274 -228 DK11-14 322.2 -48.35 -35.35 -31.26 -13.05 -232 -267 -215 DK12-13 202.8 -50.5 -32.2 -30 -12.3 -256 -246 -219 DK12-13 204.8 -49.4 -31.7 -29.7 -13.9 -255 -237 -236 DK12-13 262.9 -46.6 -35.5 -31.4 -11 -266 -267 -229 DK12-13 295.6 -45.84 -35.47 -30.87 -15.63 -270 -271 -231 DK12-13 302.5 -47.5 -37.2 -31.9 -13.9 -276 -285 -237 DK12-13 312.6 -47.8 -37.4 -32.3 -12.7 -277 -284 -246 DK12-13 316.9 -46.6 -37.5 -32.5 -9.4 -276 -284 -247 DK13-11 267.2 -52.46 -38.97 -33.63 -12.42 -242 -262 -210 烷烃气体氢同位素组成分析:研究区天然气水合物气体甲烷氢同位素(δDC1/‰VSMOW)值在-225‰~-285‰之间变化,平均为-256‰:乙烷氢同位素(δDC2/‰VSMOW)值在-228‰~-285‰之间变化,平均为-264‰;丙烷氢同位素(δDC3/‰VSMOW)值在-179‰~-253‰,平均为-232‰。Shen和Xu对中国陆上主要沉积盆地天然气氢同位素组成特征研究[26],认为来自海相源岩(或咸水湖泊相)生成的天然气,其δDC1值大于-190‰,而陆相淡水环境生成的天然气δDC1值通常小于-190‰。研究区天然气水合物气体样品的δDC1值远小于-190‰,表明水合物气体主要来源于淡水环境下形成的烃源岩。
4. 天然气水合物成因及来源
4.1 油型气的鉴别
油型气是指成气母质主要为腐泥型干酪根(Ⅰ、Ⅱ1型有机质)进入成熟阶段后在热力作用下形成的天然气。而煤成气则是指成气母质以Ⅱ2和Ⅲ型有机质为主,在煤化作用过程中形成的气态烃,包括热解气和高温裂解气[27]。
前人提出了多种鉴别油型气和煤成气的指标,考虑到前人发表的数据以烷烃气碳同位素组成为主,因此本研究也选用碳同位素组成进行鉴别比较。乙烷碳同位素组成具有较强的原始母质继承性,其受烃源岩热演化程度的影响远小于甲烷碳同位素组成,因此,乙烷碳同位素组成是区别煤层气和油型气最常用的有效指标[28]。
刚文哲等[29]研究认为,δ13C2值对天然气的母质类型反应比较灵敏,腐殖型天然气δ13C2值大于-29‰,腐泥型天然气δ13C2值小于-29‰;戴金星等[30]综合研究了中国天然气特征后指出,油型气的δ13C2值小于-29‰,而煤成气的δ13C2值大于-27.5‰;肖芝华等[31]认为,腐泥型天然气碳同位素组成比腐殖型天然气轻,尤其是δ13C2值有较明显的区别,腐泥型气的δ13C2值一般小于-30‰,而腐殖型气的δ13C2值般大于-28‰。
综合前人提出的判别标准,笔者采用δ13C2值-29‰作为油型气和煤成气的界限,即δ13C2值小于-29‰的天然气则以油型气为主,δ13C2值大于-29‰的天然气主要为煤成气。研究区所有天然气水合物气体样品δ13C2测试结果均小于-29‰(表 1),表现出热成因气的典型特征,为油型气。
为进一步探究研究区天然气水合物气体的成因类型及其来源,本文根据戴金星的V型鉴别图[32]对水合物样品气体分析结果进行投点分析。从图 6可以看出,数据点主要分布在Ⅱ区,即油型气区,仅1个样品点(DK8-19井116 m样品)δ13C1为-58.04‰,散落在Ⅵ区,为生物气和亚生物气区。在煤成气区或煤成气和油型气混合气区,基本无天然气水合物气体样品点分布,表明研究区水合物气体为油型气,与煤层气关系不大。
4.2 原油伴生气的鉴别
研究表明研究区天然气水合物气体为油型气,而油型气可根据热演化程度分为热解气(原油伴生气)、凝析油伴生气和热裂解气。为进一步探究研究区天然气水合物气体油型气热演化程度的具体阶段,本文利用戴金星甲烷碳同位素值与C1/(C2+C3)组分编制的鉴别无机成因和各类有机成因的甲烷图版[33, 34]进行投点分析(图 7),结果显示除DK8-19井浅层烃类气体可能含有少量亚生物成因气外,其余各井所有样品均位于原油伴生气区,在成熟度较高或与煤成气相关的Ⅱ2(油型裂解气区)、Ⅲ1(油型裂解气和煤层气区)、Ⅲ2(凝析油伴生气和煤层气区)区内无样品点分布,故研究区天然气水合物气体主要为热演化程度相对较低的原油伴生气。研究表明中侏罗统烃源岩处于生油高峰期和生湿气阶段,产生大量原油伴生气,应为天然气水合物主力生烃层系,而上三叠统烃源岩有机质成熟度高(主要为裂解气生成阶段),生烃潜量差,对天然气水合物成藏贡献不大。
4.3 与生物成因气的关系
生物成因气又称为细菌气、生物化学气,是干酪根在未成熟期内(R0 < 0.5%)通过甲烷菌的生物化学作用形成的天然气。由于甲烷生产菌活动温度一般不能高于75 ℃,最适于甲烷生产菌繁殖的温度是35~42 ℃,也是生物成因气强度最大阶段。这种气组分的突出特点是以甲烷含量为主,重烃含量低,C2+含量一般小于0.2%,个别的可达1%~2%,C1/(C2+C3)干燥系数一般在数百到数千以上,为典型的干气,δ13C1值小于-55‰[27]。
研究区属于高海拔冻土区,地表温度低,对甲烷生产菌的活动和繁殖较为不利。从收集的35个样品测试数据来看,水合物样品气体干燥系数多小于10,其均值仅4.1,显示湿气特征,不属于干气。为了进一步区分油型气及微生物气,本文利用Martin Schoell[35, 36]等的δDC1-δ13C1图版进行分析(图 8),结果表明,除DK8-19井中116 m处浅层样品的气源组成属混合成因外(不仅包含来自中侏罗统的原油伴生气,而且可能有少量生物成因气的混入),其余水合物样品点基本处于油型甲烷气区,为油型气。
4.3 与煤层气的关系
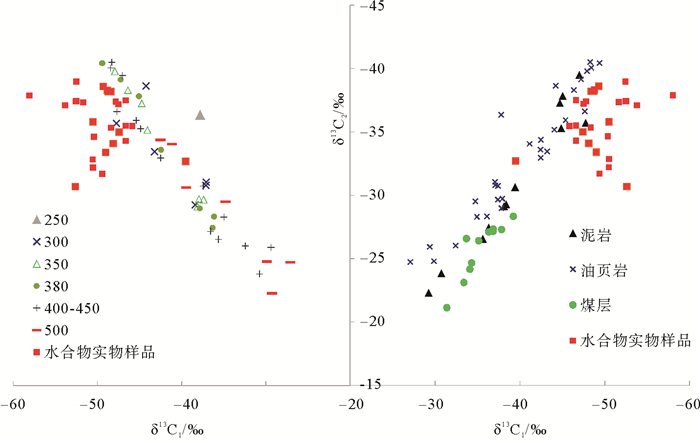
煤层气是指煤层生成的气体经运移、扩散后的剩余量,包括煤层颗粒基质表面吸附气、节理及裂隙游离气[27]。从气体组成成分来看,研究区煤层气为干气,而天然气水合物气体呈湿气特征,与煤层气关系不大。为进一步探究煤层与天然气水合物气源之间的可能联系。薛小花等[37]以热模拟实验为手段,对祁连山冻土区DK2和DK3井含天然气水合物层的岩心(泥岩、油页岩和煤)进行热模拟实验,实验结果显示:泥岩在350~400 ℃条件下或油页岩在380~400 ℃条件下所产生的烃类气体在同位素特征上与天然气水合物中烃类气体较为相似(图 9),推测天然气水合物气源与泥岩或油页岩具有地球化学成生联系,相反煤产生的烃类气体与天然气水合物中烃类气体同位素值相差较远,推测煤与天然气水合物气源关系不大。
5. 结论
(1) 南祁连盆地木里冻土区天然气水合物的气体以轻烃为主,具湿气特征,其碳同位素表现为δ13C1 < δ13C2 < δ13C3的正碳同位素系列,为典型有机成因,δ13C2多小于-29‰,成气母质主要为腐泥型干酪根(Ⅰ,Ⅱ1型有机质)的油型气,属热演化程度相对较低的原油伴生气。
(2) 除DK8-19井中116 m处浅层水合物样品的气源组成可能有少量生物成因气体混入,属混合成因外,其余天然气水合物样品均处于油型甲烷气区,为油型气,以热解成因气为主。
(3) 从气体组成成分来看,研究区煤层气为干气,而天然气水合物气体呈湿气特征;从热模拟实验的碳氢同位素组成特征来看,天然气水合物气源与泥岩或油页岩具有地球化学成生联系,煤层产生的烃类气体与天然气水合物中烃类气体碳氢同位素值相差较远,与天然气水合物气源关系不大。
(4) 中侏罗统有机质丰度高、类型较好,镜质体反射率Ro在0.48%~1.14%之间,处于生油高峰期,生油过程中的原油伴生气为天然气水合物的主要气体来源;三叠系有机质丰度较高、类型较好,成熟度高,处于生凝析气或裂解气阶段,但总体生排烃能力差,从气源对比分析来看对天然气水合物气体来源贡献不大,故下一步南祁连盆地勘查天然气水合物应着重考虑侏罗系地层的分布情况。
致谢: 成文过程中得到中国地质调查局油气资源调查中心张君峰教授级高工的指导,在此深表谢意。 -
井名 样品 深度
/m甲烷
/%乙烷
/%丙烷
/%C1/
(C2+C3)DK9 煤层气(J2m) 56 99.4 0.6 0.0 160.4 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 63 99.2 0.7 0.0 132.0 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 81 98.7 1.3 0.0 77.7 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 112 99.6 0.4 0.0 243.6 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 118 99.5 0.5 0.0 209.7 DK9 煤层气(J2m) 586 98.4 1.5 0.1 62.9 DK12 煤层气(J2m) 216 98.1 0.7 0.1 116.1 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 149 94.7 4.6 0.5 18.4 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 207 97.8 2.1 0.2 43.6 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 237 96.3 3.4 0.1 27.1 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 281 95.8 4.1 0.2 22.6 木参1 煤层气(J2m) 1 406 97.6 2.3 0.1 40.9 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 234 93.6 6.3 0.0 14.7 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 331 94.5 5.1 0.1 18.2 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 335 94.7 4.8 0.1 19.2 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 338 94.7 4.8 0.1 19.5 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 357 95.1 3.6 0.2 25.5 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 427 98.9 0.6 0.3 105.7 DK11 煤层气(J2m) 434 99.5 0.3 0.1 263.1 DK12 煤层气(J2m) 587 98.5 0.7 0.1 125.4 DK12 煤层气(J2m) 174 99.5 0.1 0.0 518.5 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 50 99.6 0.4 0.0 224.1 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 51 99.6 0.4 0.0 242.6 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 52 99.6 0.4 0.0 230.5 DK10 浅层气(J2m) 53 99.6 0.4 0.0 271.8 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 678 99.7 0.0 0.0 108 522.6 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 694 99.7 0.0 0.0 84 346.3 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 740 99.7 0.0 0.0 165 218.9 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 769 99.6 0.0 0.0 101 410.4 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 795 99.6 0.0 0.0 80 339.4 木参1 泥页岩气(T3g) 1 825 99.7 0.0 0.0 99 519.5 DK9 油浸气(J2m) 364 77.7 6.1 11.5 4.4 DK9 油浸气(J3m) 366 74.3 7.1 10.8 4.1 DK9 水合物气(录井) 188 87.5 4.1 7.3 7.7 DK9 水合物气(录井) 192 82.1 10.8 6.3 4.8 DK9 水合物气(录井) 197 83.2 8.2 7.4 5.3 DK9 水合物气(录井) 259 73.6 9.0 12.8 3.4 DK9 水合物气(录井) 271 74.2 8.9 13.0 3.4 DK9 水合物气(录井) 300 81.9 8.5 6.8 5.4 DK12 水合物气(录井) 339 68.1 12.5 12.8 2.7 DK12 水合物气(录井) 558 88.8 4.5 3.3 11.3 DK12 水合物气(录井) 560 87.7 4.8 3.5 10.6 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 116.0 62.9 8.0 23.7 2.0 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 120.0 57.3 13.9 20.1 1.7 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 126.1 64.7 8.8 22.5 2.1 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 129.2 78.9 7.7 7.6 5.2 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 143.9 63.6 10.0 21.2 2.0 DK8-19 水合物(实验室) 182.0 65.3 9.2 21.4 2.1 DK10-17 水合物(实验室) 487.3 62.0 14.9 16.9 2.0 DK11-14 水合物(实验室) 293.4 35.8 3.8 12.5 2.2 DK11-14 水合物(实验室) 322.2 61.3 6.8 25.2 1.9 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 202.8 65.8 6.3 2.4 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 203.3 85.3 3.9 7.5 7.5 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 204.8 65.3 5.7 22.0 2.4 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 262.9 62.1 9.4 22.4 2.0 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 295.6 81.4 6.2 10.4 4.9 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 302.5 61.3 8.4 25.3 1.8 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 312.6 64.3 9.8 21.2 2.1 DK12-13 水合物(实验室) 316.9 67.3 9.9 15.7 2.6 DK13-11 水合物(实验室) 267.2 66.4 6.5 21.3 2.4 DK2 水合物(实验室) 149.0 34.9 6.6 21.2 1.3 DK2 水合物(实验室) 253.0 62.6 8.6 22.4 2.0 DK2 水合物(实验室) 266.8 62.5 8.7 20.7 2.1 DK2 水合物(实验室) 336.0 63.0 9.2 21.0 2.1 DK2 水合物(实验室) 363.0 59.0 8.9 19.8 2.1 DK2 水合物(实验室) 372.6 62.5 8.9 21.2 2.1 DK3 水合物(实验室) 142.0 52.2 8.7 16.6 2.1 DK3 水合物(实验室) 395.0 87.0 2.9 0.5 26.0 表 2 研究区岩心中天然气水合物分解气的碳氢同位素组成(数据来自文献[15-17])
Table 2 Hydrocarbon isotopic compositions of hydrate gases in the study area[15-17]
井名 井深/m δ13/‰(VPDB) δD/‰(VSMOW) δ13C1/‰ δ13C2/‰ δ13C3/‰ CO2/‰ C1/‰ C2/‰ C3/‰ DK1 134 -50.5 -35.8 -31.9 -18 -262 -240 DK1 143 -39.5 -32.7 -30.8 -18 -266 DK1 143 -47.4 -35 -31.8 -17 -268 -254 DK2 149 -49 -33.4 -31.1 2.3 -227 -236 -198 DK2 253 -48.4 -38.2 -33.8 -24.9 -272 -265 -240 DK2 266.8 -49.3 -38.6 -34.7 -14.8 -285 -276 -247 DK2 336 -48.7 -38.2 -33.9 -27.9 -266 -276 -243 DK2 363 -48.8 -38.3 -33.8 -19.3 -279 -271 -244 DK2 372.6 -48.4 -38.2 -34.1 -18.6 -271 -271 -228 DK3 142 -48.1 -34.1 -30.9 -9.2 -245 -249 -200 DK3 395 -52.6 -30.7 -21.2 16.7 -255 nd nd DK8-19 116 -58.04 -37.88 -34.04 -17.7 -264 -274 -246 DK8-19 120 -53.82 -37.1 -33.67 -20.34 -249 -271 -246 DK8-19 126.1 -52.49 -37.43 -34.15 -20.45 -233 -276 -247 DK8-19 129.2 -50.38 -34.64 -33.86 -25.52 -225 -266 -248 DK8-19 143.9 -52.54 -37.42 -34.32 -18.9 -246 -276 -253 DK8-19 182 -51.67 -37.34 -34.38 -24.38 -237 -274 -252 DK10-17 487.3 -50.54 -32.85 -29.64 -17.28 -235 -228 -179 DK11-14 293.4 -46.6 -34.3 -30.7 -10.2 -234 -274 -228 DK11-14 322.2 -48.35 -35.35 -31.26 -13.05 -232 -267 -215 DK12-13 202.8 -50.5 -32.2 -30 -12.3 -256 -246 -219 DK12-13 204.8 -49.4 -31.7 -29.7 -13.9 -255 -237 -236 DK12-13 262.9 -46.6 -35.5 -31.4 -11 -266 -267 -229 DK12-13 295.6 -45.84 -35.47 -30.87 -15.63 -270 -271 -231 DK12-13 302.5 -47.5 -37.2 -31.9 -13.9 -276 -285 -237 DK12-13 312.6 -47.8 -37.4 -32.3 -12.7 -277 -284 -246 DK12-13 316.9 -46.6 -37.5 -32.5 -9.4 -276 -284 -247 DK13-11 267.2 -52.46 -38.97 -33.63 -12.42 -242 -262 -210 -
[1] Kvenvolden K A. A review of the geochemistry of methane in natural gas hydrate[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1995, 23(11-12): 997-1008. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(96)00002-2
[2] 史斗, 郑军卫.世界天然气水合物研究开发现状和前景[J].地球科学进展, 1999, 14(4): 330-339. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.04.004 SHI Dou, ZHENG Junwei. The status and prospects of research and exploitation of natural gas hydrate in the world[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1999, 14(4): 330-339. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.04.004
[3] 祝有海, 张永勤, 文怀军, 等.青海祁连山冻土区发现天然气水合物[J].地质学报, 2009, 83(11): 1762-1771. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.11.018 ZHU Youhai, ZHANG Yongqin, WEN Huaijun, et al. Gas hydrates in the Qilian mountain permafrost, Qinghai, Northwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(11): 1762-1771. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.11.018
[4] 张洪涛, 祝有海.中国冻土区天然气水合物调查研究[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(12): 1809-1815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.001 ZHANG Hongtao, ZHU Youhai. Survey and research on gas hydrate in permafrost region of China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(12): 1809-1815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.001
[5] Collett T S. Energy resource potential of natural gas hydrates[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11): 1971-1992. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8639906
[6] Makogon Y F, Holditch S A, Makogon T Y. Natural gas hydrates-a potential energy source for the 21st Century[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007, 56(1-3): 14-31. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2005.10.009
[7] 周幼吾, 郭东信, 邱国庆, 等.中国冻土[M].北京:科学出版社, 2000: 329-353. ZHOU Youwu, GUO Dongxin, QIU Guoqing, et al. Geocryology in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000: 329-353.
[8] 贾承造.论非常规油气对经典石油天然气地质学理论的突破及意义[J].石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1): 1-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201701001 JIA Chengzao. Breakthrough and significance of unconventional oil and gas to classical petroleum geological theory[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 1-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201701001
[9] 祝有海, 刘亚玲, 张永勤.祁连山多年冻土区天然气水合物的形成条件[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(1-2): 58-63. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200601010 ZHU Youhai, LIU Yaling, ZHANG Yongqin. Formation conditions of gas hydrates in permafrost of the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(1-2): 58-63. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200601010
[10] 曹代勇, 王丹, 李靖, 等.青海祁连山冻土区木里煤田天然气水合物气源分析[J].煤炭学报, 2012, 37(8): 1364-1368. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201208023 CAO Daiyong, WANG Dan, LI Jing, et al. Gas source analysis of natural gas hydrate of Muli coalfield in Qilian Mountain Permafrost, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(8): 1364-1368. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201208023
[11] 王佟, 刘天绩, 邵龙义, 等.青海木里煤田天然气水合物特征与成因[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2009, 37(6): 26-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2009.06.007 WANG Tong, LIU Tianji, SHAO Longyi, et al. Characteristics and origins of the gas hydrates in the Muli coalfield of Qinghai[J]. Coal and Geology Exploration, 2009, 37(6): 26-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2009.06.007
[12] 卢振权, 祝有海, 张永勤, 等.青海祁连山冻土区天然气水合物的气体成因研究[J].现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 581-588. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.024 LU Zhenquan, ZHU Youhai, ZHANG Yongqin, et al. Study on genesis of gases from gas hydrate in the Qilian Mountain Permafrost, Qinghai[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(3): 581-588. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.024
[13] 黄霞, 祝有海, 王平康, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物烃类气体组分的特征和成因[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(12): 1851-1856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.006 HUANG Xia, ZHU Youhai, WANG Pingkang, et al. Hydrocarbon gas composition and origin of core gas from the gas hydrate reservoir in Qilian Mountain permafrost[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(12): 1851-1856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.006
[14] 翟刚毅, 卢振权, 卢海龙, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物成矿系统[J].矿物岩石, 2014, 34(4): 79-92. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201404010 ZHAI Gangyi, LU Zhenquan, LU Hailong, et al. Gas hydrate geological system in the Qilian Mountain permafrost[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2014, 34(4): 79-92. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201404010
[15] 黄霞, 刘晖, 张家政, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物烃类气体成因及其意义[J].地质科学, 2016, 51(3): 934-945. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx201603018 HUANG Xia, LIU Hui, ZHANG Jiazheng, et al. Genetic-type and its significance of hydrocarbon gases from permafrost-associated gas hydrate in Qilian Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2016, 51(3): 934-945. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx201603018
[16] 刘昌岭, 贺行良, 孟庆国, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物分解气碳氢同位素组成特征[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(3): 489-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.03.020 LIU Changling, HE Xingliang, MENG Qingguo, et al. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic compositions characteristics of the released gas from natural gas hydrates in the Qilian Mountain Permafrost[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(3): 489-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.03.020
[17] 贺行良, 刘昌岭, 孟庆国, 等.青海聚乎更钻探区含水合物岩心气体组成及其指示意义[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(5): 1194-1200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.05.024 HE Xingliang, LIU Changling, MENG Qingguo, et al. Gas composition of hydrate-bearing cores in Juhugeng drilling area in Qinghai and its indicative significance[J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(5): 1194-1200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2015.05.024
[18] 潘语录, 田贵发, 栾安辉, 等.测井方法在青海木里煤田冻土研究中的应用[J].中国煤炭地质, 2008, 20(12): 7-9, 23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2008.12.003 PAN Yulu, TIAN Guifa, LUAN Anhui, et al. Application of well logging in frozen earth researches in Muli coalfield, Qinghai[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2008, 20(12): 7-9, 23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2008.12.003
[19] 文怀军, 鲁静, 尚潞君, 等.青海聚乎更矿区侏罗纪含煤岩系层序地层研究[J].中国煤田地质, 2006, 18(5): 19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2006.05.007 WEN Huaijun, LU Jing, SHANG Lujun, et al. A sequence stratigraphic discussion of the Jurassic coal measures in the Juhugeng coalmine area in Qinghai Province[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2006, 18(5): 19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2006.05.007
[20] 青海省地质矿产局.青海省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1991. Geology and Mineral Resources Bureau of Qinghai Province. Geological Records of Qinghai Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991.
[21] Hunt J M. Generation of gas and oil from coal and other terrestrial organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1991, 17(6): 673-680. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(91)90011-8
[22] TISSOT B P, WELTE D H石油形成和分布[M].徐永元译. 2版.北京: 石油工业出版社, 1989. TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence[M]. XU Yongyuan, Trans. 2nd ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1989.
[23] van Krevelen D W. Development of coal research-a review[J]. Fuel, 1982, 61(9): 786-790. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(82)90304-0
[24] 梁世友, 李凤丽, 付洁, 等.北黄海盆地中生界烃源岩评价[J].石油实验地质, 2009, 31(3): 249-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.03.008 LIANG Shiyou, LI Fengli, FU Jie, et al. Evaluation of Meso-Cenozoic hydrocarbon source rocks in north Yellow Sea basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2009, 31(3): 249-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.03.008
[25] 龙华山, 王绪龙, 向才富, 等.准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系烃源岩评价[J].现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1070-1080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.05.009 LONG Huashan, WANG Xulong, XIANG Caifu, et al. Evaluation on Jurassic hydrocarbon source rock developed in southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(5): 1070-1080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.05.009
[26] Shen P, Xu Y C. Isotopic compositional characteristics of terrigenous natural gases in China[J] Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 1993, 12(1): 14-24. doi: 10.1007/BF02869041
[27] 侯读杰, 冯子辉.油气地球化学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2011. HOU Dujie, FENG Zihui. Oil and Gas Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011.
[28] 戴金星, 秦胜飞, 陶士振, 等.中国天然气工业发展趋势和天然气地学理论重要进展[J].天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(2): 127-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2005.02.001 DAI Jinxing, QIN Shengfei, TAO Shizhen, et al. Developing trends of natural gas industry and the significant progress on natural gas geological theories in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(2): 127-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2005.02.001
[29] 刚文哲, 高岗, 郝石生, 等.论乙烷碳同位素在天然气成因类型研究中的应用[J].石油实验地质, 1997, 19(2): 164-167. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYSD199702010.htm GANG Wenzhe, GAO Gang, HAO Shisheng, et al. Carbon isotope of ethane applied in the analyses of genetic types of natural gas[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1997, 19(2): 164-167. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYSD199702010.htm
[30] Dai J X, Ni Y Y, Zou C N, et al. Stable carbon isotopes of alkane gases from the Xujiahe coal measures and implication for gas-source correlation in the Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2009, 40(5): 638-646. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.01.012
[31] 肖芝华, 谢增业, 李志生, 等.川中-川南地区须家河组天然气同位素组成特征[J].地球化学, 2008, 37(3): 245-250. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.03.007 XIAO Zhihua, XIE Zengye, LI Zhisheng, et al. Isotopic characteristics of natural gas of Xujiahe formation in southern and middle of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(3): 245-250. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.03.007
[32] 戴金星.天然气碳氢同位素特征和各类天然气鉴别[J].天然气地球科学, 1993, 4(2-3): 1-40. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/97226X/199302/1184634.html DAI Jinxing. Determination of hydrocarbon isotopic characteristics and natural gas of natural gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 1993, 4(2-3): 1-40. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/97226X/199302/1184634.html
[33] 戴金星.各类烷烃气的鉴别[J].中国科学B辑, 1992, 22(2): 185-193. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/88064X/199202/985597.html DAI Jinxing. Identification of various alkane gases[J]. Science in China Series B-Chemistry, Life Sciences and Earth Sciences, 1992, 35(10): 1246-1257. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/88064X/199202/985597.html
[34] 戴金星.戴金星天然气地质和地球化学论文集(卷二)[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2000. DAI Jinxing. Dai Jinxing Proceedings of Natural Gas Geology and Geochemistry (Volume Ⅱ)[M]. Beijing: China Petroleum Industry Press, 2000.
[35] Schoell M. The hydrogen and carbon isotopic composition of methane from natural gases of various origins[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(5): 649-661. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90155-6
[36] Whiticar M J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 161(1-3): 291-314. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00092-3
[37] 薛小花, 卢振权, 廖泽文, 等.祁连山冻土区含天然气水合物层段岩心热模拟实验研究[J].现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 413-424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.021 XUE Xiaohua, LU Zhenquan, LIAO Zewen, et al. Study of thermal simulation on cores at gas hydrate-bearing intervals in the Qilian Mountain permafrost[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(2): 413-424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.021
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 孟康,金敏波,徐亮,吴保祥. 南祁连木里冻土区天然气水合物气源探讨. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2020(01): 72-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何大双,张鹏辉,明承栋,裴发根,何梅兴. 南祁连盆地木里冻土区第四纪沉积物中可溶有机质的来源及其与天然气水合物的关系. 地质通报. 2020(07): 1062-1071 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宁伏龙,梁金强,吴能友,祝有海,吴时国,刘昌岭,韦昌富,王冬冬,张准,徐猛,刘志超,李晶,孙嘉鑫,欧文佳. 中国天然气水合物赋存特征. 天然气工业. 2020(08): 1-24+203 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: