NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF MESOZOIC TECTONIC PROCESSES IN THE SOUTHERN PART OF EAST CHINA SEA CONTINENTAL SHELF BASIN
-
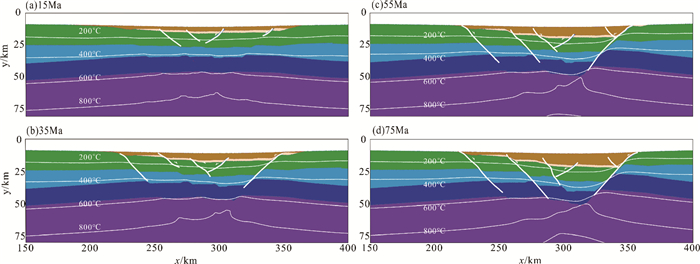
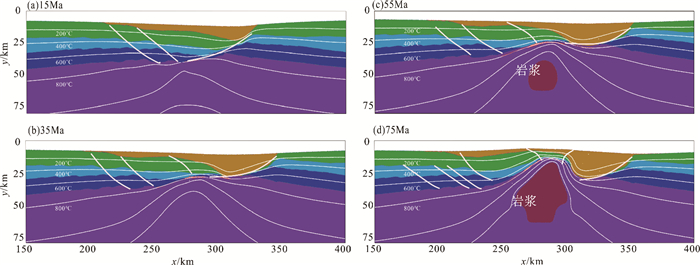
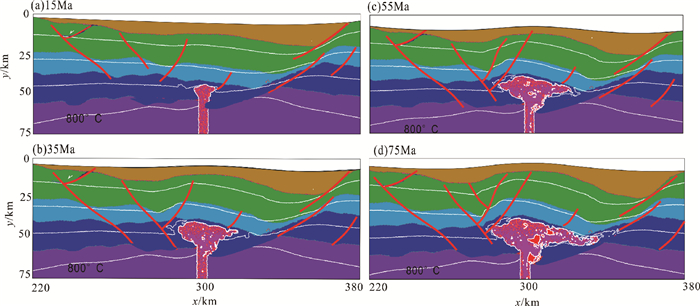
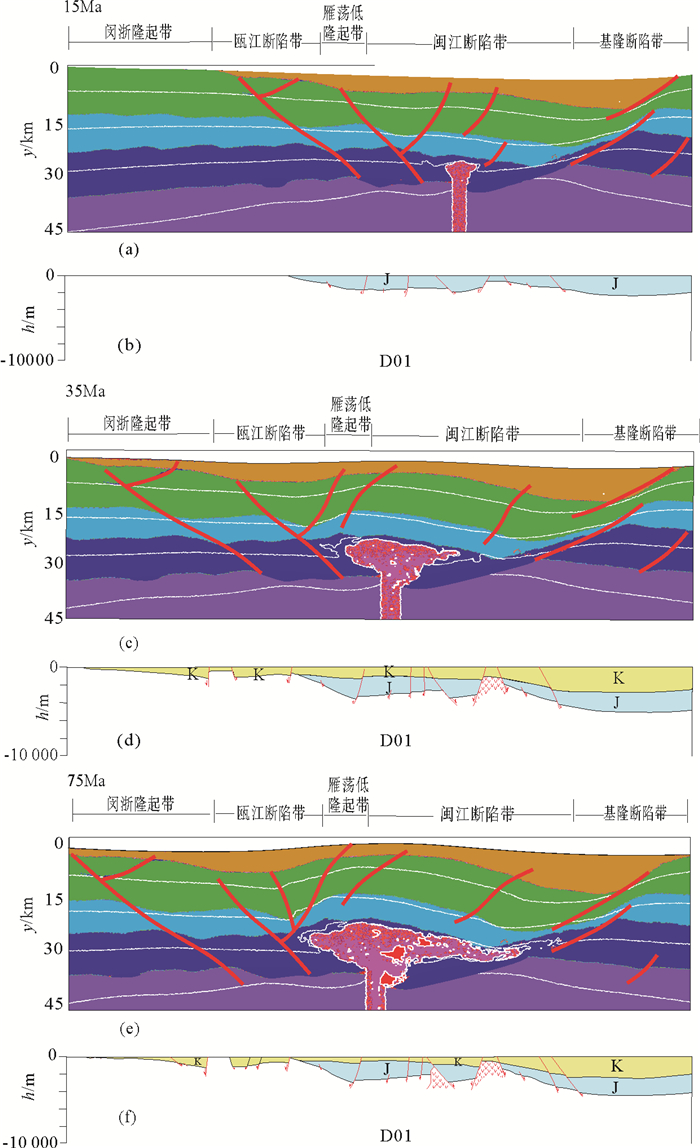
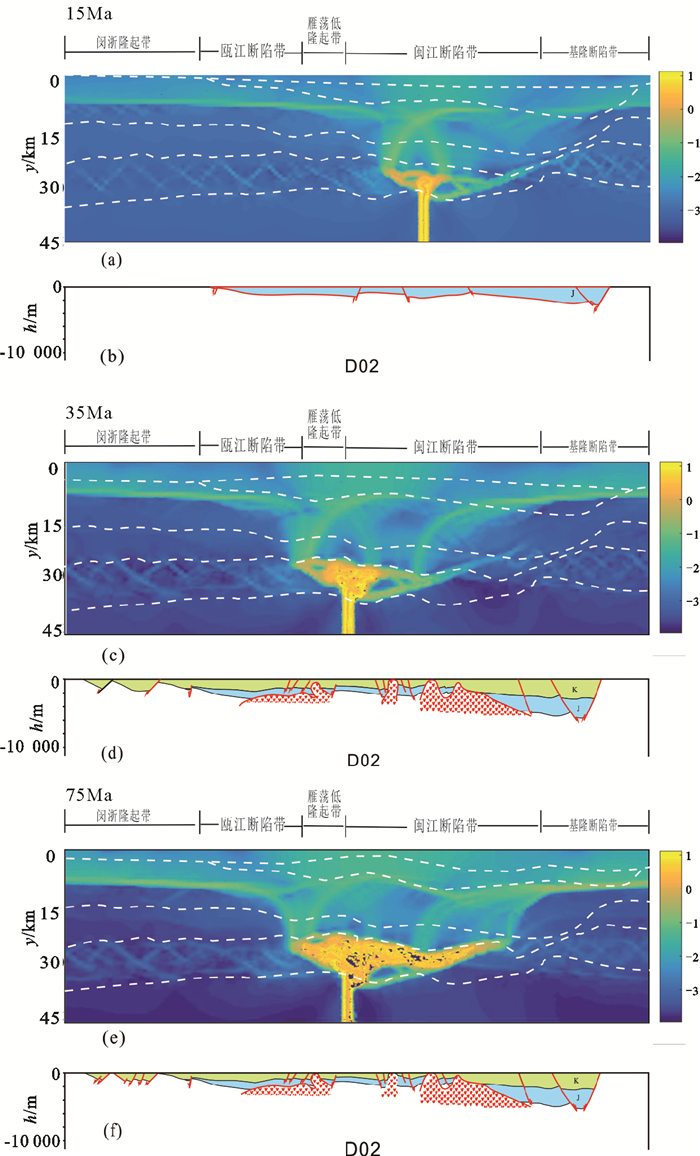
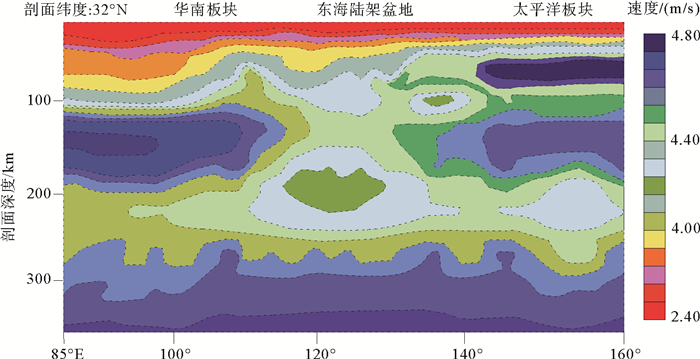
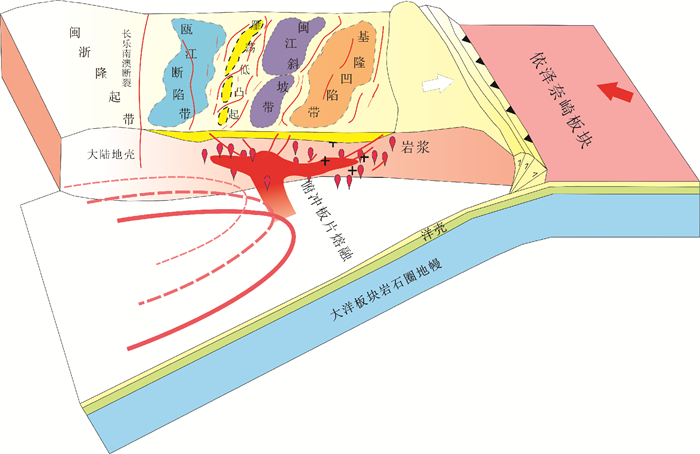
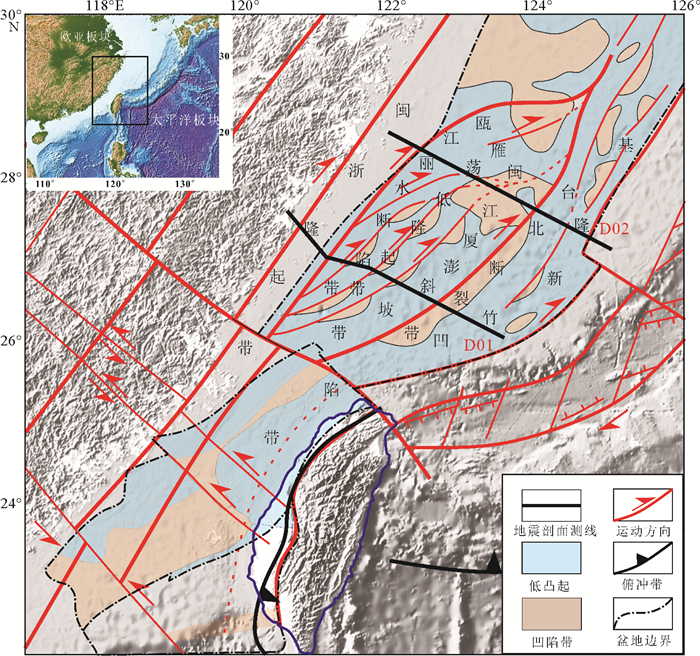
摘要: 采用I2VIS有限差分方法,模拟了东海陆架盆地南部中生代的盆地演化过程。数值模型的构建主要基于研究区域内现有的地震剖面、测井、层析成像等资料获得的中生代地层结构特征。根据模拟结果,对比已知的岩浆侵入特征和断裂组合规律,定量分析了在不同边界条件下,各阶段盆地演化的岩浆断裂及沉积特征,并探讨了影响盆地构造特征的主要因素。得出以下认识:(1)通过改变模型的边界条件发现,层状含水地幔在拉伸环境下,会对地壳结构造成破坏,中生代东海陆架盆地区域性伸展不是盆地演化过程的唯一主控因素。(2)东海陆架盆地中生代的成盆过程及属性与中生代时期上地幔物质流动有着密切关系。(3)中生代的地幔物质流动导致的大规模岩浆事件很可能作用于闽江凹陷之下,由此导致了闽江凹陷的进一步抬升,形成现今的斜坡带,而基隆凹陷进一步沉降,形成凹陷的沉积中心。基于以上结论,认为区域性伸展和上地幔物质流动导致的岩浆上涌两大因素共同控制下,影响了东海陆架盆地南部中生代的演化。Abstract: The I2VIS finite difference and mark-in-cell technique is used to simulate the evolution of Mesozoic basins in the southern part of the East China Sea Continental Shelf Basin. The numerical model was constructed based on the existing seismic profiles, drilling and tomographic data of the study area. Based on the simulation results, the magmatic intrusion and sedimentation during the basin evolution are quantitatively analyzed under different boundary conditions, and the main factors affecting the tectonic evolution of the basin are discussed. As the results, following conclusions are obtained: 1) The change of the boundary conditions for the models indicates that the stratified aquifer mantle will destroy the crustal structure under tensile environment, and the regional extension of the Mesozoic East China Sea Continental Shelf Basin is not the only master factor to the basin evolution. 2) Mesozoic basins are closely related to the material flow in upper mantle during the Mesozoic Era. 3) The large-scale magmatic events caused by the Mesozoic mantle flow are likely to affect the Minjiang Depression, leading the Depression turning to uplift, the formation of the present-day slope zone, and further settling of the Jilong Depression to become a depression center. The regional evolution and magma upwelling caused by the upper mantle flow have indeed influenced the evolution of the Mesozoic basin in the southern part of the East China Sea Continental Shelf Basin.
-
-
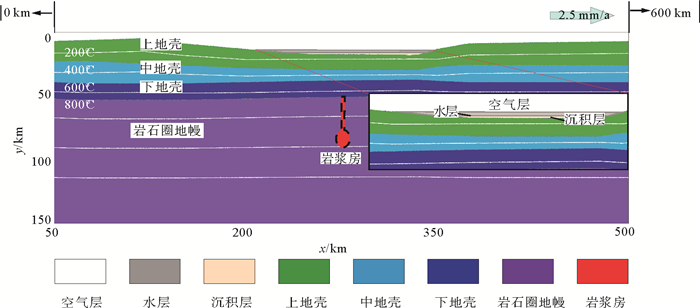
物质 状态 ρ0/kg·m-3 Cp/J·kg-1·K-1 K/W·-1·K-1 Tsolidus/K Tliquidus/K Hr/μW·m-3 α/K-1 β/MPa 黏滞性流变性质 塑性流变性质 Sin(FI0) Sin(FII) 空气 - 1 3.33×106 200 - - 0 0 0 A* 0 0 水 - 1 000 3.33×106 200 - - 0 0 0 A* 0 0 沉积层 固相 2 700 1 000 K1 T1 T3 2.0 3×10-5 1×10-5 B* 0.03 0.03 部分熔融 2 400 上地壳 固相 2 700 1 000 K1 T1 T3 1 3×10-5 1×10-5 B* 0.2 0.2 部分熔融 2 400 中地壳 固相 2 800 1 000 K1 T1 T3 1 3×10-5 1×10-5 C* 0.2 0.1 部分熔融 2 500 下地壳 固相 2 900 1 000 K1 T1 T3 0.5 3×10-5 1×10-5 D* 0.2 0.00 部分熔融 2 600 岩石圈地幔 固相 3 300 1 000 K2 T2 T4 0.022 3×10-5 1×10-5 D* 0.6 0.6 部分熔融 2 700 含水地幔 固相 3 300 1 000 K2 T2 T4 0.022 3×10-5 1×10-5 E* 0.6 0.6 部分熔融 2 700 Table 2 Physical property parameter formula used in 2-D numerical experiments
物性参数标号 物性参数公式 K1 [0.64+807/(TK+ 77)]×exp(0.000 04×P) K2 [0.73+1 293/(TK+ 77)]×exp(0.000 04×P) T1 889+17 900/(P+54)+20 200/(P+54)2, P∠1 200 MPa T2 831+0.06×P, P>1 200 MP 1 394+0.132 899×P-0.000 0051 04×P2 T3 1 262+ 0.09P T4 2 212+0.030 819×(P-10 000) -
[1] 黄汲清, 任纪舜, 姜春发, 等.中国大地构造基本轮廓[J].地质学报, 1977, 51(2): 117-135. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxb/ch/reader/key_query.aspx HUANG Jiqing, REN Jishun, JIANG Chunfa, et al. An outline of the tectonic characteristics of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1977, 51(2): 117-135. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxb/ch/reader/key_query.aspx
[2] 任纪舜.印支运动及其在中国大地构造演化中的意义[J].中国地质科学院院报, 1984, 9(2): 31-44. doi: 10.1109-TIM.2003.810035/ REN Jishun. The indosinian orogeny and its significance in the tectonic evolution of China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1984, 9(2): 31-44. doi: 10.1109-TIM.2003.810035/
[3] 李三忠, 余珊, 赵淑娟, 等.东亚大陆边缘的板块重建与构造转换[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(3): 65-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201303008 LI Sanzhong, YU Shan, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Tectonic transition and plate reconstructions of the East Asian continental margin[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(3): 65-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201303008
[4] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等.东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J].上海地质, 2003, 24(3): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2003.03.001 LIU Jinshui, LIAO Zongting, JIA Jianyi, et al. The geological structure and tectonicevolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J].Shanghai Geology, 2003, 24(3): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2003.03.001
[5] 杨传胜, 李刚, 杨长清, 等.东海陆架盆地及其邻域岩浆岩时空分布特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3): 125-133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201203016 YANG Chuansheng, LI Gang, YANG Changqing, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of the igneous rocks inthe East China Sea Shelf Basin and its adjacent regions[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 125-133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201203016
[6] 戴黎明, 李三忠, 楼达, 等.亚洲大陆主要活动块体的现今构造应力数值模拟[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2013, 43(2): 469-483. http://xuebao.jlu.edu.cn/dxb/CN/article/advancedSearchResult.do DAI Liming, LI Sanzhong, LOU Da, et al. Numerical modeling of present-day structural stress of major active blocks in the Asian continent[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2013, 43(2): 469-483. http://xuebao.jlu.edu.cn/dxb/CN/article/advancedSearchResult.do
[7] 索艳慧, 李三忠, 戴黎明, 等.东亚及其大陆边缘新生代构造迁移与盆地演化[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(8): 2602-2618. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/key_query.aspx SUO Yanhui, LI Sanzhong, DAI Liming, et al. Cenozoic tectonic migration and basin evolution in East Asia and its continental margins[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8): 2602-2618. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/key_query.aspx
[8] Suo YH, Li SZ, Yu S, et al. Cenozoic tectonic jumping and implications for hydrocarbon accumulation in basins in the East Asia Continental Margin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 88: 28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.02.019
[9] Suo Y H, Li S Z, Zhao S J, et al. Continental margin basins in East Asia: Tectonic implications of the Meso-Cenozoic East China Sea pull-apart basins[J]. Geological Journal, 2015, 50(2): 139-156. doi: 10.1002/gj.2535
[10] Dai L M, Li S Z, Lou D, et al. Numerical modeling of Late Miocene tectonic inversion in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 86:25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.033
[11] 郑求根, 周祖翼, 蔡立国, 等.东海陆架盆地中新生代构造背景及演化[J].石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(2): 197-201. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.02.012 ZHENG Qiugen, ZHOU Zuyi, CAI Liguo, et al. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic setting and evolution of East China Sea shelf basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(2): 197-201. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.02.012
[12] 姜亮.东海陆架盆地油气资源勘探现状及含油气远景[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1): 3-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200301001 JIANG Liang. Exploration status and perspective of petroleum resources in East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 2003, 17(1): 3-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200301001
[13] 何家雄, 张伟, 颜文, 等.中国近海盆地幕式构造演化及成盆类型与油气富集规律[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(2): 121-134. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8281257 HE Jiaxiong, ZHANG Wei, YAN Wen, et al. Episodic tectonic evolution, basin types and hydrocarbon accumulation in Chinese marginal basins[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(2): 121-134. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8281257
[14] 梁若冰.东海陆架盆地南部中生界分布浅析[J].海洋石油, 2012, 32(3): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2012.03.018 LIANG Ruobing. Thedistribution of Mesozoic in the Southern part of East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Offshore Oil, 2012, 32(3): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2012.03.018
[15] 郭真.东海陆架盆地演化中重要地质现象及其动力学背景分析[D].西北大学博士学位论文, 2015. GUO Zhen. Evolutionary important geological phenomena and its dynamics background in East China Sea Shelf Basin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Northwest University, 2015.
[16] 冯晓杰, 蔡东升, 王春修, 等.东海陆架盆地中新生代构造演化特征[J].中国海上油气:地质, 2003, 17(1):33-37. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200301007 FENG Xiaojie, CAI Dongsheng, WANGChunxiu. The Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution in East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1):33-37. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200301007
[17] 毛建仁.中国东南大陆中、新生代岩浆作用与壳幔演化动力学[J].火山地质与矿产, 1994, 15(2): 1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400214552 MAO Jianren. The Mesozoic-Canozoic magmatism and Geodynamicsof crustal and mantle evolution in southeast China continent[J]. Volcanology & Mineral Resources, 1994, 15(2): 1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400214552
[18] 蔡学林, 朱介寿, 曹家敏, 等.东亚西太平洋岩石圈三维结构及其地幔动力学[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(3): 21-38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.03.002 CAI Xuelin, ZHU Jieshou, CAO Jiamin, et al. Three-dimensional tectonics of lithosphere and mantle dynamics of East AsiaWest Pacific[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(3): 21-38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.03.002
[19] 孙卫东, 凌明星, 汪方跃, 等.太平洋板块俯冲与中国东部中生代地质事件[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(3): 218-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.03.002 SUN Weidong, LING Mingxing, WANG Fangyue, et al. Pacific plate subduction and Mesozoic geological event in eastern China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(3): 218-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.03.002
[20] 张少武, 李春峰.磁异常三维解析信号所揭示的中国东部及邻近海域岩浆岩特征[J].物探与化探, 2011, 35(3): 290-297. http://www.wutanyuhuatan.com/CN/article/searchArticleResult.do ZHANG Shaowu, LI Chunfeng. Magnetic activities in eastern china and adjacent seas revealed by 3D analytic signals of magnetic data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(3): 290-297. http://www.wutanyuhuatan.com/CN/article/searchArticleResult.do
[21] 毛建仁, 邢光福, 杨祝良, 等.中国东南大陆中生代构造岩浆事件与大陆地壳生长[C]//中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第九届学术年会论文摘要集.宁波: 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会, 2003. MAO Jianren, XING Guangfu, YANG Zhuliang, et al. Chinese Mesozoic tectonic magmatic events and continental crustal growth in the southeastern China[C]. Ningbo, 2003.
[22] 李廷栋, 莫杰.中国滨太平洋构造域构造格架和东海地质演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(4):1-6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200204001 LI Tingdong, MO Jie. Tectonic framework of the west circum-pacific tectonic tract and the geological evolution of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(4):1-6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200204001
[23] 张旗.中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1): 113-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.010 ZHANG Qi. Is the Mesozoic magmatism in eastern China related to the westward subduction of the Pacific plate?[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2013, 32(1): 113-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.010
[24] 石广仁, 郭秋麟, 米石云, 等.盆地综合模拟系统BASIMS[J].石油学报, 1996, 17(1): 1-9. doi: 10.7623/syxb199601001 SHI Guangren, GUO Qiulin, MI Shiyun, et al. Basin integrated modeling system "BASIMS"[J]. Acta Petroei Sinica, 1996, 17(1): 1-9. doi: 10.7623/syxb199601001
[25] Gerya T V, Burg J P. Intrusion of ultramafic magmatic bodies into the continental crust: Numerical simulation[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2007, 160(2): 124-142. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2006.10.004
[26] Vogt K, Gerya T V, Castro A. Crustal growth at active continental margins: Numerical modeling[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2012, 192-193: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2011.12.003
[27] 李忠海, Di Leo J, Neil R.大洋俯冲带的地幔变形和地震波各向异性的数值模拟[C]//2014年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集.北京: 中国地球物理学会, 中国地质学会, 2014. LI Zhonghai, Di Leo J, Neil R. Numerical simulation of mantle deformation and seismic wave anisotropy in ocean subduction zone[C]. Beijing: Chinese Geophysical Society, Geological Society of China, 2014.
[28] Li Z H, Liu M, Gerya T. Lithosphere delamination in continental collisional orogens: A systematic numerical study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2016, 121(7): 5186-5211. doi: 10.1002/2016JB013106
[29] Li Z H. A review on the numerical geodynamic modeling of continental subduction, collision and exhumation[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(1): 47-69. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4696-0
[30] Li Z H, Xu Z Q, Gerya T, et al. Collision of continental corner from 3-D numerical modeling[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 380: 98-111. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.08.034
[31] Li Z H, Gerya T V, Burg J P. Influence of tectonic overpressure on P-T paths of HP-UHP rocks in continental collision zones: Thermomechanical modelling[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2010, 28(3): 227-247. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2009.00864.x
[32] Li Z H, Xu Z Q, Gerya T V. Flat versus steep subduction: Contrasting modes for the formation and exhumation of high- to ultrahigh-pressure rocks in continental collision zones[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301(1-2): 65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.10.014
[33] Li Z H, Gerya T V. Polyphase formation and exhumation of high-to ultrahigh-pressure rocks in continental subduction zone: Numerical modeling and application to the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane in eastern China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2009, 114(B9): B09406. doi: 10.1029-2008JB005935/
[34] 侯方辉.东海陆架盆地南部中生代地层分布及构造特征研究[D].中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2014. HOU Fanghui. Research on the distribution and tectonic characteristics of the Mesozoic strata of the East China Sea Shelf Basin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[35] 高德章.东海陆架盆地岩石密度与磁性[J].上海地质, 1995(2): 38-45. GAO Dezhang. Density and magnetic of rocks in the East Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Shanghai Geology, 1995(2): 38-45.
[36] Gerya T V, Yuen D A. Characteristics-based marker-in-cell method with conservative finite-differences schemes for modeling geological flows with strongly variable transport properties[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2003, 140(4): 293-318. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2003.09.006
[37] Faccenda M, Gerya T V, Chakraborty S. Styles of post-subduction collisional orogeny: Influence of convergence velocity, crustal rheology and radiogenic heat production[J]. Lithos, 2008, 103(1-2): 257-287. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.09.009
[38] 朱介寿, 曹家敏, 严忠琼, 等.中国及邻区瑞利面波高分辨率层析成像及其地球动力学意义[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(5):759-767. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.05.002 ZHU Jieshou, CAO Jiamin, YAN Zhongqiong, et al. High-resolution Rayleigh surface wave tomographic imaging of China and adjacent regions and its geodynamic implications[J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(5):759-767. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.05.002
[39] 袁学诚.再论岩石圈地幔蘑菇云构造及其深部成因[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(5): 737-758. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.05.001 YUAN Xuecheng. Mushroom structure of the lithospheric mantle and its genesis at depth: Revisited[J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(5): 737-758. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.05.001
[40] 袁学诚, 李善芳, 管烨.瑞雷-泰勒不稳定性与中国东部岩石圈——三论岩石圈地幔蘑菇云构造[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(1): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.01.001 YUAN Xuecheng, LI Shanfang, GUAN Ye. Rayleigh-Taylor instability and lithosphere of eastern China[J].Geology in China, 2012, 39(1): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.01.001
[41] 刘光鼎.中国海地球物理场和地球动力学特征[J].地质学报, 1992, 66(4): 300-314. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxb/ch/reader/key_query.aspx LIU Guangding. Features of geophysical fields and geodynamics of the sea areas of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1992, 66(4):300-314. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxb/ch/reader/key_query.aspx
[42] 温珍河, 张训华, 姚长新, 等.中国东部海区及邻域地质构造特征与演化[C]//2008年亚洲大陆深部地质作用与浅部地质——成矿响应学术研讨会论文集.乌鲁木齐: 中国地质学会, 2008. WEN Zhenhe, ZHANG Xunhua, YAO Changxin, et al. Characteristics and evolution of geological structure in eastern China and its adjacent areas[C]. Urumqi: Geological Society of China, 2008.
[43] 滕吉文, 张中杰, 胡家富, 等.中国东南大陆及陆缘地带的瑞利波频散与剪切波三维速度结构[J].地球物理学报, 2001, 44(5): 663-677. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2001.05.010 TENG Jiwen, ZHANG Zhongjie, HU Jiafu, et al. The Rayleigh wave dispersion and three dimensional velocity structure in continent and its margin of southeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2001, 44(5): 663-677. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2001.05.010
[44] 刘光鼎.中国海地球物理场特征[J].地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(1):1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.01.001 LIU Guangding. The characteristics of geophysical fields on the China Seas[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2002, 17(1):1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.01.001
[45] 毛建仁, 陶奎元, 邢光福, 等.中国东南大陆边缘中新生代地幔柱活动的岩石学记录[J].地球学报, 1999, 20(3): 253-258. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.1999.03.006 MAO Jianren, TAO Kuiyuan, XING Guangfu, et al. Petrological records of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic mantle plume tectonics in epicontinental area of Southeast China[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1999, 20(3): 253-258. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.1999.03.006
[46] Palmeri R, Ghiribelli B, Ranalli G, et al. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and exhumation of garnet-bearing ultramafic rocks from the Lanterman Range (northern Victoria Land, Antarctica)[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2007, 25(2): 225-243. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2006.00686.x
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 孔淼淼,刘夙睿,王厚杰,毕乃双,胡利民,闫天浩,任晰熙,刘彦昊,吴晓. 现代黄河水下三角洲对尾闾改道事件的沉积响应——以1855、1976、1996年三期改道为例. 海洋地质前沿. 2025(02): 68-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙璐,单红仙,张红,刘汉露,贾永刚. 基于~(210)Pb、~(137)Cs分布和粒度特征的海床液化深度判定研究——以埕岛海域为例. 海洋学报. 2023(10): 105-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: